吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1405-1413.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200280
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制
董延华1( ),刘靓葳1,2,赵靖华1,3(
),刘靓葳1,2,赵靖华1,3( ),李亮1,解方喜3
),李亮1,解方喜3
- 1.吉林师范大学 计算机学院,吉林 四平 136000
2.长春金融高等专科学校 信息技术学院,长春 130028
3.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Real-time torque tracking control based on BPNN online learning prediction model
Yan-hua DONG1( ),Jing-wei LIU1,2,Jing-hua ZHAO1,3(
),Jing-wei LIU1,2,Jing-hua ZHAO1,3( ),Liang LI1,Fang-xi XIE3
),Liang LI1,Fang-xi XIE3
- 1.College of Computer,Jilin Normal University,Siping 136000,China
2.College of Information Technology,Changchun Finance College,Changchun 130028,China
3.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
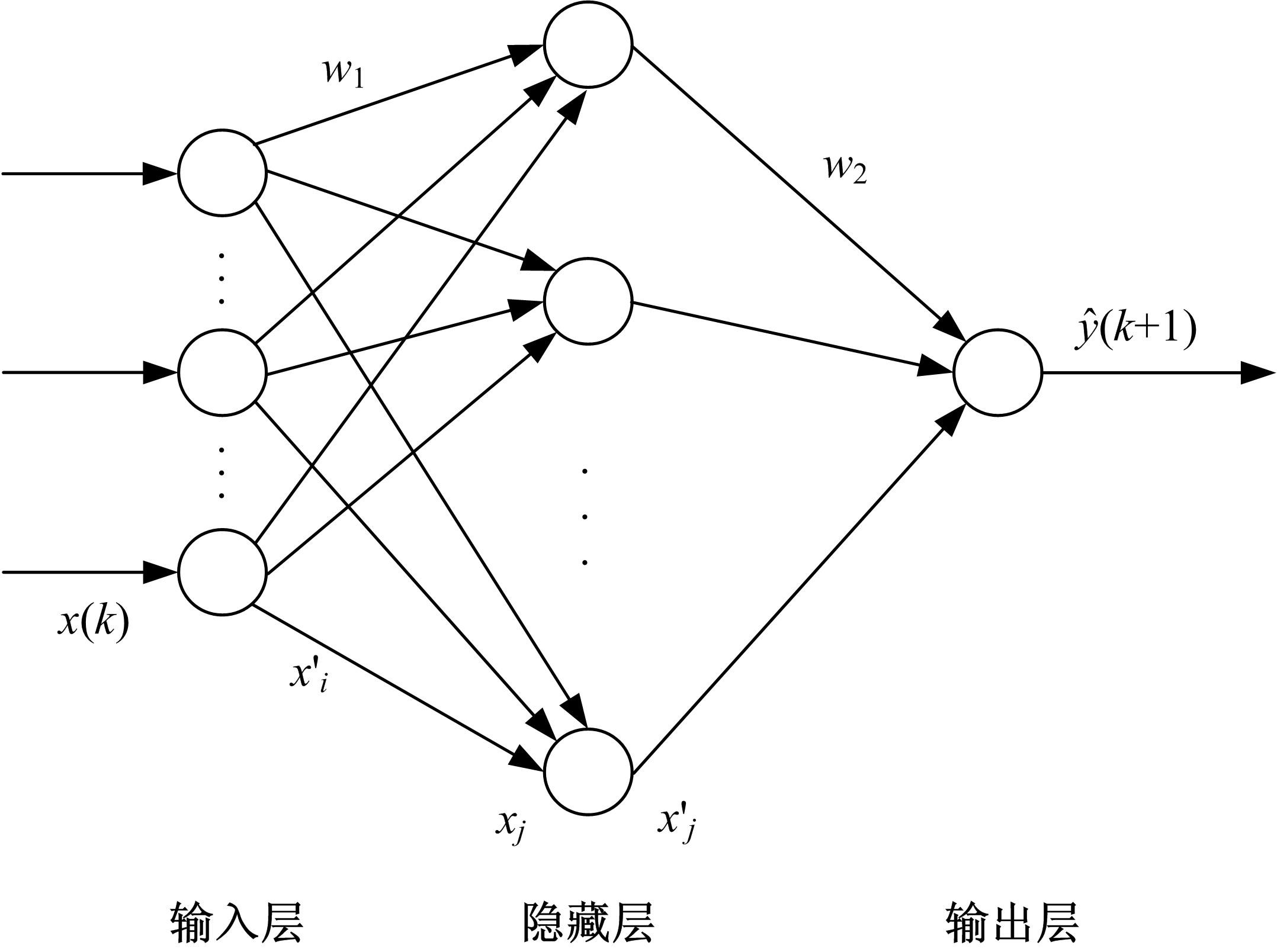
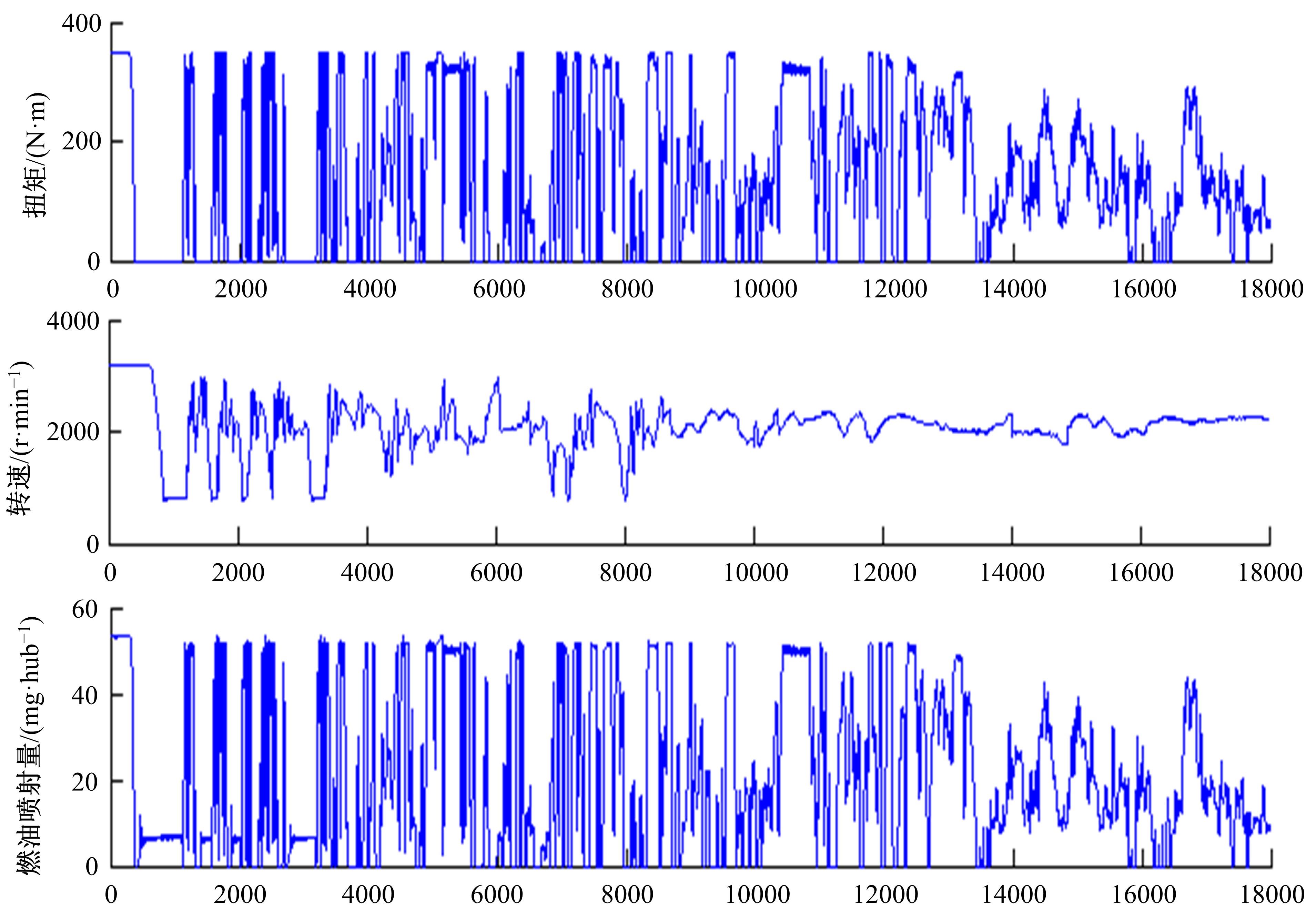
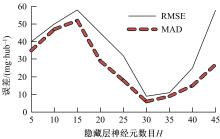
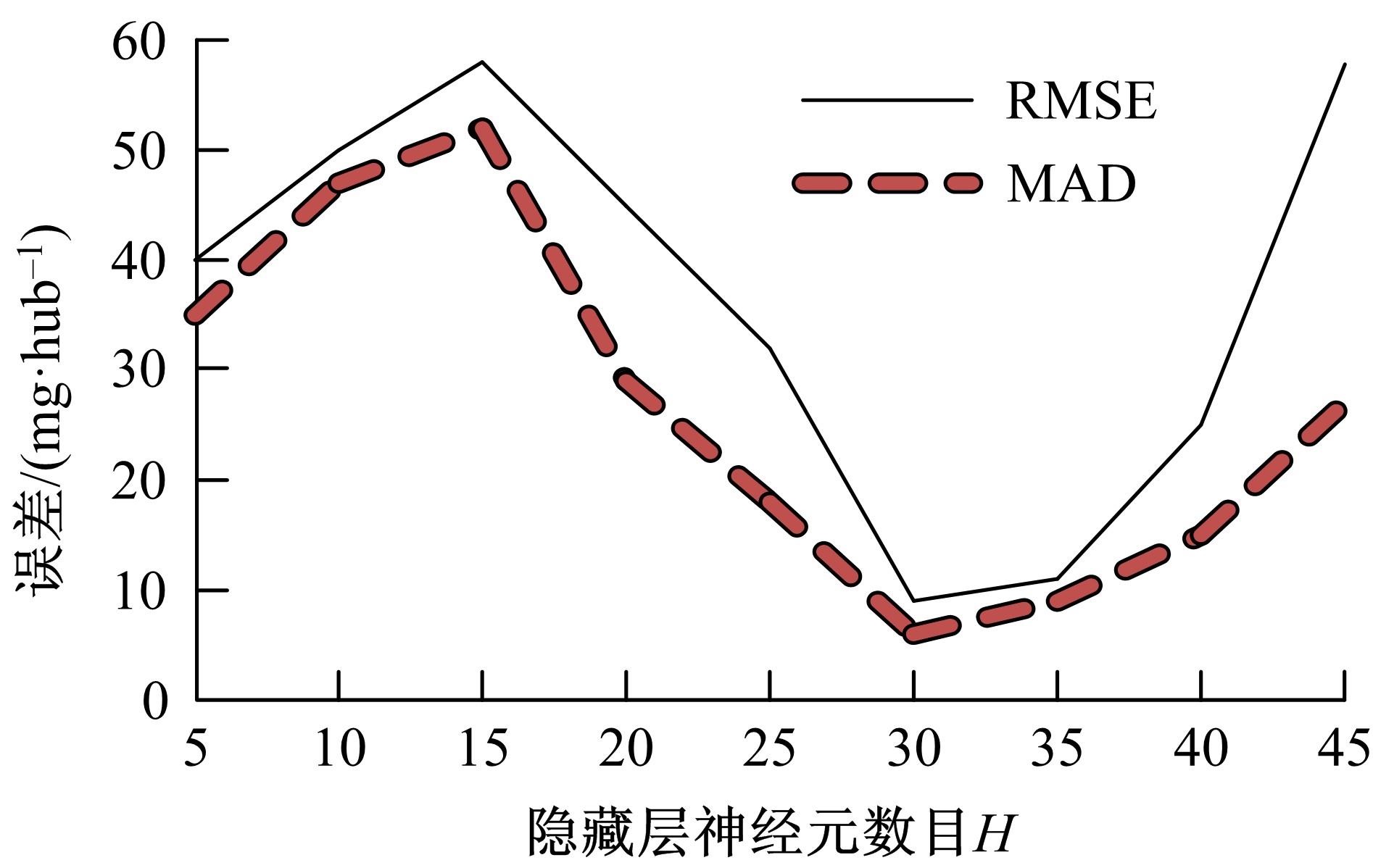
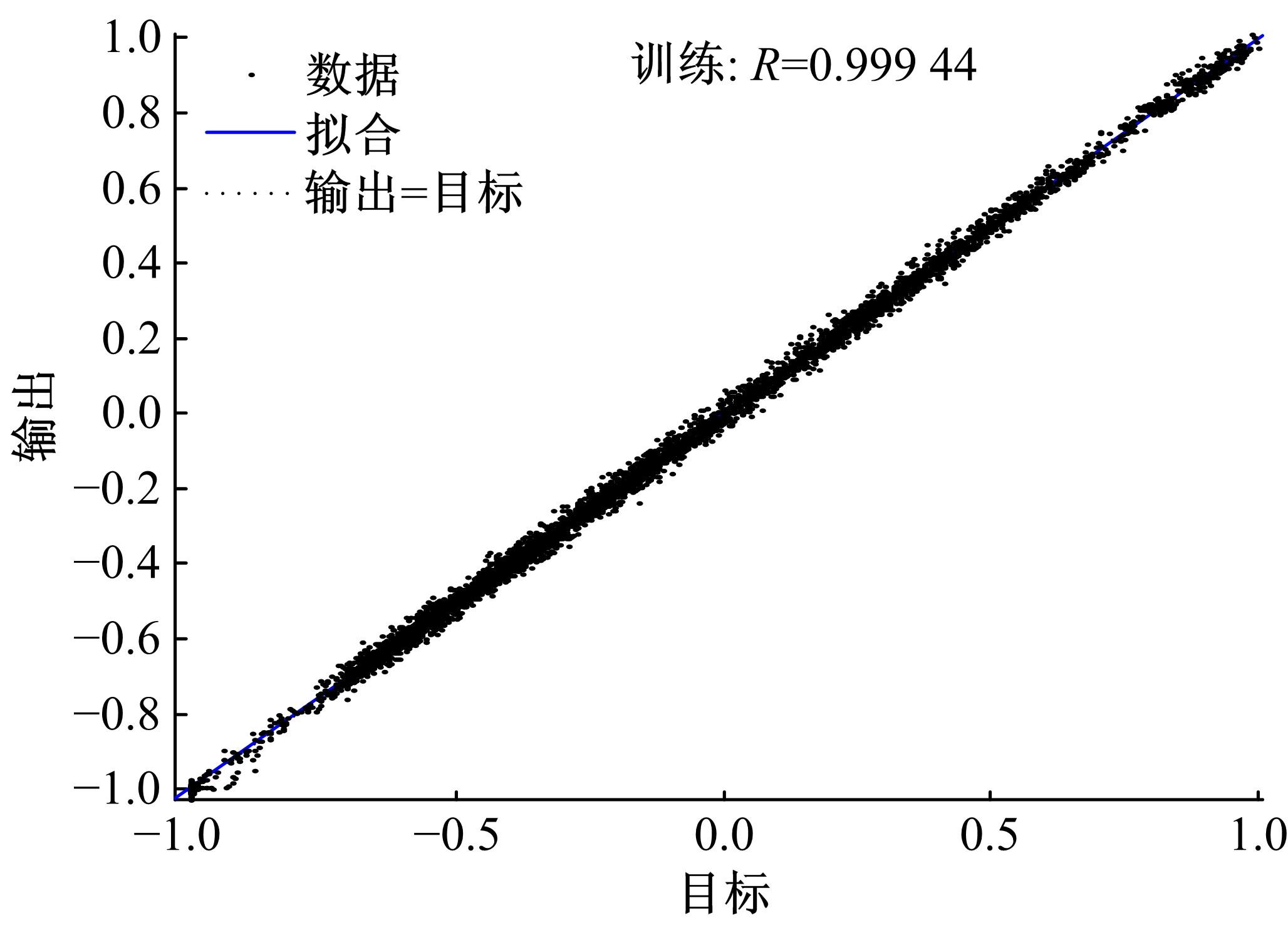
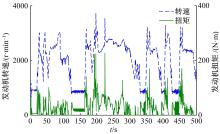
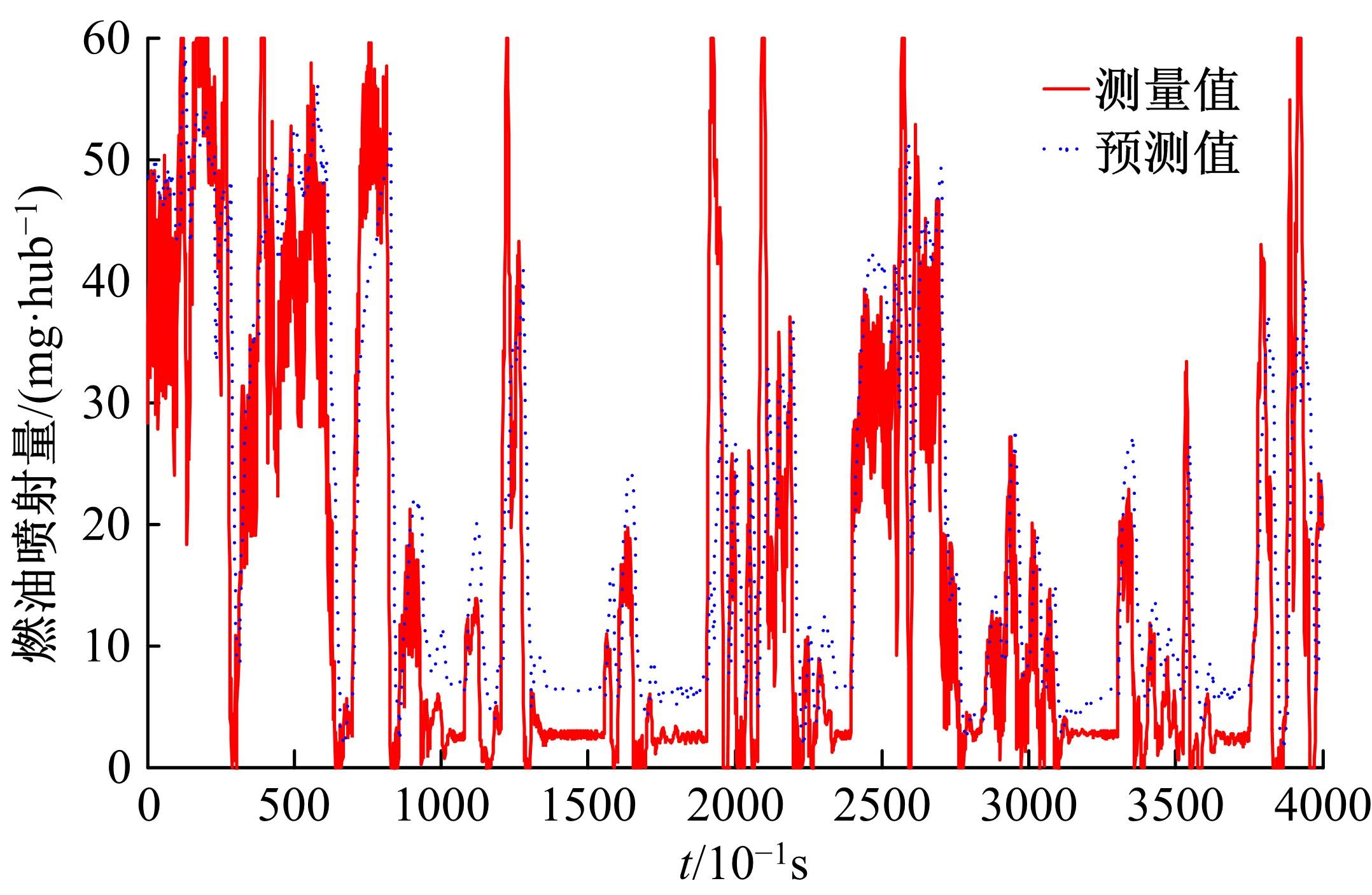
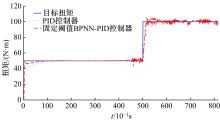
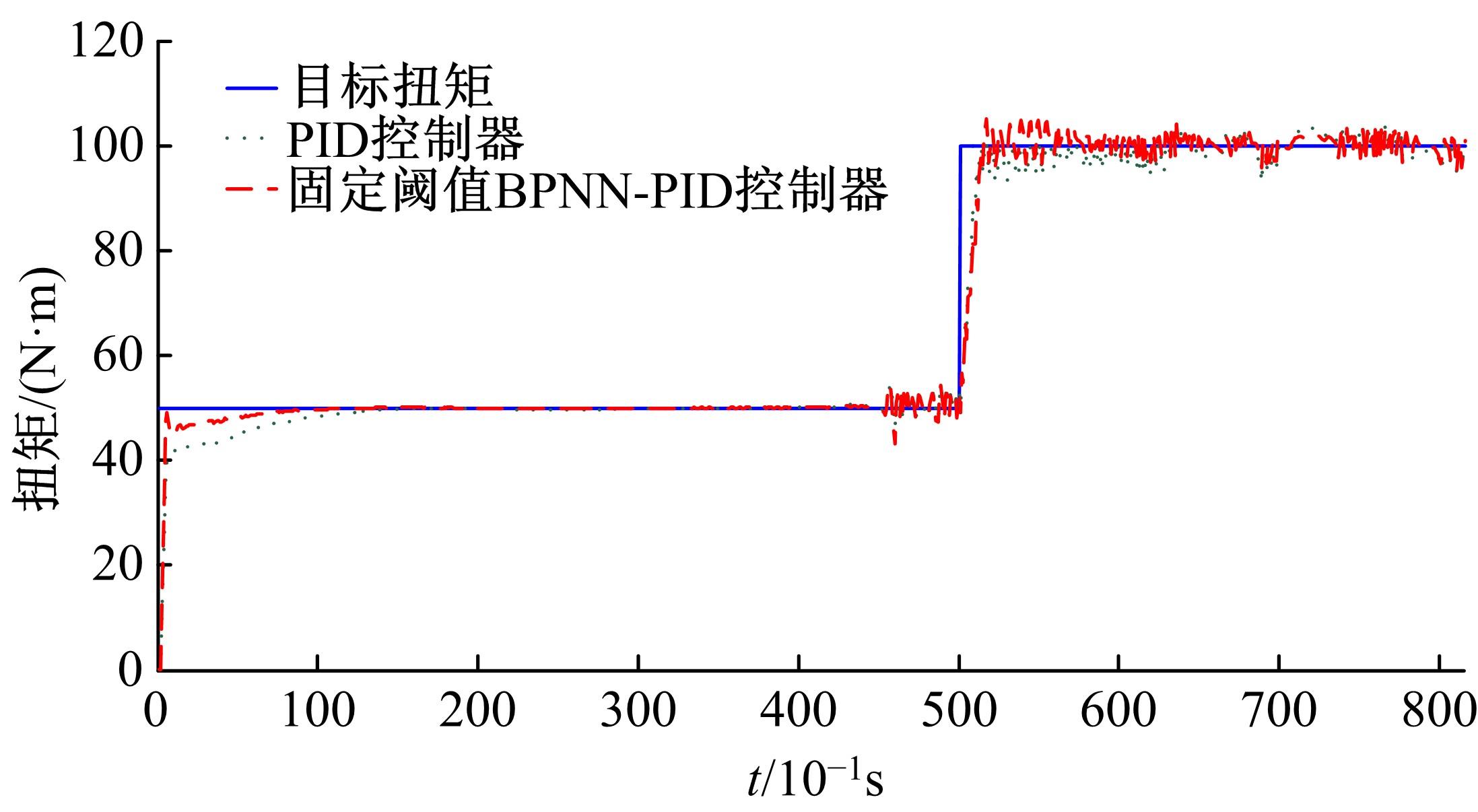
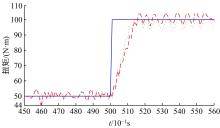
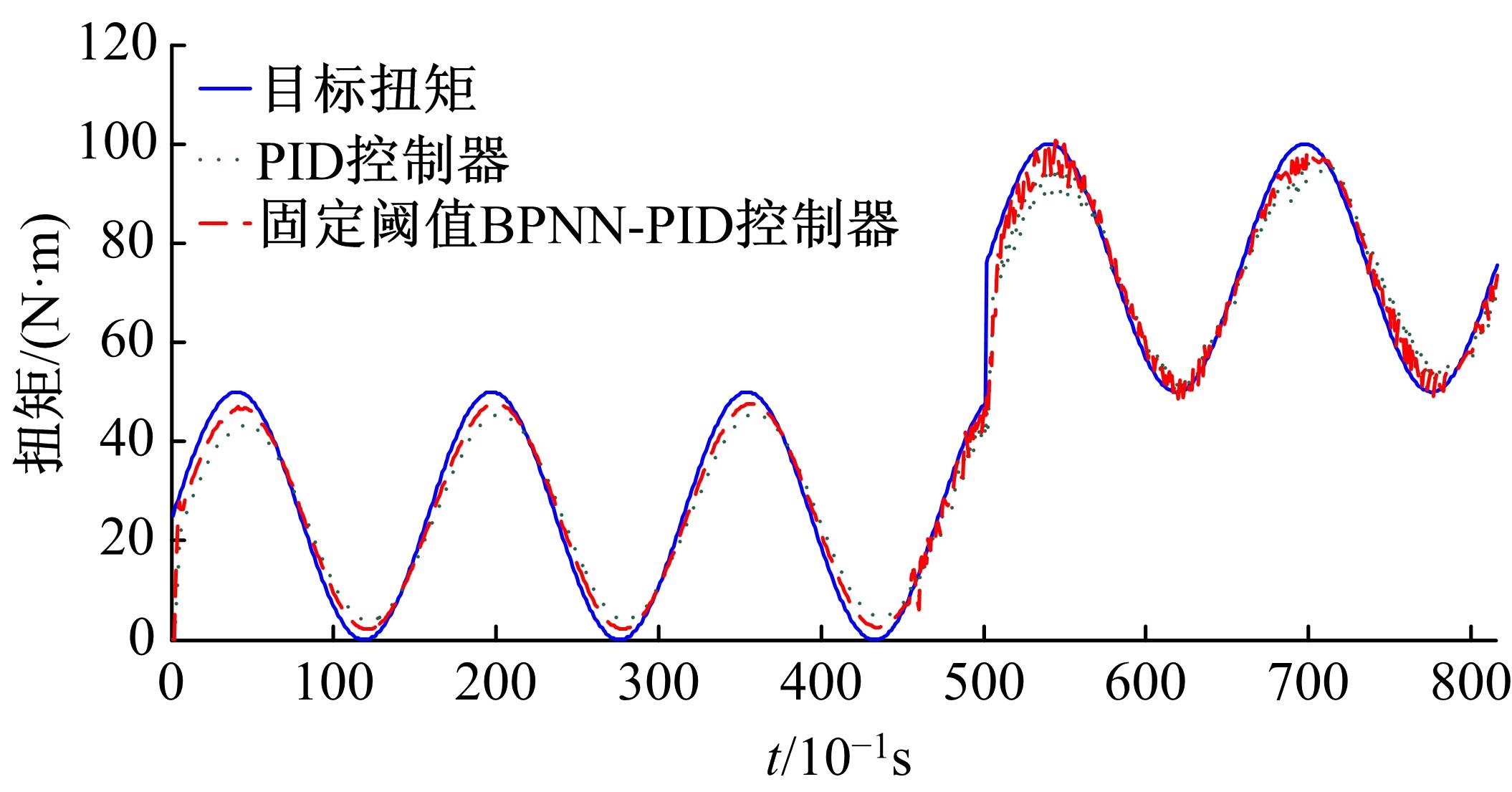
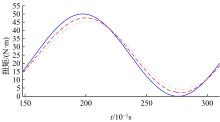
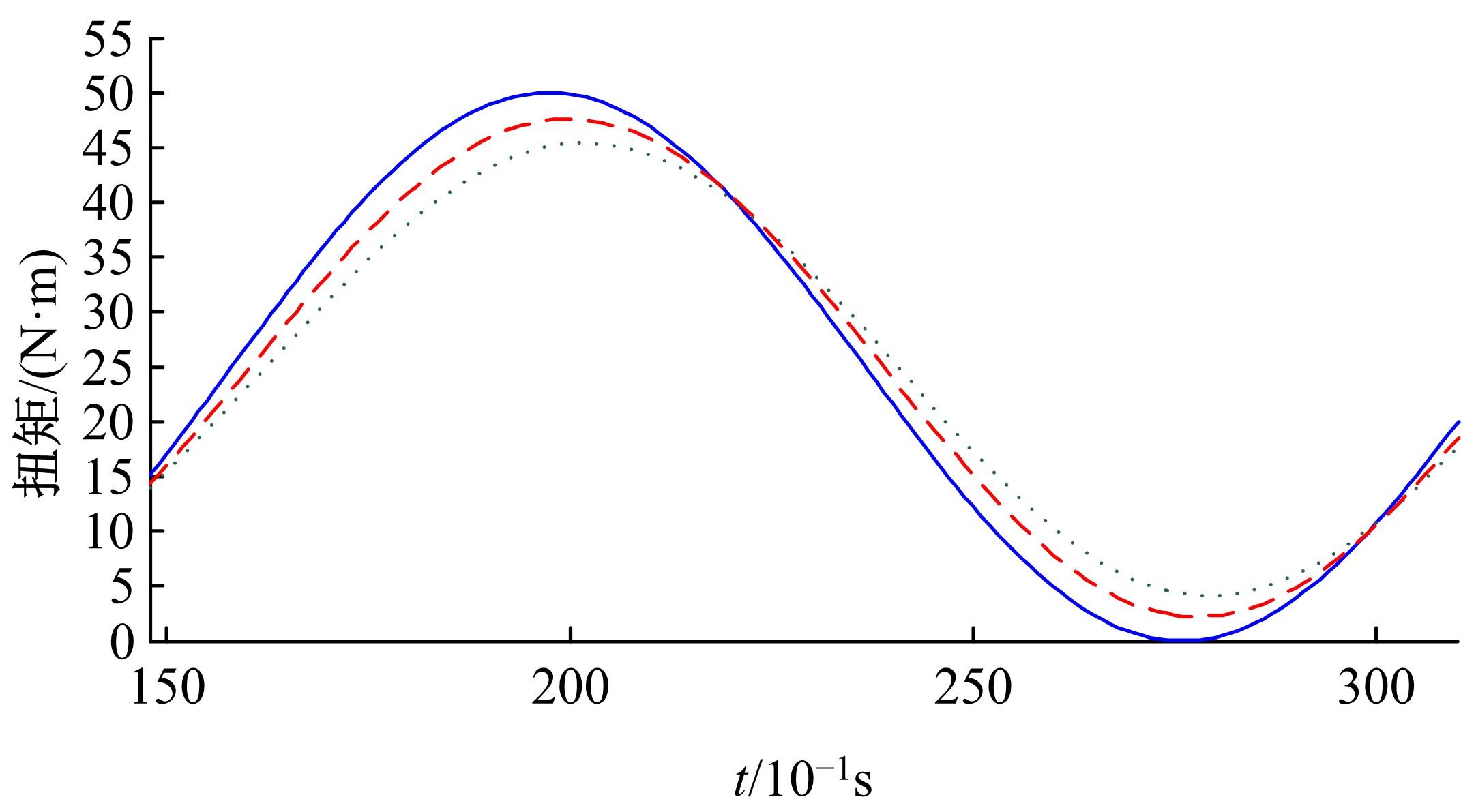
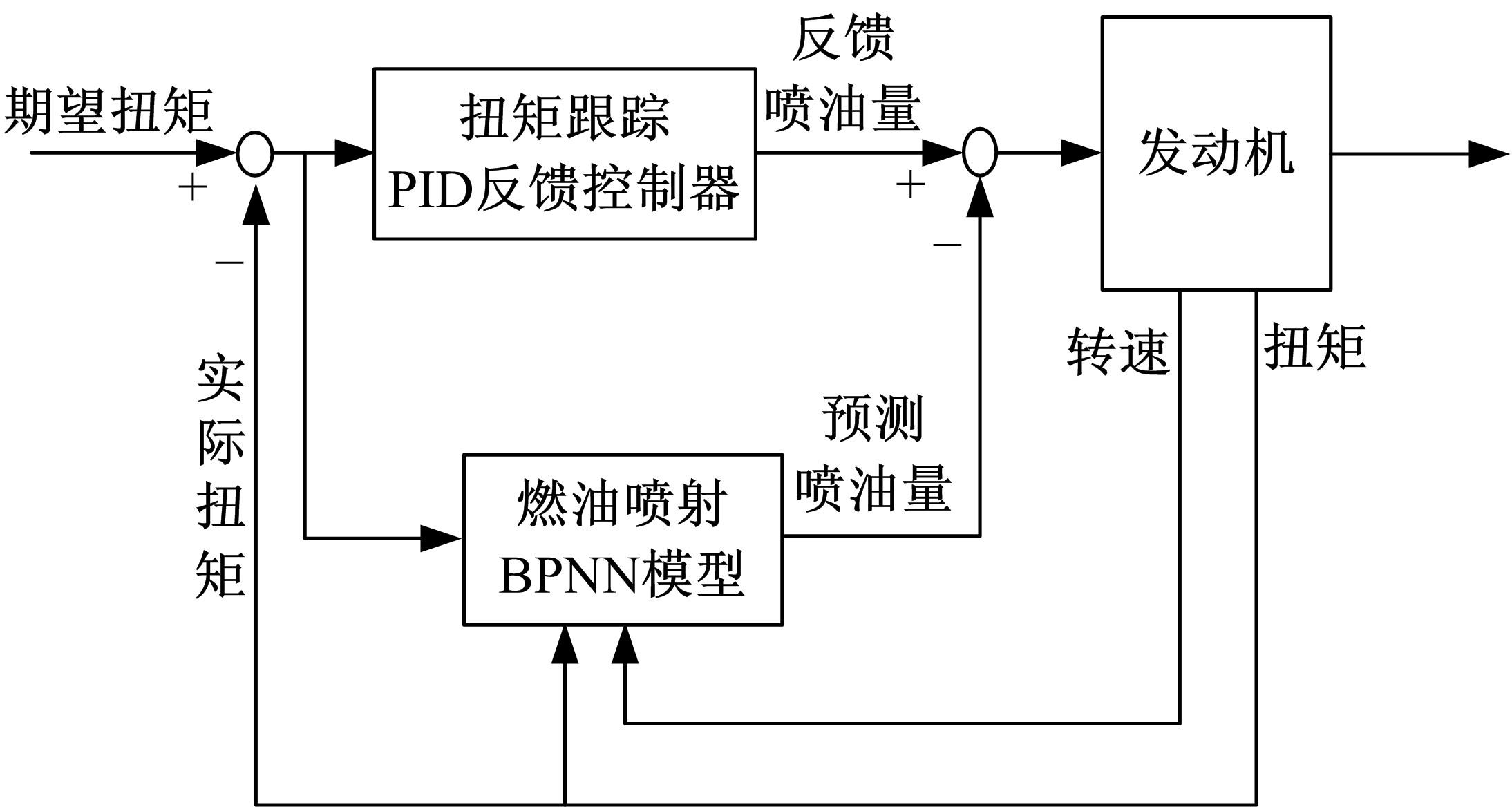
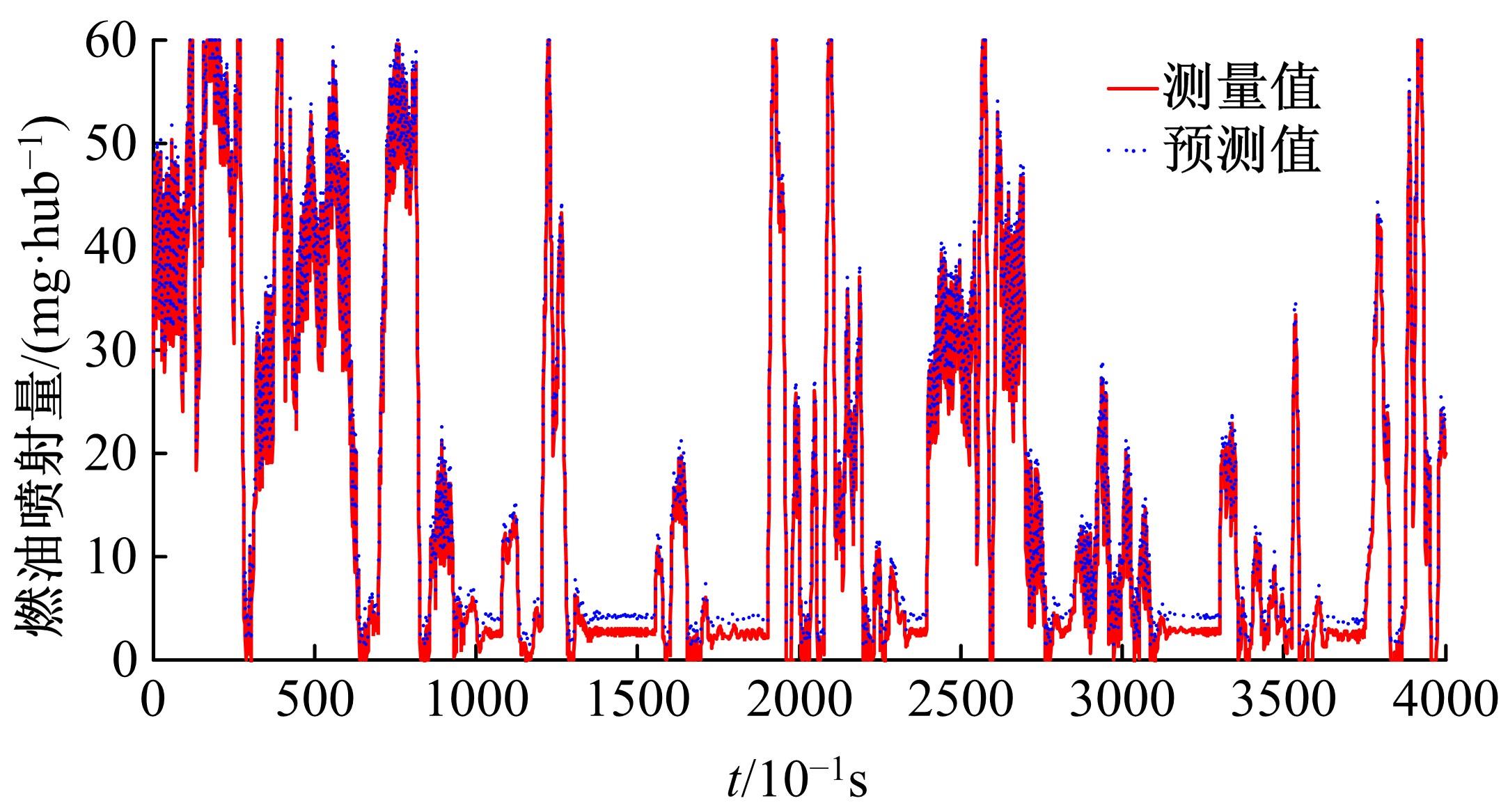
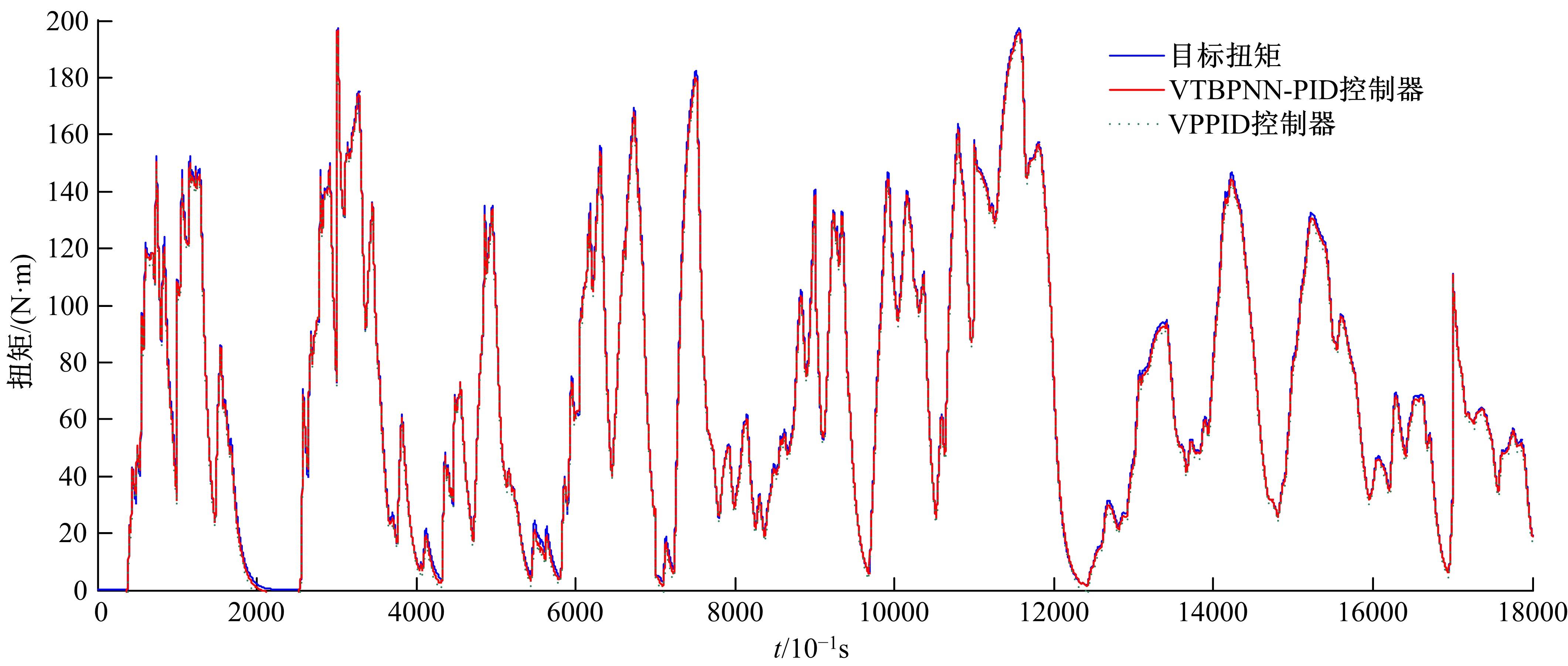
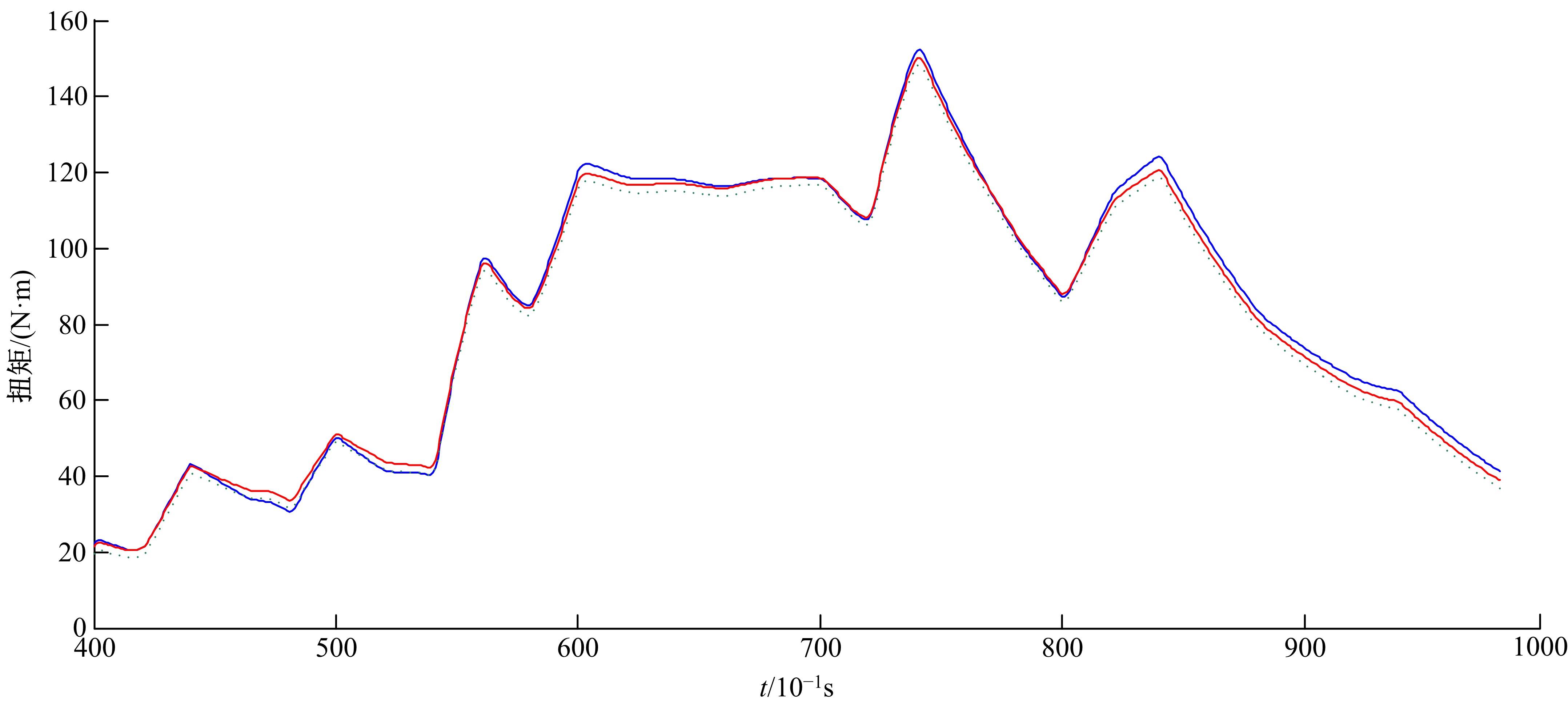
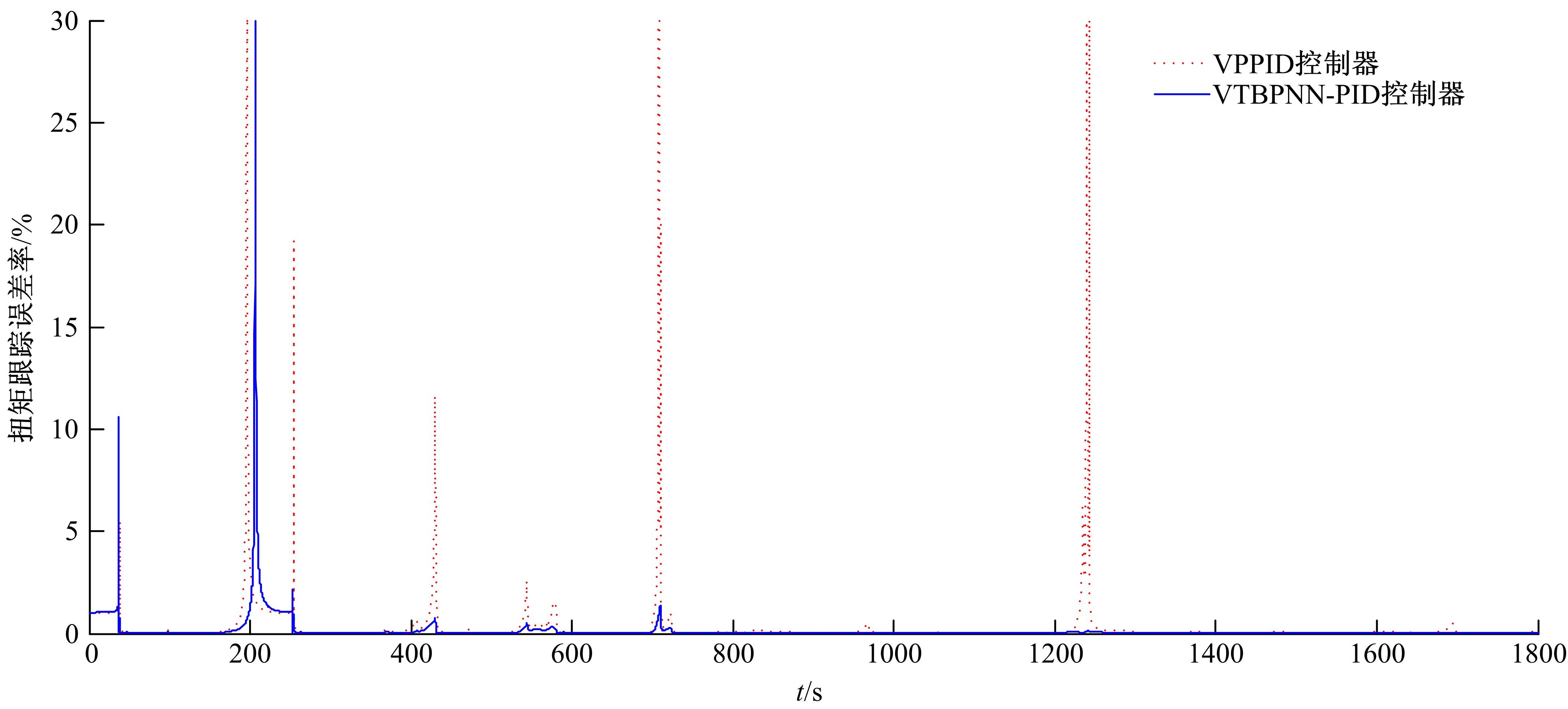
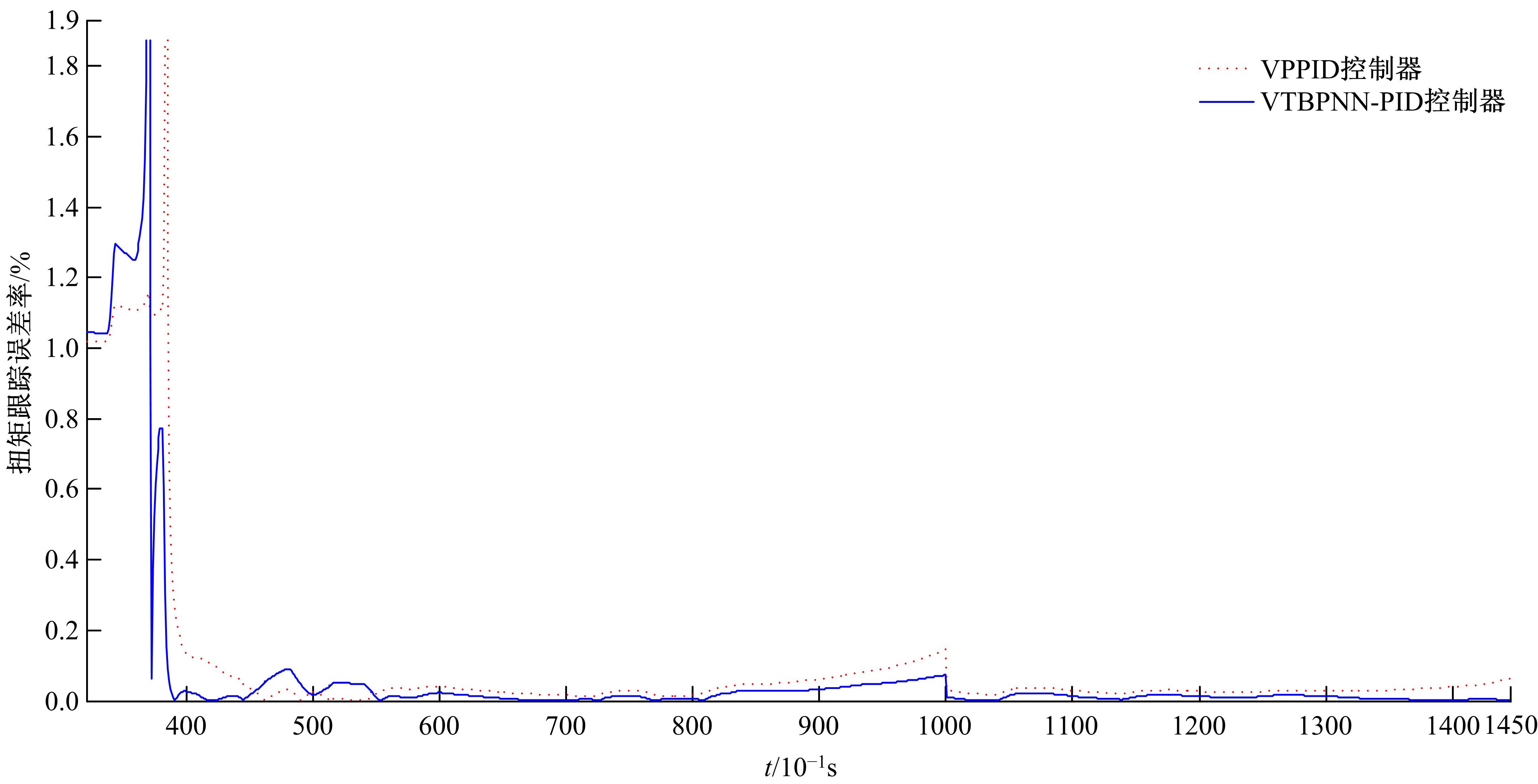
基于大量的台架试验数据,利用反向传播神经网络(BPNN)设计了燃油喷射在线学习预测模型,结合PID反馈完成扭矩跟踪的实时控制。其中,燃油喷射BPNN预测模型采用一种实时的简化离散模型,模型的阈值可以在线学习更新,具有参数自适应性。台架试验表明,相比于固定参数的BPNN模型,提出的阈值在线学习的BPNN模型具有更高的预测精度;提出的可变阈值VTBPNN预测前馈加PID反馈控制器能够满足扭矩跟踪的实时性需求,并且相比于普通可变参数VPPID控制器,在瞬态工况干扰下鲁棒性更强,跟踪误差更小。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | Liu B, Wang R, Zhao G, et al. Prediction of rock mass parameters in the TBM tunnel based on BP neural network integrated simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020,95(c):103103-103103. |
| 2 | Moskwa J J, Hedrick J K. Modeling and validation of automotive engines for control algorithm development[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurement and Control-transactions of The ASME, 1992, 114(2): 278-285. |
| 3 | Hirahara H, Yoshida K, Iwase M, et al. Torque estimation based on nonlinear engine model considering crankshaft torsion[C]∥IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Piscataway, USA,2010: 682-687. |
| 4 | Anjum R, Yar A, Yousufzai I K, et al. Second order sliding mode based speed tracking control for torque management of gasoline engines[C]∥Asian Control Conference, Kitakyushu-shi, Japan,2019: 555-560. |
| 5 | Anjum R, Yar A, Bhatti A I, et al. Dual loop speed tracking control for torque management of gasoline engines[C]∥European Control Conference, Naples, Italy,2019: 3084-3089. |
| 6 | 陈虹,郭露露,宫洵,等. 智能时代的汽车控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1313-1332. |
| Chen Hong, Guo Lu-lu, Gong Xun, et al. Automotive control in the age of intelligence[J]. Journal of Automation, 2020, 46(7): 1313-1332. | |
| 7 | Zhao J, Hu Y, Gao B, et al. Sequential optimization of eco-driving taking into account fuel economy and emissions[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:130841-130853. |
| 8 | Park J, Choi S B, Oh J, et al. Adaptive torque tracking control during slip engagement of a dry clutch in vehicle powertrain[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019,134: 249-266. |
| 9 | Kang M, Shen T. Modeling and optimal control for torque tracking of spark-ignition engines with low pumping loss[C]∥Chinese Control Conference, Chendu, China, 2016: 8956-8961. |
| 10 | Vuelvas J, Archbold G, Ruiz F. MPC Weighted sum approach applied to torque tracking and CO2emission reduction on engines[C]∥ IEEE 3rd Colombian Conference on Automatic Control (CCAC), Cartagena, Colombia, 2017: 1-6. |
| 11 | Bouvenot J B,Andlauer B,Stabat P,et al. Gas stirling engine µ CHP boiler experimental data driven model for building energy simulation[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 84: 117-131. |
| 12 | 尤晓东,苏崇宇,汪毓铎. BP神经网络算法改进综述[J]. 民营科技,2018, 23(4):146-147. |
| You Xiao-dong,Su Cong-yu,Wang Yu-duo. Summary of improvement of BP neural network algorithm[J]. Private Technology, 2018,23(4):146-147. | |
| 13 | Ong C K,Yao T K, Alfred R, et al. A Comparison of BPNN,RBF, and ENN in Number Plate Recognition[C]∥ Second International Conference on Soft Computing in Data Science, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia,2016: 37-47. |
| 14 | He J, Yang W, Wang J, et al. Fast HEVC coding unit decision based on BP-neural network[J]. International Journal of Grid and Distributed Computing, 2015, 8(4): 289-300. |
| 15 | Venayagamoorthy G K, Rohrig K, Erlich I. One step ahead: short-term wind power forecasting and intelligent predictive control based on data analytics[J]. IEEE Power & Energy Magazine, 2012, 10(5): 70-78. |
| 16 | Rahman M A, Hoque M A. On-line adaptive artificial neural net-work based vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 1998, 13 (4):311-318. |
| 17 | Hu Y, Chen H, Wang P, et al. Nonlinear model predictive controller design based on learning model for turbocharged gasoline engine of passenger vehicle[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018,109: 74-88. |
| [1] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [2] | 尚福华,曹茂俊,王才志. 基于人工智能技术的局部离群数据挖掘方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 692-696. |
| [3] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
| [4] | 欧阳丹彤,马骢,雷景佩,冯莎莎. 知识图谱嵌入中的自适应筛选[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 685-691. |
| [5] | 李贻斌,郭佳旻,张勤. 人体步态识别方法与技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| [6] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [7] | 高万夫,张平,胡亮. 基于已选特征动态变化的非线性特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [8] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [9] | 顾海军, 田雅倩, 崔莹. 基于行为语言的智能交互代理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1578-1585. |
| [10] | 董飒, 刘大有, 欧阳若川, 朱允刚, 李丽娜. 引入二阶马尔可夫假设的逻辑回归异质性网络分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1571-1577. |
| [11] | 王旭, 欧阳继红, 陈桂芬. 基于垂直维序列动态时间规整方法的图相似度度量[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1199-1205. |
| [12] | 张浩, 占萌苹, 郭刘香, 李誌, 刘元宁, 张春鹤, 常浩武, 王志强. 基于高通量数据的人体外源性植物miRNA跨界调控建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1206-1213. |
| [13] | 李雄飞, 冯婷婷, 骆实, 张小利. 基于递归神经网络的自动作曲算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [14] | 刘杰, 张平, 高万夫. 基于条件相关的特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [15] | 黄岚, 纪林影, 姚刚, 翟睿峰, 白天. 面向误诊提示的疾病-症状语义网构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 859-865. |
|
||