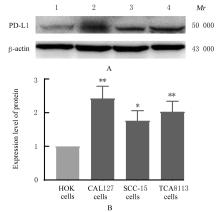
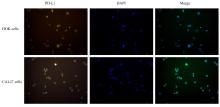
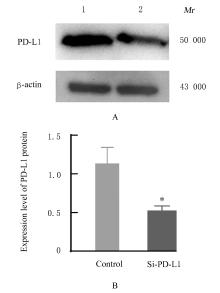
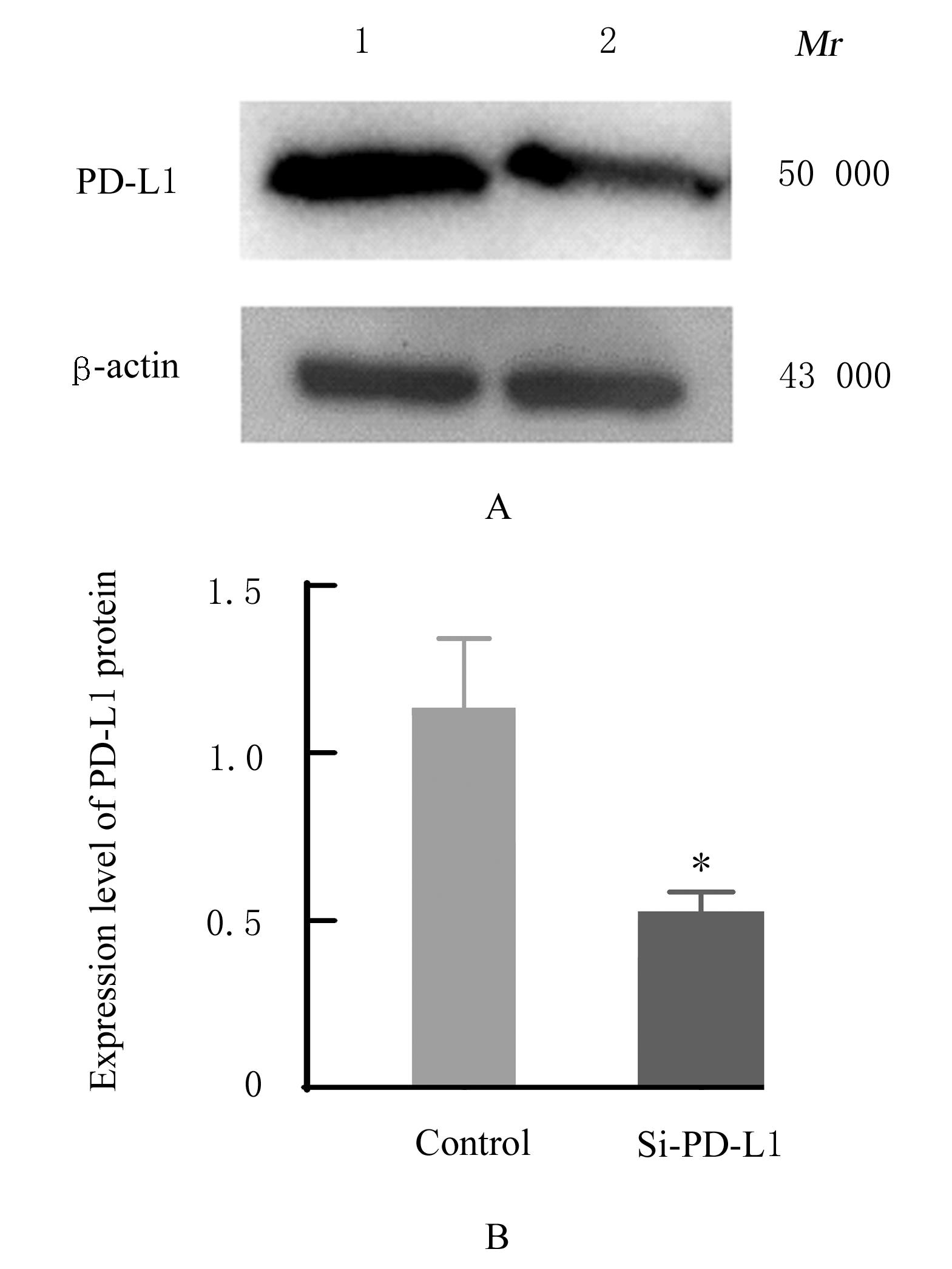
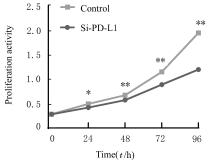
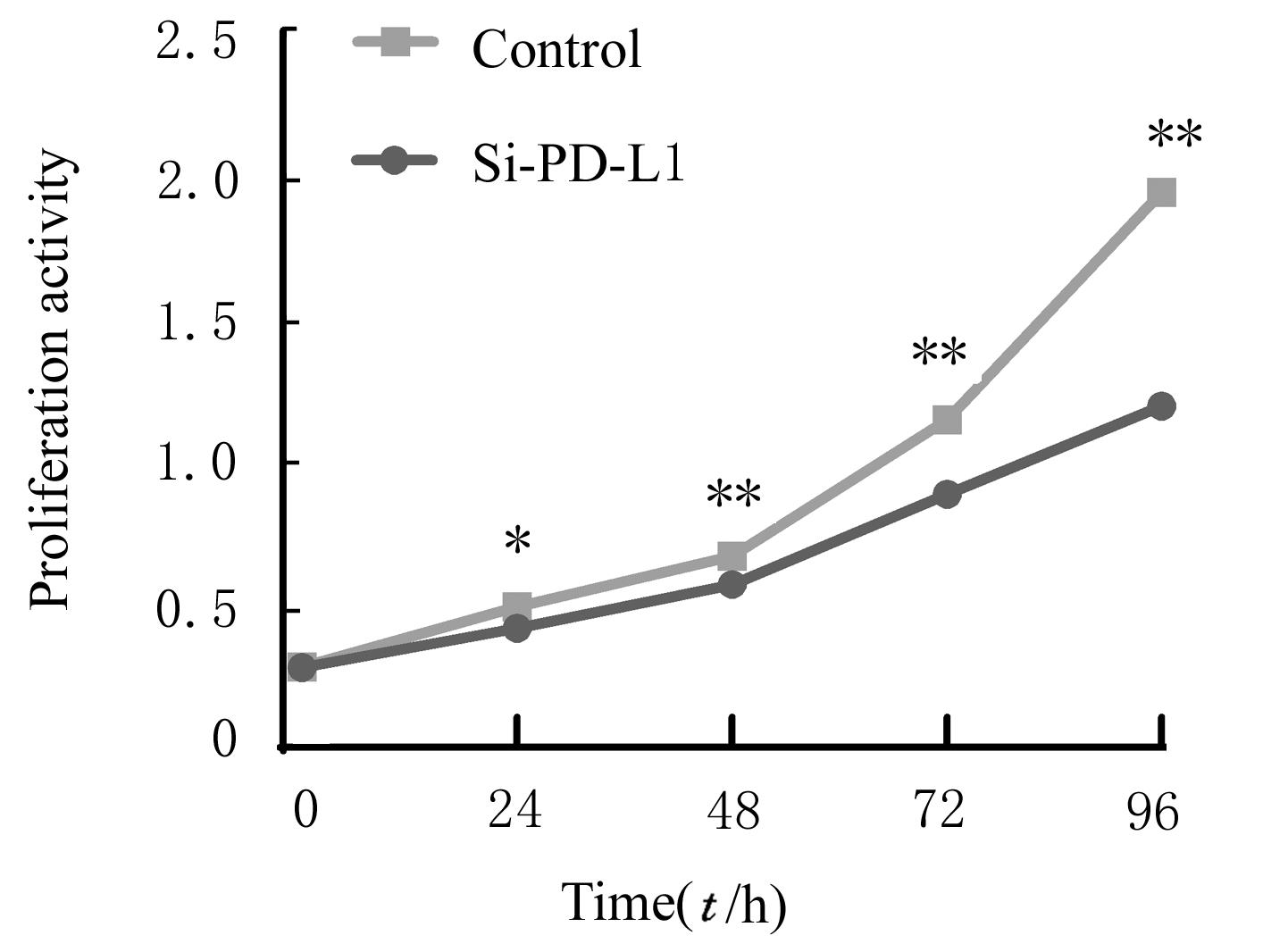
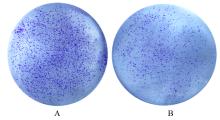
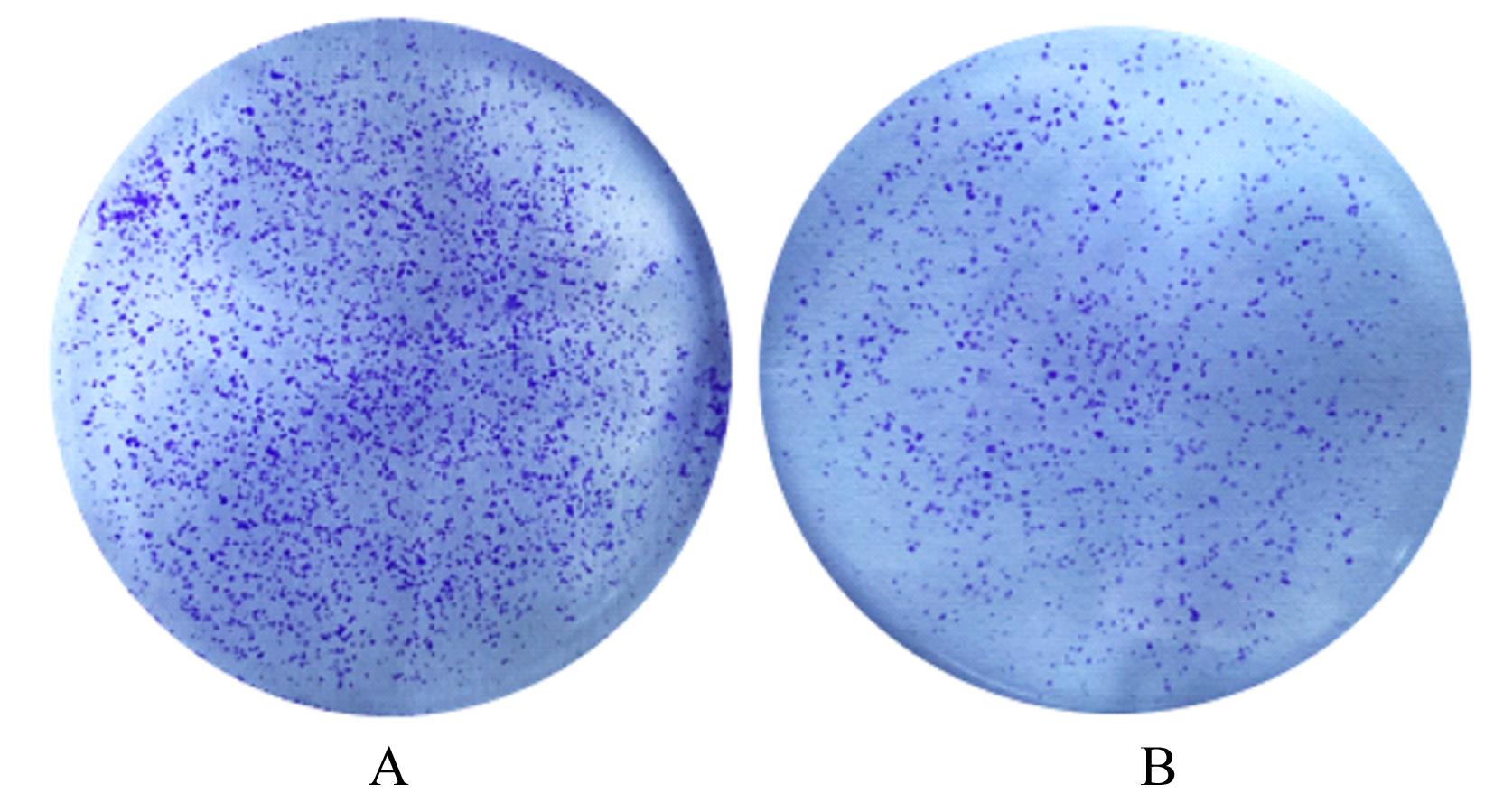
| [1] |
Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE.
Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135.
|
| [2] |
Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI.
Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149.
|
| [3] |
Xiaoni WANG,Tao GUO,Qiyun LUO,Lifeng GUAN.
Effect of usnic acid on biological behaviors of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and JNK/MAPK signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1445-1451.
|
| [4] |
Aihua REN,Xinda JU,Aofei LIU,Yongchao LIU,Yanfeng LIU.
Effect of ganoderic acid A on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1466-1472.
|
| [5] |
Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI.
Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527.
|
| [6] |
Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU.
Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139.
|
| [7] |
Na NI,Hongliang DONG,Haiyang GAO,Weiwei CHEN,Xinyu MENG,Bingjie CUI,Jing DU.
Construction of human lncRNA-GACAT2 over-expression vector and its effect on proliferation and stemness of lung cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1147-1153.
|
| [8] |
Qi WU,Jianfeng CHEN,Hao LI,Feng WEN.
Effect of paeonol on proliferation, migration, and CXCR4/STAT3 pathway of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1202-1209.
|
| [9] |
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI.
Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226.
|
| [10] |
Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG.
Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233.
|
| [11] |
Yuesheng ZHAO,Zubin LI,Haiou LIU,Kunlin TAO,Qihai ZHAO,Na LI.
Inhibitory effect of silencing CDKL1 gene on proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by regulating PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1234-1242.
|
| [12] |
Yuanying SONG,Jing KAN,Kun PENG,Yue LI.
Effect of honeysuckle extract on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic model mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1001-1007.
|
| [13] |
Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN.
Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017.
|
| [14] |
Li JIN,Xiaohong ZHANG,Chaoyang HU,Fengzhi LI,Yongliang CUI,Yang LI,Qianqian LIU,Yanjun QIAO.
Effects of quercetin on growth and lung metastasis of transplanted tumor and cell invasion, and cell migration in human lung cancer A549 cells transplanted tumor model mice and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1018-1026.
|
| [15] |
Xuying WANG,Mingzhen JING,Jin YU,Rong FU,Ru YANG.
Effects of miR-181a-5p and BACH2 expressions on apoptosis and invasion of leukemic CCRF-CEM cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 840-849.
|
 )
)