吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 259-267.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190940
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于弹塑性应力场理论的钢筋混凝土梁受剪承载力
- 长安大学 建筑工程学院,西安 710061
Shear strength of reinforced concrete beams based on elastoplastic stress field theory
Er-gang XIONG( ),Han XU,Ci TAN,Jing WANG,Ruo-yu DING
),Han XU,Ci TAN,Jing WANG,Ruo-yu DING
- School of Civil Engineering,Chang′an University,Xi′an 710061,China
摘要:
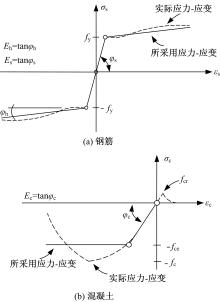
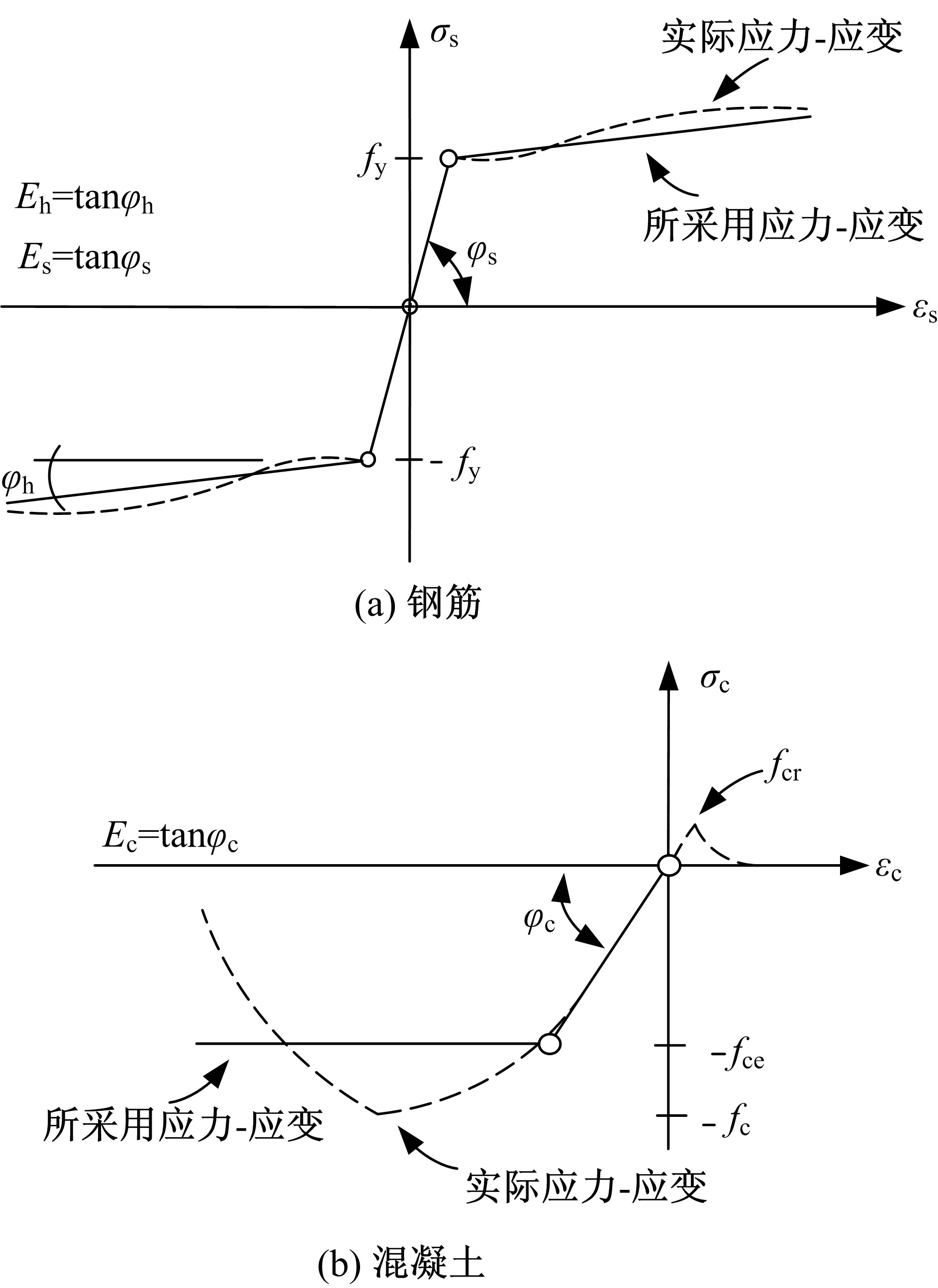
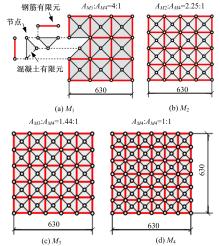
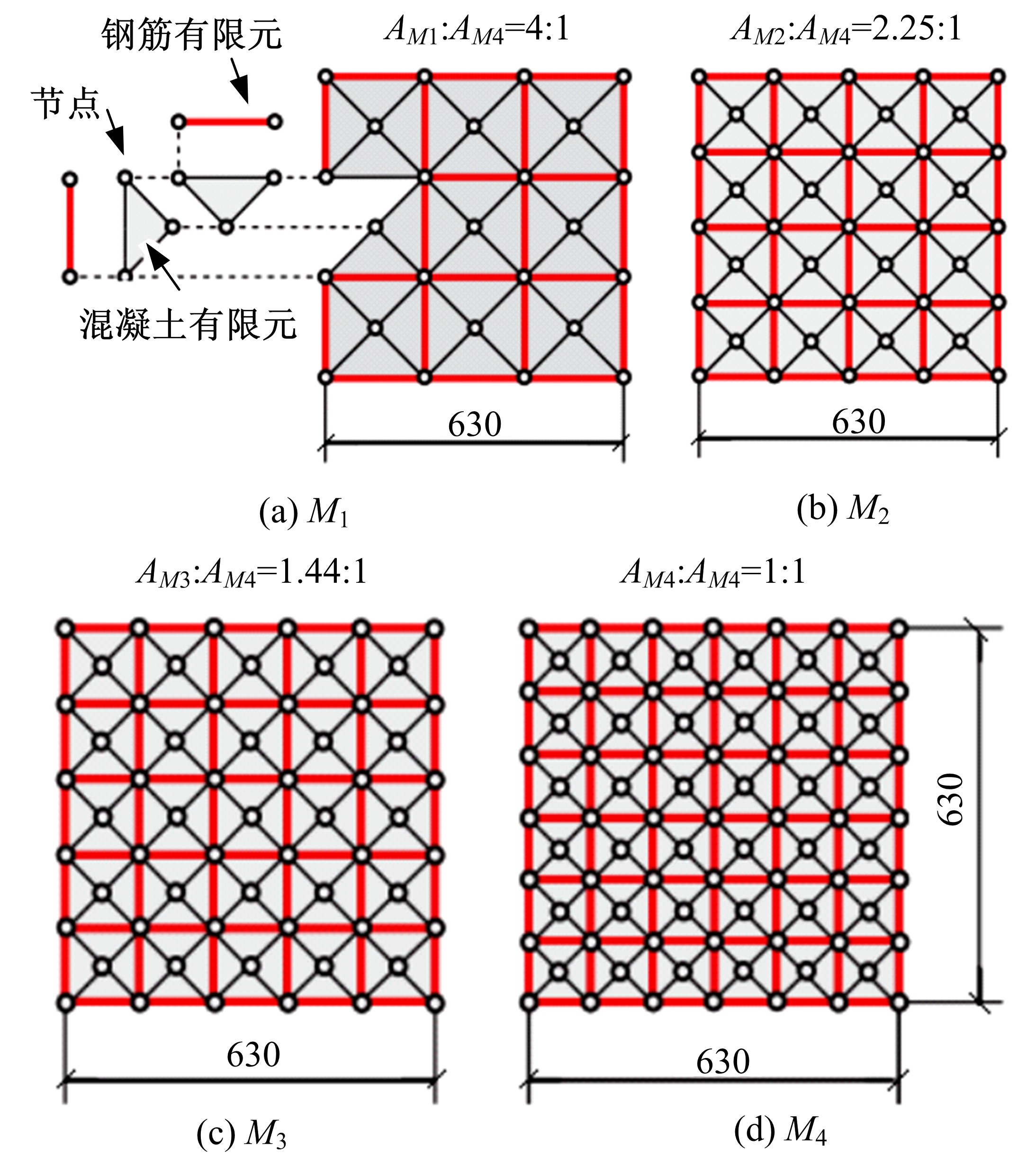
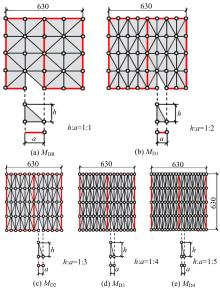
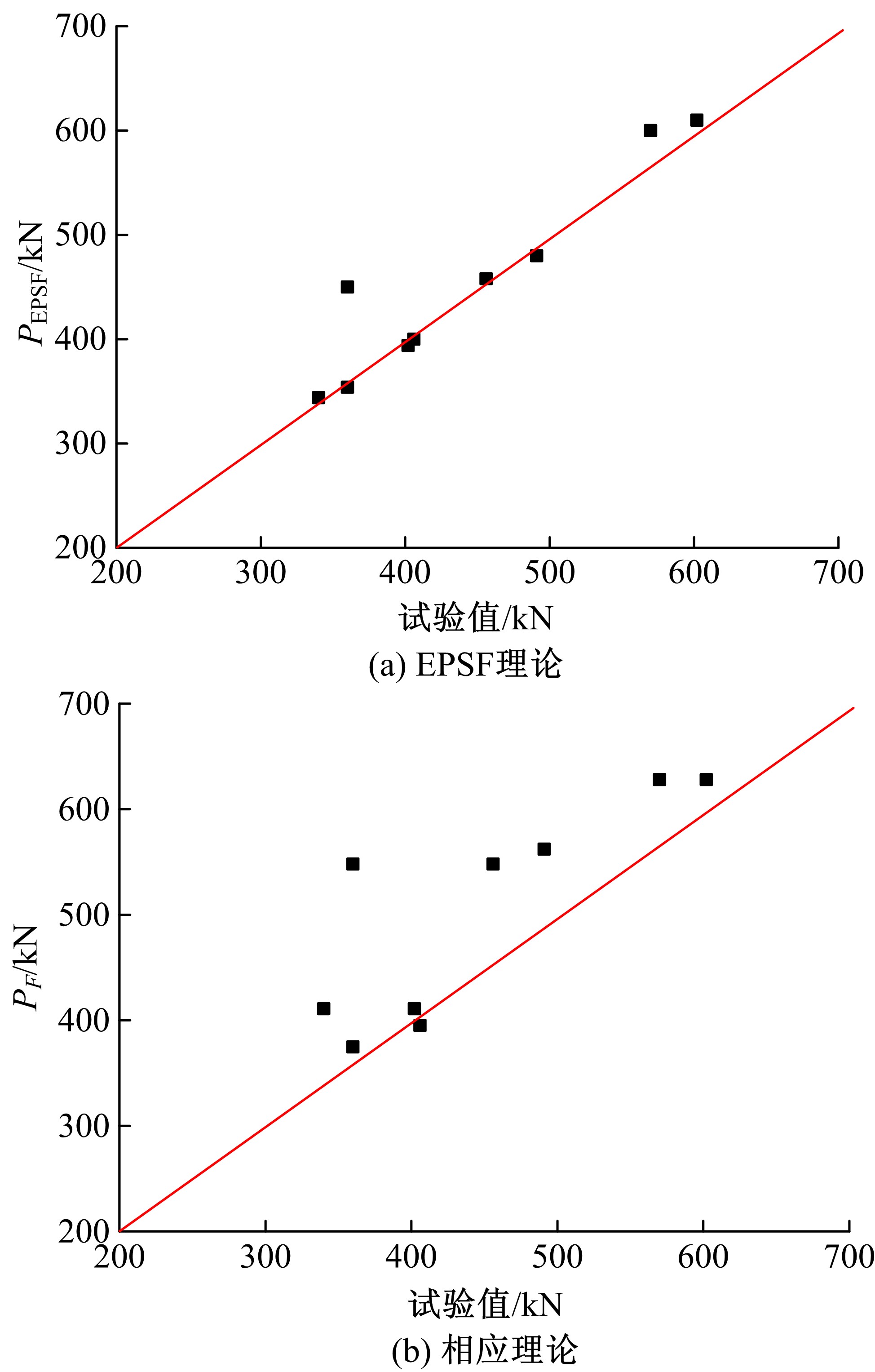
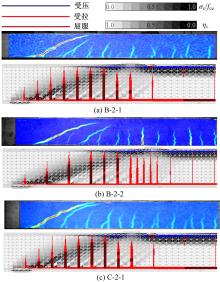
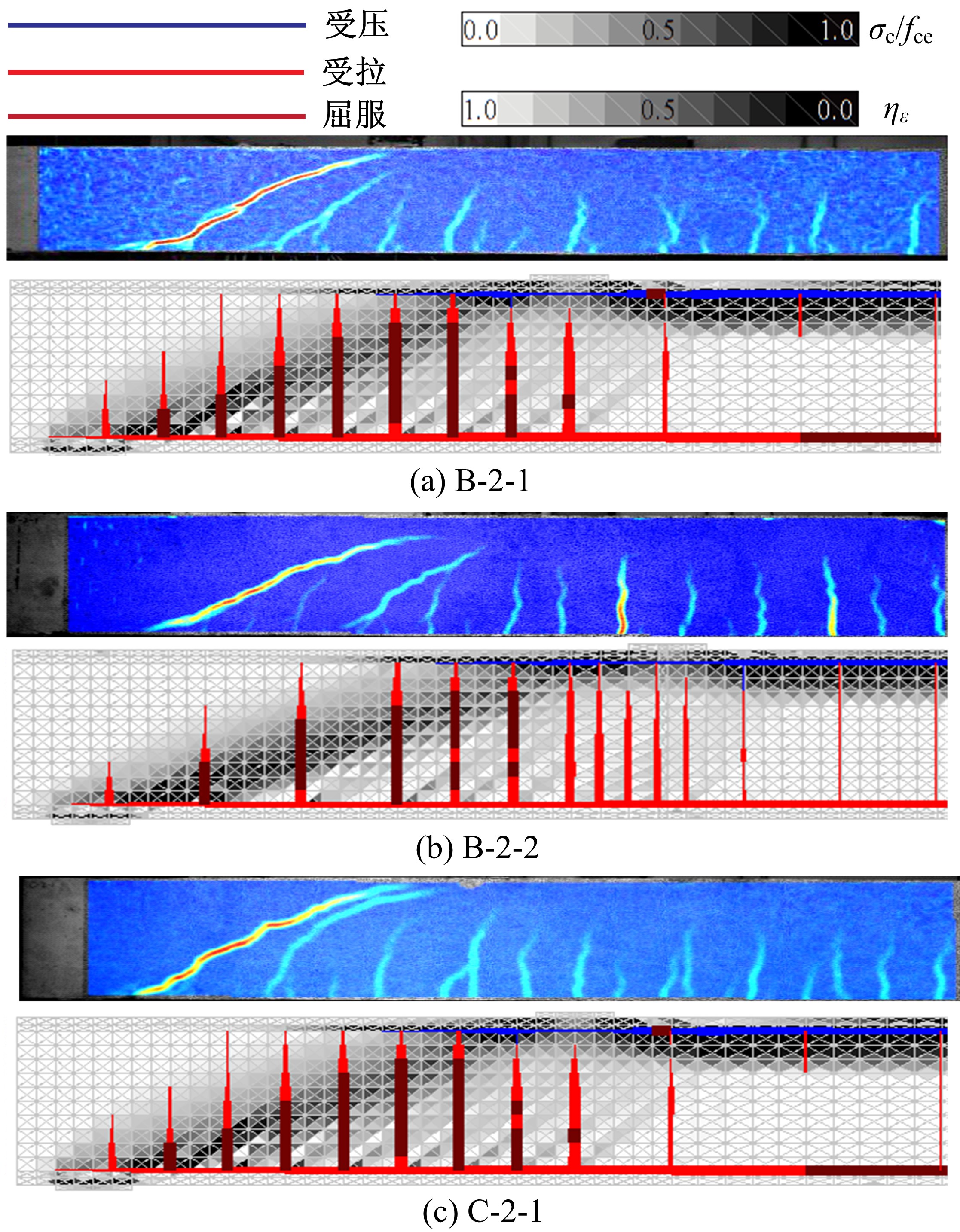
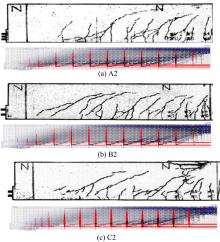
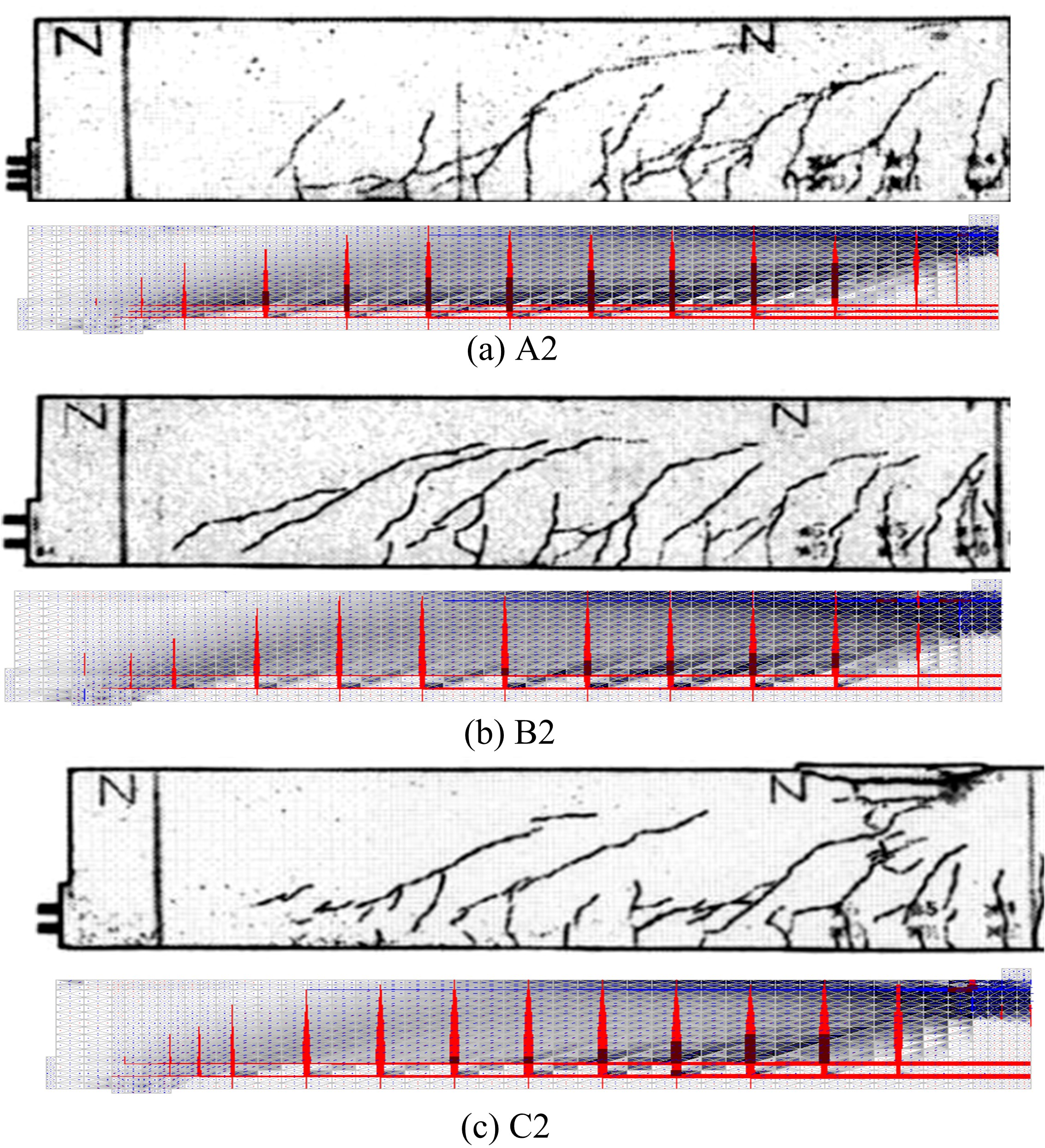
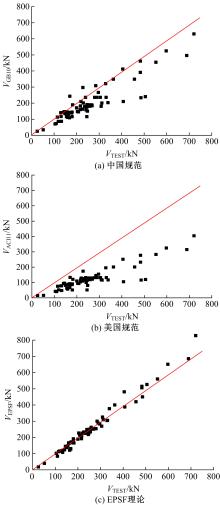
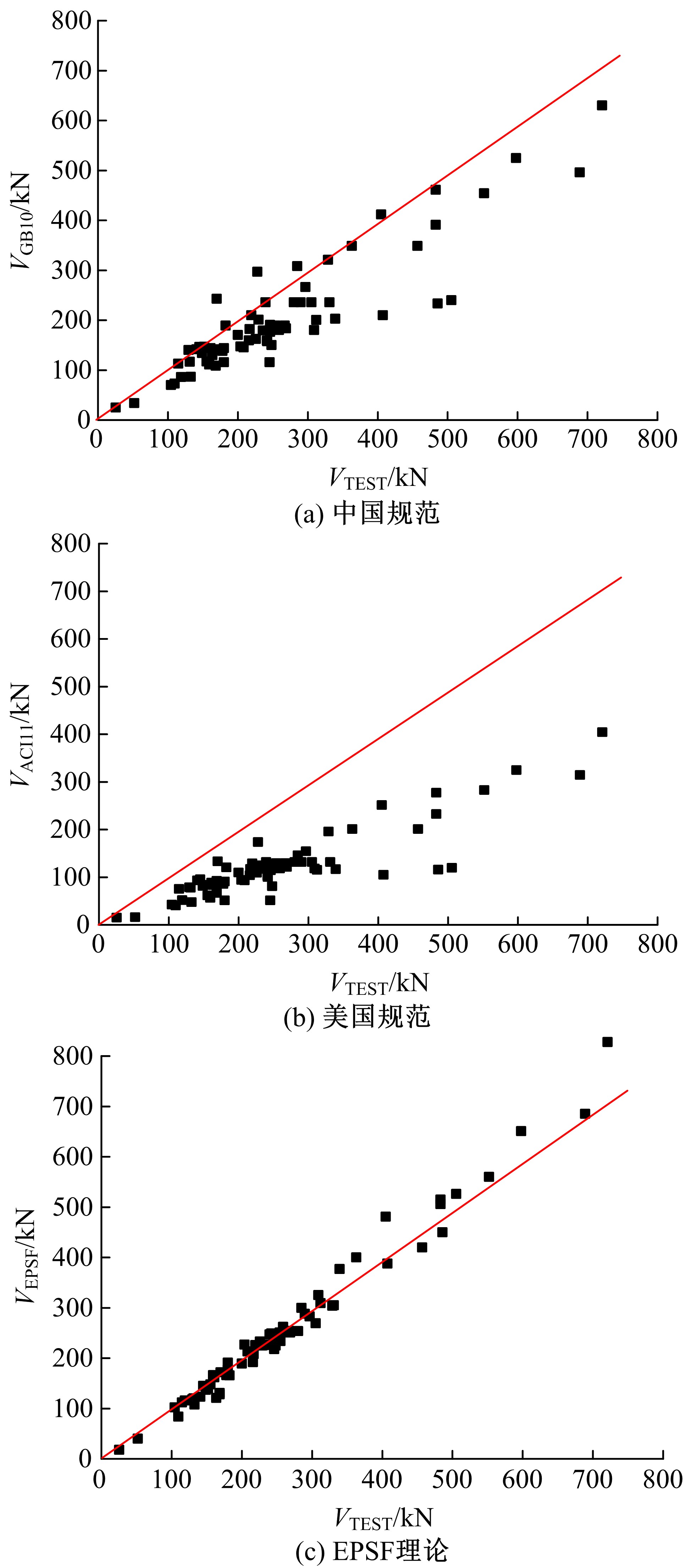
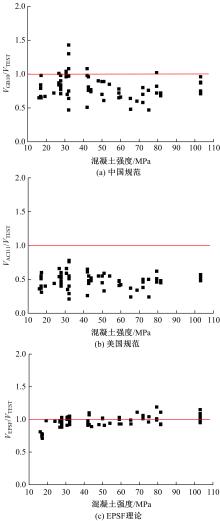
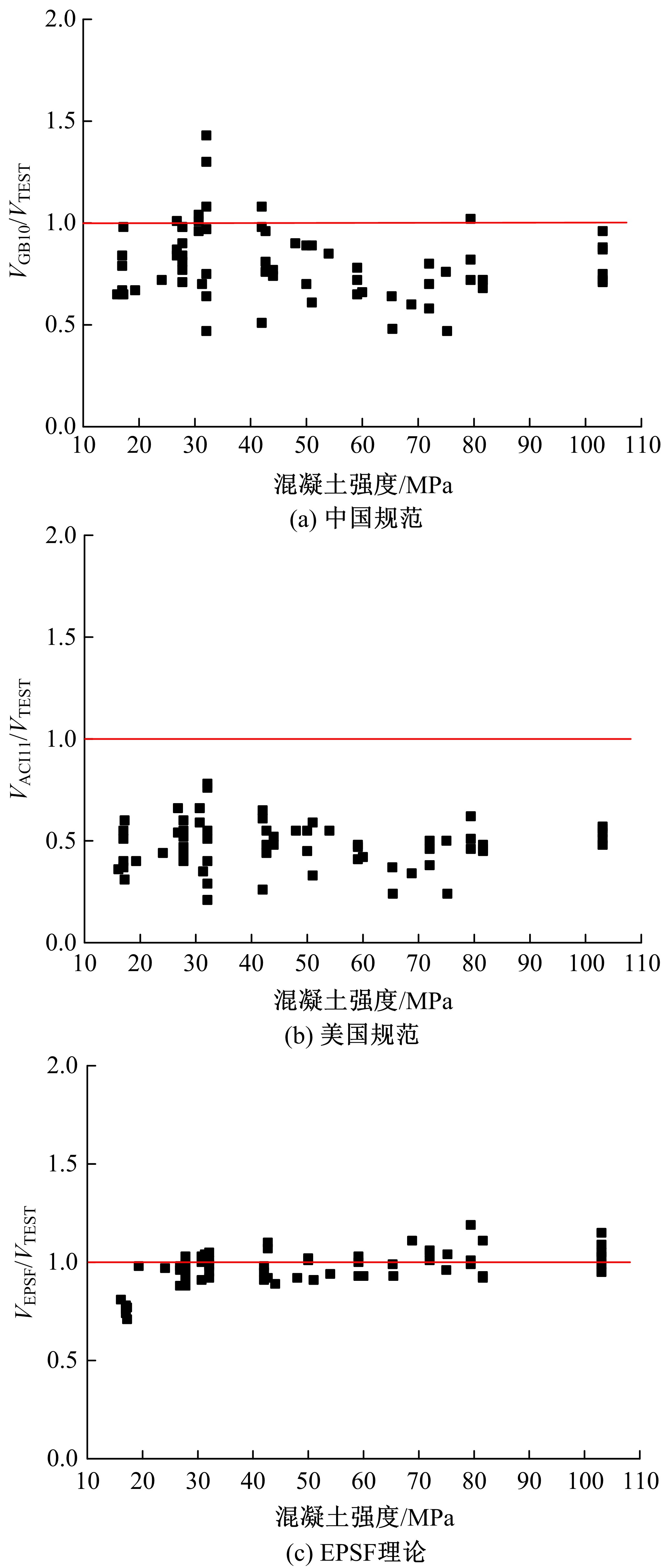
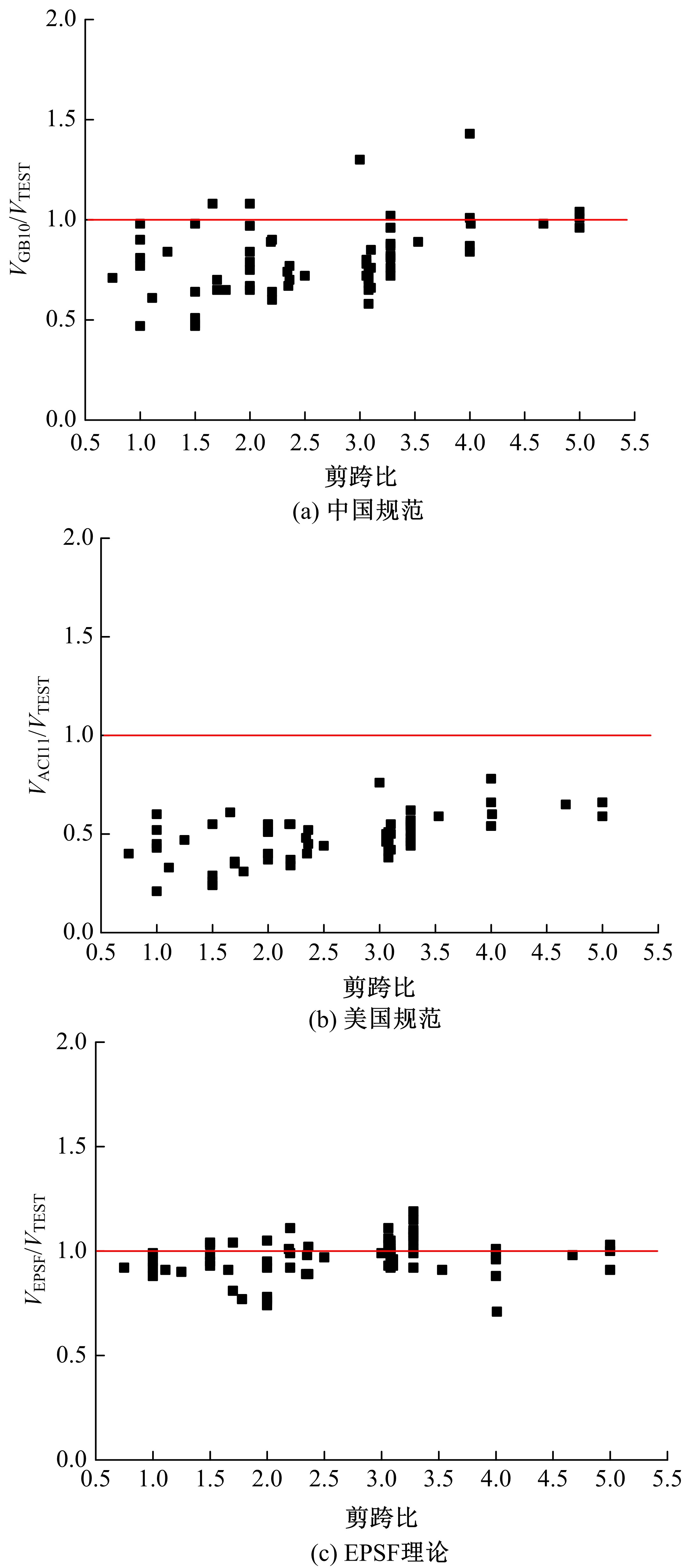
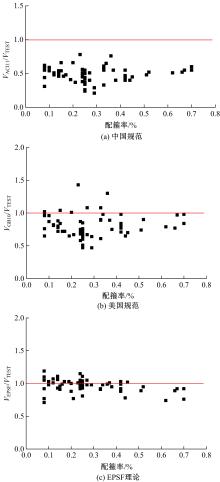
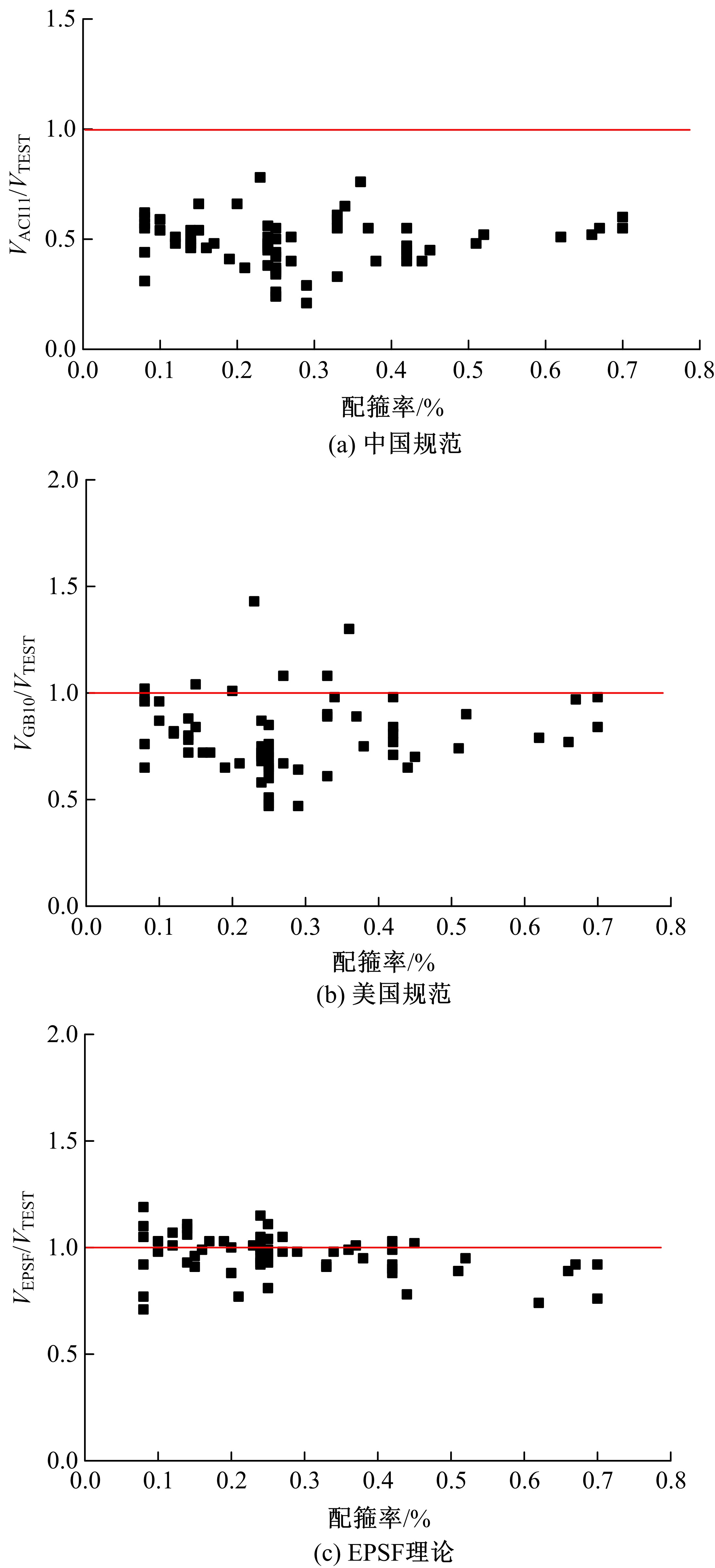
为了研究基于弹塑性应力场理论(EPSF)的钢筋混凝土梁的抗剪性能,采用基于EPSF理论的有限元程序ICONC对混凝土构件进行建模计算,探讨了有限元网格大小、形状和迭代步数对模拟结果的影响;选取12根试验梁,对比基于EPSF理论的模拟结果、试验结果和ABAQUS模拟结果,验证了基于EPSF理论计算结果的准确性。利用中美规范公式和EPSF理论对70根剪切破坏梁的受剪承载力进行了计算,并与试验值进行了对比。结果表明:有限元网格大小、形状和迭代步数对模拟结果影响甚小;程序ICONC可以较准确地模拟钢筋混凝土梁破坏现象、钢筋的屈服和混凝土的裂缝分布;与ABAQUS模拟相比,EPSF理论可以更精确、更方便、更快速地预测钢筋混凝土梁的受剪承载力;混凝土强度、剪跨比、配箍率变化对ICONC程序模拟结果影响较小,本文方法具有一定的准确性和稳定性。
中图分类号:
- TU375.1
| 1 | Niketić F. Development of a consistent approach for design and assessment of structural concrete members using stress fields and strut-and-tie models[D]. Lausanne: EPFL, Switzerland, 2017. |
| 2 | Ruiz M F, Muttoni A. On development of suitable stress fields for structural concrete[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2007, 104(4): 495-502. |
| 3 | Vecchio F J, Collins M P. The modified compression-field theory for reinforced concrete elements subjected to shear[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 1986, 83(2): 219-231. |
| 4 | Muttoni A, Schwartz J, Thürlimann B. Design of Concrete Structures with Stress Fields[M]. Basel:Birkhäuser Verlag, 1997. |
| 5 | Muttoni A. Die Anwendbarkeit der Plastizitätstheorie in der Bemessung von Stahlbeton[M]. Basel:Birkhäuser Verlag, 1990. |
| 6 | CEB-FIB. Model code 2010 First final draft –Volumes 1 fib Bulletin 65[Z]. |
| 7 | Vecchio F J, Shim W. Experimental and analytical investigation of classic concrete beam tests[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2004, 130(3): 460-469. |
| 8 | Frey F, Jirousek J. Méthode des éléments finis Analyse des structures et milieux continues[M]. Lausanne, Suisse: Presses Polytechnique et Universitaires Romandes, 2001. |
| 9 | 赵娜娜. 基于压力路径法钢筋混凝土梁的抗剪试验研究[D]. 西安:长安大学建筑工程学院, 2017. |
| Zhao Na-na. Behaviour of reinforced concrete beams for shear in compliance with compressive force path method[D]. Xi'an: School of Architectural Engineering, Chang'an University, 2017. | |
| 10 | ―2010. 混凝土结构设计规范[S]. |
| 11 | 阎昭琦. 基于压力路径法的大尺寸钢筋混凝土梁斜截面抗剪性能研究[D]. 西安:长安大学建筑工程学院, 2018. |
| Yan Zhao-qi. Behaviour of big size reinforced concrete beams for shear in compliance with compressive force path method[D]. Xi'an: School of Architectural Engineering, Chang'an University, 2018. | |
| 12 | 易伟建, 吕艳梅. 高强箍筋高强混凝土梁受剪试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2009, 30(4): 94-101. |
| Yi Wei-jian, Lv Yan-mei. Experimental study on shear behavior of high-strength concrete beams with high-strength stirrups[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2009, 30(4): 94-101. | |
| 13 | 中国建筑科学研究院. 钢筋混凝土构件试验数据集——85年设计规范背景资料续编[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,1985. |
| 14 | Cladera Bohigas A. Shear design of reinforcement high-strength concrete beams[D]. Barcelona: Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2002. |
| 15 | Yoon Y S, Cooc W D, Mitchell D. Minimum shear reinforcement in normal, medium and high-strength concrete beams[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 1996, 93(5): 576-584. |
| 16 | Hong S G, Kim D J, Kim S Y. Shear strength of reinforced concrete deep beams with end anchorage failure[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2002, 99(1): 12-22. |
| 17 | 李娟. HRB500级箍筋混凝土梁斜截面受力性能试验研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院,2007. |
| Li Juan. Experimental Study on mechanical behavior of diagonal section of reinforced concrete beams with HRB500 stirrups[D]. Changsha: School of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, 2007. | |
| 18 | ACI 318M―14. Building code requirements for structural concrete and commentary[S]. |
| [1] | 樊学平,屈广,刘月飞. 应用新数据同化算法的桥梁极值应力预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 572-580. |
| [2] | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. |
| [3] | 于天来,李海生,黄巍,王思佳. 预应力钢丝绳加固钢筋混凝土梁桥抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [4] | 戴岩, 聂少锋, 周天华. 带环梁的方钢管约束钢骨混凝土柱-钢梁节点滞回性能有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| [5] | 杨昕卉, 薛伟, 郭楠. 钢板增强胶合木梁的抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 468-477. |
| [6] | 于天来, 刘兴国, 姚爽, 穆罕默德马苏. 碳纤维筋体外预应力加固钢筋混凝土梁的疲劳性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1867-1873. |
| [7] | 王少杰, 徐赵东, 李舒, 王凯洋,Dyke Shirley J. 基于应变监测的连续梁支承差异沉降识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1090-1096. |
| [8] | 苏迎社, 杨媛媛. 高温对建筑混凝土材料抗震抗压的作用及原理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1436-1442. |
| [9] | 宿晓萍,王清. 复合盐浸-冻融-干湿多因素作用下的混凝土腐蚀破坏[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 112-120. |
| [10] | 郭俊平1, 邓宗才1, 卢海波2, 林劲松2. 预应力高强钢绞线网抗剪加固钢筋混凝土梁试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 968-977. |
| [11] | 姜浩, 郭学东. 基于地震激励的混凝土桥梁模态参数识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 185-188. |
| [12] | 孙绪杰,潘景龙,郑文忠 . 玻璃纤维增强聚合物混凝土小型空心 砌块复合墙片的抗震性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(05): 1054-1059. |
| [13] | 李春良,程永春 . 碳纤维布加固钢筋混凝土梁的 预应力控制过程[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 393-0398. |
|
||