| [1] |
Xingqi SU,Lingmin ZHAO,Di MA,Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG.
Analysis on correlation of cerebral infarct area with cytokines and immune status in patients with acute ischemic stroke
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 124-132.
|
| [2] |
Xiao SUN,Yini WANG,Fangsheng GAO,Ying ZHANG,Ping LIN.
Characteristics of intestinal flora in patients with depression based on GMrepo database and correlation analysis between depression and intestinal flora
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 157-163.
|
| [3] |
Dan ZHAO,Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI.
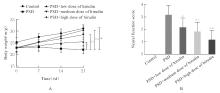
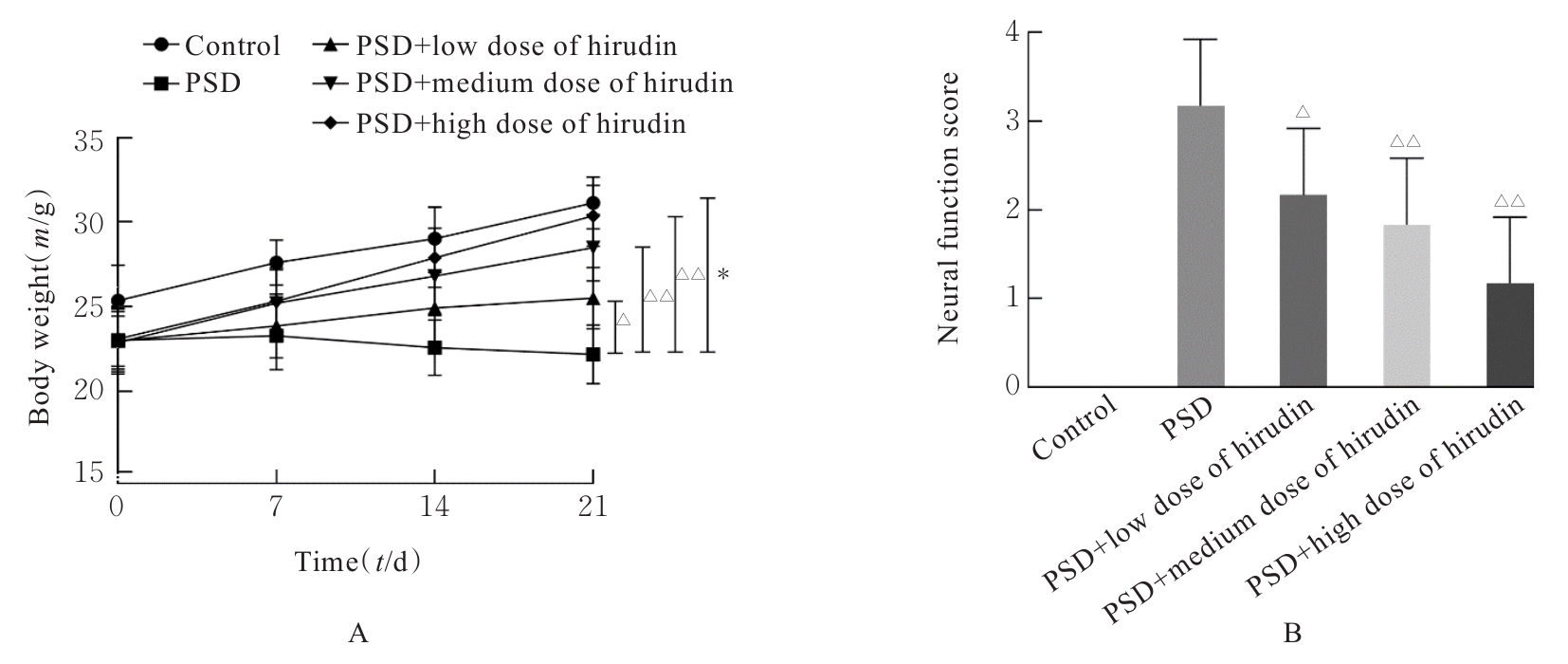
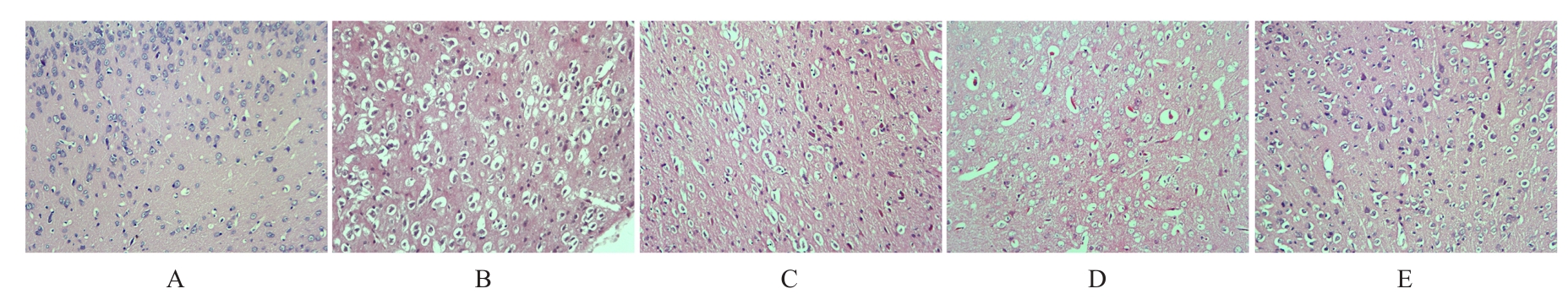
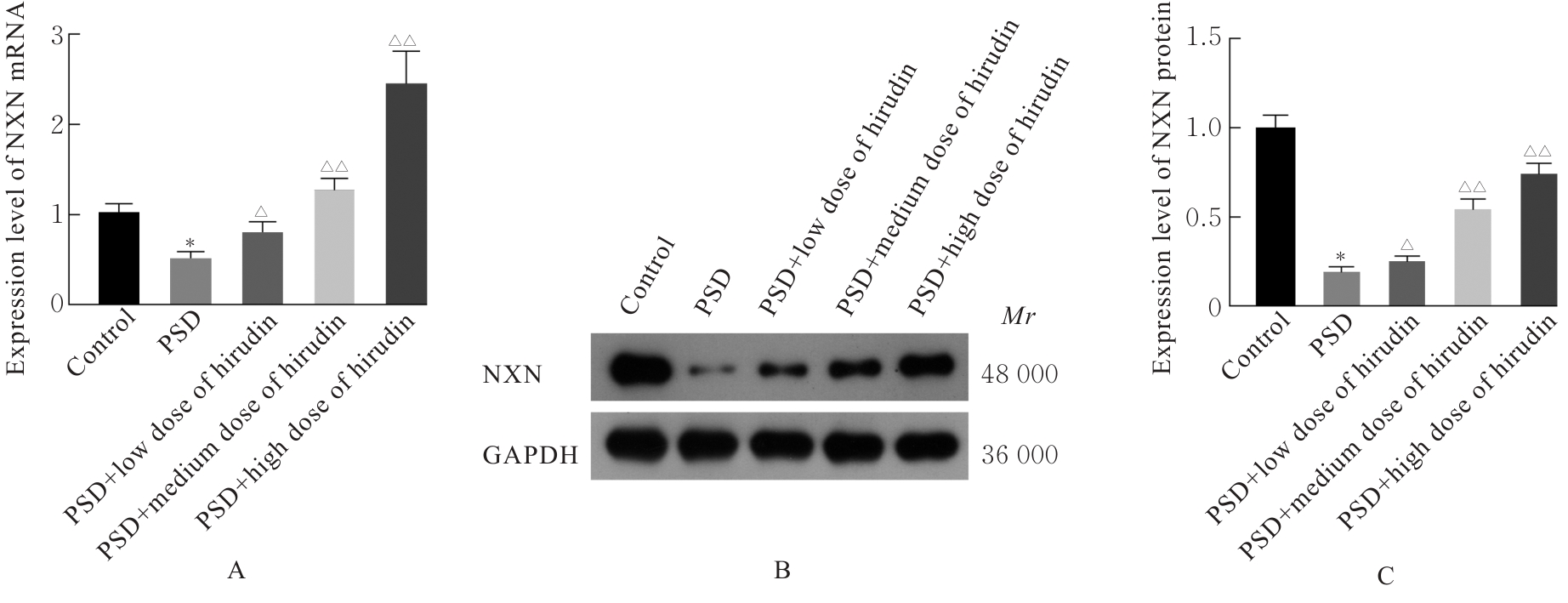
Effect of nucleoredoxin in medial prefrontal cortex on depression-like behavior in mice with post-stroke depression and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1606-1613.
|
| [4] |
Yawen LIAN,Yinghua LI,Guoxing XU,Xixi XIE,Zhenlan LI.
Evaluation of recovery effect of finger motor dysfunction in patients with stroke after treated with force feedback perceptual rehabilitation training
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1116-1122.
|
| [5] |
Jing TANG,Huan LI,Shuo ZHANG,Ligang JING.
Analysis on association between serum homocysteine and inflammatory response and oxidative stress in patients with acute ischemic stroke
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 786-790.
|
| [6] |
Guanfei LI,Xunjuan ZHANG,Meng PANG,Song LI.
Prospective study on association between hemodynamic patterns and risk of ischemic stroke in people with chronic orthostatic intolerance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 473-480.
|
| [7] |
Xiuling ZHOU,Deyu CONG,Ye ZHANG,Hongshi ZHANG.
Effect of head acupuncture on neurological function and HIF-1α and VEGFR2 expressions in brain tissue in rats with focal cerebral ischemia and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1431-1436.
|
| [8] |
Canfei XU,Yan HUANG,Kaizhi ZHANG.
Acute ischemic stroke patients with onset time within 4.5 h identified by machine learning combined with magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1635-1641.
|
| [9] |
Xian ZHU,Xinxu CHEN,Yibin CHEN,Changxuan LI,Jie LIU,Tan WANG.
Improvement effect of sodium cromoglycate on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1182-1191.
|
| [10] |
Zhengnan JIANG,Yijia ZHANG,Zhen LIU,Yunfei CHEN.
Construction of neuropathic pain model in rats and its mechanism of depressive state complicated with insomnia
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 905-912.
|
| [11] |
Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI.
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922.
|
| [12] |
Tianzhen ZHANG,Hongtao SHEN,Zheng GONG,Bin ZHAO,Yan WANG.
Effect of GRK5 over-expression on depression- like behavior in P301S Tau transgenic mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 573-579.
|
| [13] |
Dongming TAN,Hongying YIN,Xiangmin DENG,Xu DING.
Antidepressant effect of carnosic acid on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in rats and its SIRT1/ERS regulatory mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 360-368.
|
| [14] |
Lingling FAN,Shuping DING,Guomin SHEN,Zhihong HU,Aihong REN,Bo DENG.
Effect of mediodorsal thalamic nucleus lesions on electrical activity in medial prefrontal cortex of rats with Parkinson’s disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1382-1388.
|
| [15] |
Cong FU,Yang YANG,Mingtu XU,Zeying QIN,Jingyang LI.
Analysis on related influencing factors of life quality of inpatients with coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 478-486.
|
 ),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI