吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 497-503.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200800
• 车辆工程·机械工程 •
基于触月压痕的表层月壤力学状态试验分析
薛龙1( ),姚猛2,李立犇3,李因武3,邓湘金2,李建桥3,邹猛3(
),姚猛2,李立犇3,李因武3,邓湘金2,李建桥3,邹猛3( )
)
- 1.江西农业大学 江西省现代农业装备重点实验室,南昌 330045
2.中国空间技术研究院 北京空间飞行器总体设计部,北京 100094
3.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
Experimental analysis of mechanical properties of surface lunar soil based on lunar indentation
Long XUE1( ),Meng YAO2,Li-ben LI3,Yin-wu LI3,Xiang-jin DENG2,Jian-qiao LI3,Meng ZOU3(
),Meng YAO2,Li-ben LI3,Yin-wu LI3,Xiang-jin DENG2,Jian-qiao LI3,Meng ZOU3( )
)
- 1.Key Lab of Modern Agricultural Equipment,Jiangxi Agricultural University,Nanchang 330045,China
2.Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering,China Academy of Space Technology,Beijing 100094,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
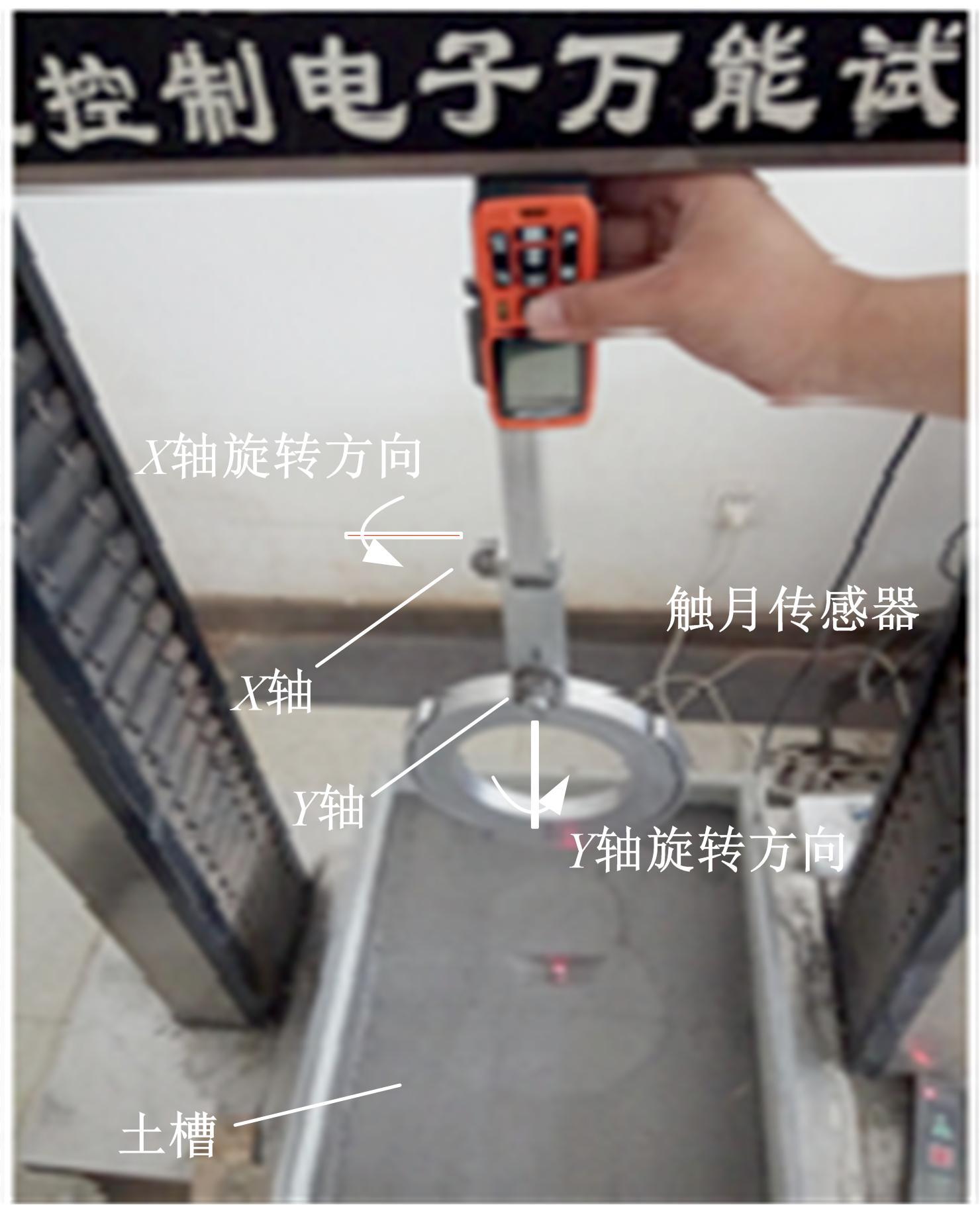
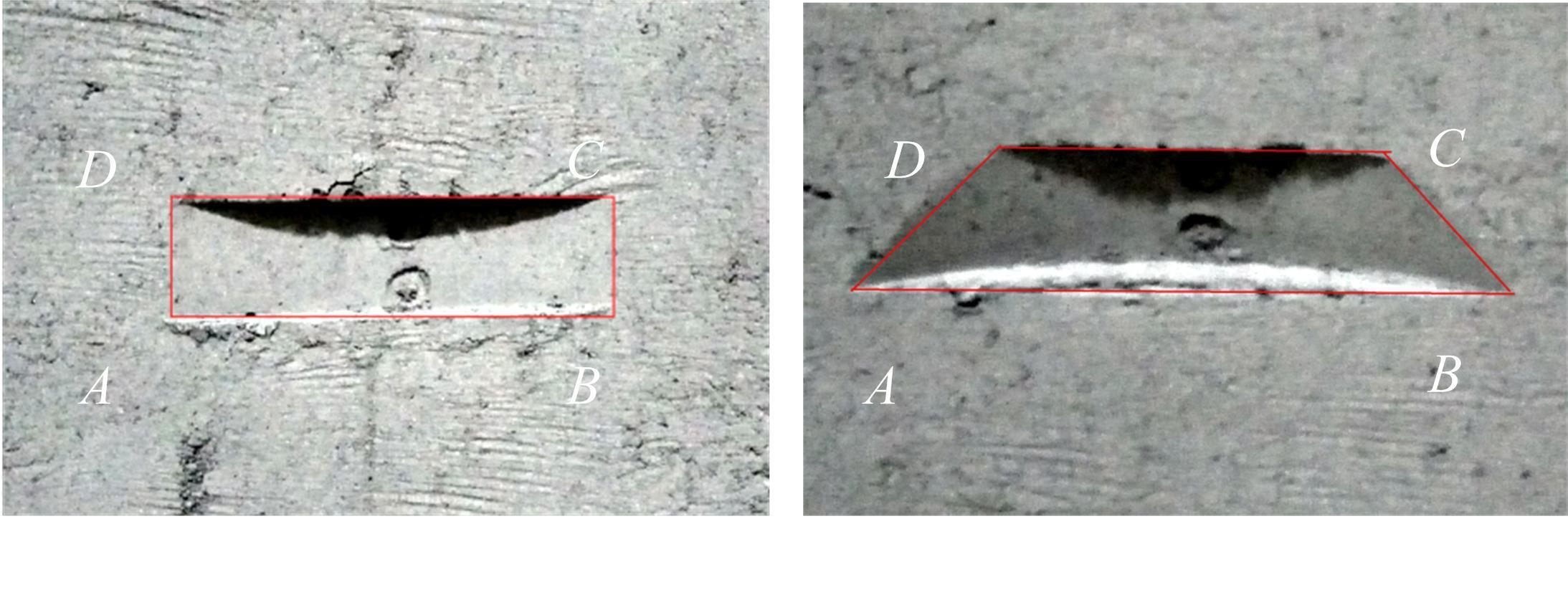
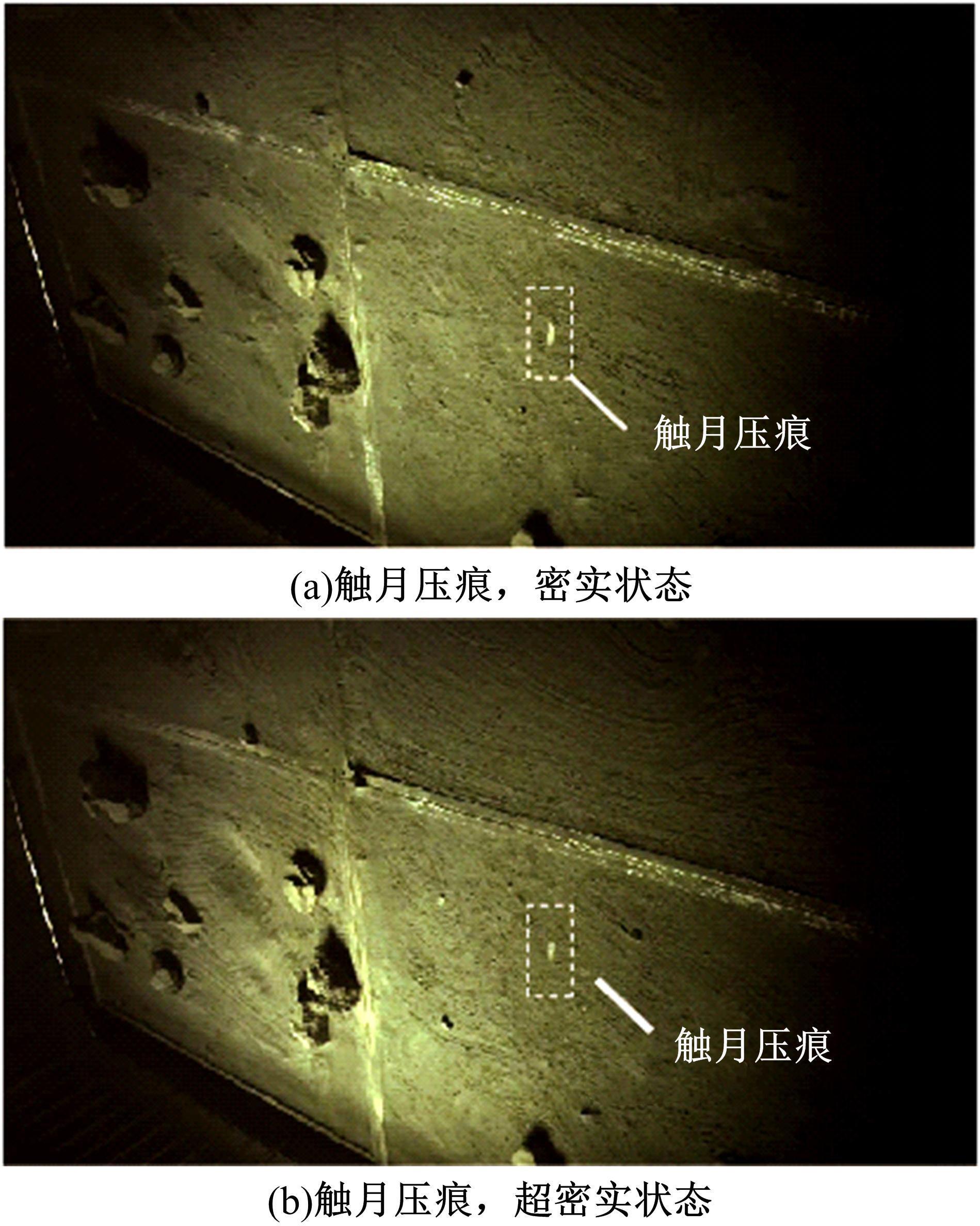
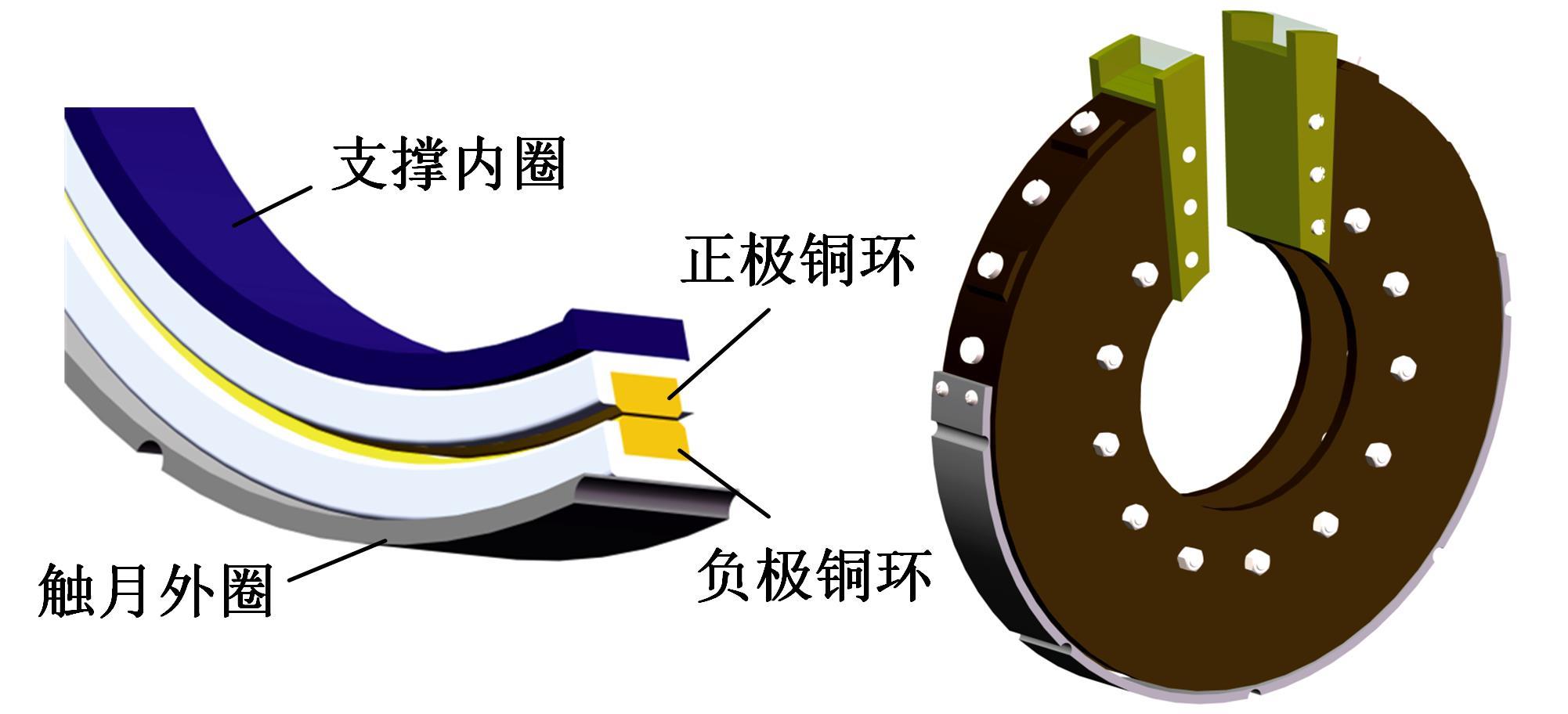
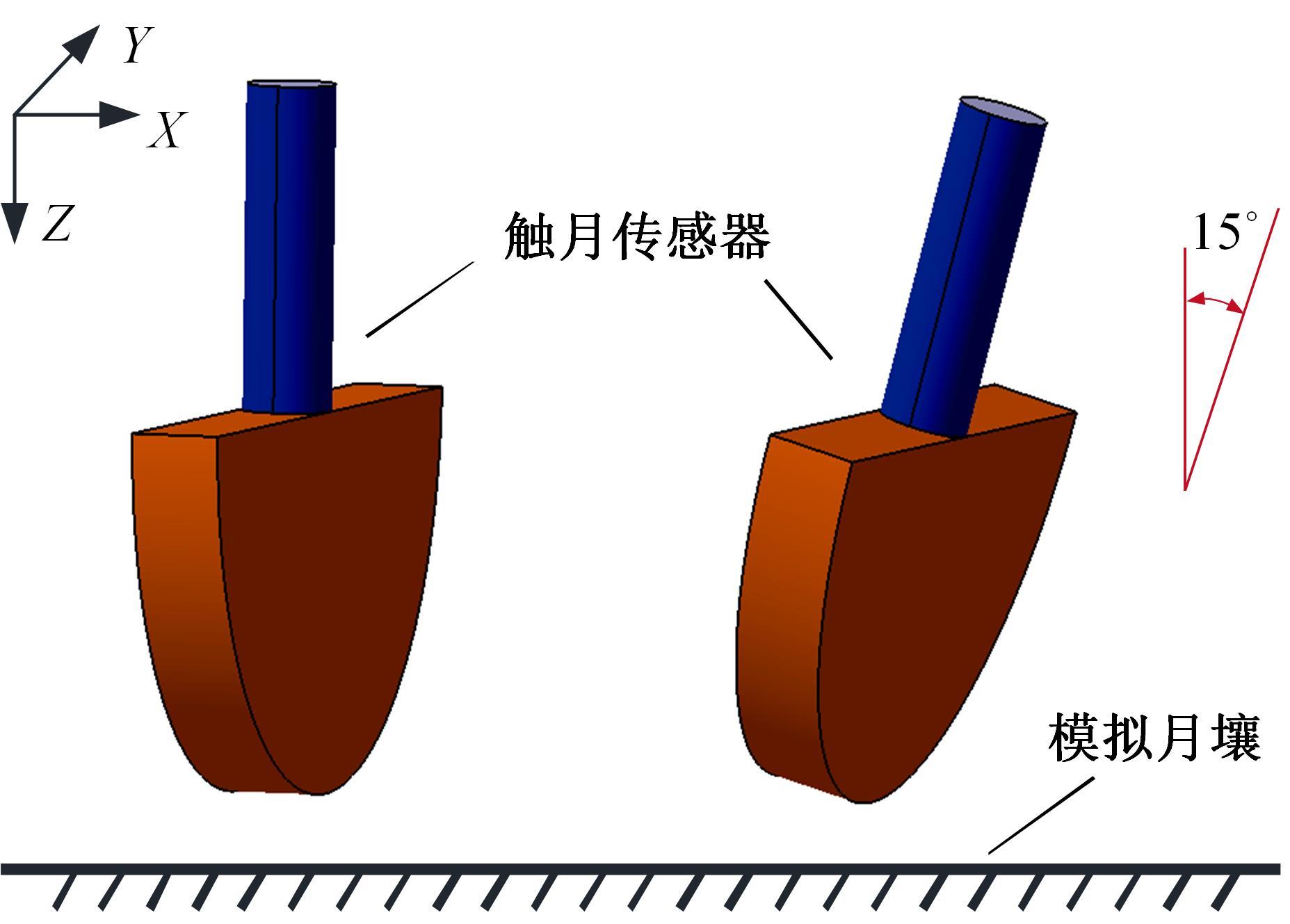
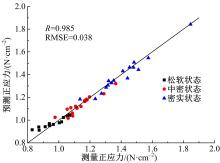
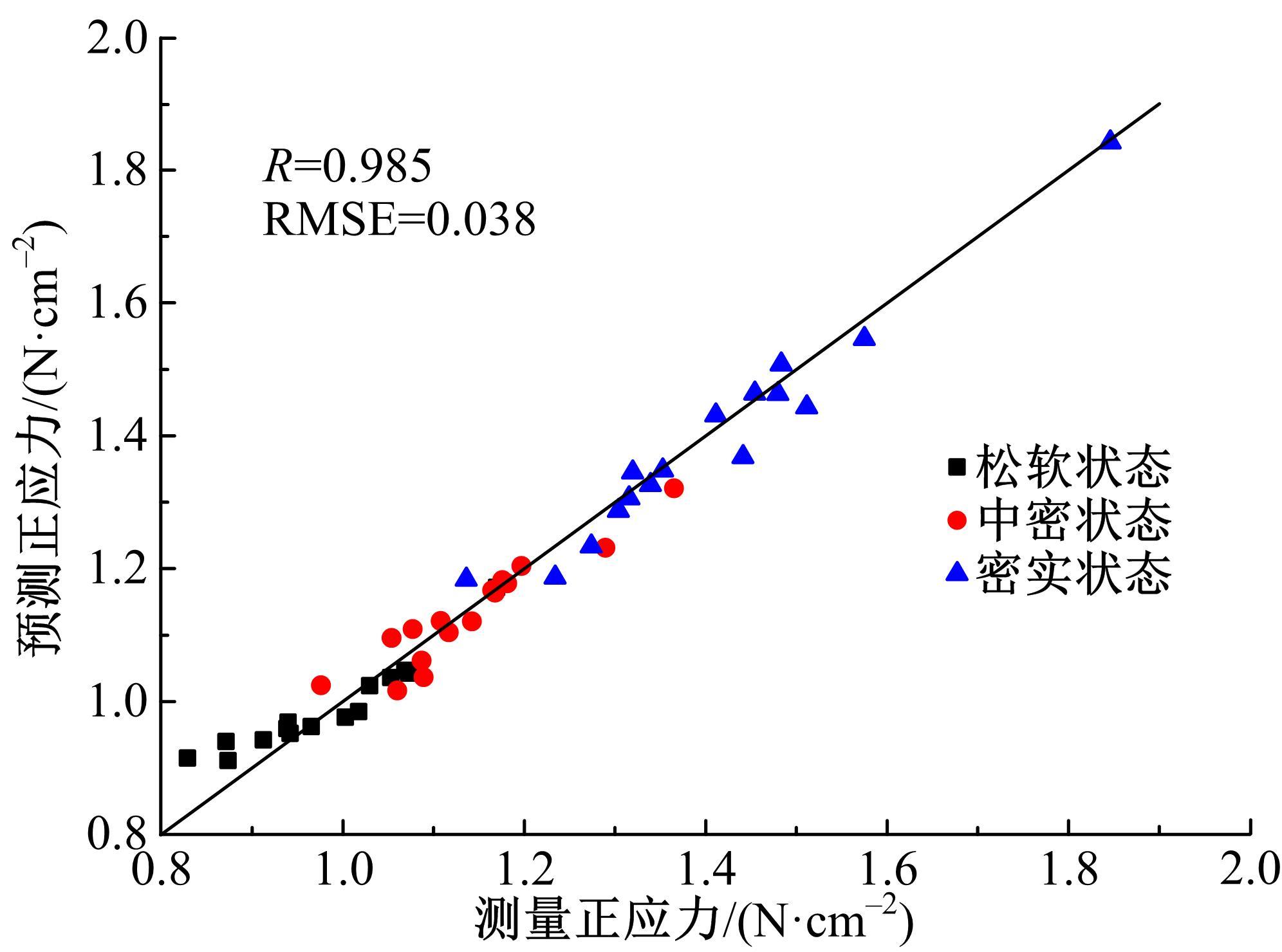
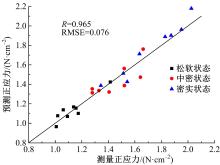
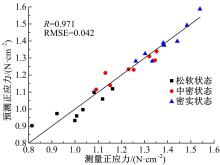
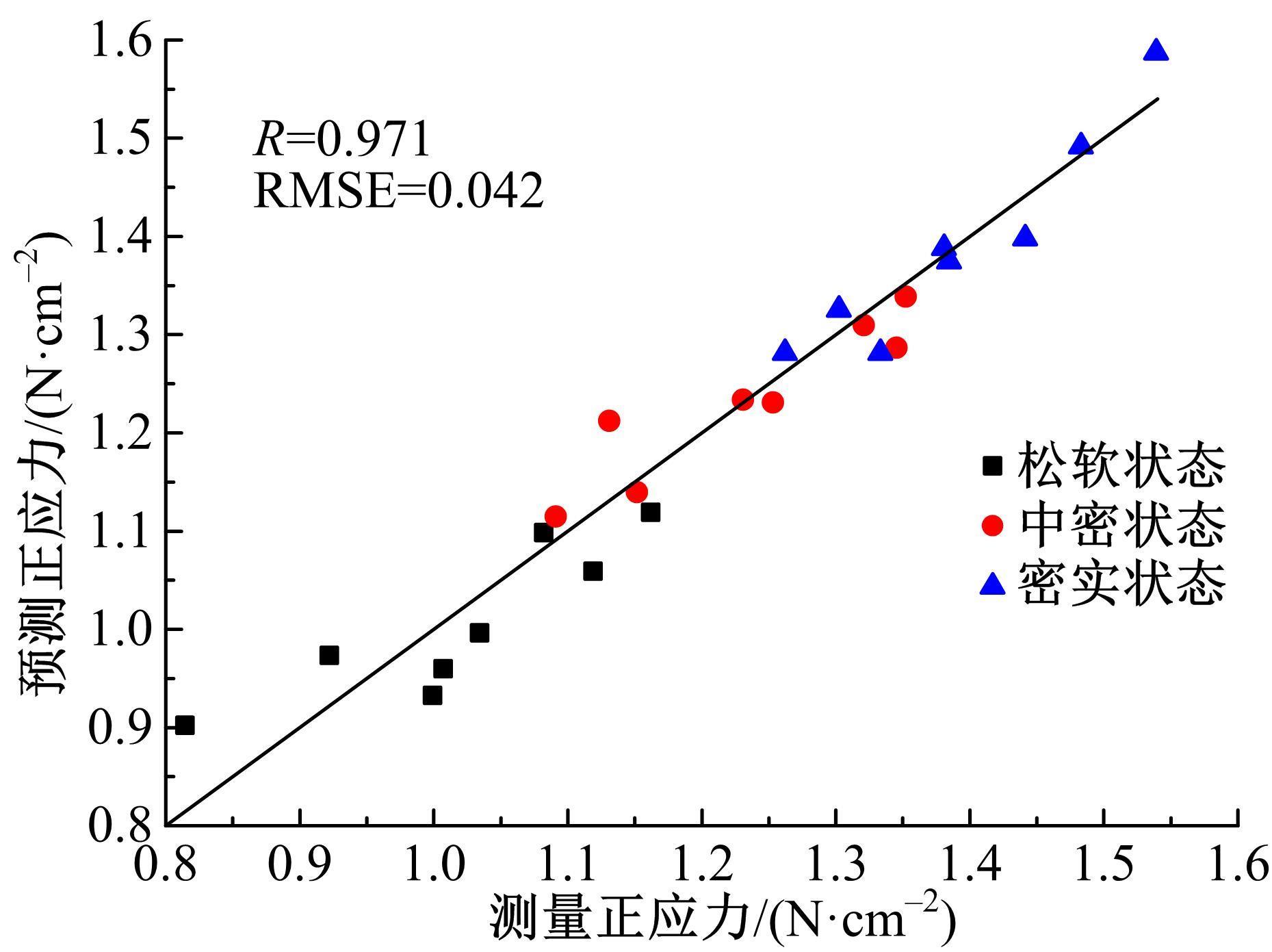
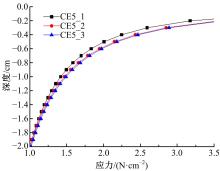
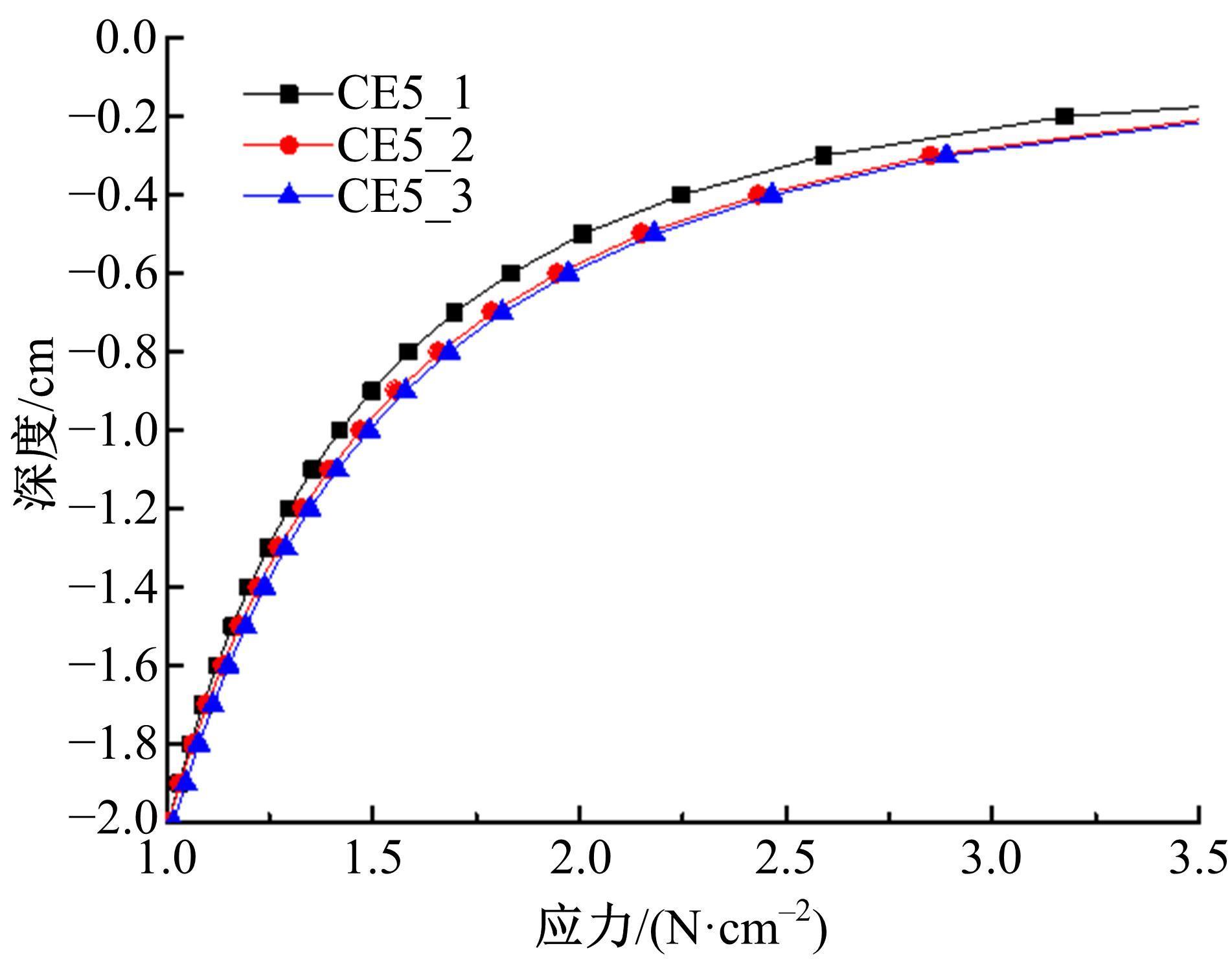
以触月传感器触月压痕为研究对象,通过压痕的几何特征参数和触月压力,结合最小二乘法建立了采样区域表层月壤的承压模型,确定了表层月壤的软硬程度。应用3种模拟月壤(CE5_1、CE5_2、CE5_3),以相对密实度为依据,把模拟月壤整备为松软、中密和高密3种状态。共采集试验数据264组,每种模拟月壤的试验数据按照3∶2的比例随机划分为建模组和预测组。预测组中预测正应力与实际正应力的相关系数分别为0.985、0.965和0.971。结果表明,该模型可以对表层月壤的承压能力进行评估,用于判别表层月壤的软硬程度,为表取采样深度的确定提供参考。
中图分类号:
- TB17
| 1 | 郑燕红, 邓湘金, 庞勇, 等. 月球风化层钻取采样过程密实度分类研究[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(4):No.223391. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Deng Xiang-jin, Peng Yong, et al. Research on classification of relative density in lunar regolith drilling[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(4):No.223391. | |
| 2 | 姚猛,郑燕红,赵志晖,等. 一种月表采样器合理铲挖深度的研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(3):50-56. |
| Yao Meng, Zheng Yan-hong, Zhao Zhi-hui, et al. Research on reasonable excavation depth for lunar regolith sampler[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(3):50-56. | |
| 3 | 姜水清,刘荣凯,林云成,等. 铲挖式表层月壤采样器设计与试验[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2019, 39(1):49-58. |
| Jiang Shui-qing, Liu Rong-kai, Lin Yun-cheng,et al. Design and test of a sampler for lunar surface regolith[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2019, 39(1):49-58. | |
| 4 | Shaw A, Arvidson R E, Bonitz R, et al. Phoenix soil physical properties investigation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E1):No.E00E05. |
| 5 | Tsuchiya K, Ishigami G. Vision-based measurement of spatio-temporal deformation of excavated soil for the estimation of bucket resistive force[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2020, 90:11-21. |
| 6 | Jiang Xiao-hu, Tong Jin, Ma Yun-hai, et al. Development and verification of a mathematical model for the specific resistance of a curved subsoiler[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 190:107-119. |
| 7 | Malaguti F. Soil machine interaction in digging and earthmoving automation[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th ISARC, Brighton, United Kingdom, 1994:187-191. |
| 8 | Blouin S, Hemami A, Lipsett M. Review of resistive force models for earthmoving processes[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2001, 14(3):102-111. |
| 9 | Swick W C, Perumpral J V. A model for predicting soil-tool interaction[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 1988, 25(1):43-56. |
| 10 | Xi Bang-lu, Jiang Ming-jing, Cui Liang, et al. Experimental verification on analytical models of lunar excavation[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2019, 83:1-13. |
| 11 | Yang Qin-sen, Sun Shu-ren. A soil-tool interaction model for bulldozer blades[J]. Journal of Terramechanics,1994,31(2):55-65. |
| 12 | Luth H J, Wismer R D. Performance of plane soil cutting blades in sand[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1971, 14(2):255-259. |
| 13 | 薛龙, 邹猛, 李建桥,等. 基于轮地作用参数和PLSDA方法的月壤力学性能评估[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(11):3751-3758. |
| Xue Long, Zou Meng, Li Jian-qiao, et al. Mechanical performance estimation of lunar soil using wheel-soil interaction parameter and PLSDA[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(11):3751-3758. | |
| 14 | 郑燕红, 姚猛, 金晟毅,等. 月面复杂地形表层采样可采点确定方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术,2019,39(2):41-48. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Yao Meng, Jin Sheng-yi, et al. Lunar surface sampling point selection for uneven terrain[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2019, 39(2):41-48. | |
| 15 | 郑燕红, 邓湘金, 彭兢,等. 基于人工势场法的月球表层采样装置避障规划[J]. 中国空间科学技术. 2015(6):66-74. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Deng Xiang-jin, Peng Jing,et al. Lunar surface sampling device collision avoidance planning based on artificial potential field methon[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2015(6):66-74. | |
| 16 | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,等. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2021,51(3):1146-1152. |
| Wang Kang, Yao Meng, Li Li-ben, et al. Mechanical performance identification for lunar soil in lunar surface sampling[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3):1146-1152. | |
| 17 | 王康, 张沛, 林云成,等. 采样机械臂关节月表环境适应性设计[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2017, 34(5):482-489. |
| Wang Kang, Zhang Pei, Lin Yun-cheng, et al. Environmental adaptive design of joint for a lunar surface sampling arm[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2017, 34(5):482-489. |
| [1] | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,李建桥,邓湘金,邹猛,薛龙. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [2] | 黄晗, 李建桥, 陈百超, 吴宝广, 邹猛. 着陆器足垫冲击特性模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1194-1200. |
| [3] | 崔金生, 侯绪研, 邓宗全, 潘万竞, 姜生元. 真空颗粒系统有效导热系数测量试验台研制及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 457-464. |
| [4] | 李建桥,黄晗,党兆龙,邹猛,王洋. 轻载荷条件下的筛网轮沉陷[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 167-173. |
| [5] | 邹猛,李建桥,张金换,刘国敏,李因武. 月球车驱动轮在不同介质上的牵引性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(01): 25-0029. |
| [6] | 张朋,邓宗全,胡明,高海波. 基于地面力学的变质心月球探测车移动性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(06): 1573-1578. |
| [7] | 邹猛,李建桥,贾阳,任露泉,李因武 . 月壤静力学特性的离散元模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 383-0387. |
| [8] | 李雯,高峰,孙鹏. 复合材料深空探测车车轮的设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(04): 502-505. |
|
||