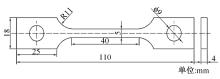
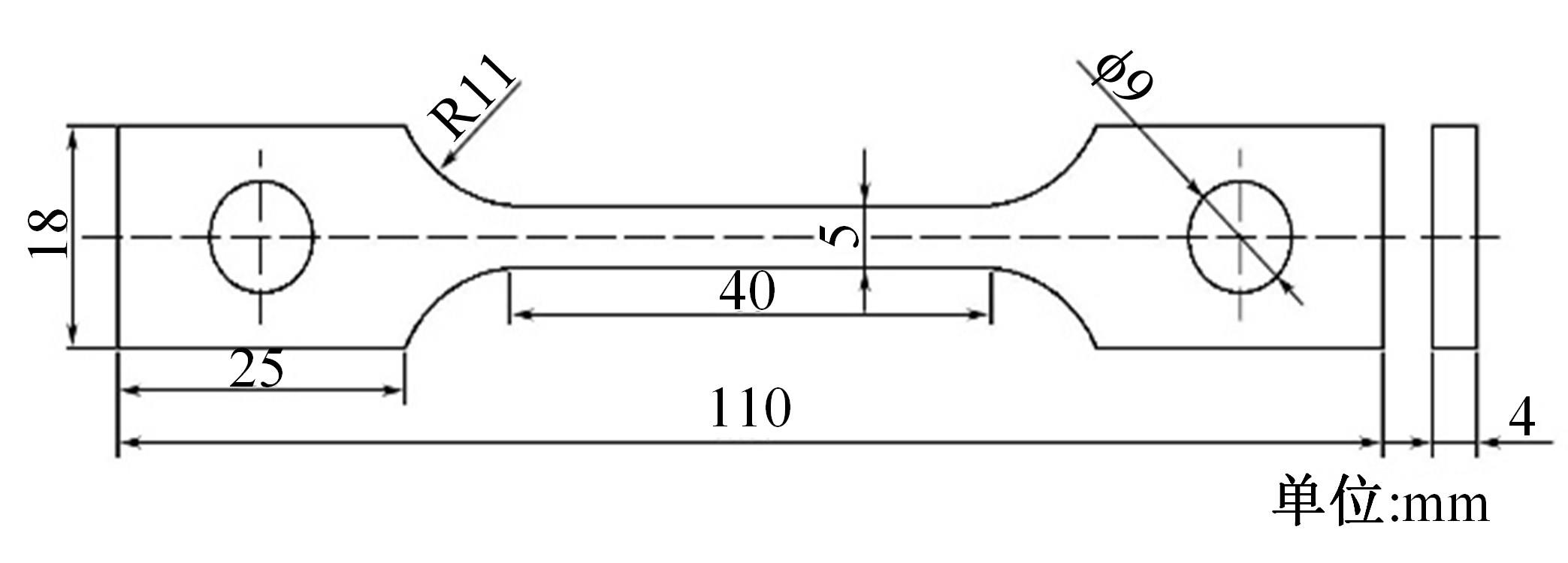
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2792-2798.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221562
• 材料科学与工程 • 上一篇
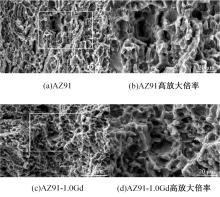
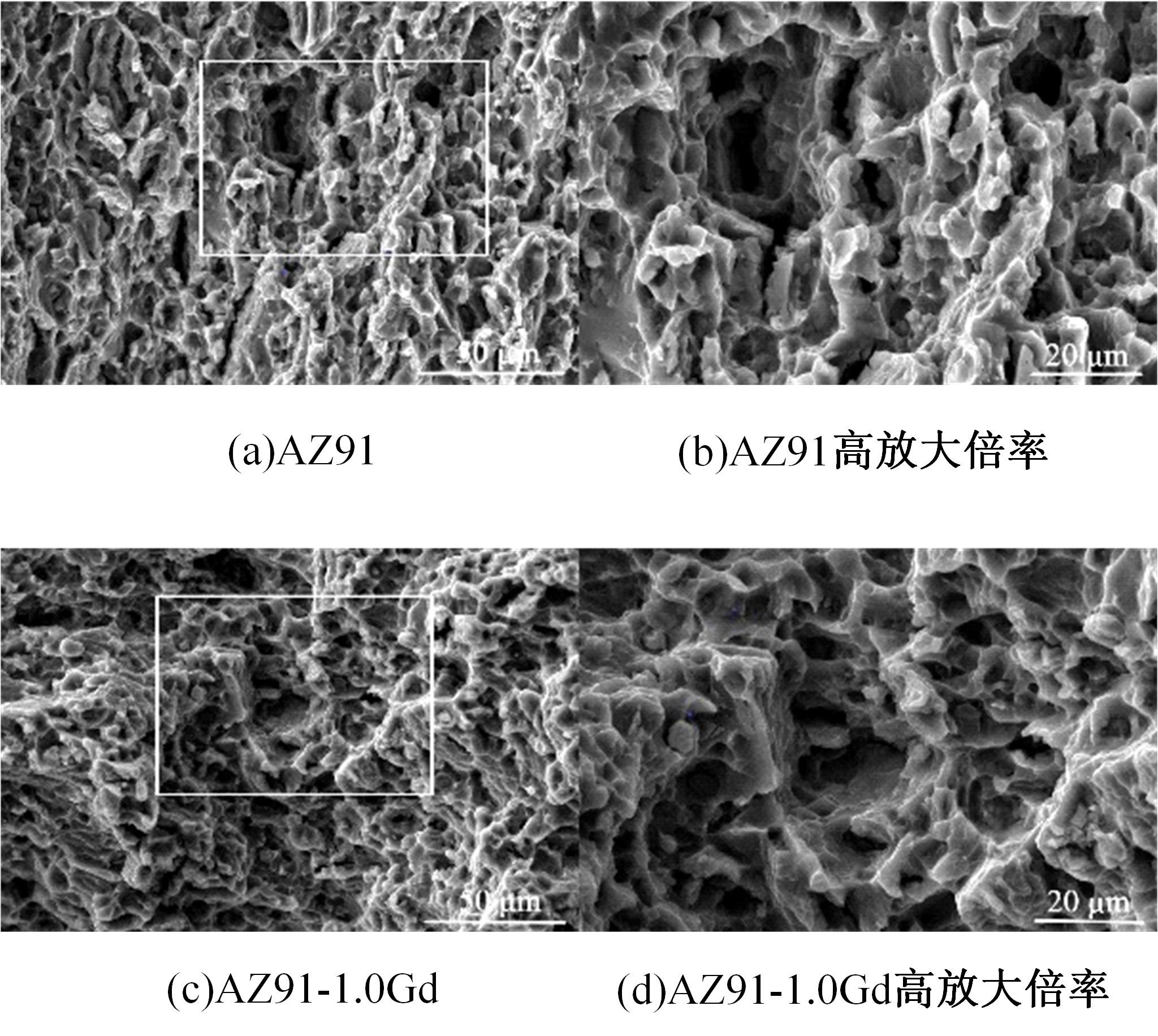
Gd对挤压镁合金AZ91组织和氢脆的影响
宋雨来1,2( ),李伟光1,2,张林阳3,宋庆军3,张华3,李军3,刘庆1,2
),李伟光1,2,张林阳3,宋庆军3,张华3,李军3,刘庆1,2
- 1.吉林大学 汽车材料教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 材料科学与工程学院,长春 130022
3.中国一汽研发总院 材料与轻量化开发院金属材料开发部,长春 130011
Effect of Gd on microstructure and hydrogen embrittlement of AZ91‐extruded magnesium alloy
Yu-lai SONG1,2( ),Wei-guang LI1,2,Lin-yang ZHANG3,Qing-jun SONG3,Hua ZHANG3,Jun LI3,Qing LIU1,2
),Wei-guang LI1,2,Lin-yang ZHANG3,Qing-jun SONG3,Hua ZHANG3,Jun LI3,Qing LIU1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Automobile Materials,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Materials Science and Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Metal Materials Department of Materials & lightweight Institute,General R&D Institute,China FAW Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130011,China
摘要:
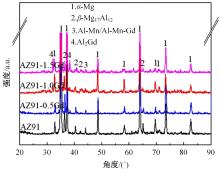
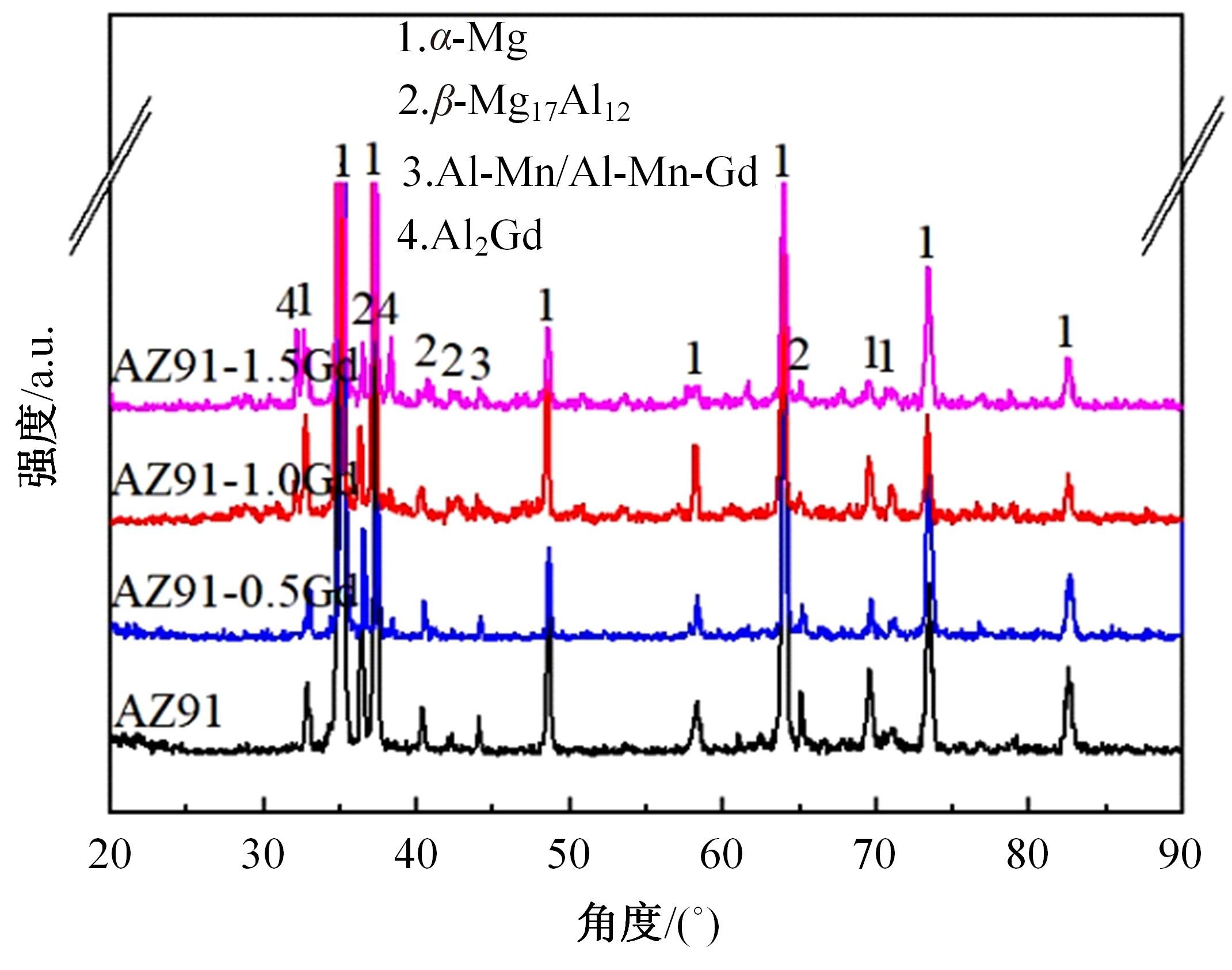
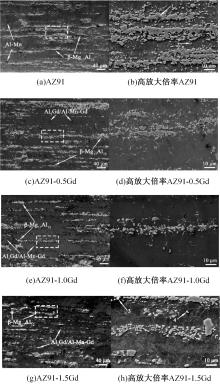
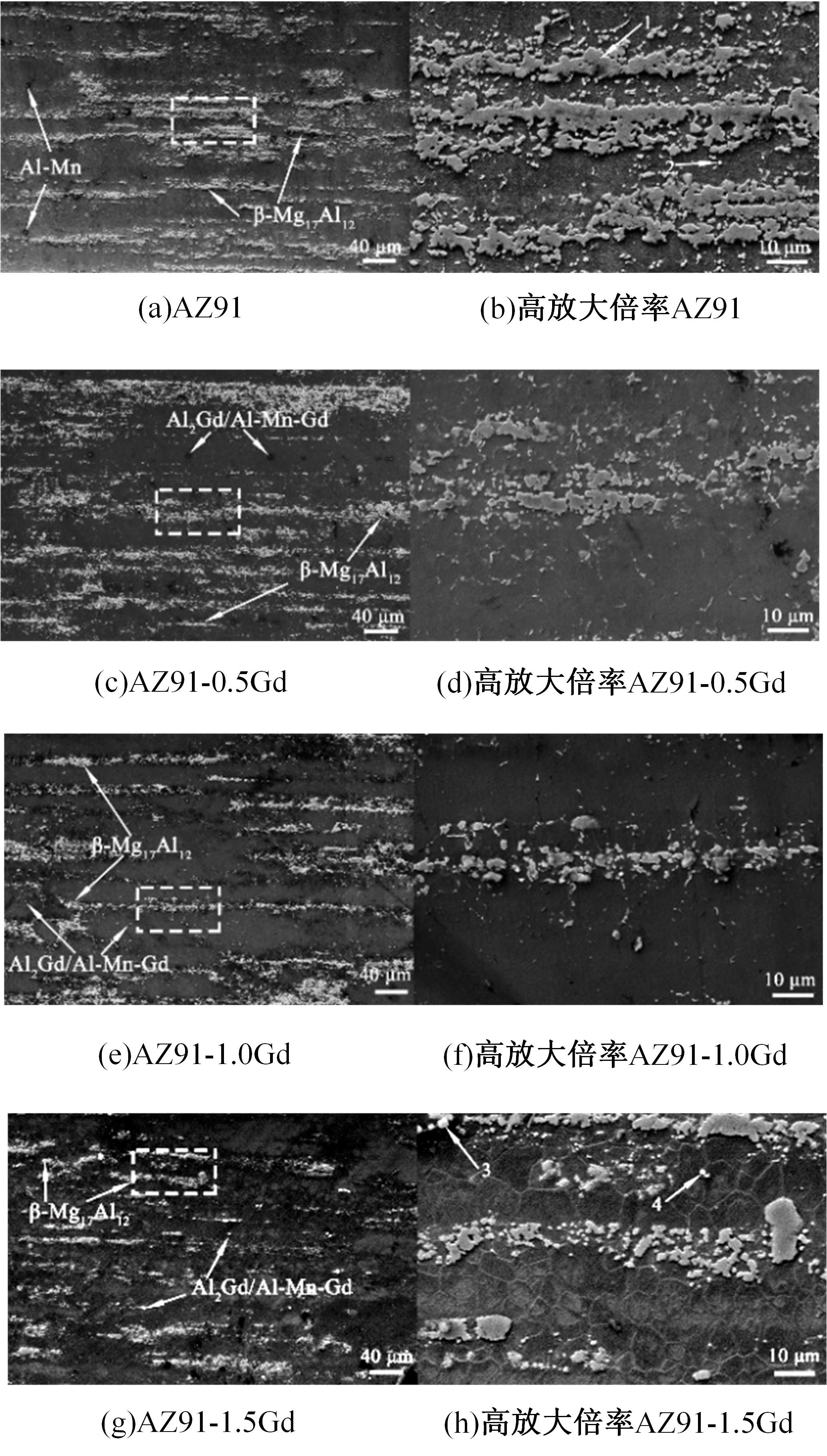
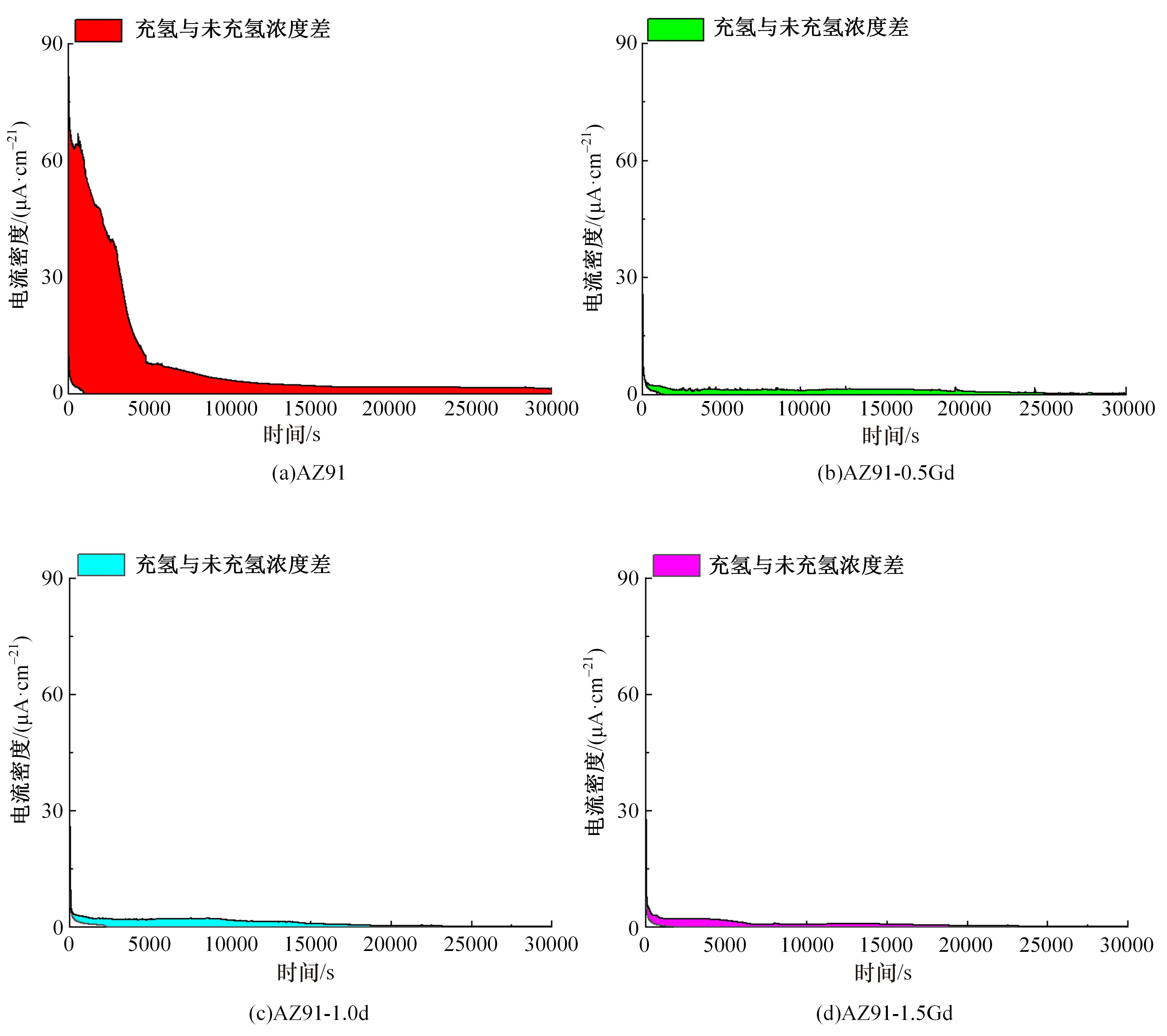
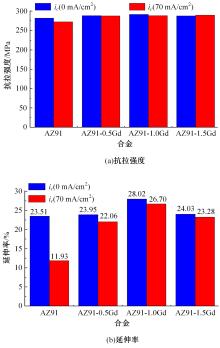
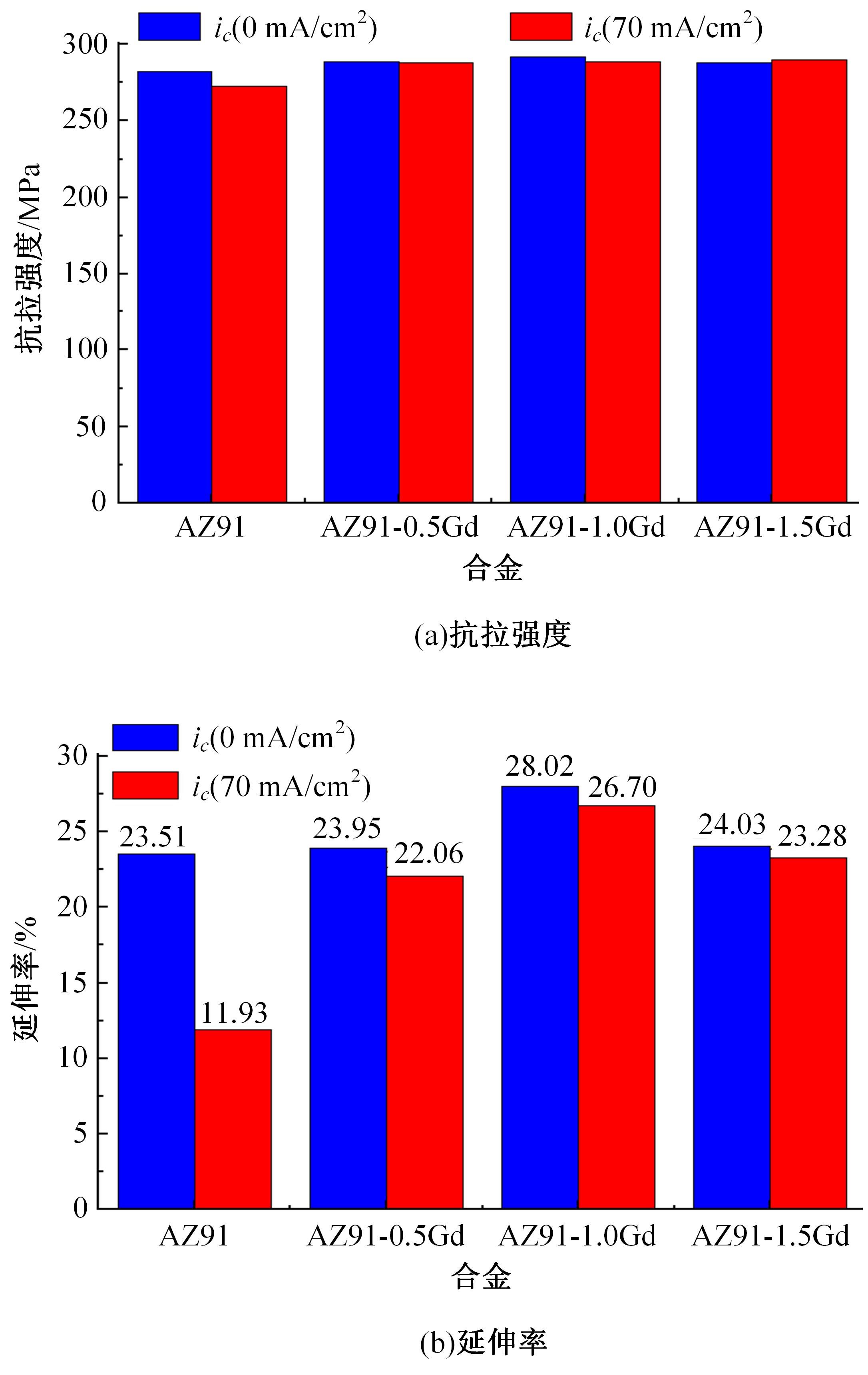
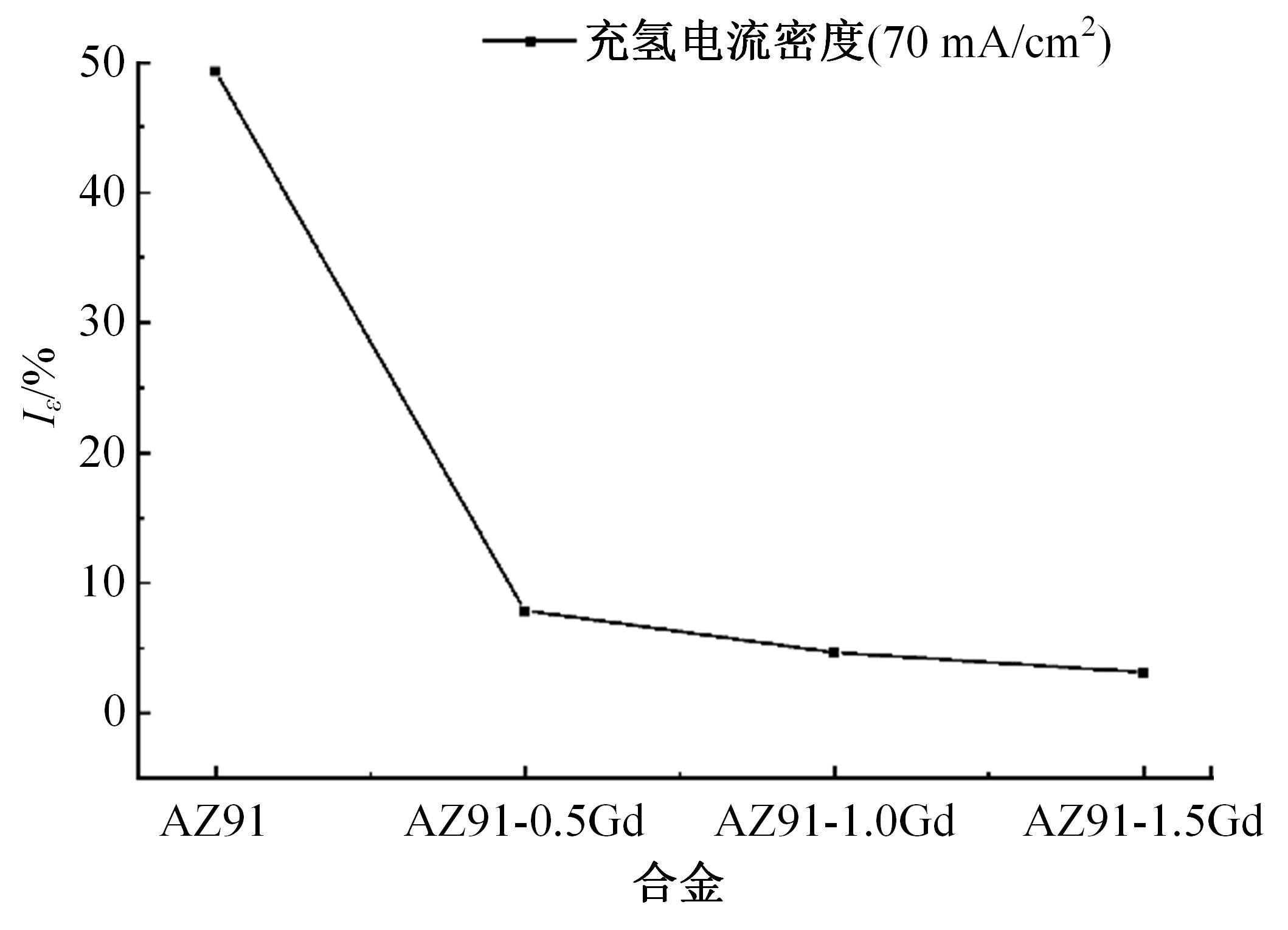
采用挤压法制备了AZ91和AZ91-xGd(x=0.5、1.0、1.5)镁合金。采用扫描电镜、电化学氧化法、慢应变速率拉伸法,研究了挤压镁合金AZ91和AZ91-xGd的微观组织、充氢及氢脆行为。结果表明:随着Gd的加入,AZ91中的β-Mg17Al12尺寸减小,数量减少,分布均匀。在相同的充氢条件下,随着稀土Gd含量的增加,挤压镁合金AZ91中的氢浓度逐渐降低,在一定程度上解决了氢在合金中的偏聚问题,使氢脆敏感性大大降低,有效提升了抗氢脆性能。
中图分类号:
- TG146.22
| 1 | Yang Y, Xiong X M, Chen J, et al. Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(3): 705-747. |
| 2 | Atrens A, Song G L, Liu M, et al. Review of recent developments in the field of magnesium corrosion[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015, 17(4): 400-453. |
| 3 | Xu S W, Kamado S, Honma T. Effect of homogenization on microstructures and mechanical properties of hot compressed Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(6): 2385-2393. |
| 4 | Satya Prasad S V, Prasad S B, Verma K, et al. The role and significance of magnesium in modern day research—a review[J].Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2022, 10(1): 1-61. |
| 5 | Luo K, Zhang L, Wu G H, et al. Effect of Y and Gd content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Y-RE alloys[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2019, 7(2): 345-354. |
| 6 | Yan M, Weng Y. Study on hydrogen absorption of pipeline steel under cathodic charging[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(2): 432-444. |
| 7 | Carter T J, Cornish L A. Hydrogen in metals[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2001, 8(2): 113-121. |
| 8 | Chen J, Wang J, Han E, et al. Effect of hydrogen on stress corrosion cracking of magnesium alloy in 0.1M Na2SO4 solution[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 488(1-2): 428-434. |
| 9 | Merson E, Poluyanov V, Myagkikh P, et al. Fractographic features of technically pure magnesium, AZ31 and ZK60 alloys subjected to stress corrosion cracking[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2020, 772(13):No.138744. |
| 10 | Winzer N, Cross C E. On the role of β particles in stress corrosion cracking of Mg-Al alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 40(2): 273-274. |
| 11 | Chen J, Wang J Q, Han E H, et al. Effect of hydrogen on corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of AZ91 alloy in aqueous solutions[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2016, 29(1): 1-7. |
| 12 | Winzer N, Atrens A, Dietzel W, et al. Characterisation of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of Mg–Al alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 488(1-2): 339-351. |
| 13 | Winzer N, Atrens A, Dietzel W, et al. Fractography of stress corrosion cracking of Mg-Al alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39(5): 1157-1173. |
| 14 | Kamilyan M, Silverstein R, Eliezer D. Hydrogen trapping and hydrogen embrittlement of Mg alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(18): 11091-11100. |
| 15 | Xi G, Zhao X, Ma Y, et al. Comparative study on corrosion behavior and mechanism of As-Cast Mg-Zn-Y and Mg-Zn-Gd alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica(English Letters), 2022,35(1): 1-13. |
| 16 | Wu G, Wang C, Sun M, et al. Recent developments and applications on high-performance cast magnesium rare-earth alloys[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(1): 1-20. |
| 17 | Zhao T L, Liu Z Y, Hu S S, et al. Effect of hydrogen charging on the stress corrosion behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steel under 3.5wt.% NaCl thin electrolyte layer[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26(6): 2837-2846. |
| 18 | Mościcki A, Chmiela B, Sozańska M. Corrosion of WE43 and AE44 magnesium alloys in sodium sulfate solution[J]. Solid State Phenomena, 2015, 3763(227): 91-94. |
| [1] | 娄淑梅,李一明,李鑫,陈鹏,白雪峰,程宝嘉. 基于BP神经网络和Arrhenius本构模型的石墨烯/7075复合材料热变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1237-1245. |
| [2] | 朱先勇,谢良稳,樊跃香,姜城,孙炜佳,王鹏,肖雄. 搅拌摩擦加工参数对镁合金表面改性层的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2263-2271. |
| [3] | 梁策,黄富雷,梁继才,李义. 日字形防护梁绕弯成形形变数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3397-3403. |
| [4] | 梁言,王强,宋雨来,刘耀辉. 新型5Cr5MoV模具钢修复性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1301-1307. |
| [5] | 兰凤崇, 李忠超, 周云郊, 陈吉清. 铝镁合金单搭接胶接接头应力分布及强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 726-732. |
| [6] | 阮德文, 苏达格, 梁雅琴, 伊兰哲田, 连建设. 表面活性剂对镁合金基体上的非铬化镀镍涂层的腐蚀特性的作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 363-367. |
| [7] | 宋雨来, 刘耀辉, 朱先勇, 王文琴. Ho对AZ91镁合金腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(02): 366-0370. |
| [8] | 张文雪,周振君,何成,李钢. 镁合金无铬前处理工艺及化学镀镍[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(01): 78-0083. |
| [9] | 杨悦, 庄宇, 由晓军. AZ91D镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-Ti-C涂层的显微组织和性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1567-1571. |
| [10] | 张文雪, 江中浩, 连建设. 镁合金化学镀NiWP合金[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1562-1566. |
| [11] | 吕晓霞, 苏振国, 陆有, 安健, 李光玉. 经激光表面熔凝处理的Mg-11Y-2.5Zn合金的显微组织和摩擦学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(05): 1250-1255. |
| [12] | 王强,刘耀辉,宋雨来,张大伟,于思荣 . 基于固体培养基(SCM)的镁合金的微生物腐蚀[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(03): 604-0607. |
| [13] | 王明星,周宏,王林,李伟,赵宇 . Y和Ce对AZ91D镁合金显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(01): 6-10. |
| [14] | 宋雨来,刘耀辉,朱先勇,王素环,于思荣. 钕对AZ91镁合金组织及机械性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(03): 289-0293. |
| [15] | 牛丽媛, 李光玉,江中浩,孙丽萍,韩冬,连建设. 镁合金镀镍磷合金及无铬前处理工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(02): 148-0152. |
|
||