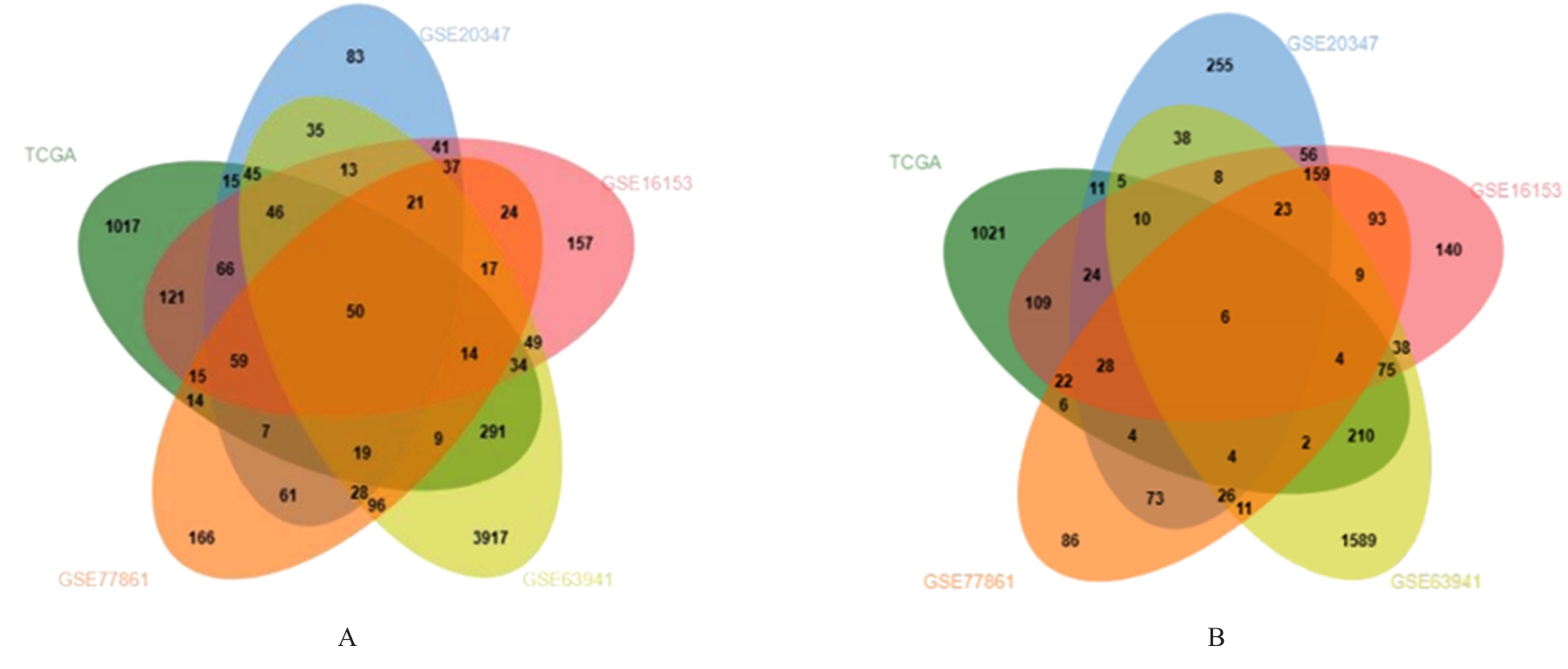
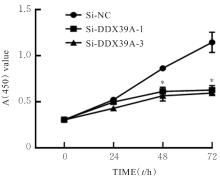
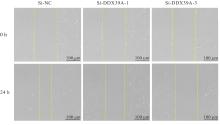
| 1 |
MILLER K D, NOGUEIRA L, MARIOTTO A B, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(5): 363-385.
|
| 2 |
XIA C F, DONG X S, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-590.
|
| 3 |
MORGAN E, SOERJOMATARAM I, RUMGAY H, et al. The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: new estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020[J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 163(3): 649-658.
|
| 4 |
王立东, 蒋宁宁, 马 磊, 等. 营养状况对中国食管癌疾病谱和精准防控策略的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024, 59(5): 593-597.
|
| 5 |
方金梅, 赵于飞, 龙腾飞, 等. 基于美国国家癌症研究所监测、 流行病学、 结果数据库食管癌病人预后影响因素分析[J]. 安徽医药, 2022, 26(3): 475-480.
|
| 6 |
GUSTAFSON E A, WESSEL G M. DEAD-box helicases: posttranslational regulation and function[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2010, 395(1): 1-6.
|
| 7 |
SUGIURA T, NAGANO Y, NOGUCHI Y. DDX39, upregulated in lung squamous cell cancer, displays RNA helicase activities and promotes cancer cell growth[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2007, 6(6): 957-964.
|
| 8 |
BAO Y W, JIANG A M, DONG K, et al. DDX39 as a predictor of clinical prognosis and immune checkpoint therapy efficacy in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(12): 3158-3172.
|
| 9 |
XING C J, TIAN H, ZHANG Y N, et al. DDX39 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis and promotes aggressiveness of melanoma by cooperating with SNAIL[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 1261.
|
| 10 |
齐英男, 麦秀滢, 姜晓勃, 等. 食管癌个体化临床靶区-计划靶区外扩边界剂量研究及摆位误差分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 2023, 40(12): 1453-1458.
|
| 11 |
SUGIURA T, SAKURAI K, NAGANO Y. Intracellular characterization of DDX39, a novel growth-associated RNA helicase[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2007, 313(4): 782-790.
|
| 12 |
GROMADZKA A M, STECKELBERG A L, SINGH K K, et al. A short conserved motif in ALYREF directs cap-and EJC-dependent assembly of export complexes on spliced mRNAs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(5): 2348-2361.
|
| 13 |
WEN X H, ZHANG S F, ZHANG Y A. Research progress in DEAD-box family protein in cancer[J]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2017, 42(11): 1311-1315.
|
| 14 |
WANG X D, LI P P, WANG C Y, et al. DEAD-box RNA helicase 39 promotes invasiveness and chemoresistance of ER-positive breast cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(7): 1846-1858.
|
| 15 |
熊建新, 于立丽. DDX39在胃癌组织中的表达及其与临床病理特征和预后的关系[J]. 国际消化病杂志,2019, 39(5): 366-368.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG T, MA Z J, LIU L J, et al. DDX39 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(6): 675.
|
| 17 |
WU Z L, CHEN Y J, ZHANG G Z, et al. SKI knockdown suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and ameliorates disc degeneration[J]. Apoptosis, 2022, 27(1/2): 133-148.
|
| 18 |
ZHANG Y, WANG X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 165.
|
| 19 |
CHEN Z Y, DU Y, WANG L, et al. MiR-543 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by targeting Dickkopf 1 through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(20): 3660-3668.
|
| 20 |
LIN Y B, CHEN X, LIN L P, et al. Sesamolin serves as an MYH14 inhibitor to sensitize endometrial cancer to chemotherapy and endocrine therapy via suppressing MYH9/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2024, 29(1): 63.
|
| 21 |
YU F Y, YU C H, LI F F, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 307.
|
| 22 |
顾嘉伟, 牛耿明, 柯重伟. 经典Wnt信号通路中β-catenin在细胞核内外分布的调控机制及潜在治疗靶点的研究进展[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2022, 49(2): 300-308.
|
| 23 |
WANG B Q, LI X P, LIU L, et al. β-Catenin: oncogenic role and therapeutic target in cervical cancer[J]. Biol Res, 2020, 53(1): 33.
|
| 24 |
XU Q X, LI X Z, LI Y, et al. Kinesin family member 23 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal carcinoma by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Funct Integr Genomics, 2023, 23(2): 154.
|
| 25 |
LIU H J, LIU Y, ZHOU Y J, et al. TM7SF2-induced lipid reprogramming promotes cell proliferation and migration via CPT1A/Wnt/β-Catenin axis in cervical cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1): 207.
|
| 26 |
LECARPENTIER Y, SCHUSSLER O, HÉBERT J L, et al. Multiple targets of the canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling in cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1248.
|
| 27 |
罗 刚, 谢敏慧, 杨 娟, 等. REGγ通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞增殖、 迁移和侵袭[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(21): 5285-5289.
|
| 28 |
KATOH M, KATOH M. WNT signaling and cancer stemness[J]. Essays Biochem, 2022, 66(4): 319-331.
|
 )
)