Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 191-201.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250123
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Expressions of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 in serum and lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances
Peiqin JIANG1,Zheng ZHANG1,Zhong HUANG2( ),Xianling LU1(
),Xianling LU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
2.Emergency Medical Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
-
Received:2024-02-10Accepted:2024-04-07Online:2025-01-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Zhong HUANG,Xianling LU E-mail:10082404@qq.com;luxianlingmary@163.com
CLC Number:
- R563.9
Cite this article
Peiqin JIANG,Zheng ZHANG,Zhong HUANG,Xianling LU. Expressions of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 in serum and lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 191-201.
share this article
Tab.1
Clinical data of subjects in control group and COPD stable group"
| Group | Age (x±s, year) | BMI | FEV1%pred (x±s, η/%) | FEV1/FVC (x±s, η/%) | Percentage of male [n(η/%)] | Percentage of smoking [n(η/%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 69.70±7.40 | 24.18±2.30 | 97.10±6.82 | 78.05±3.56 | 19(47.5) | 13(32.5) |
| COPD stable | 69.85±7.32 | 24.91±2.38 | 48.88±6.55 | 51.08±7.47 | 23(57.5) | 18(45.0) |
| t/χ2 | 0.091 | 1.389 | 0.802 | 1.317 | ||
| P | 0.928 | 0.169 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.370 | 0.251 |
Tab.2
Correlations between serum ATX levels and clinical indicators of patients in AECOPD group and COPD stable group"
| Index | AECOPD group | COPD stable group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | |
| Smoking | 0.052 | 0.749 | 0.107 | 0.512 |
| WBC | 0.110 | 0.499 | 0.384 | 0.014 |
| NEUT% | 0.074 | 0.650 | 0.054 | 0.738 |
| NLR | 0.046 | 0.776 | -0.020 | 0.902 |
| BMI | 0.043 | 0.791 | 0.245 | 0.127 |
| CAT | 0.581 | <0.001 | 0.463 | 0.003 |
| FEV1%pred | - | - | -0.393 | 0.012 |
| FEV1/FVC | - | - | -0.353 | 0.025 |
Tab.3
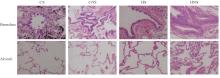
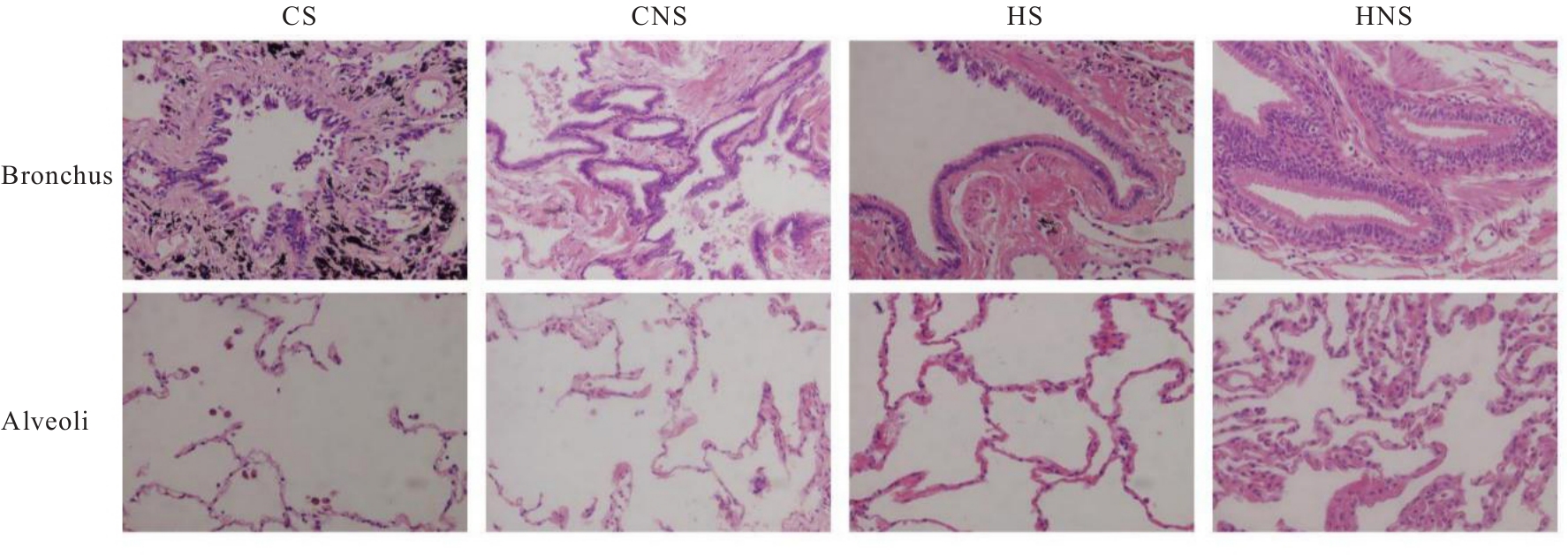
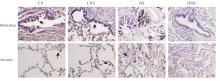
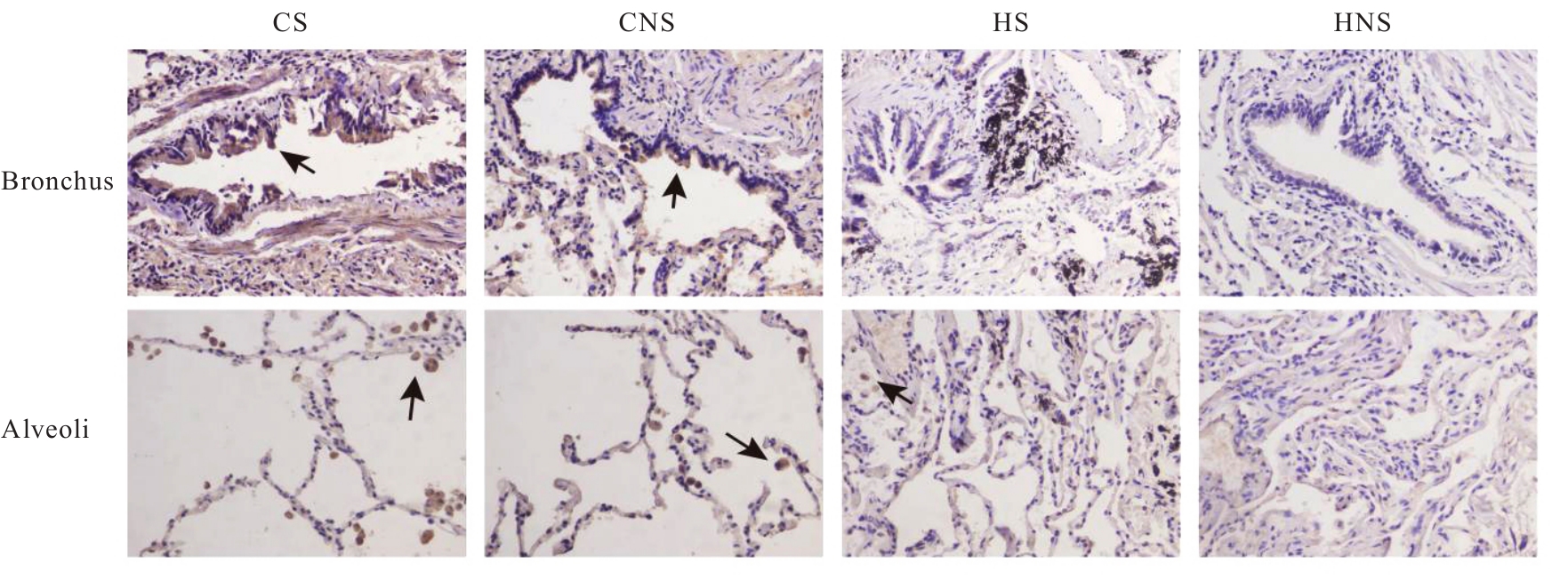
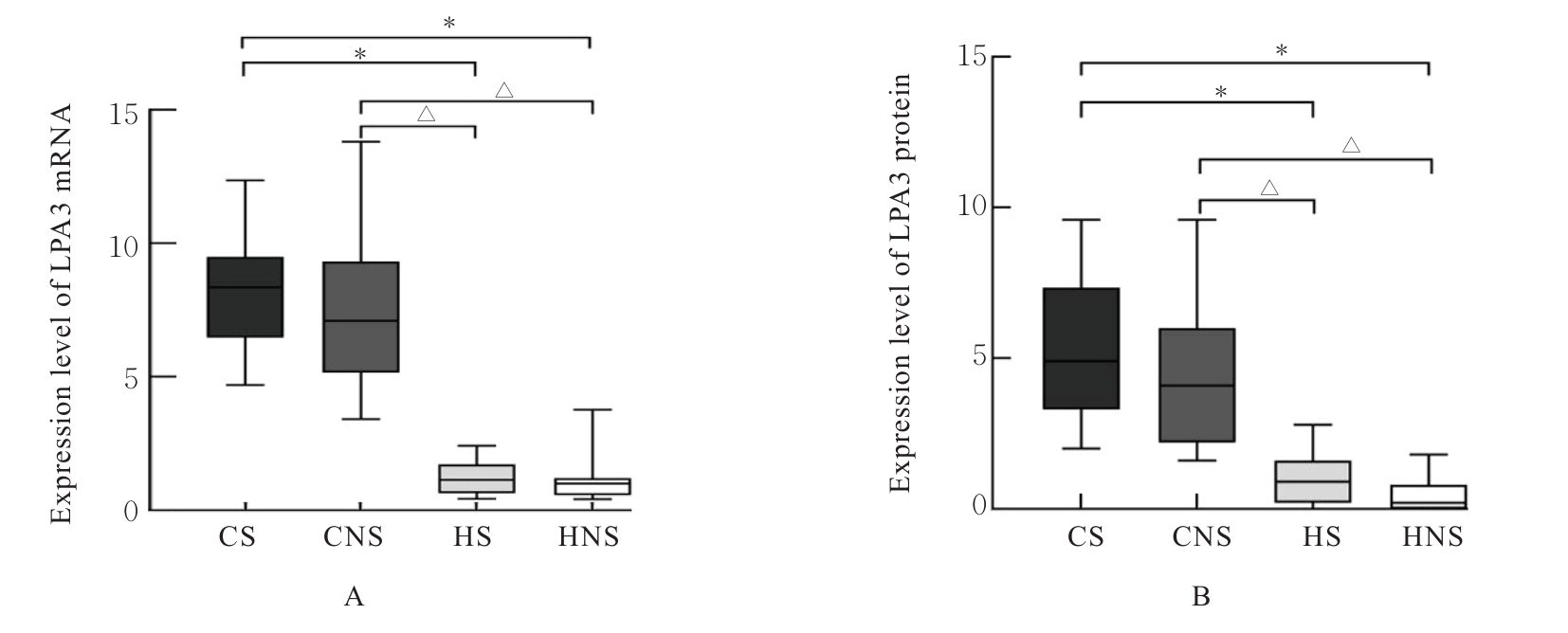
Clinical data of patients in various groups"
| Group | Age (x±s, year) | BMI (x±s, kg·m-2) | SI (x±s) | FEV1%pred (x±s, η/%) | FEV1/FVC (x±s, η/%) | Percentage of male [n(η/%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 64.10±9.88 | 24.43±1.59 | 620.00±311.47 | 77.65±7.58 | 62.85±4.11 | 14(70.0) |
| CNS | 64.20±7.27 | 23.59±1.71 | - | 77.45±8.09 | 63.25±4.23 | 11(55.0) |
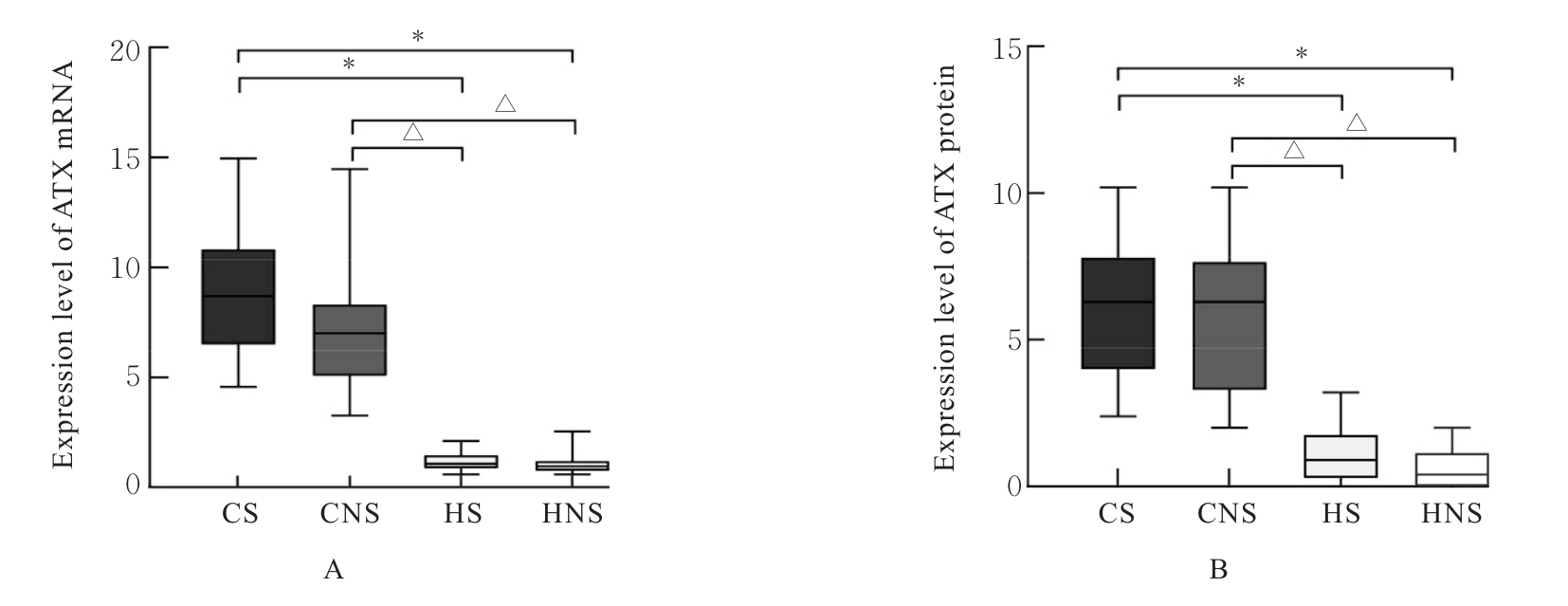
| HS | 63.50±8.63 | 24.74±2.02 | 608.00±334.81 | 95.60±9.13*△ | 76.70±3.92*△ | 14(70.0) |
| HNS | 62.45±8.68 | 24.52±2.04 | - | 100.40±11.86*△ | 78.90±4.96*△ | 10(50.0) |
| F/χ2 | 0.172 | 1.501 | 0.014 | 33.025 | 78.503 | 2.686 |
| P | 0.915 | 0.221 | 0.907 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.443 |
| 1 | GUO P, LI R, PIAO T H, et al. Pathological mechanism and targeted drugs of COPD[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2022, 17: 1565-1575. |
| 2 | ZHANG X T, LI M M, YIN N, et al. The expression regulation and biological function of autotaxin[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(4): 939. |
| 3 | KANO K, AOKI J, HLA T. Lysophospholipid mediators in health and disease[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2022, 17: 459-483. |
| 4 | ZHAO J, ZHAO Y T. Lysophospholipids in lung inflammatory diseases[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2021, 1303: 373-391. |
| 5 | SOLÍS K H, ROMERO-ÁVILA M T, GUZMÁN-SILVA A, et al. The LPA3 receptor: regulation and activation of signaling pathways[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(13): 6704. |
| 6 | SAATIAN B, ZHAO Y T, HE D H, et al. Transcriptional regulation of lysophosphatidic acid-induced interleukin-8 expression and secretion by p38 MAPK and JNK in human bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Biochem J, 2006, 393(Pt 3): 657-668. |
| 7 | 范 傲, 黄 钟, 段宇清, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血浆中性粒细胞胞外诱捕网和白细胞介素-8及白细胞介素-33的表达水平及其临床意义[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2022(2): 84-89. |
| 8 | 中华医学会呼吸病学分会慢性阻塞性肺疾病学组, 中国医师协会呼吸医师分会慢性阻塞性肺疾病工作委员会. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指南(2021年修订版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2021, 44(3): 170-205. |
| 9 | SHENG H Y, ZHANG Y J, SHI X Q, et al. Functional, ultrastructural, and transcriptomic changes in rat diaphragms with different durations of cigarette smoke exposure[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2020, 15: 3135-3145. |
| 10 | ZHENG X R, ZHANG L Y, CHEN J, et al. Dendritic cells and Th17/Treg ratio play critical roles in pathogenic process of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 1141-1151. |
| 11 | 盛梅梅, 罗专波. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病发病机制的研究现状及进展[J]. 现代医学与健康研究(电子版), 2023, 7(1): 38-41. |
| 12 | 张 地, 张俊杰. Autotaxin表达调控机制及其生物学功能[J]. 中国科学:生命学, 2022, 52(8): 1148-1162. |
| 13 | BRINDLEY D N, TANG X Y, MENG G M, et al. Role of adipose tissue-derived autotaxin, lysophosphatidate signaling, and inflammation in the progression and treatment of breast cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(16): 5938. |
| 14 | BENESCH M G K, MACINTYRE I T K, MCMULLEN T P W, et al. Coming of age for autotaxin and lysophosphatidate signaling: clinical applications for preventing, detecting and targeting tumor-promoting inflammation[J]. Cancers, 2018, 10(3): 73. |
| 15 | BLANQUE R, DESROY N, DUPONT S, et al. Pharmacological profile and efficacy of GLPG1690, a novel ATX inhibitor for COPD treatment[C]//5.1 Airway Pharmacology and Treatment. European Respiratory Society, 2015: PA2129. |
| 16 | LI Q L, WONG W, CHAKRABARTI A, et al. Serum lysophosphatidic acid measurement by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in COPD patients[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2021, 32(8): 1987-1997. |
| 17 | 洪静雪, 黄 钟, 张 妤, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血浆溶血磷脂酸和可溶性ST2的表达水平及其临床意义[J]. 西部医学, 2024, 36(1): 57-62. |
| 18 | ZHAO Y T, NATARAJAN V. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and its receptors: role in airway inflammation and remodeling[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1831(1): 86-92. |
| 19 | JIANG S F, YANG H L, LI M Q. Emerging roles of lysophosphatidic acid in macrophages and inflammatory diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(15): 12524. |
| 20 | 王 蕾, 王桐生, 王雅娟, 等. 巨噬细胞在慢性阻塞性肺疾病发展及治疗中的研究进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2024, 29(2): 293-297. |
| 21 | OIKONOMOU N, MOURATIS M A, TZOUVELEKIS A, et al. Pulmonary autotaxin expression contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2012, 47(5): 566-574. |
| 22 | NIKITOPOULOU I, FANIDIS D, NTATSOULIS K, et al. Increased autotaxin levels in severe COVID-19, correlating with IL-6 levels, endothelial dysfunction biomarkers, and impaired functions of dendritic cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18): 10006. |
| 23 | HIKICHI M, MIZUMURA K, MARUOKA S, et al. Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(): S2129-S2140. |
| 24 | ZHAO C Q, SARDELLA A, CHUN J, et al. TNF-alpha promotes LPA1- and LPA3-mediated recruitment of leukocytes in vivo through CXCR2 ligand chemokines[J]. J Lipid Res, 2011, 52(7): 1307-1318. |
| 25 | ZHAO Y, HASSE S, ZHAO C Q, et al. Targeting the autotaxin-Lysophosphatidic acid receptor axis in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2019, 164: 74-81. |
| 26 | LI S, XIONG C Y, ZHANG J J. ATX and LPA receptor 3 are coordinately up-regulated in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated THP-1 cells through PKR and SPK1-mediated pathways[J]. FEBS Lett, 2012, 586(6): 792-797. |
| [1] | Xiaoyu HOU,Ya LI,Yian SONG,Tianhui HE,Jie ZHANG,Jianhui XU. Effect of prostaglandin E2 on discharge activity of warm-sensitive neurons in median preoptic nucleus of hypothalamus in female mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 17-25. |
| [2] | Xinyue MA,Hui XU,Jiawen DIAO,Aihua JIN,Jishu QUAN. Inhibitory effect of Boschnikia rossica polysaccharides on THP-1 macrophage inflammation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1499-1511. |
| [3] | Guobin HE,Huan WANG. Effect of knockdown of RIP3 on autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced human renal tubular epithelial HK2 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1644-1653. |
| [4] | Weichao WU,Yan GUO,Xiangkai ZHAO,Zhiguang GU,Yijia GUO,Zipeng LAN,Hui HUANG,Lei KUANG,Ming ZHANG,Dongsheng HU,Yongli YANG,Wei WANG,Jinru CHEN. Correlation analysis on occupational acid fog exposure and accelerated biological aging in workers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1741-1750. |
| [5] | Yuxuan CAO,Wei CHEN,Chengbiao SUN,Na ZHAO,Yan WANG,Mingxin DONG,Na XU,Wensen LIU,Yongmei LI. Damage effect of VSV on vascular endothelial barrier function in vitro and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1275-1285. |
| [6] | Wenhui LIU,Miao YU,Ying GUO,Yupeng LIU,Yang XING,Xinyu HONG,Jiale CUI. Research progress in effect of CXC chemokine receptor 3 on occurrence and development of nervous system diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1474-1480. |
| [7] | Lin CHEN,Limin YAN,Huaijie XING,Min CHEN,Xiaoyan LI,Chaosheng ZENG. Improvement effect of Xuebijing on brain tissue injury and Th17/Treg immune imbalance in cerebrospinal fluid in NMDA receptor encephalitis model mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 697-707. |
| [8] | Ying ZHANG,Zhaohui WAN,Xianxun JIANG. Effect of over-expression of NDRG1 on resistance of castration-resistant prostate cancer resistant cell line C4-2/ENZA and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 708-717. |
| [9] | Li ZHANG,Binfeng XIA,Huihui HUANG,Ru WANG,Min KONG,Xia YIN. Research progress in pathophysiological mechanism and clinical diagnosis and treatment of hypertension associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor inhibitors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 854-863. |
| [10] | Yingxin RUAN,Junya JIA,Zhanfei WU,Wenya SHANG,Pengyu ZHANG. Effect of NLRP3 inflammatome in renal interstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 587-595. |
| [11] | Jialiang CHEN,Qi LI,Xiangdong ZHOU,Xiaomei CHEN,Feng LIU,Chang LIU,Youqing ZHONG,Liang LI. Inhibitory effect of nobiletin on airway mucus hypersecretion in model rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 295-302. |
| [12] | Yu ZHANG,Xianling LU. Expressions of IL-33, IL-8, and NETs in lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 498-507. |
| [13] | Zhongyan ZHAO,Zhiyu XU,Chanji WU,Eryi ZHAO,Dan HUANG,Shixiong HUANG. Autoimmune encephalitis with double positive anti-NMDAR and anti-GABABR secondary to herpes simplex virus encephalitis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 236-242. |
| [14] | Xinqiang ZHANG,Bo WANG,Huicheng FENG. Effect of local impulse vibration stimulation on proprioception recovery after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in rabbits [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1407-1414. |
| [15] | Xiuling ZHOU,Deyu CONG,Ye ZHANG,Hongshi ZHANG. Effect of head acupuncture on neurological function and HIF-1α and VEGFR2 expressions in brain tissue in rats with focal cerebral ischemia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1431-1436. |
|
||