吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 847-854.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200180
温热成形对AA5754铝合金静态力学性能的影响
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.太原学院 机电工程系,太原 030032
3.一汽-大众汽车有限公司,长春 130011
Effect of hot forming on static mechanical properties of AA5754 aluminum alloy
Wei-min ZHUANG1( ),Peng-yue WANG1,Rui-juan GAO2,Dong-xuan XIE3
),Peng-yue WANG1,Rui-juan GAO2,Dong-xuan XIE3
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Taiyuan University,Taiyuan 030032,China
3.FAW-Volkswagen Automotive Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130011,China
摘要:
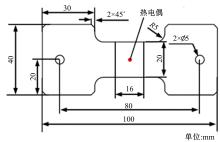
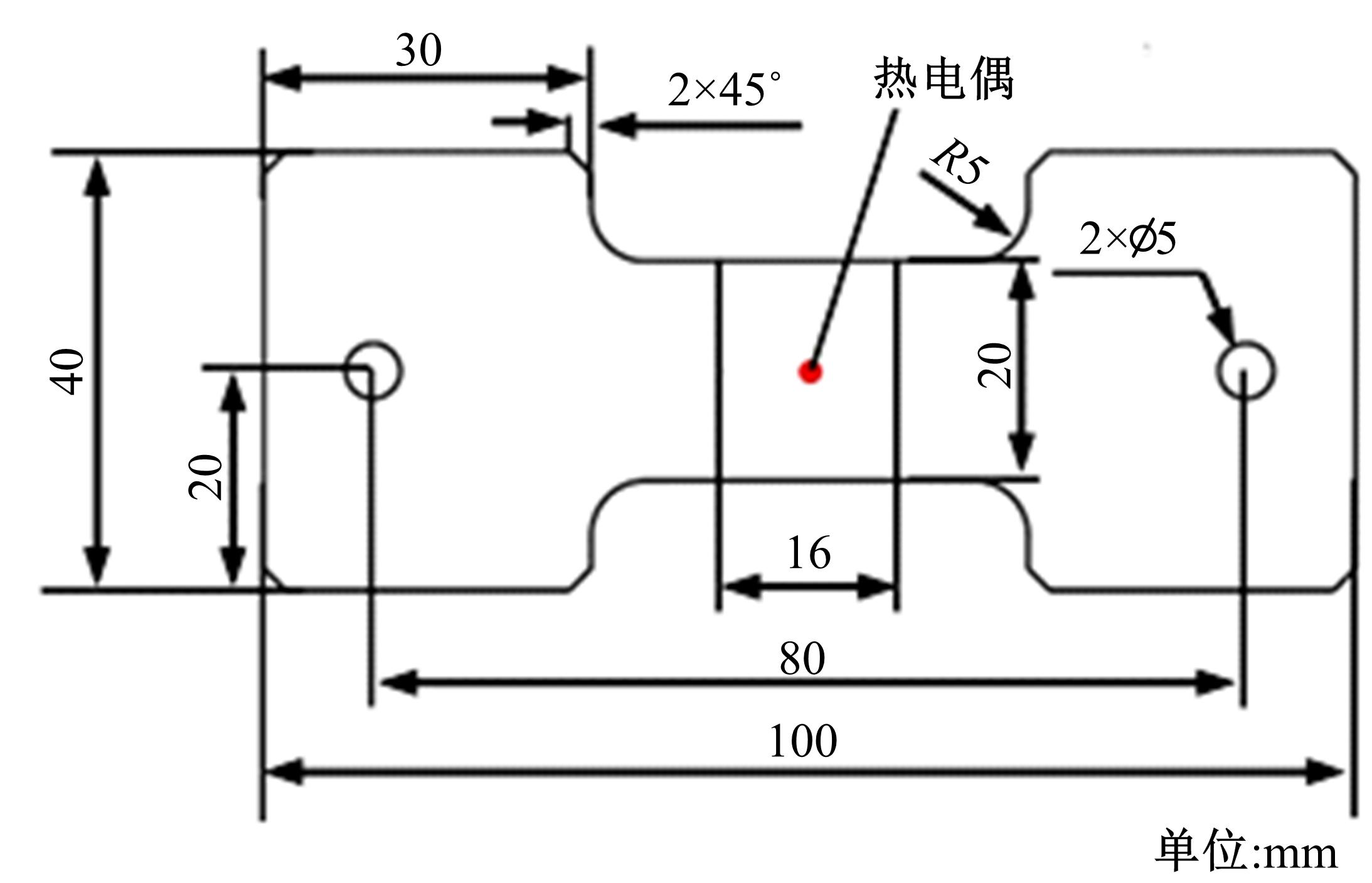
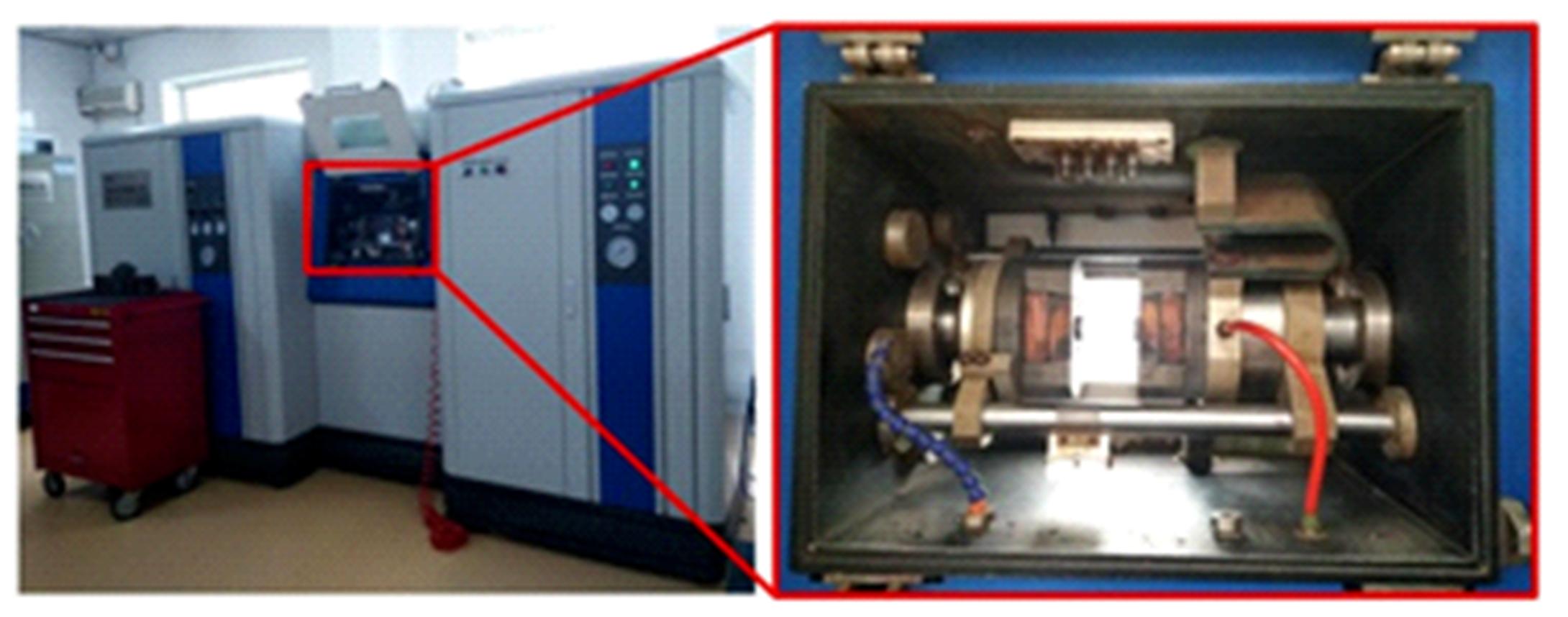
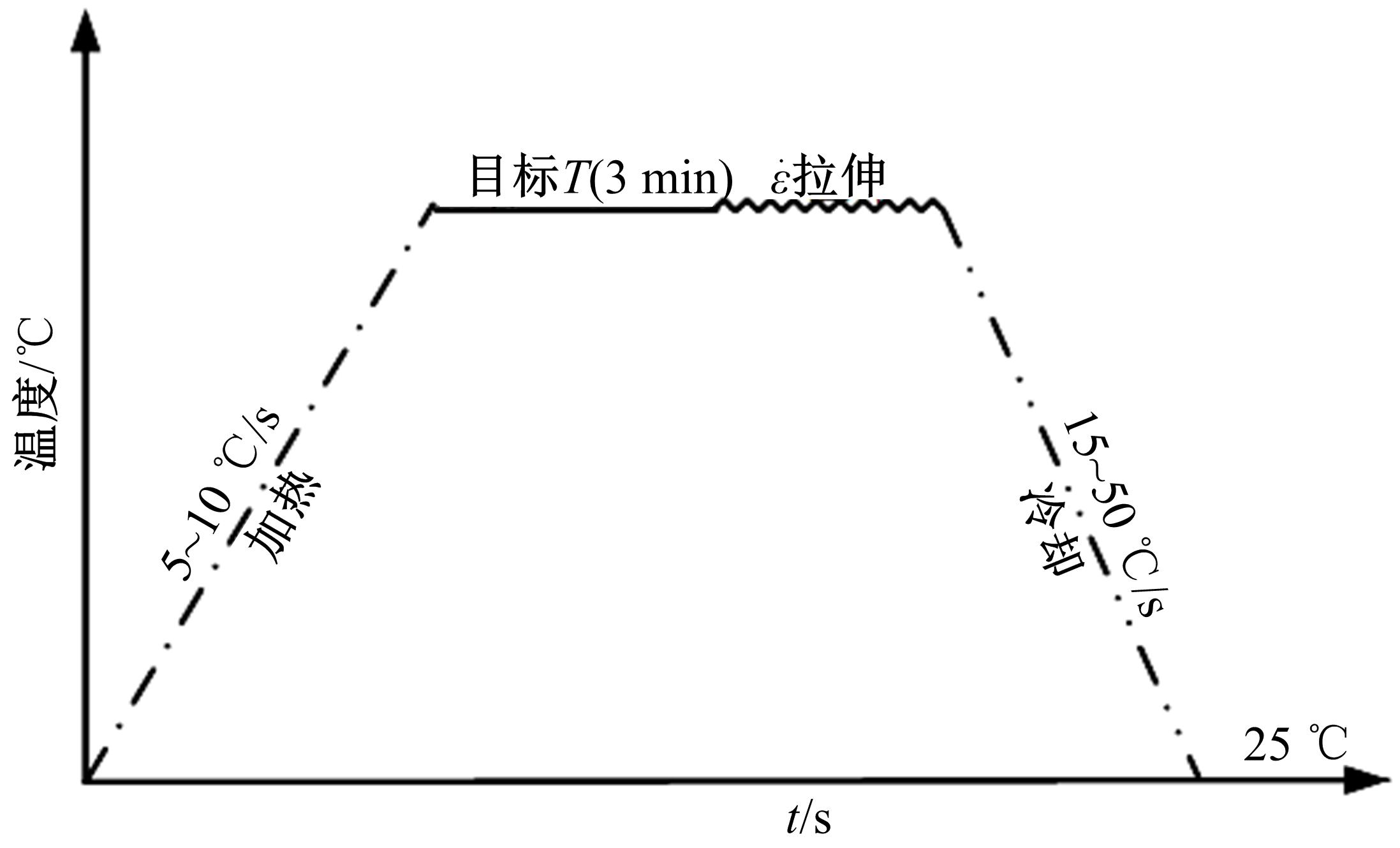
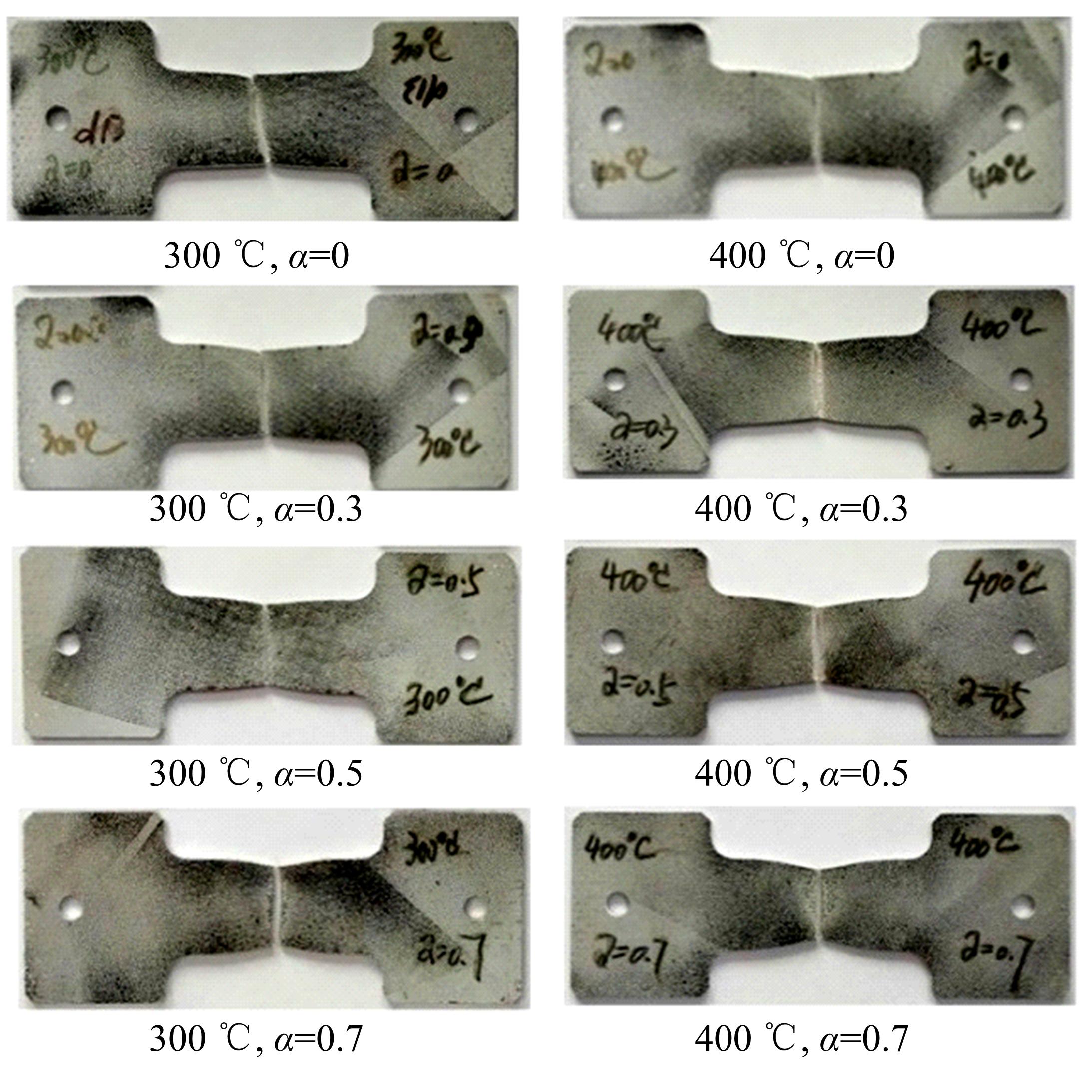
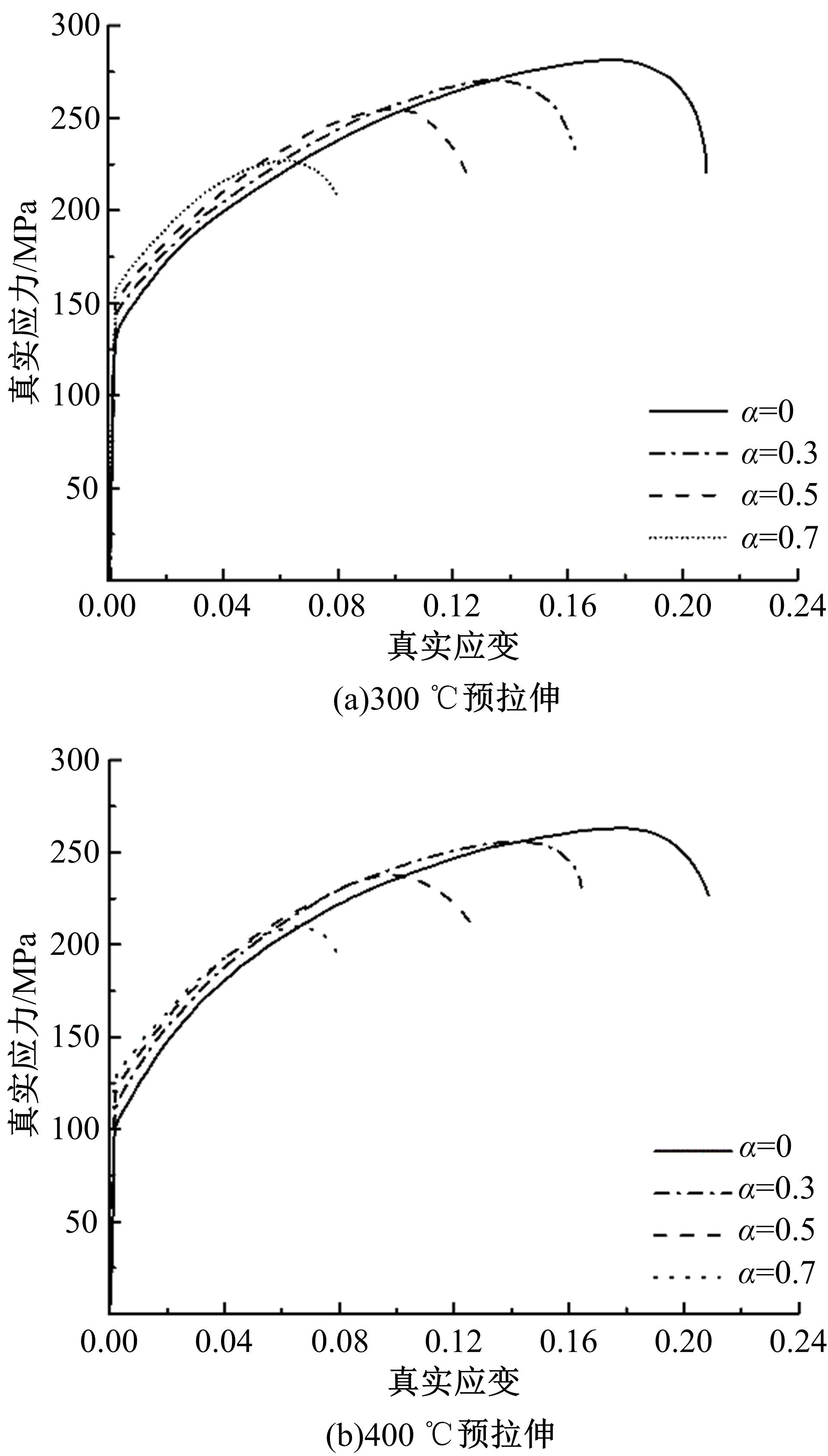
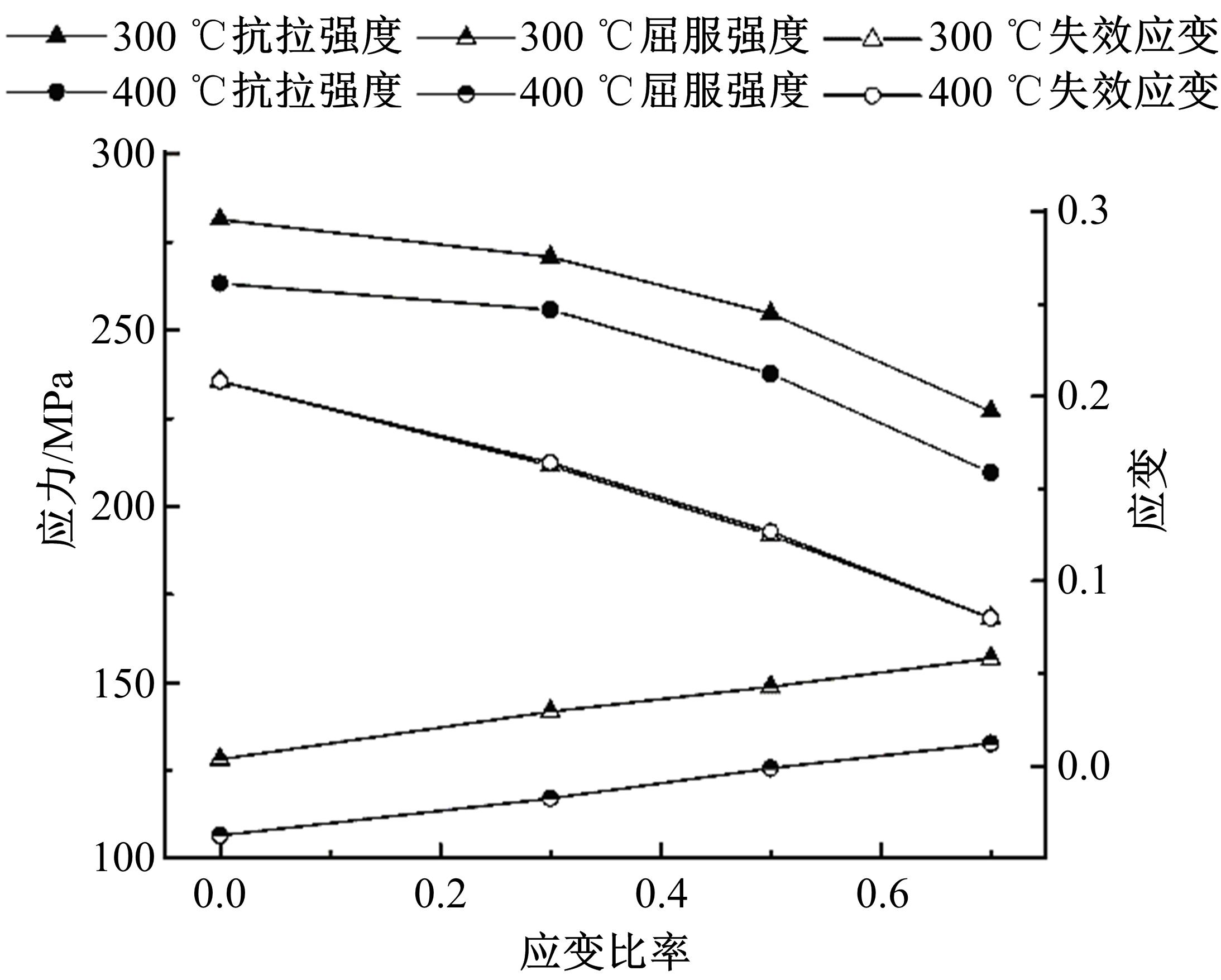
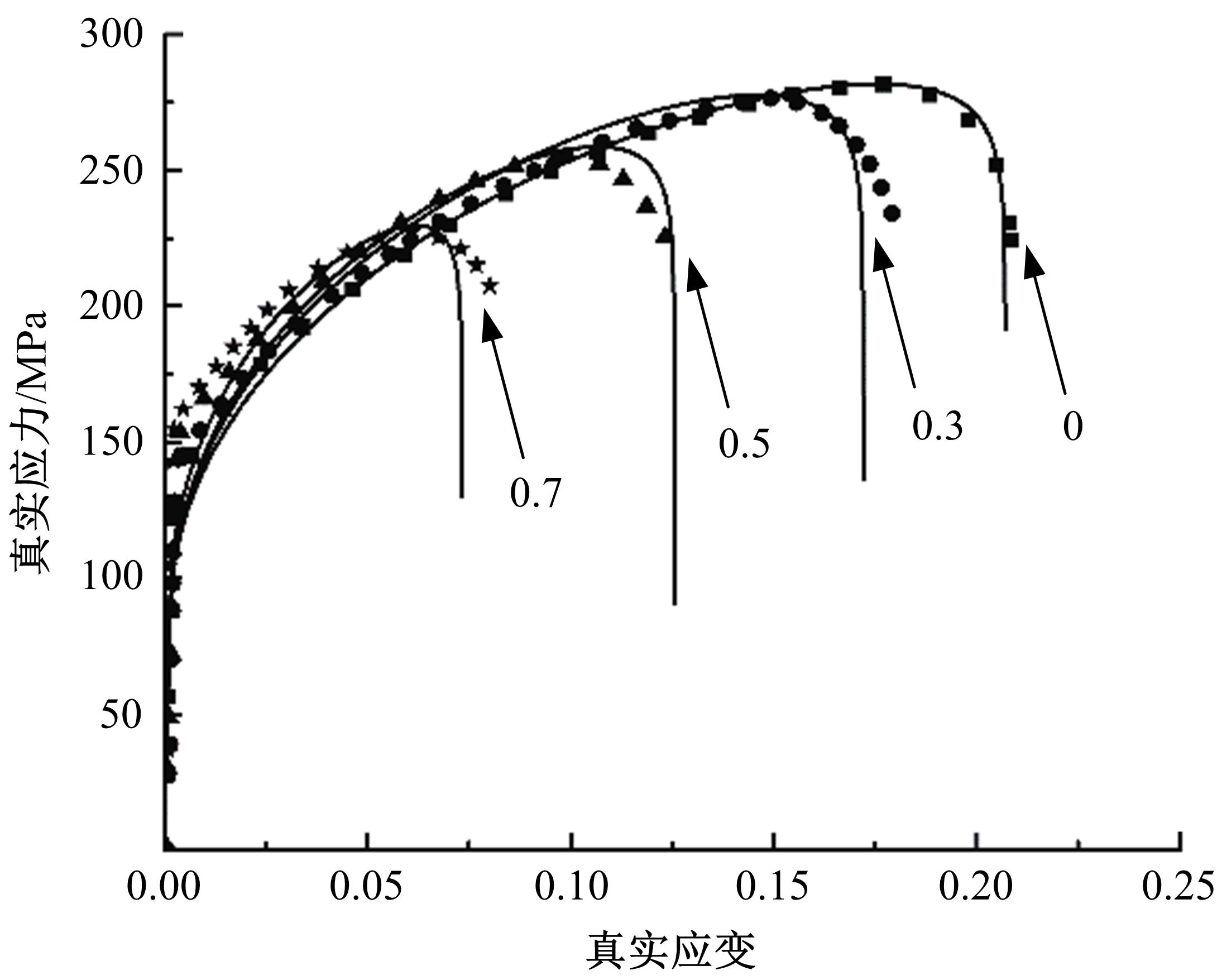
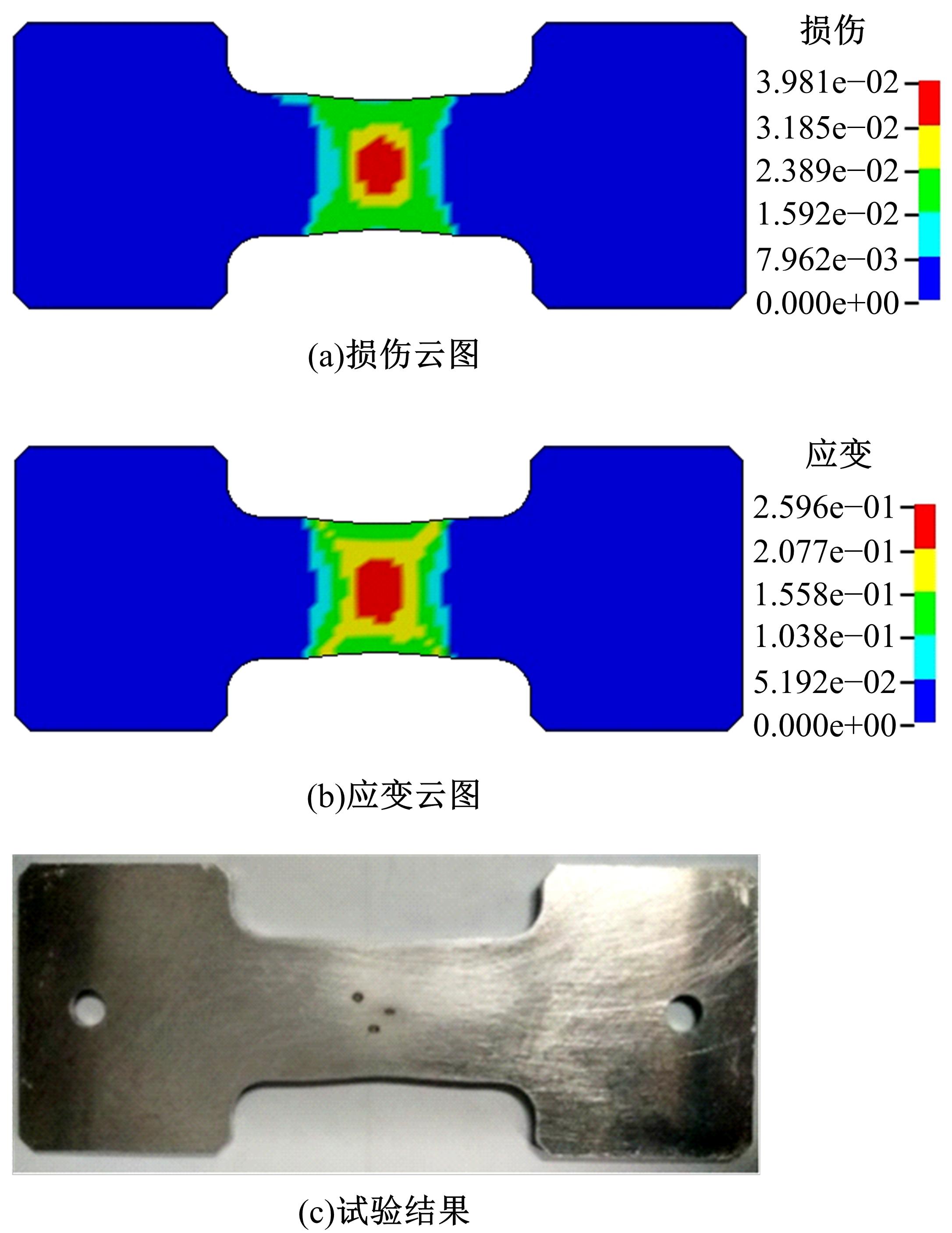
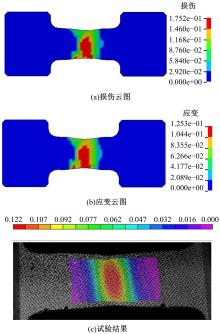
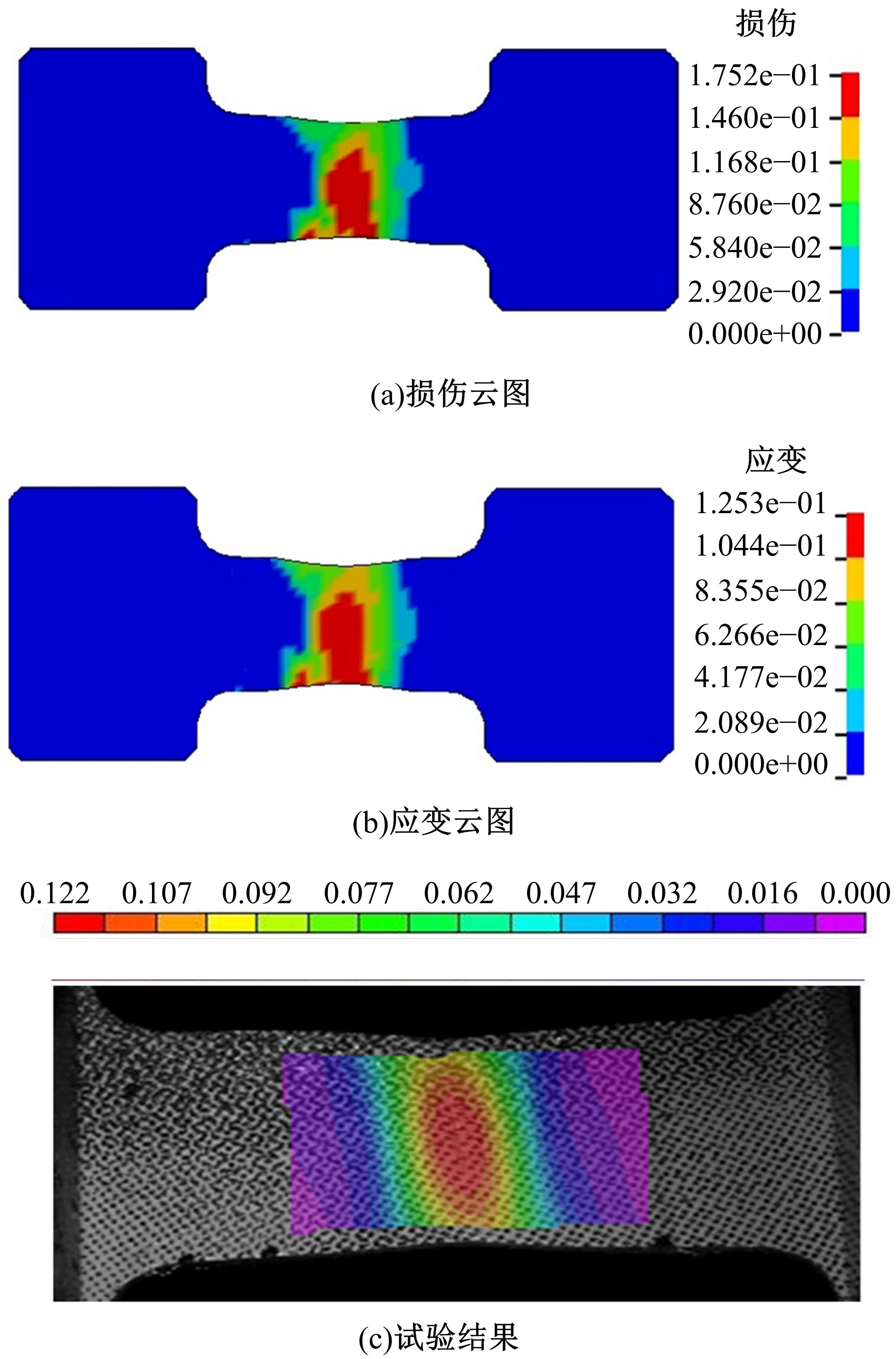
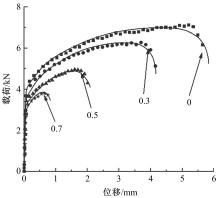
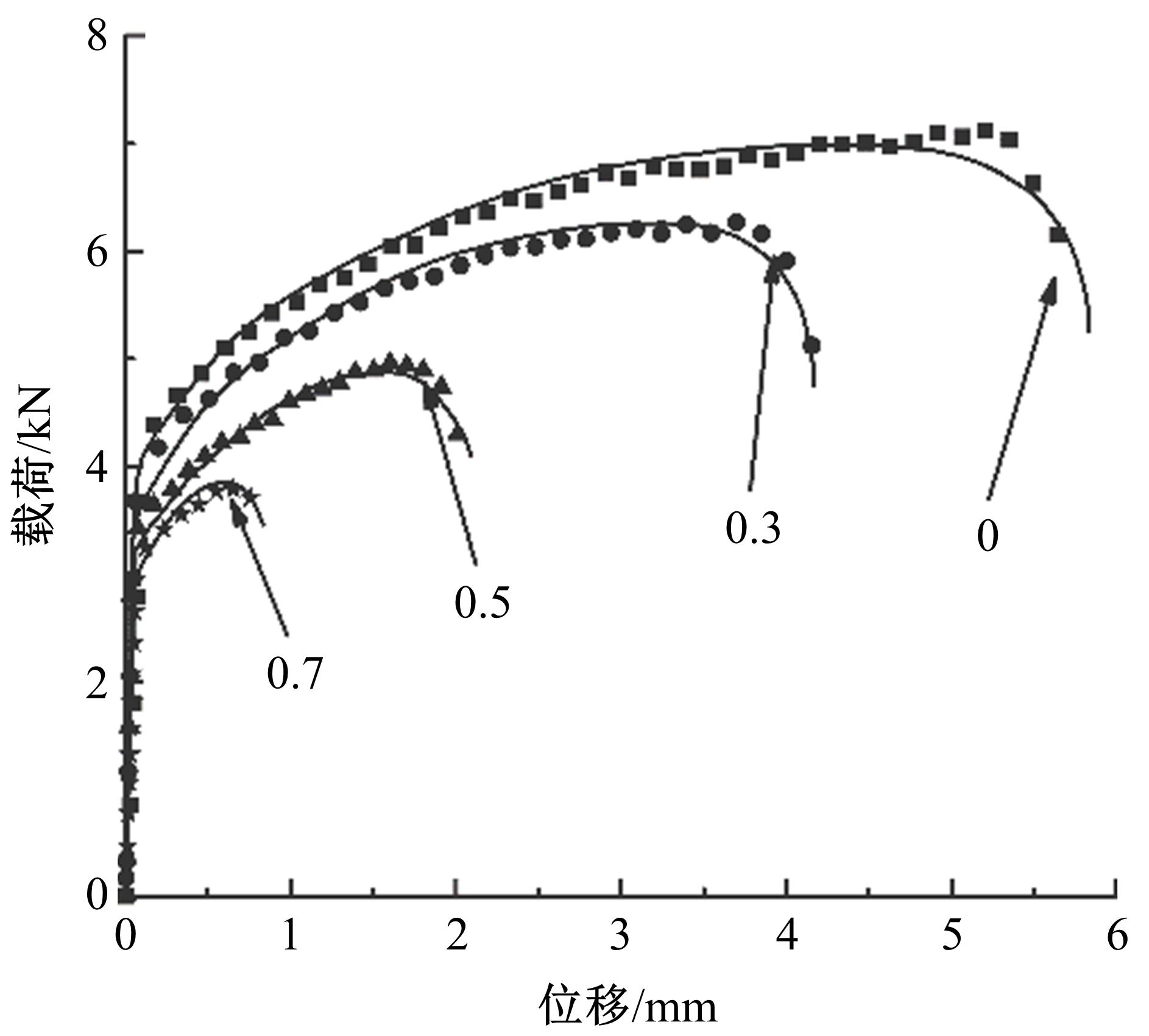
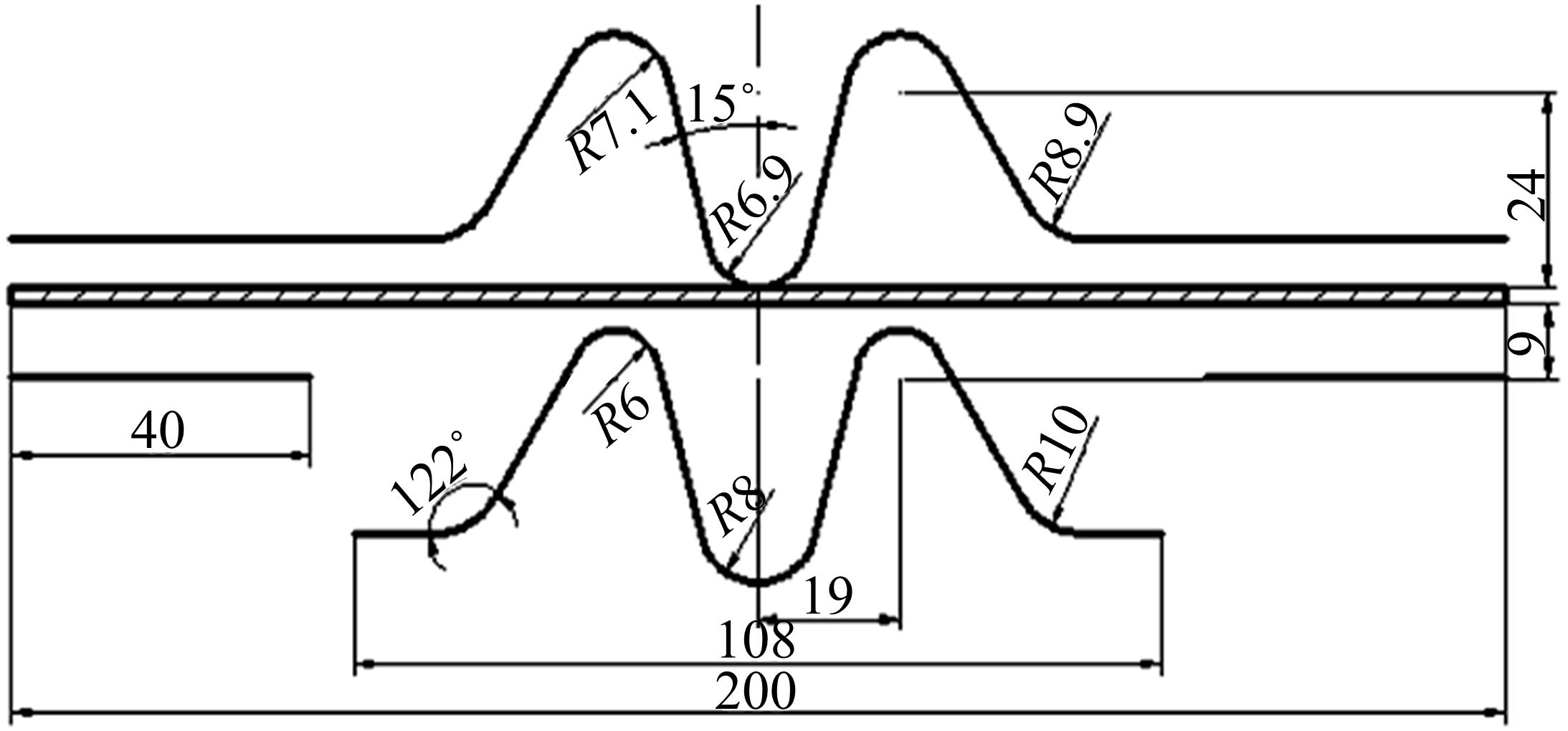
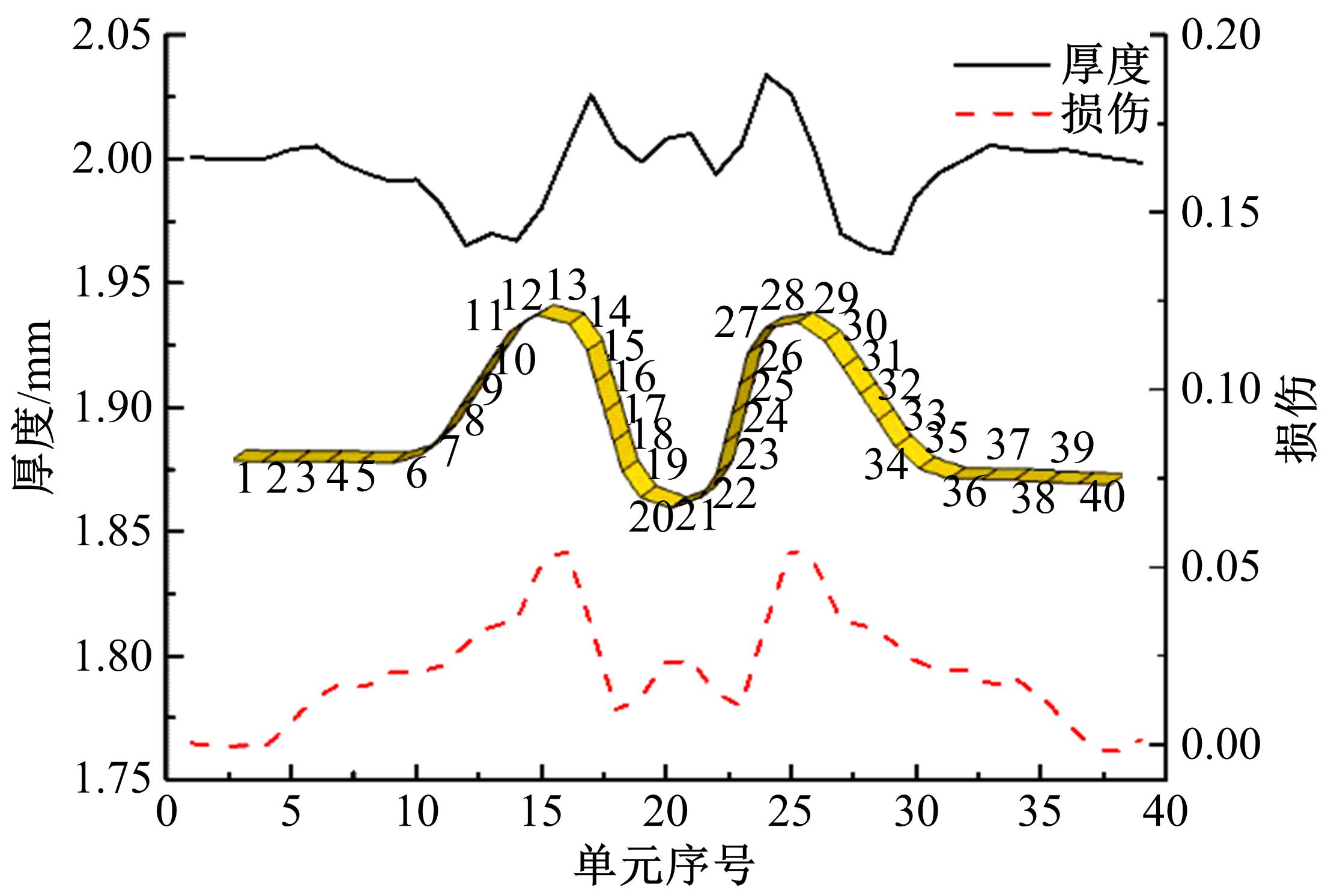
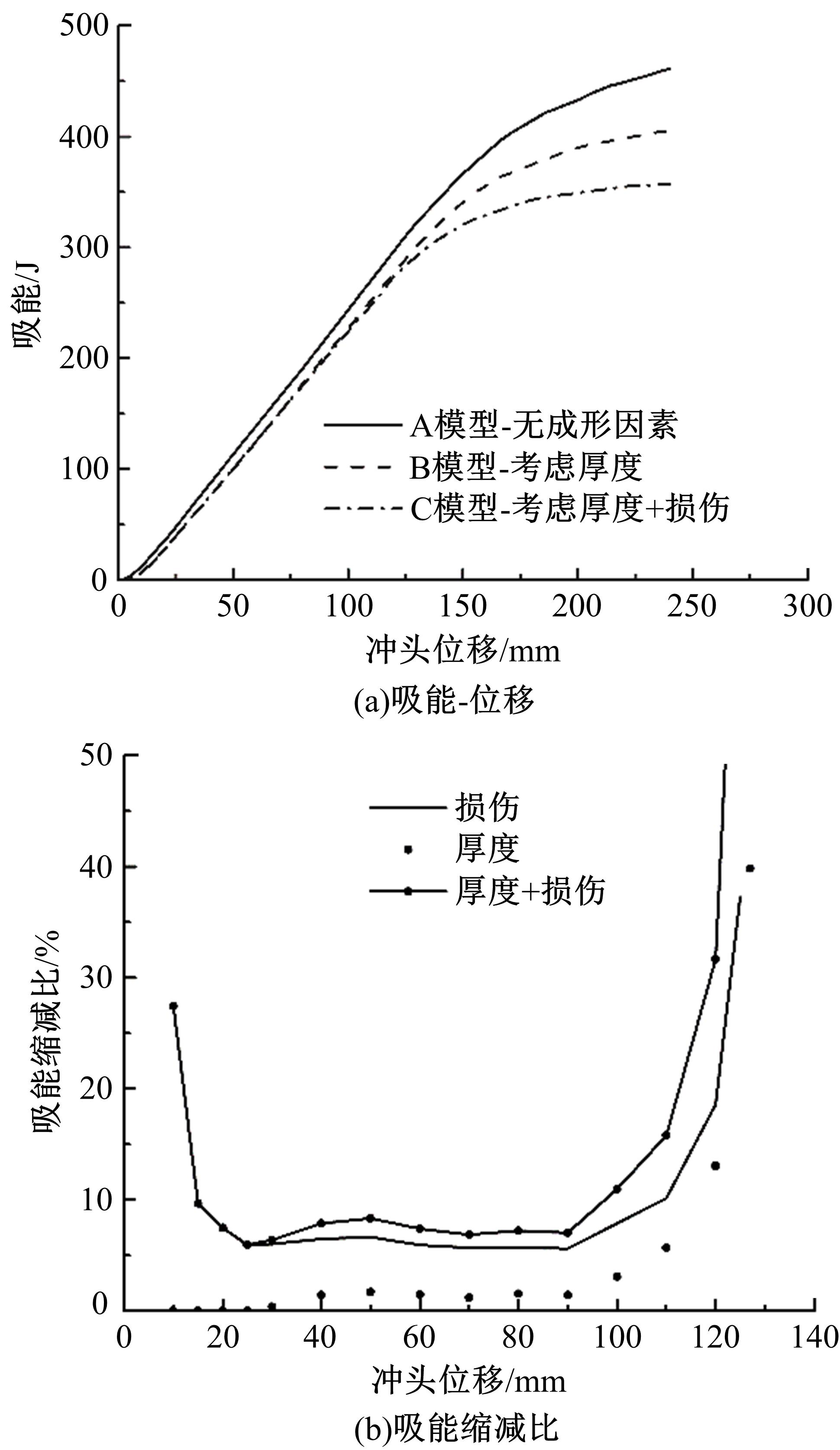
通过高温预拉伸试验和室温拉伸试验分析了温热预变形对AA5754铝合金失效应变、抗拉强度、屈服强度的影响规律。建立了损伤耦合预变形本构模型,以表征不同预应变材料的静态力学性能。以车门防撞梁为例,应用该本构模型分析了热冲压过程中的预变形和厚度变化对其弯曲性能的影响。结果表明:温热预变形会直接降低AA5754铝合金的静态力学性能;300 ℃下0.7的应变比率使试样的失效应变和抗拉强度分别减少了62%和16%;本文所建立的本构模型可以准确地预测温热成形对AA5754铝合金静态力学性能的影响。
中图分类号:
- U463.82
| 1 | Zheng K L, Dong Y C, Zheng J H, et al. The effect of hot form quench (HFQ) conditions on precipitation and mechanical properties of aluminium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 761:138017. |
| 2 | Ghiotti A, Simonetto E, Bruschi S. Influence of process parameters on tribological behaviour of AA7075 in hot stamping[J]. Wear, 2019, 426-427:348-356. |
| 3 | Zhou J, Wang B, Lin J, et al. Forming defects in aluminum alloy hot stamping of side-door impact beam[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(11):3611-3620. |
| 4 | Zhuang Wei-min, Xie Dong-xuan, Chen Yan-hong. Experimental investigation of the effect of the material damage induced in sheet metal forming process on the service performance of 22MnB5 steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 29:747-755. |
| 5 | George R, Worswick M J, Detwiler D, et al. Impact testing of a hot-formed B-pillar with tailored properties-experiments and simulation[J]. SAE International Journal of Materials and Manufacturing2013, 6(2):157-162. |
| 6 | Cheng W, Zhang H L, Fu S, et al. A process-performance coupled design method for hot-stamped tailor rolled blank structure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 140:132-143. |
| 7 | Li N, Lin J G, Dean T A. Development of unified viscoplastic damage model for crashworthiness analysis of boron steel safety components with tailored microstructures[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 784:427-434. |
| 8 | Zhuang Wei-min, Wang Peng-yue, Xie Dong-xuan, et al. Experimental study and a damage model approach to determine the effect of hot forming deformation on the service performance of 22MnB5 steel[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019,47: 10-21. |
| 9 | Na J, Mu W, Qin G, et al. Effect of temperature on the mechanical properties of adhesively bonded basalt FRP-aluminum alloy joints in the automotive industry[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2018, 85:138-148. |
| 10 | Huang C, Liu J, Jia X. Effect of thermal deformation parameters on the microstructure, texture, and microhardness of 5754 aluminum alloy[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2019, 26(9):1140-1150. |
| 11 | Lin J, Mohamed M, Balint D, et al. The development of continuum damage mechanics-based theories for predicting forming limit diagrams for hot stamping applications[J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2014, 23(5):684-701. |
| [1] | 陈学文,王继业,杨喜晴,皇涛,宋克兴. Cr8合金钢热变形行为及位错密度演变规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 91-99. |
| [2] | 叶辉,朱艳荣,蒲永锋. 纤维增强复合材料应变率效应的数值仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1622-1629. |
| [3] | 叶辉, 胡平, 申国哲, 孙宏图, 杨姝. 利用高强度钢板温热成形结构件改善车身侧面抗撞性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 101-0105. |
|
||