吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 1169-1173.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180415
• • 上一篇
基于多源时空数据的建筑宜居性动态设计
- 1. 东北林业大学 土木工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
2. 黑龙江省鸡西市水务局,黑龙江 鸡西 158100
Dynamic design of building livability based on multi⁃source spatiotemporal data
Jun ZHANG1( ),Cheng QIAN1,Chun⁃yan GUO1,Yu⁃jun QIAN2
),Cheng QIAN1,Chun⁃yan GUO1,Yu⁃jun QIAN2
- 1. School of Civil Engineering,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150001,China
2. Water Bureau of Jixi City of Heilongjiang Province,Jixi 158100,China
摘要:
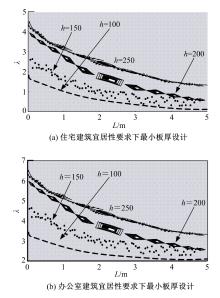
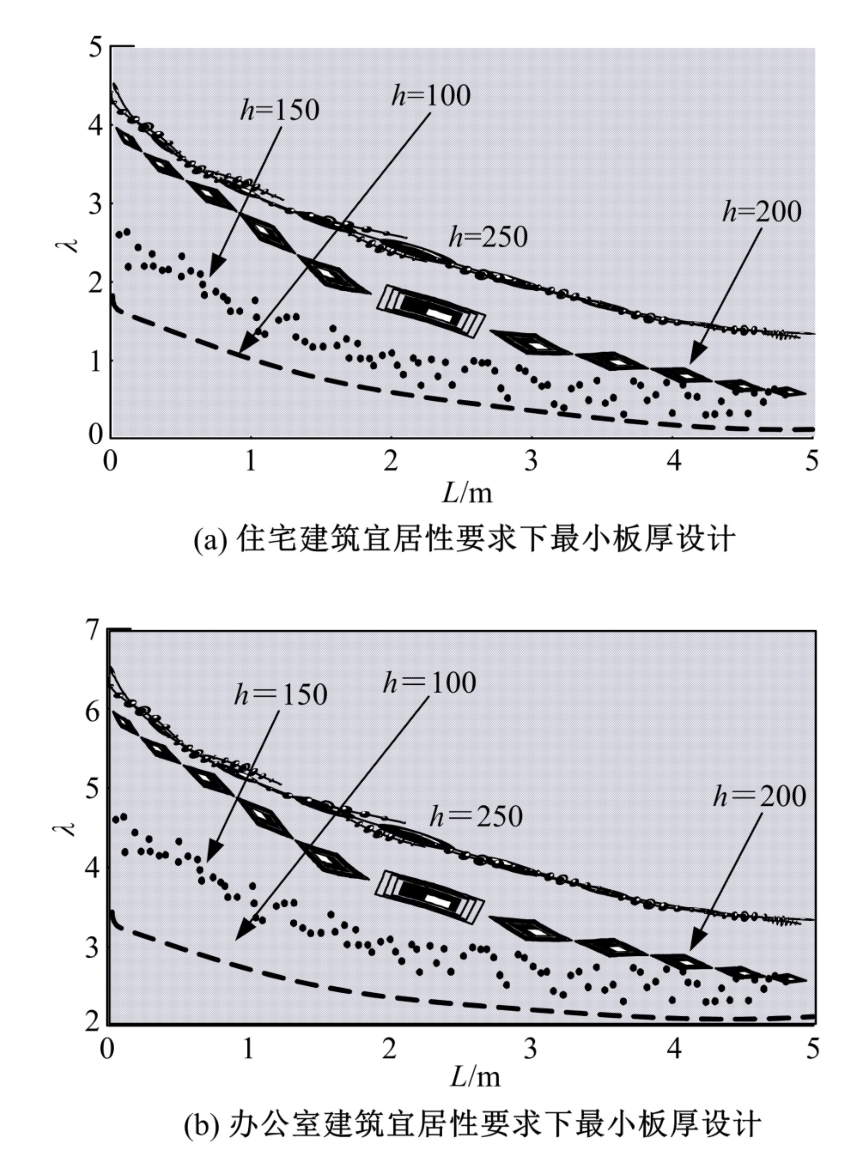
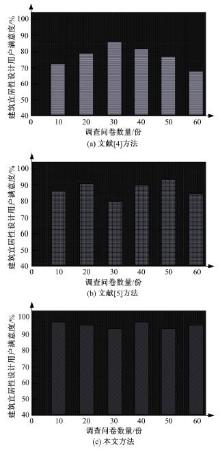
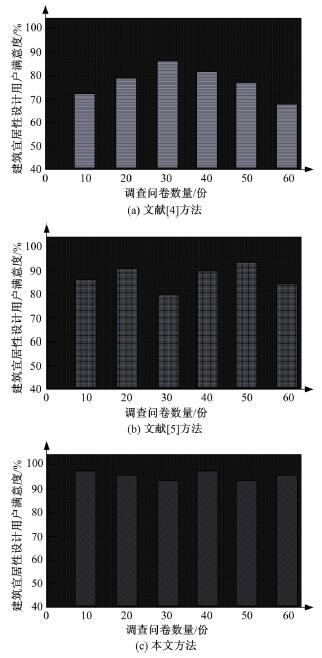
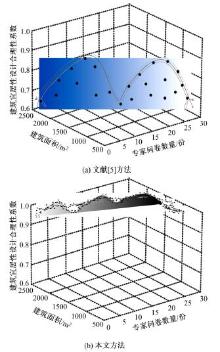
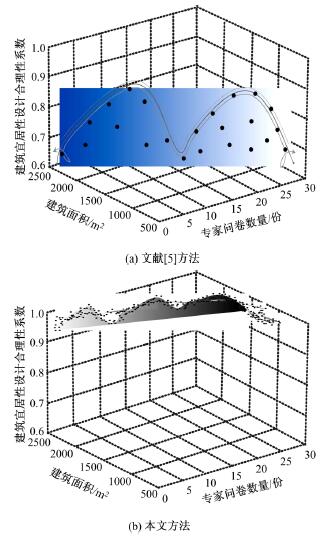
为解决当前建筑宜居性设计方法中存在的设计结果用户满意度较低、合理性差和宜居性达不到要求的问题,提出了基于多源时空数据的建筑宜居性动态设计方法。将建筑道路交通景观设计的关键点划分为路面视觉造型构建、路基景观构建、分隔带景观构建。基于建筑道路交通及景观分析结果,得到相关多源时空数据,通过乘幂关系对建筑楼板边长与厚度之间的关系进行拟合,获取楼板厚度与楼板短边长度、楼板长宽比值的关系,以此得到建筑宜居性要求下最小板厚的设计结果,完成建筑振动舒适度动态设计。结合可靠性理论,定义了建筑结构宜居性的功能函数,将函数计算结果与加速度限值相关规范相结合,以人体加速度对应的不同适应度来指导实际建筑宜居性设计,实现建筑宜居性动态构建。试验结果表明,该方法用户满意度平均约为95.8%,建筑宜居性系数平均为0.9,合理性较强。
中图分类号:
- TU318
| 1 | 赵昕, 李浩, 秦朗 . 周期与层间位移角双约束条件下超高层结构优化设计方法[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2018, 39(1): 129⁃135. |
| Zhao Xin , Li Hao , Qin Lang . Optimal design method for super tall buildings under period and story drift constraints[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2018, 39(1): 129⁃135. | |
| 2 | 魏德辉, 谌丽, 杨翌朝 . 美国波特兰的宜居城市建设经验及启示[J]. 国际城市规划,2016,31(5): 20⁃25. |
| Wei De⁃hui , Chen Li , Yang Yi⁃chao . Experience and Portland, Oregon, the USA[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(1): 20⁃25. | |
| 3 | 毕硕本, 凌德泉, 计晗, 等 . 郑洛地区史前聚落遗址人居环境宜居度指数模糊综合评价[J]. 地理科学, 2017, 37(6): 904⁃911. |
| Bi Shuo⁃ben , Ling De⁃quan , Ji Han . Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the human settlement environment of the prehistoric settlement sites in the Zhengzhou⁃Luoyang area[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 904⁃911. | |
| 4 | 黄安, 许月卿, 刘超, 等 . 基于土地利用多功能性的县域乡村生活空间宜居性评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(8): 252⁃261. |
| Huang An , Xu Yue⁃qing , Liu Chao , et al . Evaluation on livability of living space based on multiple functions of land use at county level[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(8): 252⁃261. | |
| 5 | 周勇, 王蒙恩 . 城中村安置社区宜居性评价——以西安曲江为例[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(12): 289⁃294. |
| Zhou Yong , Wang Men⁃en . Assessment of livability of resettlement community in urban villages: a case study of Qujiang in Xi’an City[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(12): 289⁃294. | |
| 6 | 党云晓, 周亚明 . 基于居民幸福感视角理解宜居城市[J]. 国际城市规划, 2016, 31(5): 14⁃19. |
| Dang Yun⁃xiao , Zhou Ya⁃ming . Understanding livable city based on the perspective of resident’s happiness[J]. Urban Planning International, 2016, 31(5): 14⁃19. | |
| 7 | 邵磊, 袁周, 詹浩 . 保障性住区公共服务设施的不同人群需求特征与满意度分析[J]. 规划师, 2016, 32(8): 106⁃111. |
| Shao Lei , Yuan Zhou , Zhan Hao . An analysis of the character and satisfaction of public housing service facilities for varied needs[J]. Planners, 2016, 32(8): 106⁃111. | |
| 8 | 徐文辉, 唐立舟 . 美丽乡村规划建设“四宜”策略研究[J]. 中国园林, 2016, 32(9): 20⁃23. |
| Xu Wen⁃hui , Tang Li⁃zhou . Research on the “four desirable" strategy in beautiful countryside planning and construction[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2016, 32(9): 20⁃23. | |
| 9 | 何璘, 周颖悟 .黔东南地区人居环境评价及优化策略研究[J].中国农业资源与区划,2016,37(10):83⁃87. |
| He Lin , Zhou Ying⁃wu . Assessmentand optimization of human settlement environment⁃a case study of southeast region[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning,2016,37(10):83⁃87. | |
| 10 | 杜红波, 刘少坤, 韩颖 . 设计以人为本的街道——以东莞市东城世博商业圈道路设计为例[J]. 城市交通, 2017, 15(3): 36⁃42. |
| Du Hong⁃bo , Liu Shao⁃kun , Han Ying . Designing user⁃oriented street: a case study of Dongcheng Shibo commercial area in Dongguan City[J]. Urban Transport of China, 15(3): 36⁃42. |
| [1] | 梁宁慧,缪庆旭,刘新荣,代继飞,钟祖良. 聚丙烯纤维增强混凝土断裂韧度及软化本构曲线确定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1144-1152. |
| [2] | 张磊,刘保国,储昭飞. 深厚孔隙砂岩含水层疏干排水对盾构斜井的 影响模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 788-797. |
| [3] | 郑一峰, 赵群, 暴伟, 李壮, 于笑非. 大跨径刚构连续梁桥悬臂施工阶段抗风性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 466-472. |
| [4] | 陈忠敏, 侯力, 段阳, 张祺, 杨忠学, 蒋易强. 新型摆线针轮行星减速器传动系统的振动特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 174-185. |
| [5] | 王腾, 周茗如, 马连生, 乔宏霞. 基于断裂理论的湿陷性黄土劈裂注浆裂纹扩展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1472-1481. |
| [6] | 郭楠, 张平阳, 左煜, 左宏亮. 竹板增强胶合木梁受弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 778-788. |
| [7] | 张静, 刘向东. 混沌粒子群算法优化最小二乘支持向量机的混凝土强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| [8] | 郭学东, 马立军, 张云龙. 集中力作用下考虑剪切滑移效应的双层结合面组合梁解析解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 432-438. |
| [9] | 赵玉, 李衍赫, 张培, 赵科, 刘伟超. 粘土的动力特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1791-1797. |
| [10] | 侯忠明, 王元清, 夏禾, 张天申. 移动荷载作用下的钢-混简支结合梁动力响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1420-1427. |
| [11] | 王甲春, 阎培渝. 海洋环境下钢筋混凝土中钢筋锈蚀的概率[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 352-357. |
| [12] | 张大山, 董毓利, 吴亚平. 混凝土单向板的受拉薄膜效应计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1253-1257. |
| [13] | 柴寿喜, 王沛, 魏丽. 以峰值轴向应变评价麦秸秆和石灰加筋固化盐渍土的抗变形性能 [J]. , 2012, (03): 645-650. |
| [14] | 李春良, 王国强, 赵凯军, 朱春凤. 地面荷载作用盾构隧道纵向力学行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 180-184. |
| [15] | 潘明远, 姚继涛. 钢筋混凝土结构构件的可靠性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 218-0221. |
|
||