Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 881-890.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240401
• Research in basic medicine • Next Articles
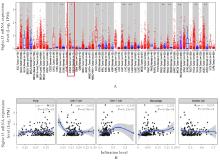
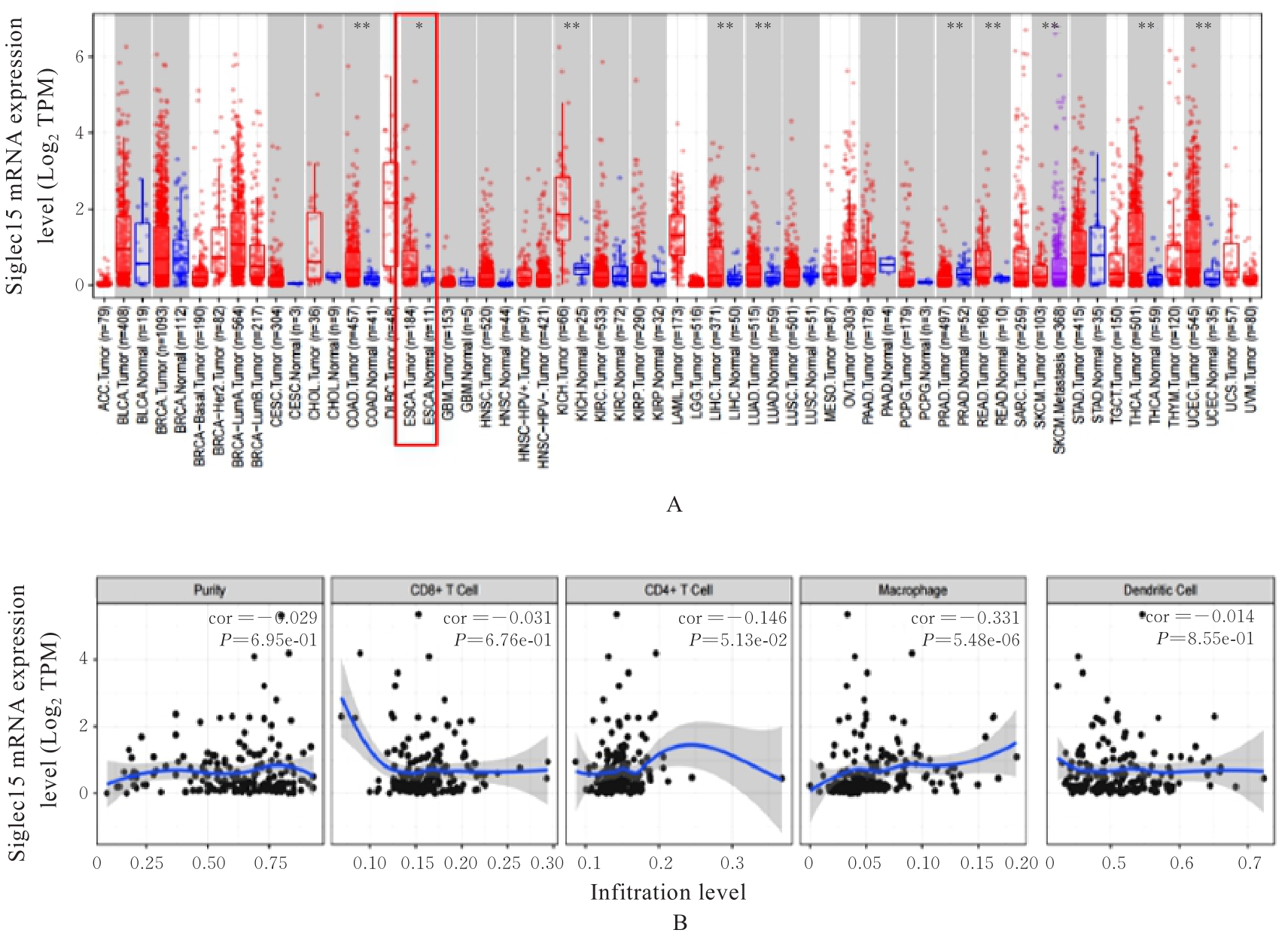
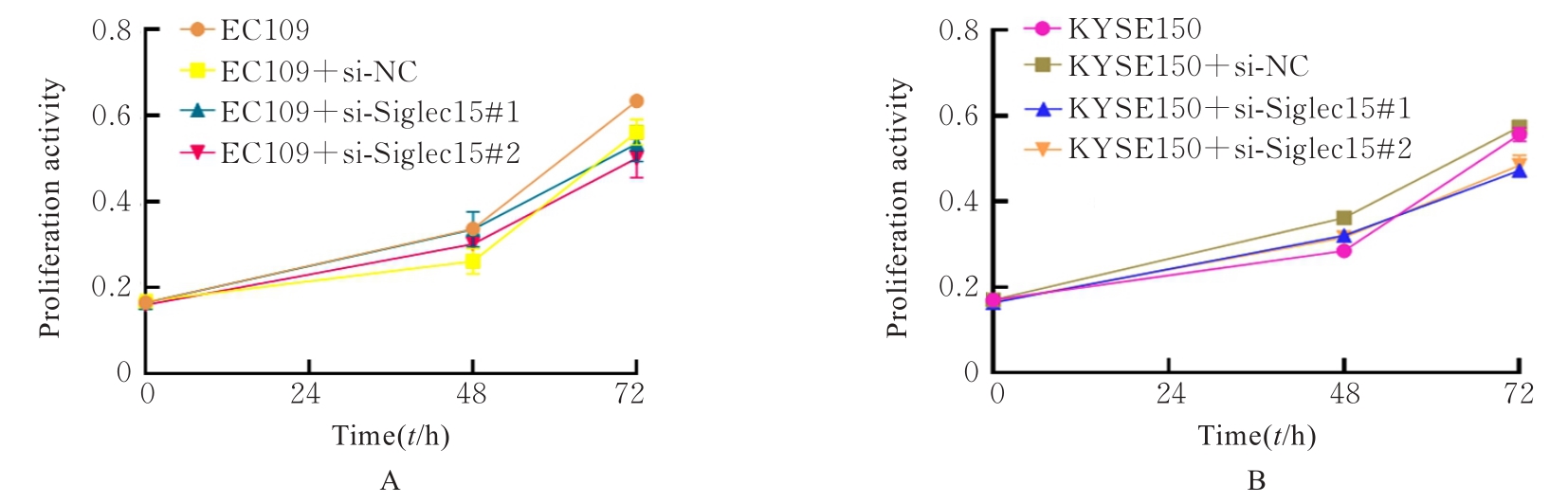
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation
Yilin REN1,Yichen ZANG1,Lele XUE1,Kaige YANG1,Sufang CHEN1,Weinan WANG1,Chenghua LUO1,Weihua LIANG1,Lianghai WANG1,Feng LI1,Jianming HU1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, China
2.Department of Patholegy, School of Medical Sciences, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, China
-
Received:2023-09-01Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Jianming HU E-mail:jianming.120@163.com
CLC Number:
- R735.1
Cite this article
Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890.
share this article
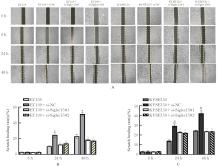
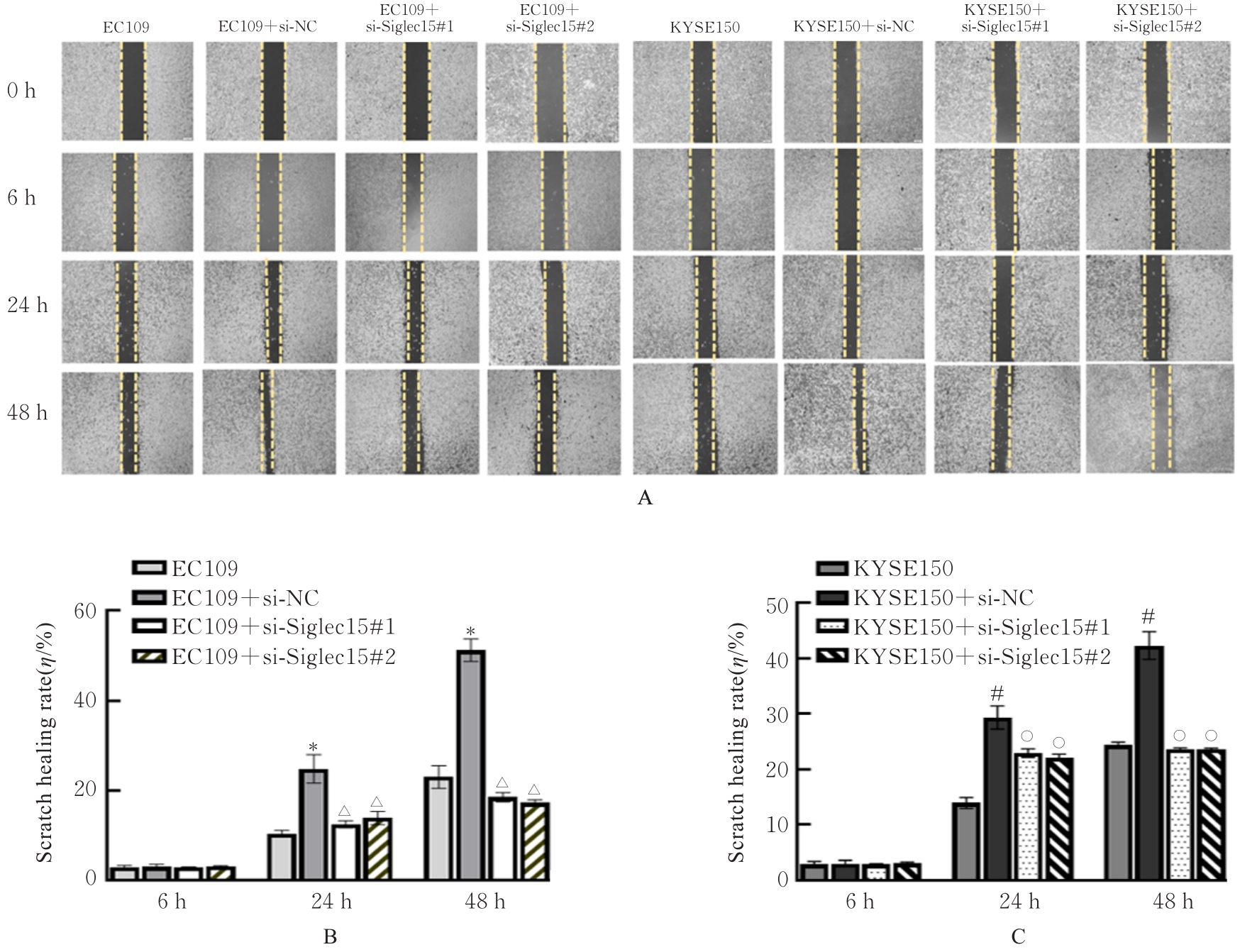
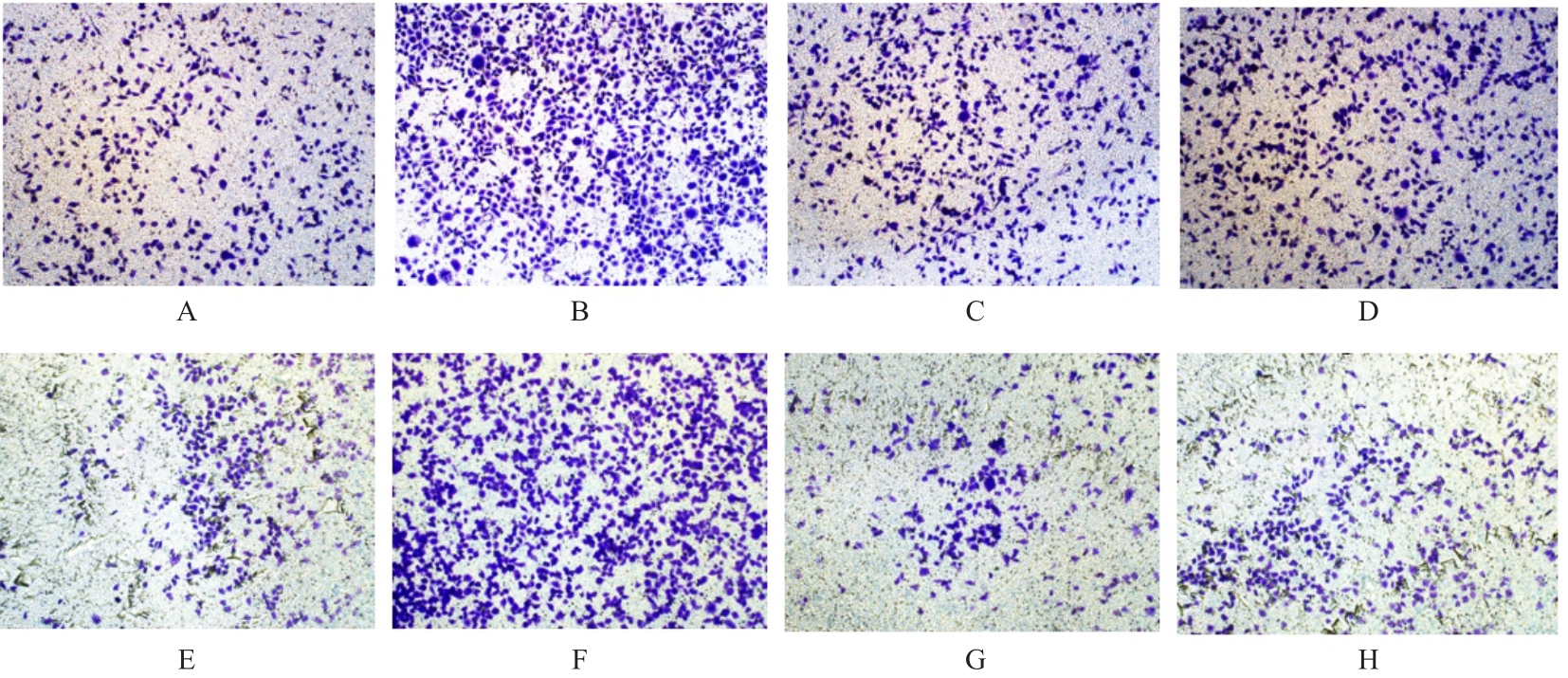
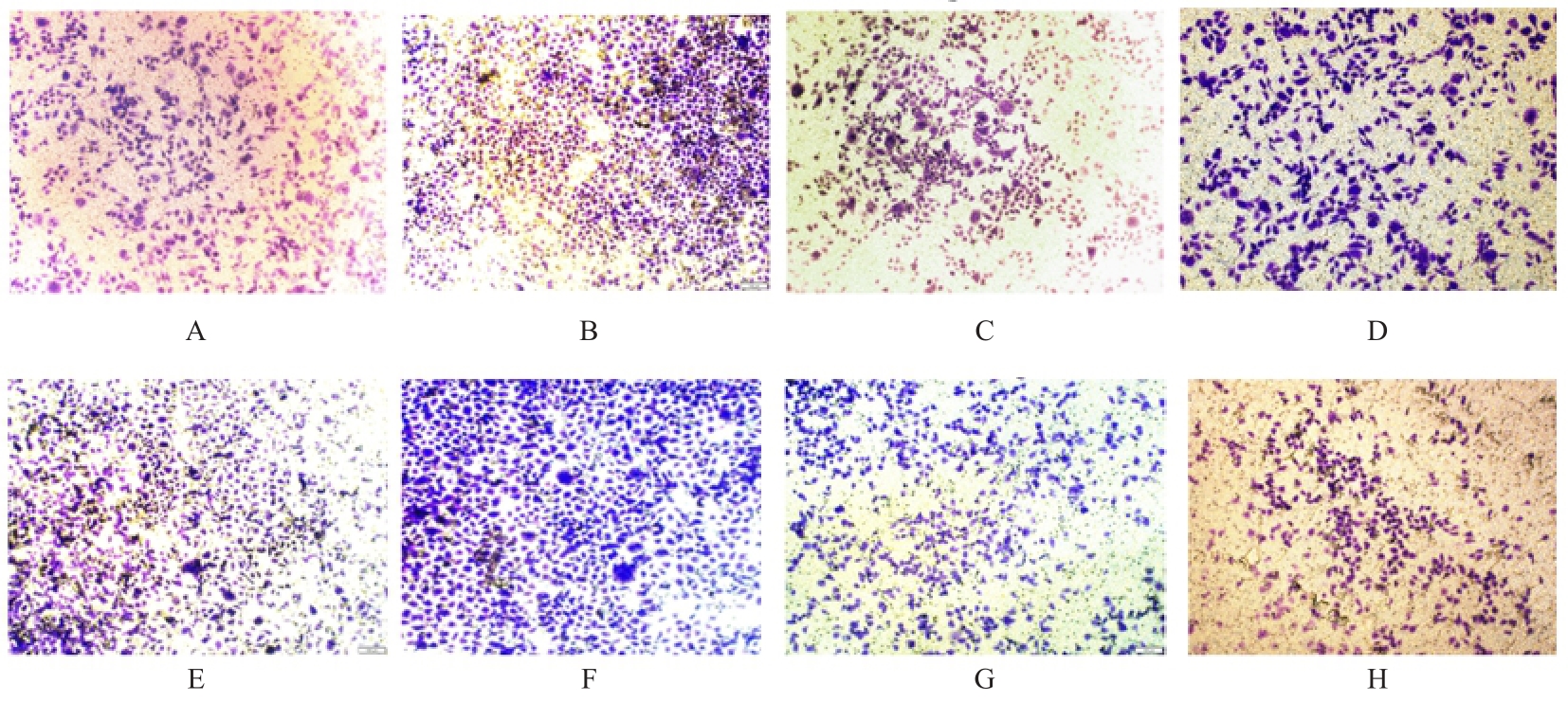
Tab. 1
Numbers of migration and invasion cells in various groups"
| EC109 | 175.750±7.349 | 123.330±6.743 |
| EC109+si-NC | 234.870±9.523* | 186.330±5.163* |
| EC109+si-Siglec15#1 | 178.850±6.246△ | 103.420±2.165△ |
| EC109+si-Siglec15#2 | 163.560±5.566△ | 112.650±5.443△ |
| KYSE150 | 216.410±4.685 | 212.470±4.694 |
| KYSE150+si-NC | 345.350±4.654# | 325.350±8.789# |
| KYSE150+si-Siglec15#1 | 194.850±2.253○ | 193.870±4.767○ |
| KYSE150+si-Siglec15#2 | 187.450±6.378○ | 199.750±8.773○ |
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | 地力亚尔·吾斯曼江, 王 岩, 张玉俊, 等. 2006—2020年中国食管癌死亡趋势及其年龄-时期-队列模型分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(7): 1323-1329. |
| 3 | ANDERSON N R, MINUTOLO N G, GILL S, et al. Macrophage-based approaches for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(5): 1201-1208. |
| 4 | LI M J, HE L Y, ZHU J, et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages for cancer treatment[J]. Cell Biosci, 2022, 12(1): 85. |
| 5 | CAO X, ZHOU Y D, MAO F, et al. Identification and characterization of three Siglec15-related immune and prognostic subtypes of breast-invasive cancer[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 106: 108561. |
| 6 | FAN M K, ZHANG G C, XIE M F, et al. Siglec-15 as a new perspective therapy target in human giant cell tumor of bone[J]. Curr Oncol, 2022, 29(10): 7655-7671. |
| 7 | MUTKA M, JOENSUU K, HEISKALA M, et al. Core needle biopsies alter the amounts of CCR5, Siglec-15, and PD-L1 positivities in breast carcinoma[J]. Virchows Arch, 2023, 483(2): 215-224. |
| 8 | LIANG H F, CHEN Q, HU Z C, et al. Siglec15 facilitates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer and is correlated with spinal metastasis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(6): 281. |
| 9 | DU H, TANG J L, LI X Y, et al. Siglec-15 is an immune suppressor and potential target for immunotherapy in the pre-metastatic lymph node of colorectal cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 691937. |
| 10 | ROGERS J E, SEWASTJANOW-SILVA M, WATERS R E, et al. Esophageal cancer: emerging therapeutics[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2022, 26(2): 107-117. |
| 11 | RUSTGI A K, EL-SERAG H B. Esophageal carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(26): 2499-2509. |
| 12 | SALMI S, SIISKONEN H, SIRONEN R, et al. The number and localization of CD68+ and CD163+ macrophages in different stages of cutaneous melanoma[J]. Melanoma Res, 2019, 29(3): 237-247. |
| 13 | PETRILLO A, SMYTH E C. Immunotherapy for squamous esophageal cancer: a review[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12(6): 862. |
| 14 | QI L, YU H Q, ZHANG Y, et al. IL-10 secreted by M2 macrophage promoted tumorigenesis through interaction with JAK2 in glioma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(44): 71673-71685. |
| 15 | BOSTEELS C, NEYT K, VANHEERSWYNGHELS M, et al. Inflammatory type 2 cDCs acquire features of cDC1s and macrophages to orchestrate immunity to respiratory virus infection[J]. Immunity, 2020, 52(6): 1039-1056.e9. |
| 16 | TOOR S M, MURSHED K, AL-DHAHERI M, et al. Immune checkpoints in circulating and tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T cell subsets in colorectal cancer patients[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2936. |
| 17 | QUARANTA V, SCHMID M C. Macrophage-mediated subversion of anti-tumour immunity[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(7): 747. |
| 18 | HUANG R L, WANG S Q, WANG N, et al. CCL5 derived from tumor-associated macrophages promotes prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis via activating β-catenin/STAT3 signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(4): 234. |
| 19 | MATLUNG H L, SZILAGYI K, BARCLAY N A, et al. The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 276(1): 145-164. |
| 20 | JIA X, YAN B J, TIAN X Q, et al. CD47/SIRPα pathway mediates cancer immune escape and immunotherapy[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(13): 3281-3287. |
| 21 | 汪 鹏, 仇建南, 王忠夏, 等. 肝癌微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(5): 1212-1218. |
| 22 | HU J, YU A Z, OTHMANE B, et al. Siglec15 shapes a non-inflamed tumor microenvironment and predicts the molecular subtype in bladder cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(7): 3089-3108. |
| 23 | CHEN J, TAN Y, SUN F H, et al. Single-cell transcriptome and antigen-immunoglobin analysis reveals the diversity of B cells in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Genome Biol, 2020, 21(1): 152. |
| 24 | LIU W T, JI Z, WU B R, et al. Siglec-15 promotes the migration of liver cancer cells by repressing lysosomal degradation of CD44[J]. FEBS Lett, 2021, 595(17): 2290-2302. |
| 25 | ZHOU S, WANG Y T, ZHANG R, et al. Association of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 15 with phenotypes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in the setting of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2023, 6(1): e2250965. |
| 26 | KELLER A A, MAEß M B, SCHNOOR M, et al. Transfecting macrophages[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1784: 187-195. |
| 27 | ZHENG B X, SONG K L, SUN L L, et al. Siglec-15-induced autophagy promotes invasion and metastasis of human osteosarcoma cells by activating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Beclin-1/ATG14 pathway[J]. Cell Biosci, 2022, 12(1): 109. |
| 28 | 张绍谨, 闫泽晨, 李 腾, 等. 长链非编码RNA SNHG15对肾细胞癌细胞增殖、 凋亡、 迁移和侵袭的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2023, 58(6): 781-785. |
| [1] | Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU. Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008. |
| [2] | Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015. |
| [3] | Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043. |
| [4] | Shilei GAO,Jiaqiang WANG,Weitao YAO,Zhichao TIAN,Chao LI,Xiaoxiao LIANG,Xin WANG. Effect of miR-761 on epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma MG63 cells by regulating tumor-associated macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 978-988. |
| [5] | Yuan WANG,Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Liping YE. Effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 on invasion and migration of lung cancer A549 and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 666-675. |
| [6] | Bo YUAN,Jiayi XIE,Siyu JIANG,Yajun MENG,Qinghua ZHU,Xiaofei LI,Xiumei FU,Lide XIE. Effect of adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes on migration ability of macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 718-727. |
| [7] | Yan QU,Lin DAI,Biao WANG,Duji RUAN,Yuchang ZHONG,Xuefeng YANG. Inhibitory effect of miR-487a on M2-type polarization of gastric cancer tumor-associated macrophages by targeting TIA1 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 728-738. |
| [8] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [9] | Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI. Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149. |
| [10] | Jie ZENG,Xueyan YU,Ting LUO,Jiang XU. Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 18-24. |
| [11] | Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG. Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32. |
| [12] | Yuxue SUN,Ziqiang LIU,Hao WU,Liming ZHAO,Tao GAO,Haiyan HUANG,Chaoyue LI. Inhibitory effect of berberine on migration and invasion of human glioma T98G cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 50-57. |
| [13] | Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI. Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527. |
| [14] | Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU. Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139. |
| [15] | Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI. Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226. |