吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1331-1341.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200246
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
典型道路场景以及场景切换时的速度行为特性
- 1.重庆交通大学 山区复杂道路环境“人-车-路”协同与安全重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400074
2.重庆交通大学 交通运输学院,重庆 400074
Speed behavior characteristic on typical driving scenarios and along switched scenarios
Jin XU1,2( ),Cun-shu PAN2,Jing-hou FU2,Jun LIU2,Dan-qi WANG2
),Cun-shu PAN2,Jing-hou FU2,Jun LIU2,Dan-qi WANG2
- 1.Chongqing Key Laboratory of “Human-Vehicle-Road” Cooperation & Safety for Mountain Complex Environment,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.College of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
摘要:
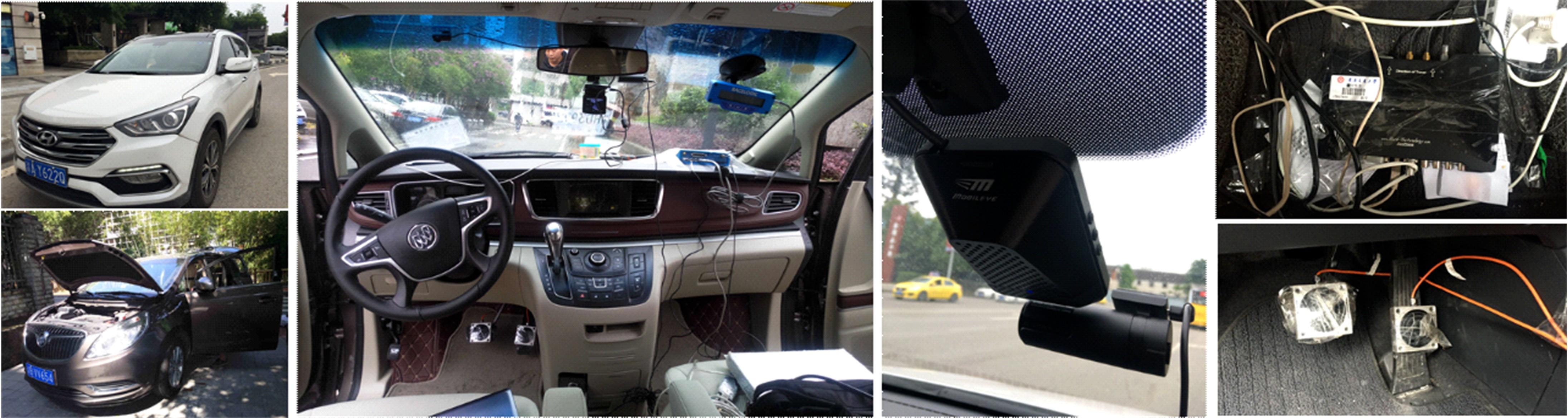
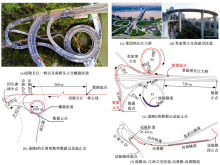
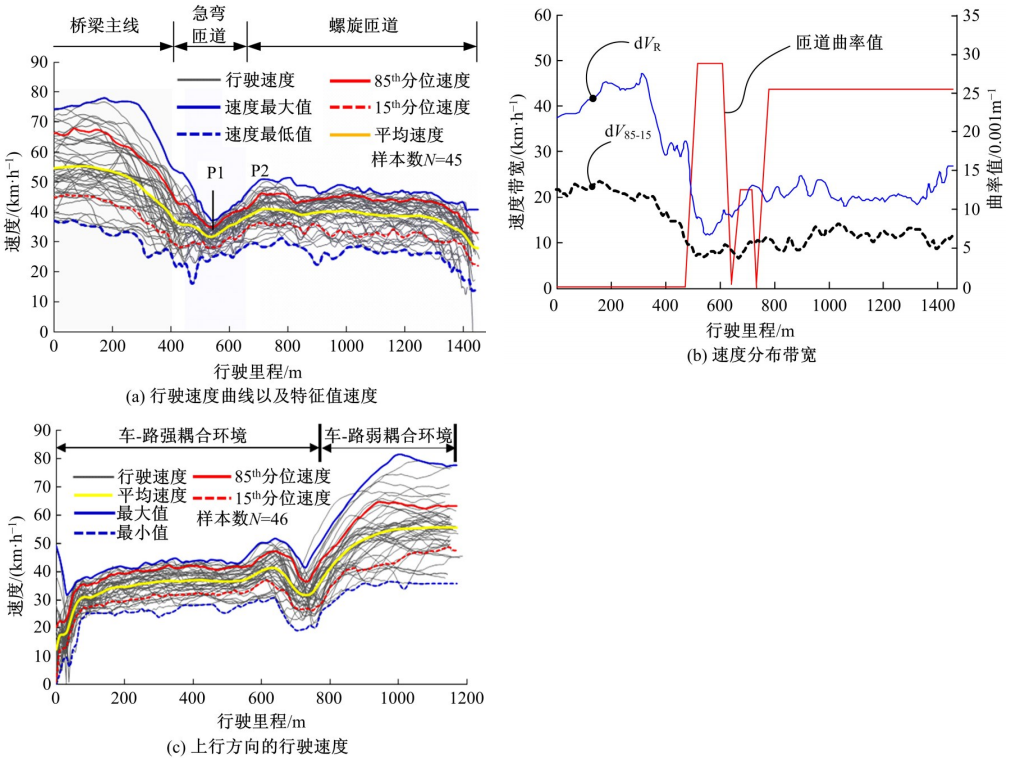
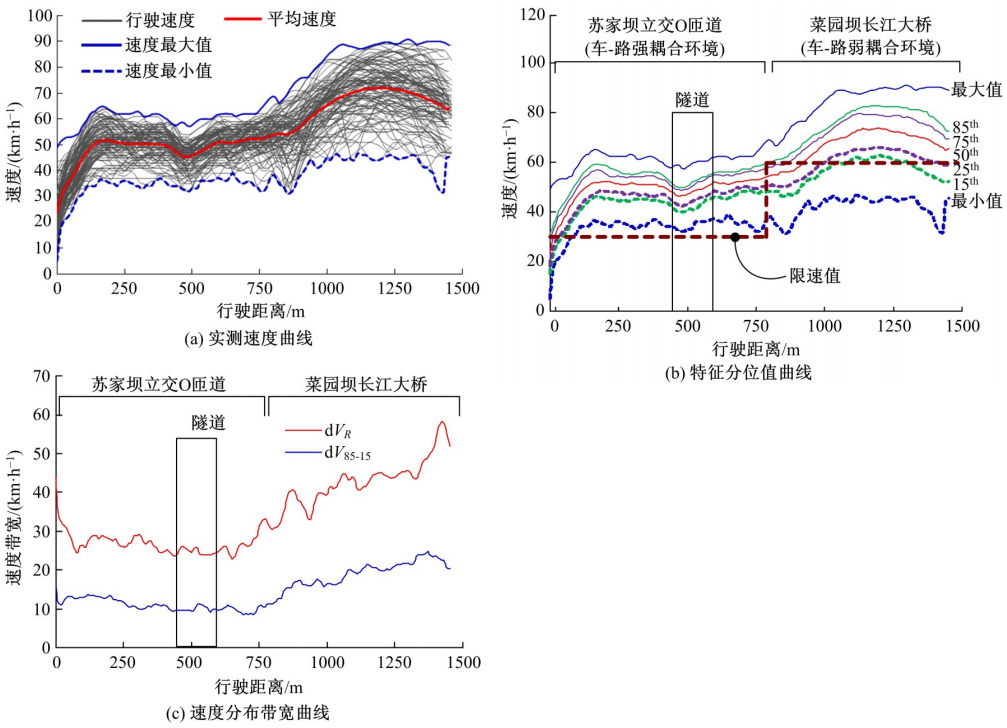
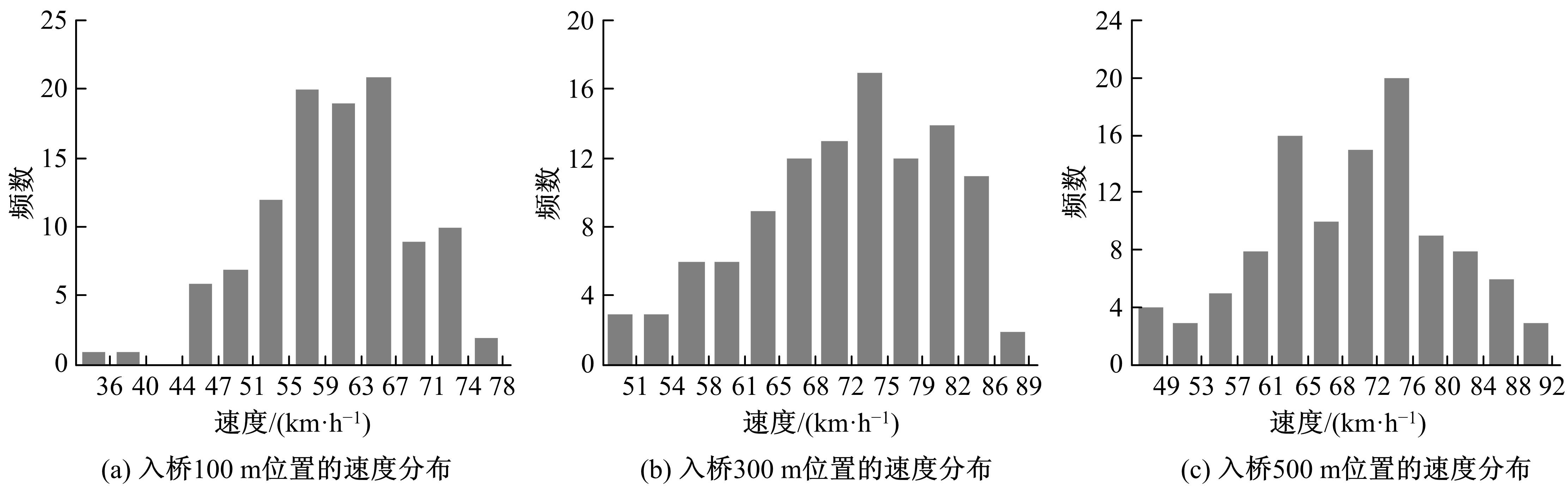
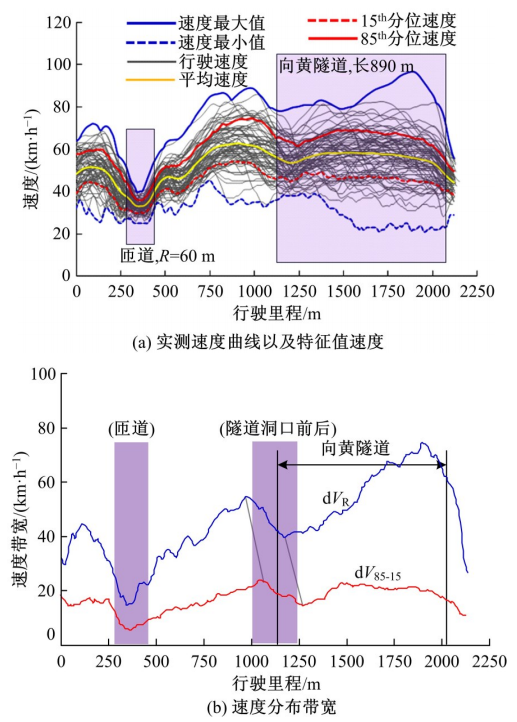
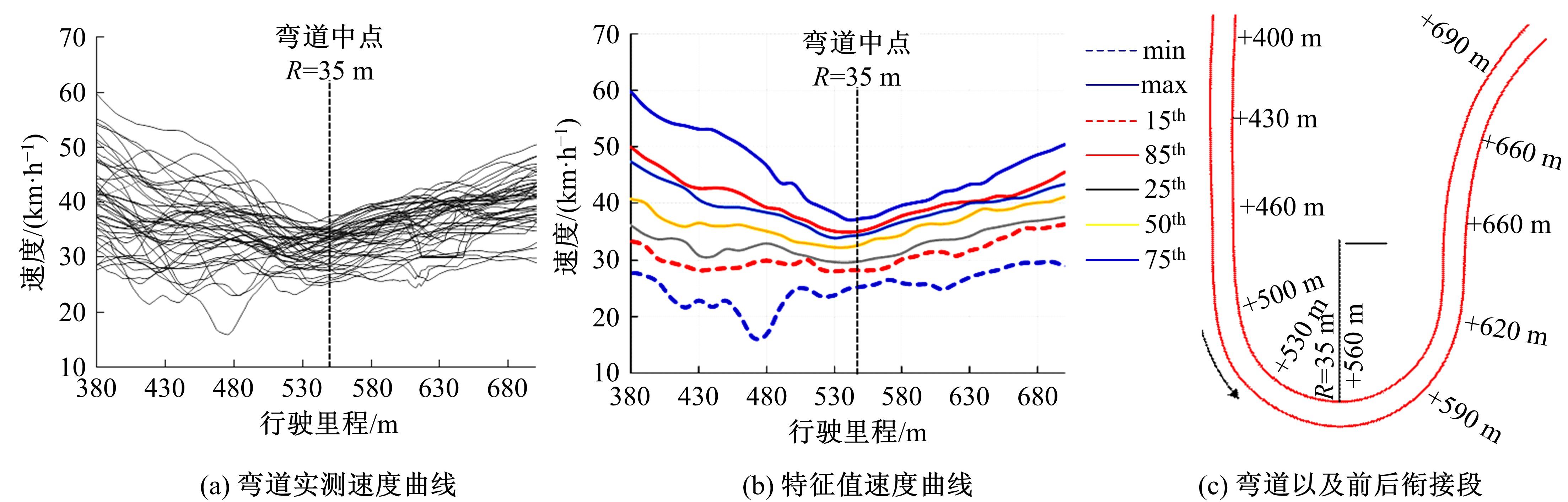
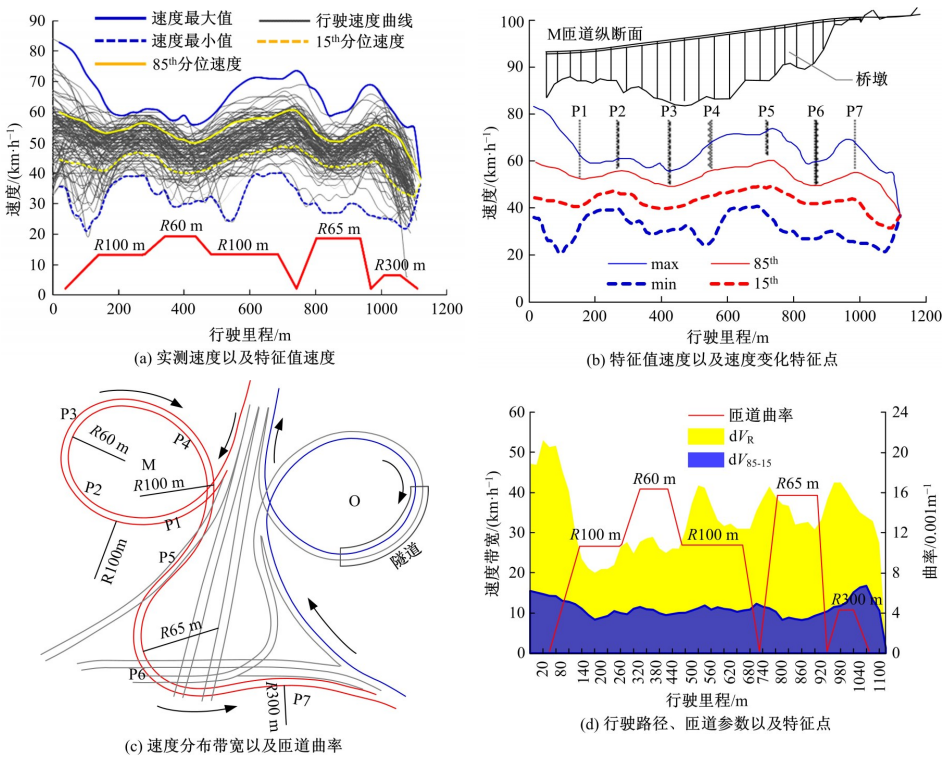
为明确典型道路场景以及场景切换时的速度行为特性,在重庆选择3条路段开展超过70位被试的实车驾驶试验,用车载仪器采集了自然状态下的车辆运行数据,分析了不同场景对驾驶行为的约束性以及行驶场景交替时的速度变化特征,具体发现如下:驾驶人在跨江大桥主线上的速度选择行为具有较强的离散性,即该环境对驾驶行为的约束性较弱,车辆间的速度差异增加了追尾事故的发生几率。从大桥主线驶入小半径匝道时,驾驶人会提前在主线上减速,驾驶行为受到的约束性增加。驶入隧道时驾驶人会将减速行为持续到隧道洞内一段距离,速度幅值的离散性同时降低,表明隧道入口的环境突变会提高驾驶人速度选择行为的趋同性。驶入小半径曲线匝道时,驾驶人的减速行为会持续至匝道圆曲线范围内,驶入速度越高,减速度越大;匝道圆曲线较长时仅有少部分驾驶人会在圆曲线中部定速行驶;而圆曲线较短时未观察到恒速行驶行为;行驶速度在多层螺旋匝道范围内维持恒定。70%驾驶人的速度幅值分布在较窄的区间内,因此在较小的范围内调整设计参数便可以照顾到大多数驾驶人的行为习惯。
中图分类号:
- U491.25
| 1 | Shallam R D K, Venthuruthiyil S P, Chunchu M, et al. Empirical analysis of operating speed performance on undivided hilly roads[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2019, 145(8): 04019034. |
| 2 | Xu J, Lin W, Wang X, et al. Acceleration and deceleration calibration of operating speed prediction models for two-lane mountain highways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2017, 143(7): 1-13. |
| 3 | Jacob A, Anjaneyulu M V L R. Operating speed of different classes of vehicles at horizontal curves on two-lane rural highways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2013, 139(3): 287-294. |
| 4 | Fitzpatrick K, Miaou S, Marcus B, et al. Exploration of the relationships between operating speed and roadway features on tangent sections[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 261-269. |
| 5 | Semeida A M. Application of artificial neural networks for operating speed prediction at horizontal curves: a case study in Egypt[J]. Transportation in Developing Economies, 2019, 5(14): 1-8. |
| 6 | Sekhar C R, Nataraju J, Velmurugan S, et al. Free flow speed analysis of two lane inter urban highways[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2016 17: 664 -673. |
| 7 | 刘硕, 王俊骅, 张兰芳, 等. 城市地下道路车速特征及运行车速模型[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 43(11): 1677-1683. |
| Liu Shuo, Wang Jun-hua, Zhang Lan-fang, et al. Characteristic and prediction model for operating speed model in urban underground road[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science):2015, 43(11): 1677-1683. | |
| 8 | 徐进,邵毅明,赵军,等. 山区道路弯坡组合路段重载车辆行驶速度模型[J]. 长安大学学报, 2015, 35(2): 67-74. |
| Xu Jin, Shao Yi-ming, Zhao Jun, et al. Speed prediction model of heavy truck driving on curved segment with a slope of mountainous highway[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 35(2): 67-74. | |
| 9 | 王志新, 余强, 赵轩, 等. 长大下坡路段载货汽车行驶速度预测研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2017, 34(7): 130-135. |
| Wang Zhi-xin, Yu Qiang, Zhao Xuan, et al. Study on truck speed prediction in long and steep downhill sections[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2017, 34(7): 130-135. | |
| 10 | 徐进, 邵毅明, 杨奎, 等. 基于人-车-路协同仿真的山区道路大型车辆行驶适应性分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2015, 28(2): 14-25. |
| Xu Jin, Shao Yi-ming, Yang Kui, et al. Analysis of adaptability of large vehicles on mountainous highways based on driver-vehicle-road collaborative simulation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(2): 14-25. | |
| 11 | Choudhari T, Maji A. Effect of horizontal curve geometry on the maximum speed reduction: a driving simulator‑based study[J]. Transportation in Developing Economies, 2019, 5(14): 1-8. |
| 12 | Bassani M, Catani L, Salussolia A, et al. A driving simulation study to examine the impact of available sight distance on driver behavior along rural highways[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 131: 200-212. |
| 13 | Deng Z, Chu D, Wu C, et al. Curve safe speed model considering driving style based on driver behaviour questionnaire[J]. Transportation Research Part F, 2019, 65: 536-547. |
| 14 | Zhao X, Xu W, Ma J, et al. Effects of connected vehicle-based variable speed limit under different foggy conditions based on simulated driving[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 128: 206-216. |
| 15 | Bassani M, Catani L, Cirillo C, et al. Night-time and daytime operating speed distribution in urban arterials[J]. Transportation Research Part F, 2016 42: 56-69. |
| 16 | Yang Q, Overton R, Han L D, et al. The influence of curbs on driver behaviors in four-lane rural highways—a driving simulator based study[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2013, 50: 1289-1297. |
| 17 | Larocca A P C, Ribeiro R L, Figueira A C, et al. Analysis of perception of vertical signaling of highways by drivers in a simulated driving environment[J]. Transportation Research Part F, 2018, 58: 471-487. |
| 18 | Schneidereit T, Petzoldt T, Keinath A, et al. Using SHRP 2 naturalistic driving data to assess drivers' speed choice while being engaged in different secondary tasks[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2017, 62: 33-42. |
| 19 | Dhahir B, Hassan Y. Using horizontal curve speed reduction extracted from the naturalistic driving study to predict curve collision frequency[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 123: 190-199. |
| 20 | Al-Sahili K, Dwaikat M, Abu-Eisheh S, et al. Effectiveness of consistency measures in crash prediction models for two-lane highways in palestine[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2018, 43(10): 5645-5656. |
| 21 | Borsati M, Cascarano M, Bazzana F. On the impact of average speed enforcement systems in reducing highway accidents: evidence from the Italian safety tutor[J]. Economics of Transportation, 2019, 20: 100123. |
| 22 | Sayed T, Sacchi E. Evaluating the safety impact of increased speed limits on rural highways in British Columbia[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2016: 95: 172-177. |
| [1] | 刘志伟,刘建荣,邓卫. 基于潜在类别的无人驾驶汽车选择行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1261-1268. |
| [2] | 李春良,林志豪,赵珞珞. 铰缝及板损伤后对空心板桥横向受力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 611-619. |
| [3] | 查伟雄,蔡其燕,李剑,严利鑫. 边路车辆出入条件下城市干线信号协调相位差优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 565-574. |
| [4] | 王芳,胡佳,景升,程伟,赫小英,李晓光. 荒漠长直线段公路行驶速度微观模型建立及分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 575-582. |
| [5] | 刘柳,冯卫星. 基于NNBR模型的隧道盾构施工地表沉降实测与计算分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 245-251. |
| [6] | 万平,吴超仲,马晓凤. 基于ROC曲线和驾驶行为特征的驾驶愤怒强度判别阈值[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [7] | 江亮,贺宜. 电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [8] | 张磊,刘保国,储昭飞. 深厚孔隙砂岩含水层疏干排水对盾构斜井的 影响模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 788-797. |
| [9] | 宫亚峰, 王博, 魏海斌, 何自珩, 何钰龙, 申杨凡. 基于Peck公式的双线盾构隧道地表沉降规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1411-1417. |
| [10] | 万平, 吴超仲, 林英姿, 马晓凤. 基于驾驶行为多元时间序列特征的愤怒驾驶状态检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1426-1435. |
| [11] | 王海玮, 温惠英, 刘敏. 夜间环境驾驶员精神负荷的生理特性评估与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 420-428. |
| [12] | 郭应时, 付锐, 赵凯, 马勇, 袁伟. 驾驶人换道意图实时识别模型评价及测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1836-1844. |
| [13] | 张波,王文军,魏民国,成波. 基于机器视觉的驾驶人使用手持电话行为检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1688-1695. |
| [14] | 孙轶轩, 邵春福, 岳昊, 朱亮. 基于SVM灵敏度的城市交通事故严重程度影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1315-1320. |
| [15] | 金立生,牛清宁,刘景华,秦彦光,吕欢欢. 不同道路线形下驾驶人认知分散状态监测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 642-647. |
|
||