吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1755-1764.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190554
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于生成对抗网络的低剂量能谱层析成像去噪算法
- 1.天津大学 微电子学院,天津 300072
2.天津市成像与感知微电子技术重点实验室,天津 300072
3.天津师范大学 数学科学学院,天津 0087
Low⁃dose spectral computer⁃tomography imaging denoising method via a generative adversarial network
Zai-feng SHI1,2( ),Jin-zhuo LI1,Qing-jie CAO3,Hui-long LI1,Qi-xing HU1
),Jin-zhuo LI1,Qing-jie CAO3,Hui-long LI1,Qi-xing HU1
- 1.School of Microelectronics, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072,China
2.Tianjin Key Laboratory of Imaging and Sensing Microelectronic Technology, Tianjin 300072,China
3.School of Mathematical Sciences, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300387,China
摘要:
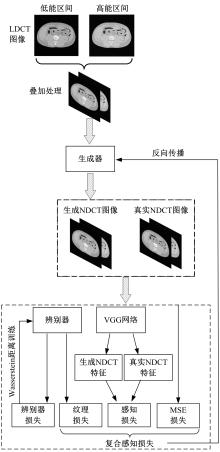
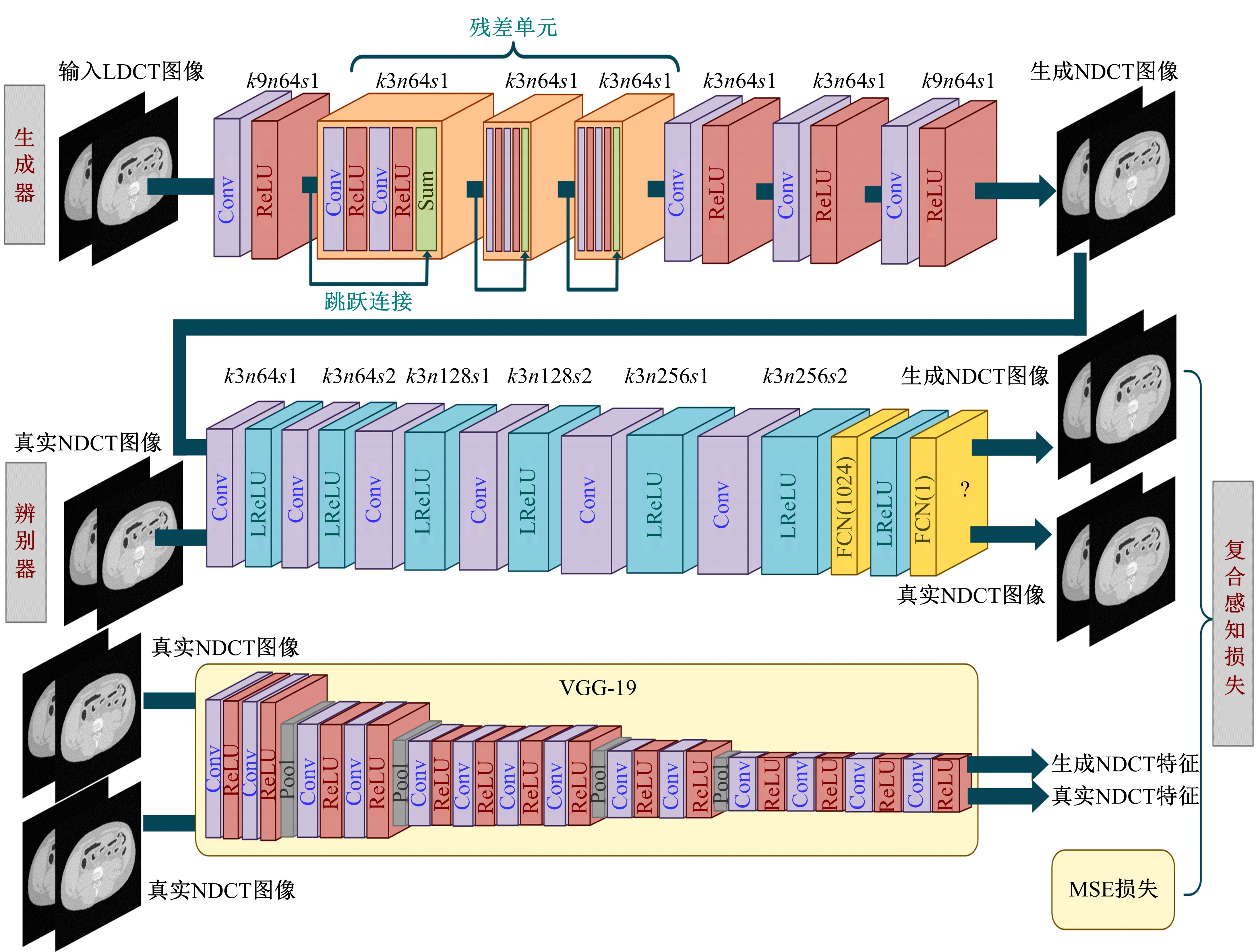
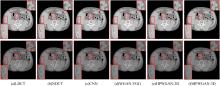
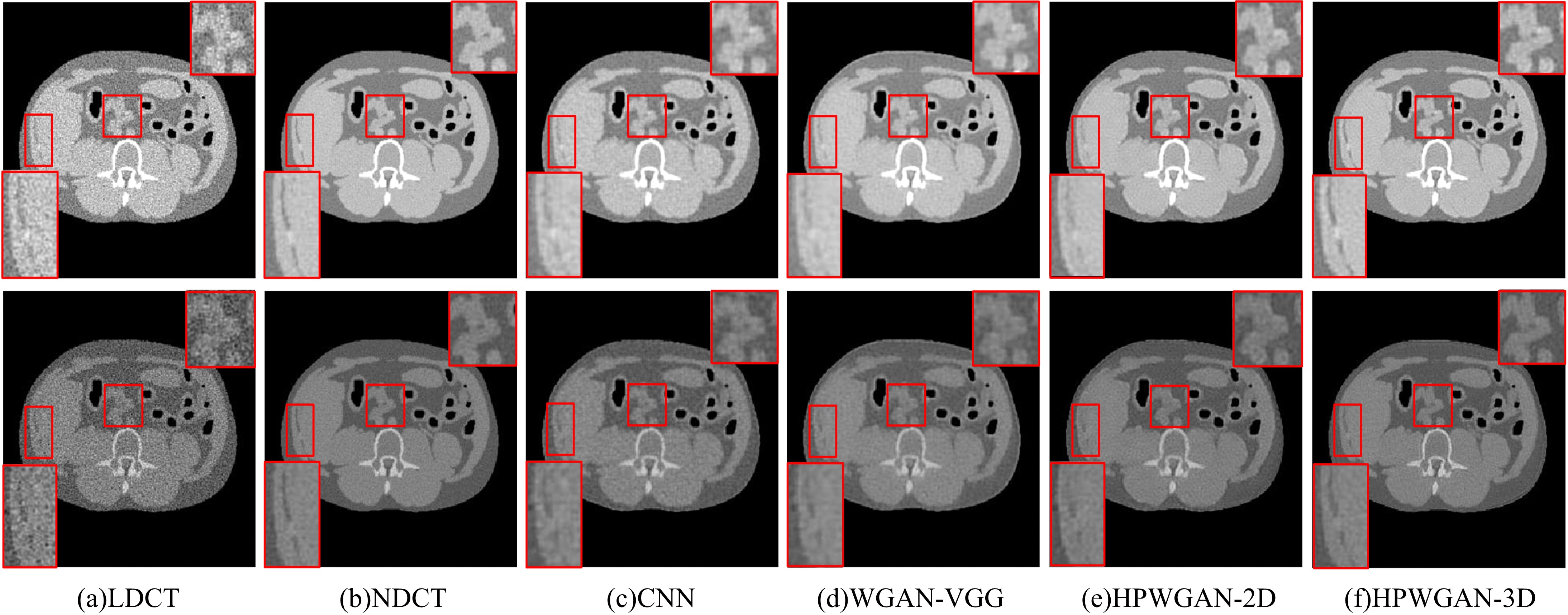
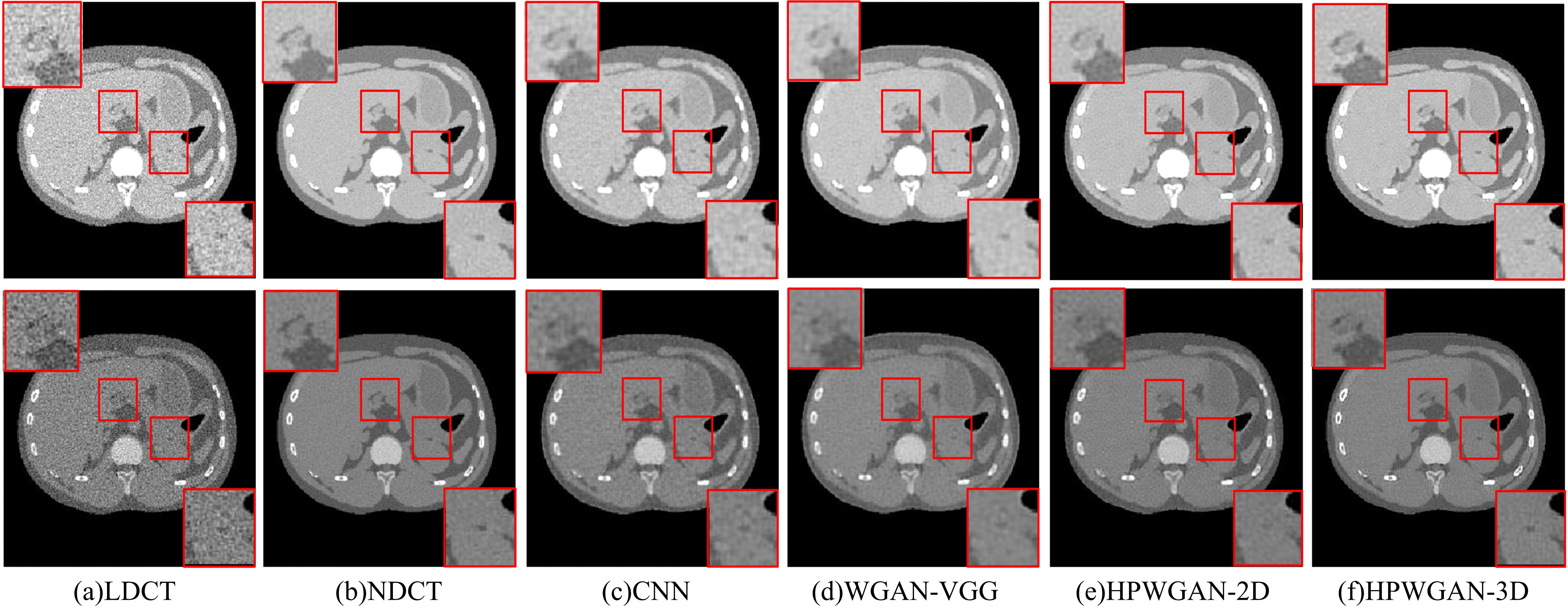
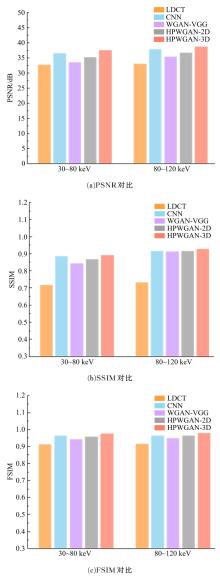
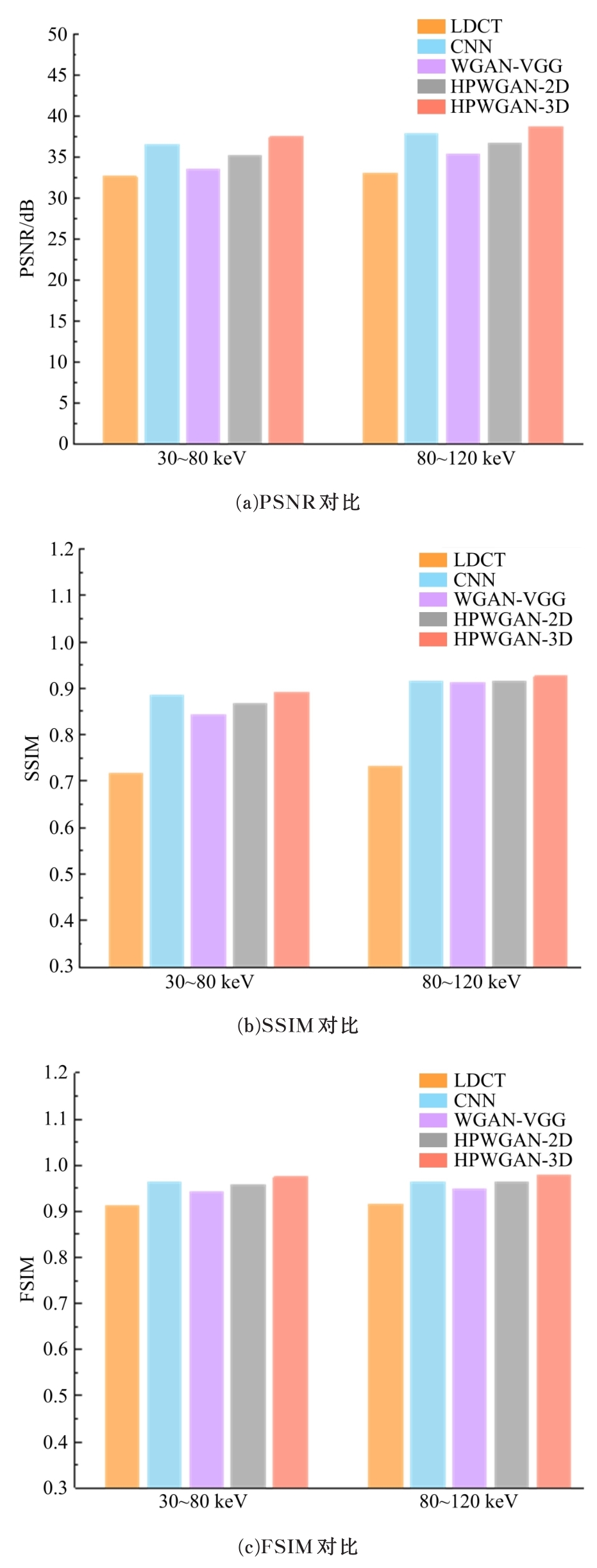
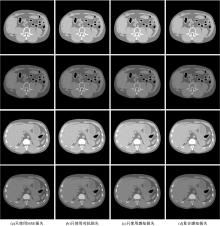
为提升在低辐射剂量条件下能谱式计算机断层扫描(CT)的重建图像质量,提出了一种基于复合感知损失函数的生成对抗网络去噪模型。此方法将像素空间与人类感知的特征空间结合到网络的生成对抗过程,并引入残差学习解决网络层数加深导致的图像细节丢失问题。通过采用多个能段的CT图像作为输入,同时利用了能段内的空间相关性和能段间的能量相关性,提高了能谱CT图像的视觉灵敏度。实验结果表明:该方法将峰值信噪比提高约5 dB,结构相似性指数提高约0.2,特征相似性指数提高约0.06。与当前的低剂量CT影像去噪算法相比,本文模型可实现更好的噪声去除效果,同时能保留诊断必要的细节信息,显著提高了低剂量能谱CT图像的质量。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Brenner D J, Hall E J. Computed tomography-an increasing source of radiation exposure[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2007, 357(22): 2277-2284. |
| 2 | de Gonzalez A B, Mahesh M, Kim K P, et al. Projected cancer risks from computed tomographic scans performed in the united states in 2007[J]. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2009, 169(22): 2071-2077. |
| 3 | Wang J, Li T F, Lu H B, et al. Penalized weighted least-squares approach to sinogram noise reduction and image reconstruction for lowdose X-ray computed tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25(10): 1272-1283. |
| 4 | Beister M, Kolditz D, Kalender W A. Iterative reconstruction methods in X-ray CT[J]. Physica Medica, 2012, 28(2): 94-108. |
| 5 | Liu Y, Ma J H, Fan Y, et al. Adaptive-weighted total variation minimization for sparse data toward low-dose X-ray computed tomography image reconstruction[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2012, 57(23): 7923-7956. |
| 6 | Yang C, Yin X D, Shi L Y, et al. Improving abdomen tumor low-dose CT images using a fast dictionary learning based processing[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2013, 58(16): 5803-5820. |
| 7 | Fumene F P, Vinegoni C, Gros J, et al. Block matching 3D random noise filtering for absorption optical projection tomography[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2010, 55(18): 5401-5415. |
| 8 | 郜峰利, 陶敏, 李雪妍, 等. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| Gao Feng-li, Tao Min, Li Xue-yan, et al. Accurate segmentation of stroke in CT image based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. | |
| 9 | 司建波, 杨芳, 郭蔚莹, 等. 基于BP神经网络的两阶段疾病预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(): 481-484. |
| Si Jian-bo, Yang Fang, Guo Wei-ying, et al. Two-stage disease prediction model based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(Sup.1): 481-484. | |
| 10 | Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhang W H, et al. Low-dose CT via convolutional neural network[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(2): 679-694. |
| 11 | Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Viergever M A, et al. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2536-2545. |
| 12 | Yang Q S, Yan P K, Zhang Y B, et al. Low dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with Wasserstein distance and perceptual loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1348-1357. |
| 13 | Zhang Y B, Mou X Q, Wang G, et al. Tensor-based dictionary learning for spectral CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(1): 142-154. |
| 14 | Shi Z F, Yang H Y, Cong W X, et al. An edge-on charge-transfer design for energy-resolved X-ray detection[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2016, 61(11): 4183-4200. |
| [1] | 张薇,韩勇,金铭,乔晓林. 基于托普利兹矩阵集重构的相干信源波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 703-710. |
| [2] | 程艳芬,姚丽娟,袁巧,陈先桥. 水下视频图像清晰化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 668-677. |
| [3] | 于晓辉,张志成,李新波,孙晓东. 基于状态空间模型的指数衰减正弦信号参数估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2083-2088. |
| [4] | 刘富, 权美静, 王柯, 刘云, 康冰, 韩志武, 侯涛. 仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2076-2082. |
| [5] | 马子骥,卢浩,董艳茹. 双通道单图像超分辨率卷积神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2089-2097. |
| [6] | 郭继昌,吴洁,郭春乐,朱明辉. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| [7] | 曹运合,曾丽,王宇. 基于特征空间的子阵级自适应和差波束测角方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1735-1744. |
| [8] | 卢洋,王世刚,赵文婷,赵岩. 基于离散Shearlet类别可分性测度的人脸表情识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1715-1725. |
| [9] | 董超,刘晶红,徐芳,王仁浩. 光学遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1369-1376. |
| [10] | 王柯俨,胡妍,王怀,李云松. 结合天空分割和超像素级暗通道的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. |
| [11] | 托乎提努尔,张海龙,王杰,王娜,冶鑫晨,王万琼. 基于图形处理器的高速中值滤波算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 979-985. |
| [12] | 付银娟,李勇,徐丽琴,张昆辉. NLFM⁃Costas射频隐身雷达信号设计及分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 994-999. |
| [13] | 苏寒松,代志涛,刘高华,张倩芳. 结合吸收Markov链和流行排序的显著性区域检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1887-1894. |
| [14] | 应欢,刘松华,唐博文,韩丽芳,周亮. 基于自适应释放策略的低开销确定性重放方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1917-1924. |
| [15] | 陆智俊,钟超,吴敬玉. 星载合成孔径雷达图像小特征的准确分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1925-1930. |
|
||