吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 101-109.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200796
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
车联网环境下车辆换道博弈行为及模型
- 青岛理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,山东 青岛 266520
Game behavior and model of lane-changing on the internet of vehicles environment
Da-yi QU( ),Kai-xian HEI,Hai-bing GUO,Yan-feng JIA,Tao WANG
),Kai-xian HEI,Hai-bing GUO,Yan-feng JIA,Tao WANG
- School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,QingDao University of Technology,Qingdao 266520,China
摘要:
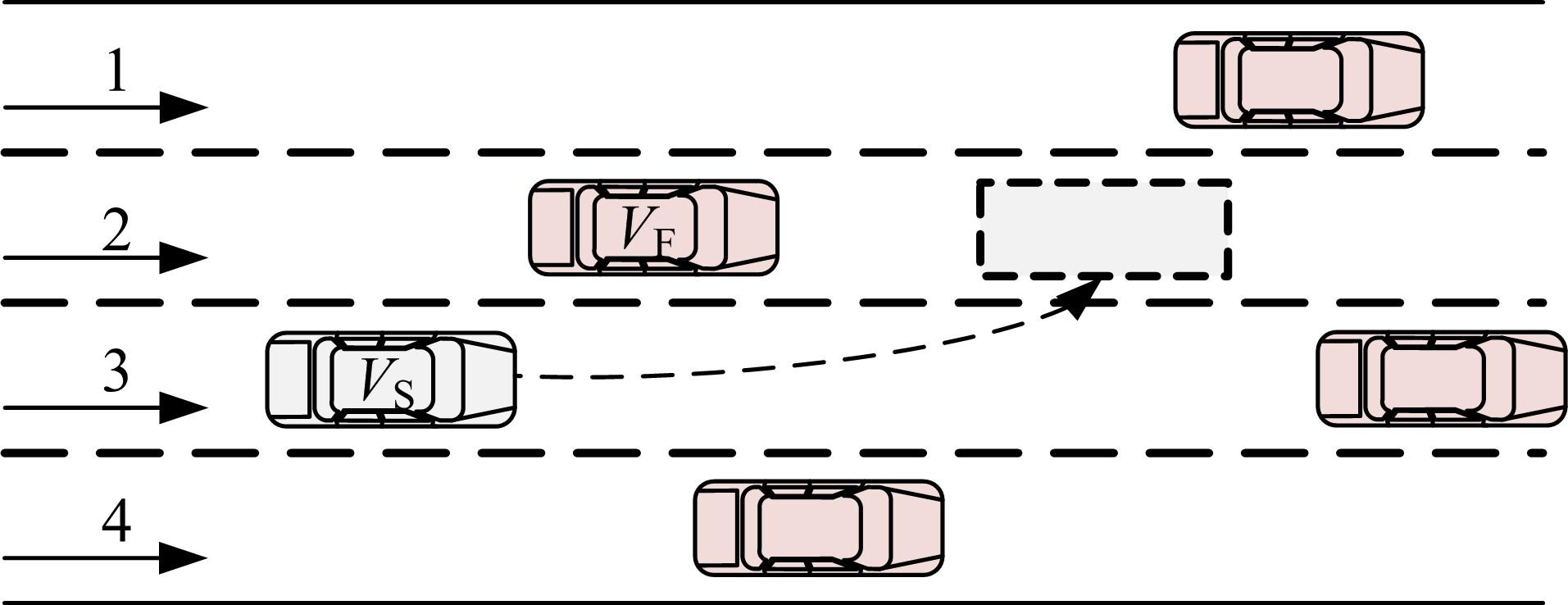
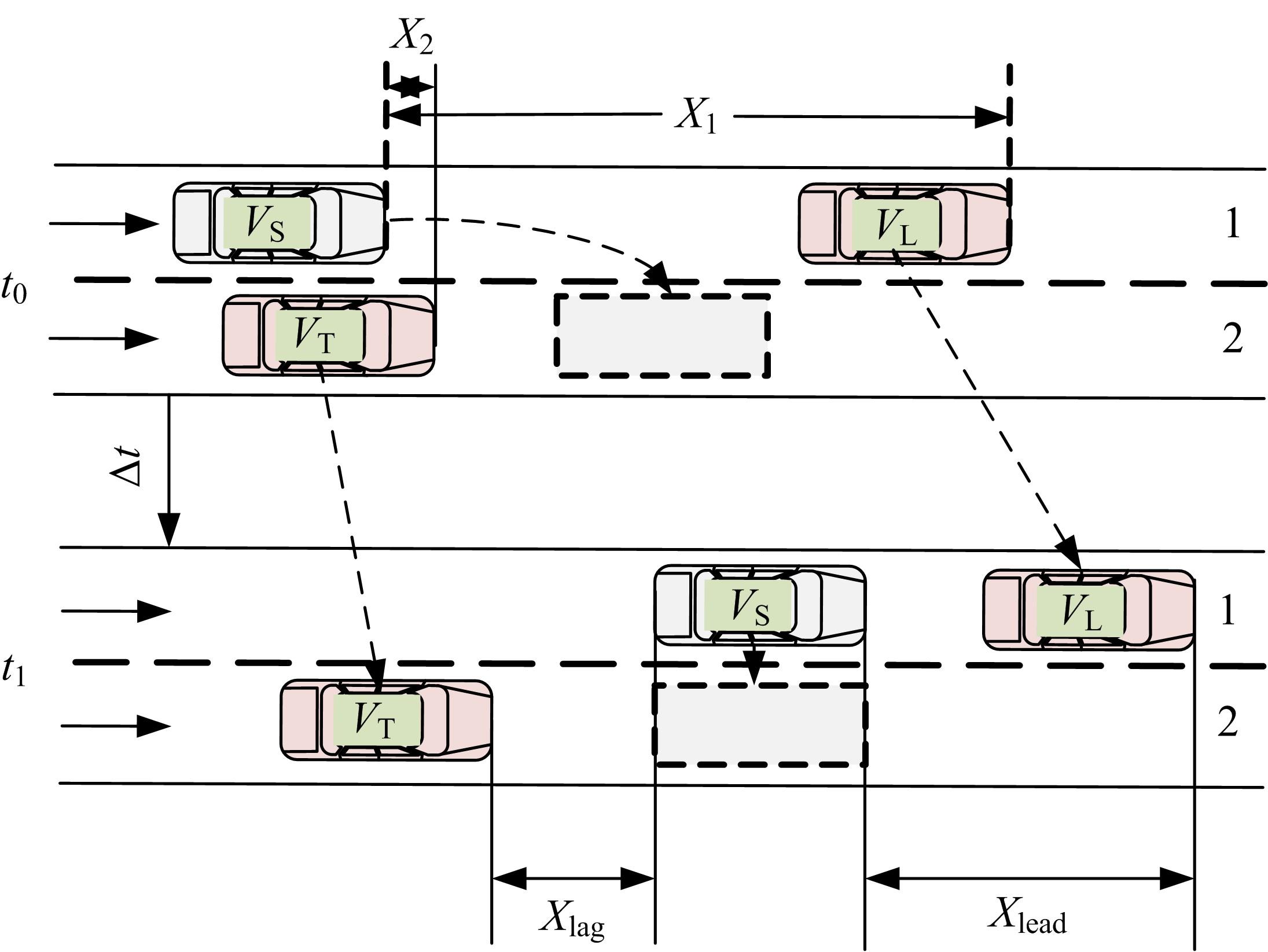
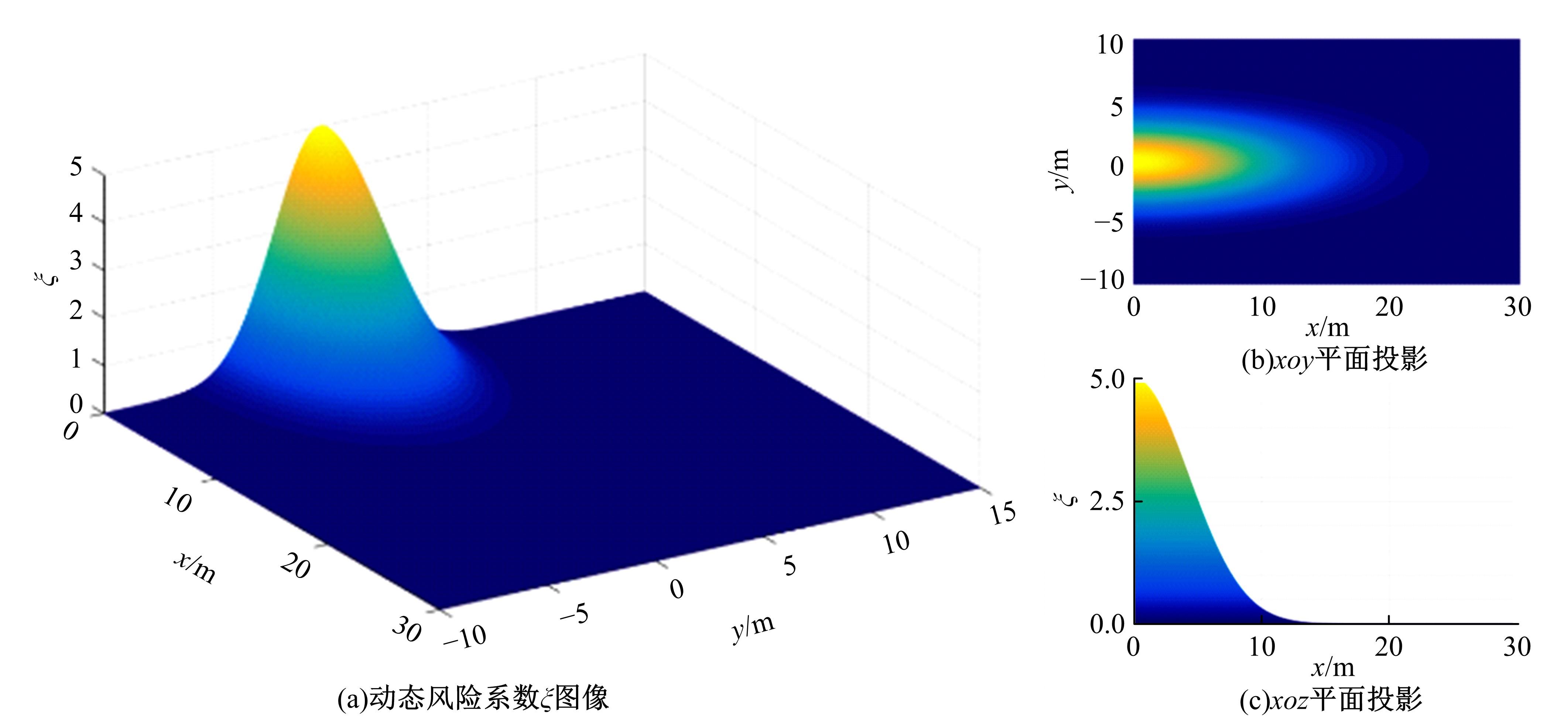
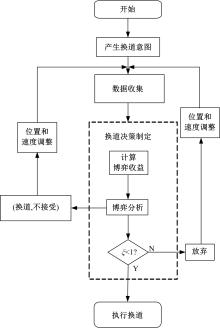
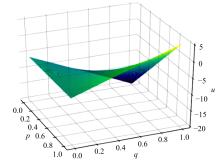
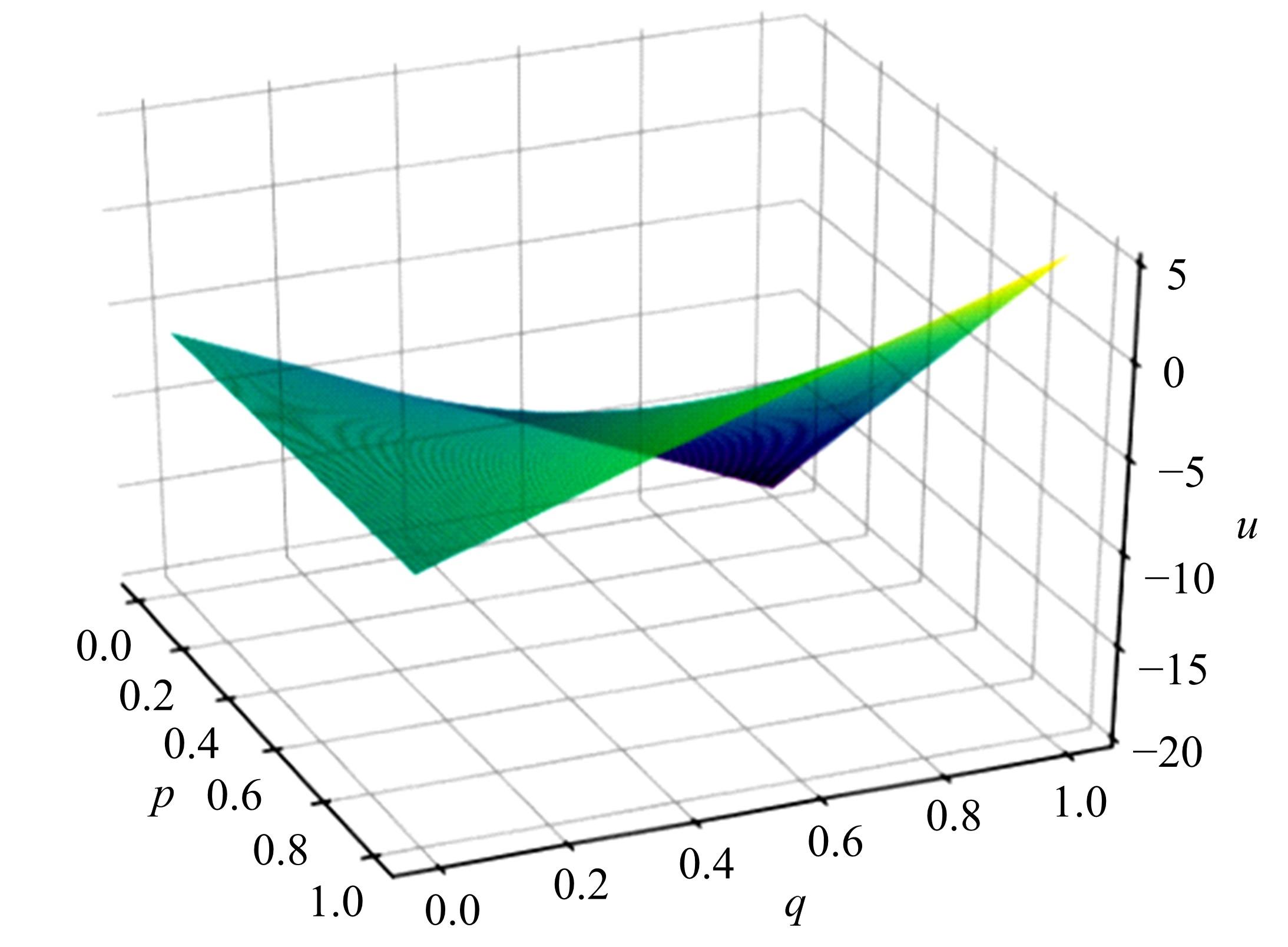
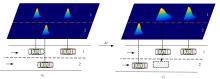
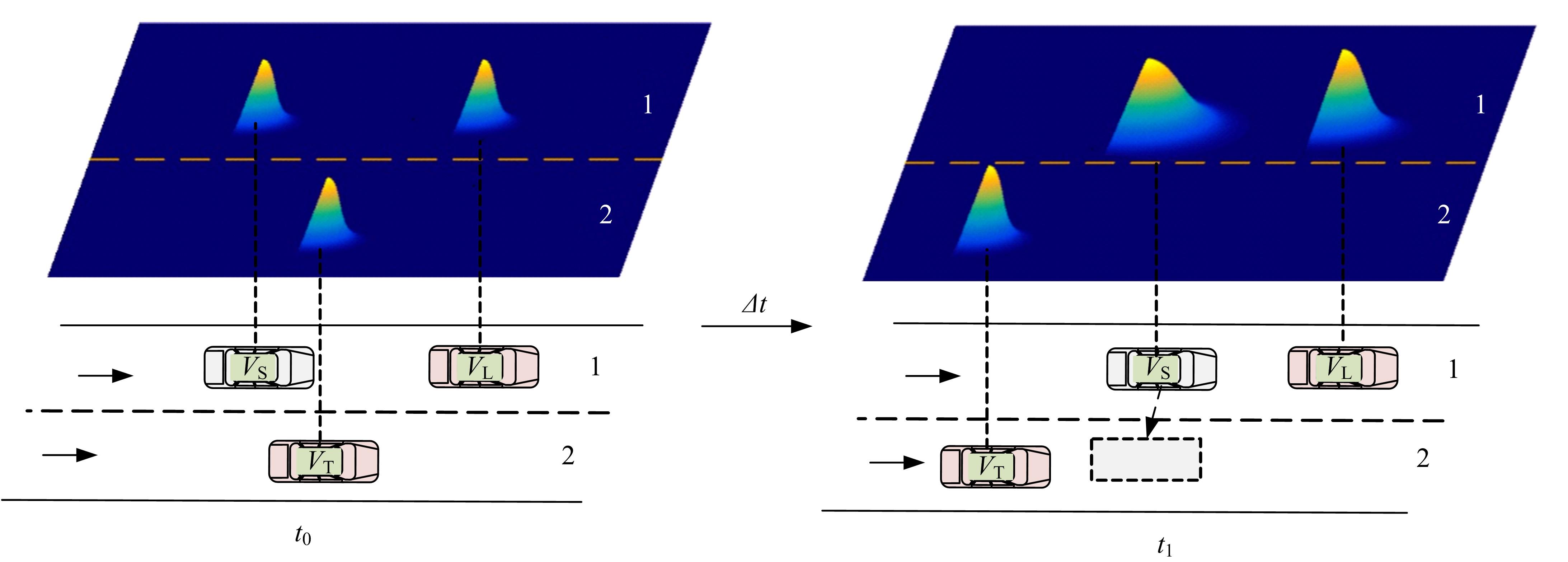
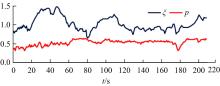
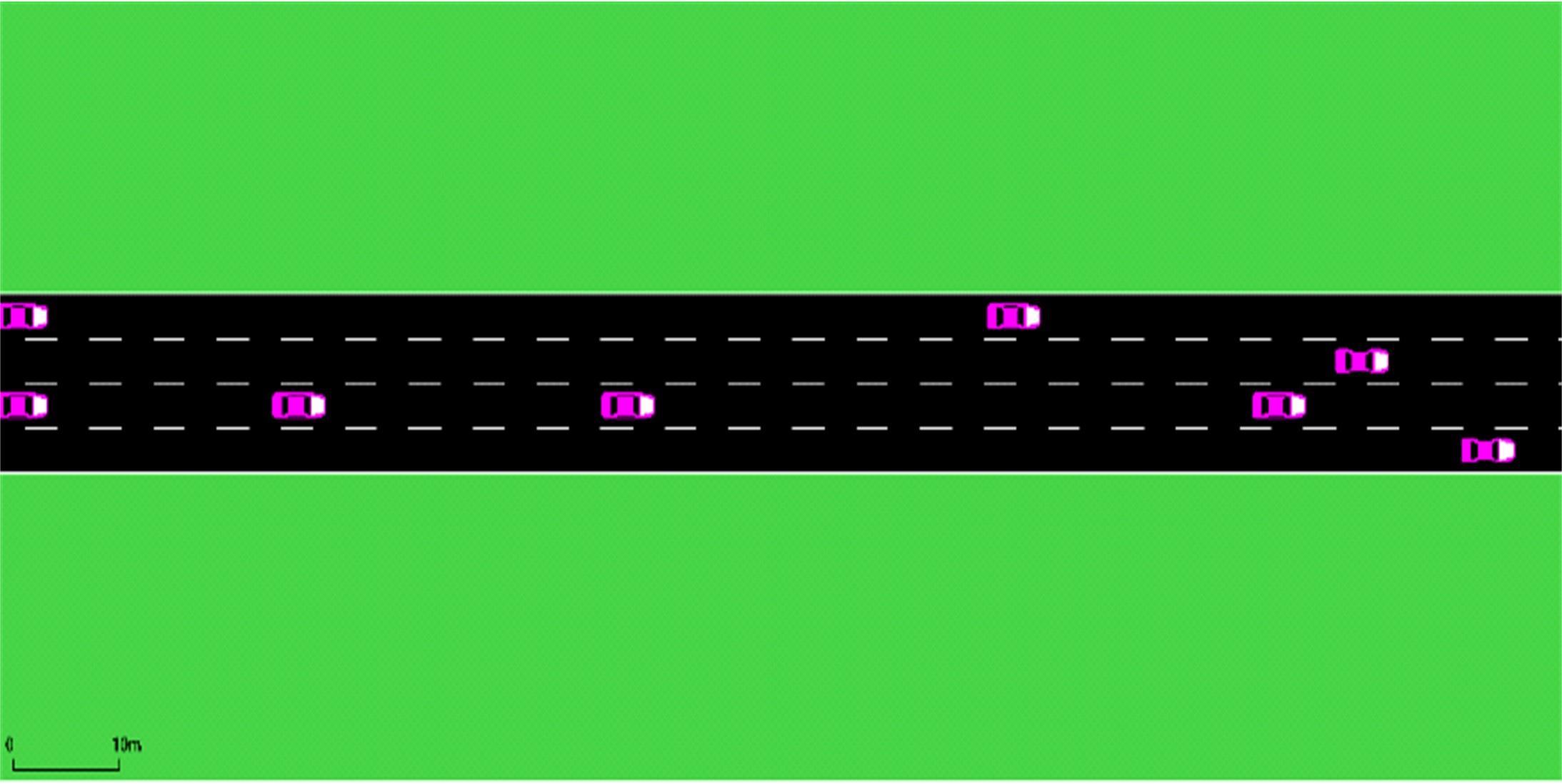
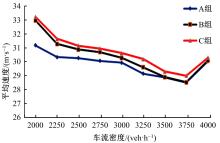
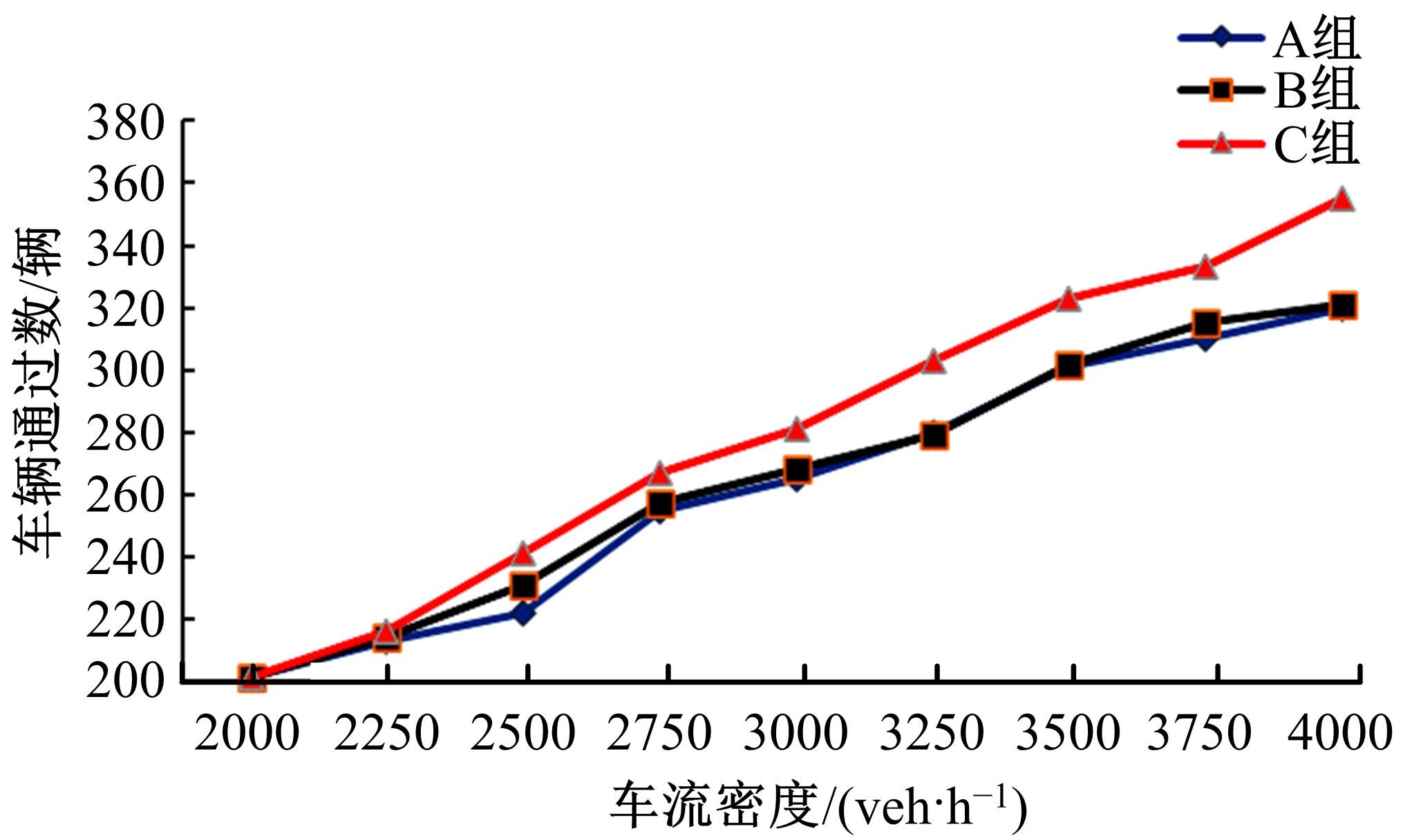
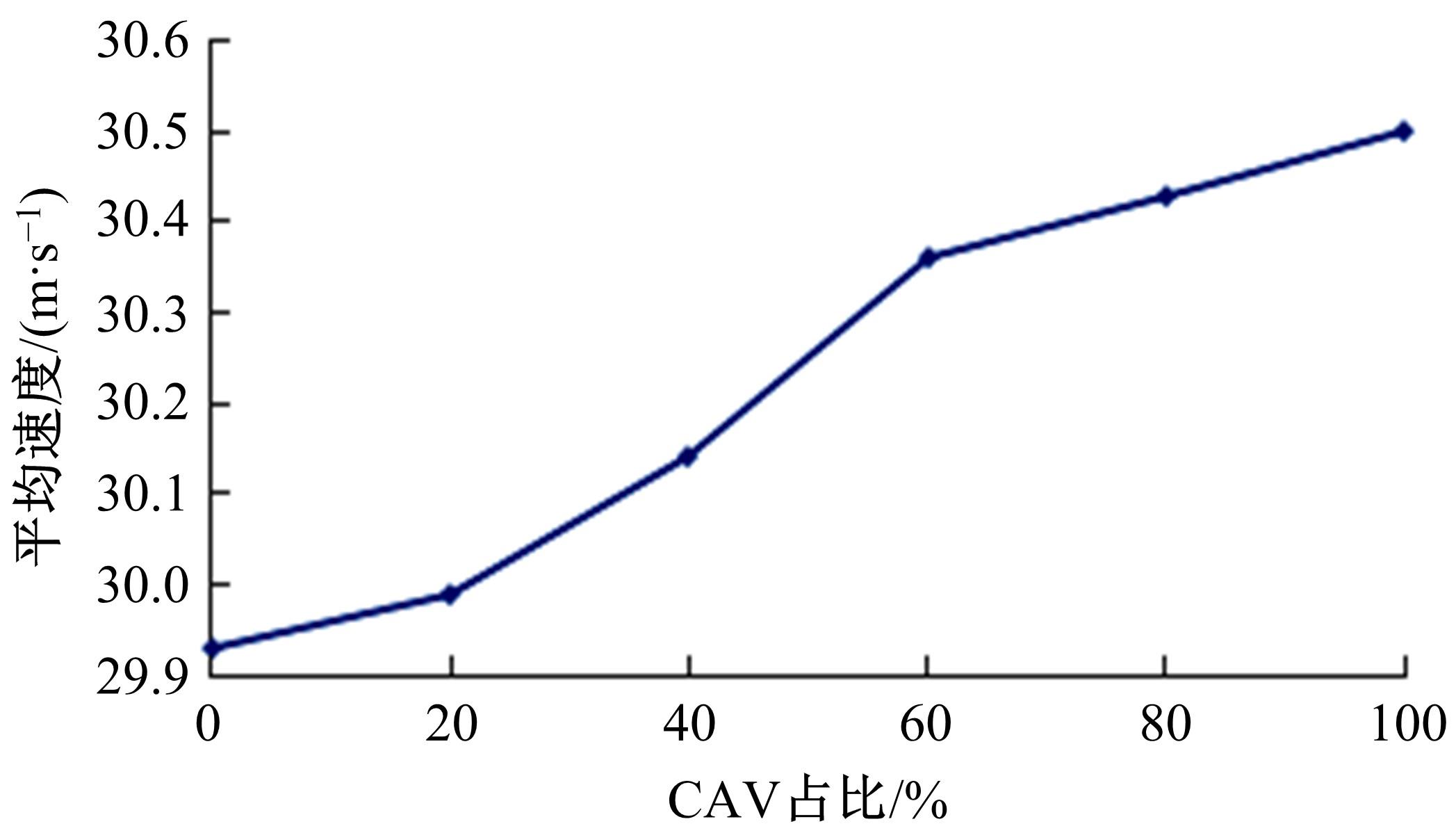
车联网环境中,交通系统将长期呈现智能网联汽车和传统人工驾驶车辆混合共存的状况,聚焦智能网联交通环境下的新型混合车流,建立了车辆换道行为的决策模型。引入车辆换道过程中动态风险模型,建立网联混合交通流自主车辆与传统车辆的交互作用关系;基于博弈论的思想进行混合交通流中自主车辆换道行为建模。自主车辆之间的换道行为非合作博弈的性质,车辆以自身行驶状态为博弈收益,寻求行驶条件更优的车道。运用SUMO软件对提出的换道行为模型进行了仿真验证分析,仿真结果表明,博弈换道模型相比于传统间隙阈值接受模型具有更高的车道利用率和安全稳定性。
中图分类号:
- U491.2
| 1 | 黎宇科, 刘宇. 国内智能网联汽车发展现状及建议[J]. 汽车与配件, 2016, 2016(41): 56-59. |
| Li Yu-ke, Liu Yu. Development status and suggestions of domestic intelligent connected cars[J]. Automobile& Parts technology, 2016(41): 56-59. | |
| 2 | Gipps P G. A model for the structure of lane changing decisions[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1986, 20(5): 403-414. |
| 3 | 邹智军, 杨东援. 微观交通仿真中的车道变换模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2002,15(2): 108-111. |
| Zou Zhi-jun, Yang Dong-yuan. Lane changing model for micro traffic simulation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2002,15(2):108-111. | |
| 4 | 王荣本, 游峰, 崔高健,等. 车辆安全换道分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2005,35(2): 179-182. |
| Wang Rong-ben,You Feng,Cui Gao-jian, et al. Analysis on lane-changing safety of vehicle[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2005,35(2): 179-182. | |
| 5 | Jula H, Kosmatopoulos E B, Ioannou P A. Collision avoidance analysis for lane changing and merging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2000, 49(6): 2295-2308. |
| 6 | Hidas P. Modelling lane changing and merging in microscopic traffic simulation[J]. Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies, 2002, 10(5): 351-371. |
| 7 | 曲大义, 李娟, 刘聪, 等. 基于分层Logit模型的车辆换道行为研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(5): 307-311. |
| Qu Da-yi, Li Juan, Liu Cong, et al. Research on vehicle lane changing behavior based on hierarchical Logit model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(5): 307-311. | |
| 8 | Toledo T, Koutsopoulos H N, Ben-Akiva M. Estimation of an integrated driving behavior model[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2009, 17(4): 365-380. |
| 9 | 曲大义, 杨建, 邴其春, 等.车辆交互行为与车流特性及控制优化[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2020. |
| 10 | Worrall R D, Bullen A G. An empirical analysis of lane changing on multilane highways[R]. Washington: Highway Research Board, 1970. |
| 11 | 曲大义, 邴其春, 贾彦峰, 等. 基于分子动力学的车辆换道交互行为特性及其模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2019, 19(3): 68-74. |
| Qu Da-yi, Bing Qi-chun, Jia Yan-feng, et al. Molecular dynamics characteristics and models of vehicle lane changing interaction behavior[J]. Journal of Transportation System Engineering and Information Technology, 2019, 19(3): 68-74. | |
| 12 | Kitah W. A merging-giveway interaction model of cars in a merging section: a game theoretic analysis[J]. Transportation Research, Part A (Policy and Practice), 1999, 33(3/4):308-312. |
| 13 | Talebpour A, Mahmassani H S, Hamdar S H. Modeling lane-changing behavior in a connected environment: a game theory approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2015,59(7):420-440. |
| 14 | Bell M H. A game theory approach to measuring the performance reliability of transport networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B Methodological, 2000,34(6): 533-545. |
| 15 | Drew F, Jean T. Game Theory[M]. 北京:中国人民大学出版社, 2010. |
| [1] | 刘志伟,刘建荣,邓卫. 基于潜在类别的无人驾驶汽车选择行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1261-1268. |
| [2] | 徐进,潘存书,符经厚,刘俊,王郸祁. 典型道路场景以及场景切换时的速度行为特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1331-1341. |
| [3] | 查伟雄,蔡其燕,李剑,严利鑫. 边路车辆出入条件下城市干线信号协调相位差优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 565-574. |
| [4] | 宋现敏, 刘焕峰, 李志慧, 陶鹏飞, 杨秋杰. 基于OD分布的环形交叉口车辆行程时间建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 70-75. |
| [5] | 魏丽英, 吴荣华, 王志龙, 朱建辉. 基于混合交通流的车辆换道行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1321-1326. |
| [6] | 孙轶轩, 邵春福, 岳昊, 朱亮. 基于SVM灵敏度的城市交通事故严重程度影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1315-1320. |
| [7] | 冯建鑫, 王挺峰, 郭劲. 测量丢失不确定性系统的迭代鲁棒滤波[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1057-1061. |
| [8] | 丛犁, 张海林, 刘毅, 赵力强, 张国鹏. 基于粒子群优化的协作网络资源分配的博弈策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 207-212. |
| [9] | 林赐云1,2,龚勃文1,2,赵丁选1,3,杨兆升1,2. 基于博弈论的突发灾害下区域间交通信号协调控制技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1257-1261. |
| [10] | 董宏辉,孙晓亮,贾利民,秦勇. 多模态的交通流量预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 645-649. |
| [11] | 姜桂艳,吴超腾. 基于GPS采集车辆行程时间的路段划分模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 177-0181. |
| [12] | 吕能超,严新平,RanBin,徐堃. 基于道路出行者行为的大型活动停车模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 135-0139. |
| [13] | 宋现敏,王殿海,金盛. 感应式协调控制下绿信比优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 154-0157. |
| [14] | 王殿海,孙锋,金盛 . 两相位交叉口左转车通行能力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(04): 767-771. |
| [15] | 李洪萍,裴玉龙,杨中良 . 快速路自由流速度及其影响因素 [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(04): 772-776. |
|
||