吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 483-490.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211087
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于等效加工时间模型的机床退化过程建模
- 1.温州大学 激光加工机器人国际科技合作基地,温州 325035
2.长沙理工大学 汽车与机械工程学院,长沙 410114
Modelling degradation processes of machine tools using an equivalent processing time model
Ren-yan JIANG1,2( ),Bin-bin XIONG2
),Bin-bin XIONG2
- 1.National International Cooperation Base of Laser Processing Robot,Wenzhou University,Wenzhou 325035,China
2.Faculty of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering,Changsha University of Science and Technology,Changsha 410114,China
摘要:
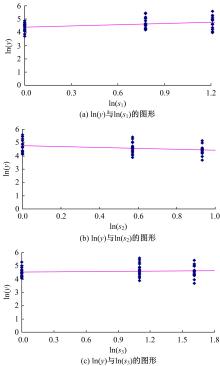
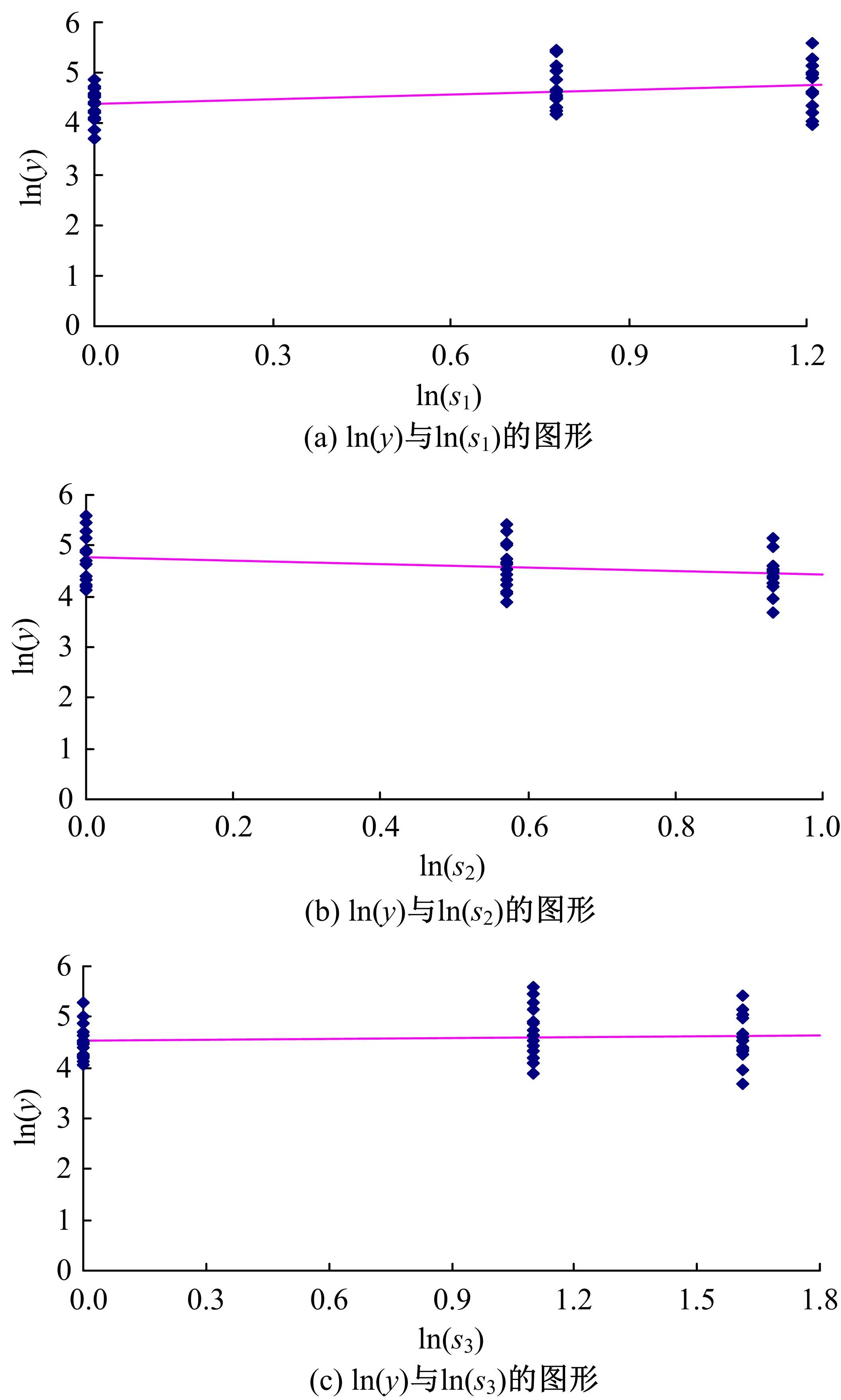
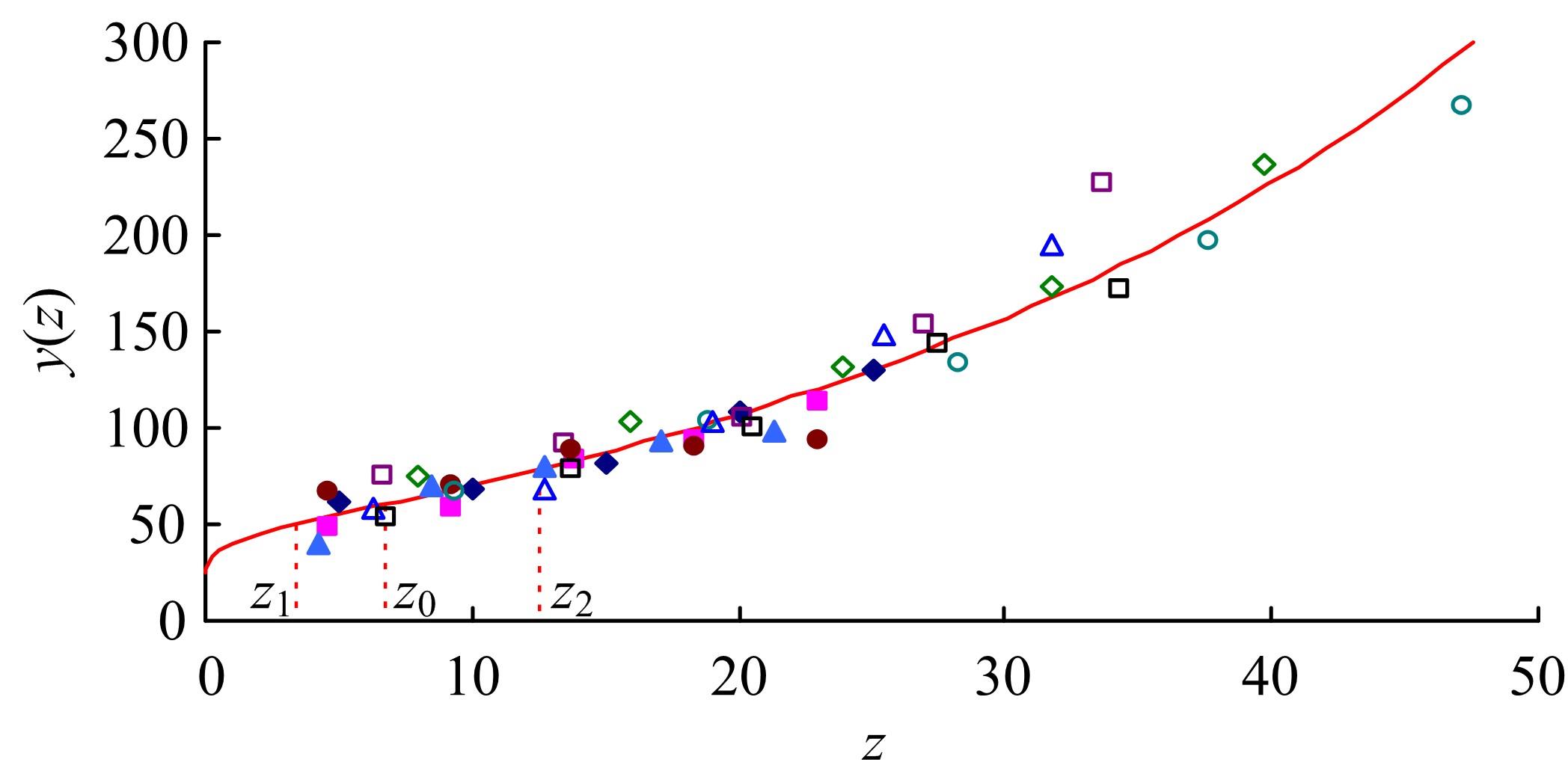
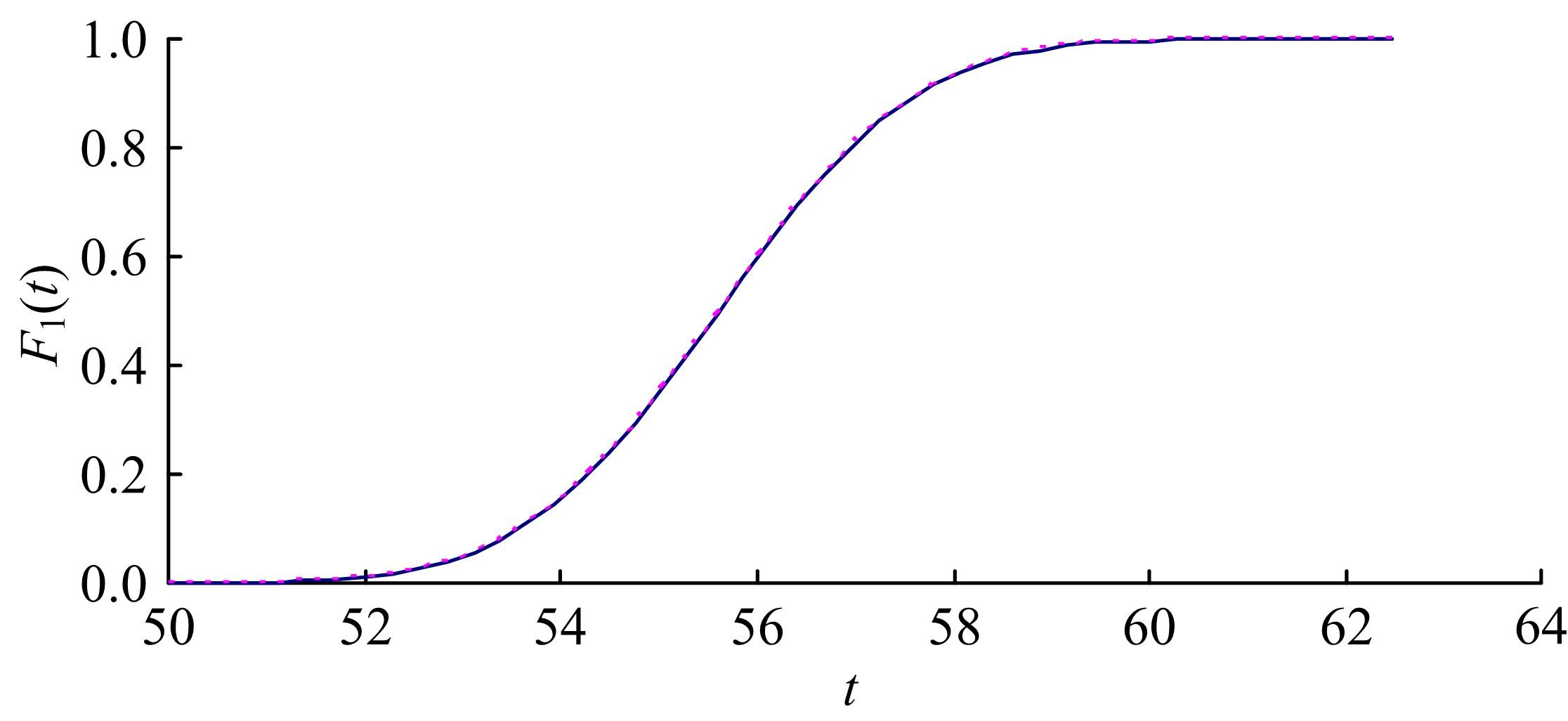
机床性能退化引起加工质量下降和其他问题,加工参数影响退化率。因为有多个加工参数,机床退化建模涉及多个变量,广泛使用的建模方法是回归分析。回归分析的主要缺点是精度依赖于所选平均退化函数,且不给出到退化限的时间分布。为克服上述问题,提出一个基于等效加工时间的建模方法,它将每个加工参数看作为一个“应力”,通过乘积模型组合多个加工参数成为一个“复合应力”;使用加速退化模型组合复合应力与实际加工时间成为一个等效加工时间,从而使多变量退化建模问题简化为单变量退化建模问题。最后,通过一个刀具磨损的实例例证了该方法的优越性。
中图分类号:
- TH17
| 1 | 许彬彬, 杨兆军, 陈菲, 等. 非齐次泊松过程的数控机床可靠性建模[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(2): 210-214. |
| Xu Bin-bin, Yang Zhao-jun, Chen Fei, et al. Reliability model of CNC machine tools based on non-homogenous poisson process[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(2):210-214. | |
| 2 | 申桂香, 戚晓艳, 张英芝, 等. 基于等效样本法的系统组件运行可靠性建模[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3):914-919. |
| Shen Gui-xiang,Qi Xiao-yan,Zhang Ying-zhi, et al. Operational reliability modeling of system components based on equivalent sample method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 914-919. | |
| 3 | Lad B K, Kulkarni M S. A parameter estimation method for machine tool reliability analysis using expert judgement[J]. International Journal of Data Analysis Techniques and Strategies, 2010, 2(2): 155-169. |
| 4 | Hu W, Yang Z, Chen C, et al. Reliability assessment of machine tools considerin[C]∥IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing, 2021: 032036. |
| 5 | Mikolajczyk T, Nowicki K, Bustillo A, et al. Predicting tool life in turning operations using neural networks and image processing[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 503-513. |
| 6 | Lin Y, He S, Lai D, et al. Wear mechanism and tool life prediction of high-strength vermicular graphite cast iron tools for high-efficiency cutting[J]. Wear, 2020, 454: 203319. |
| 7 | 王新刚, 张鑫垚, 杨禄杰, 等. 竞争失效条件下针对磨损退化数据的刀具可靠性分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(14): 1672-1677+1746. |
| Wang Xin-gang, Zhang Xin-yao,Yang Lu-jie, et al. Tool reliability analysis for wear degradation data under competitive failure conditons[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(14): 1672-1677+1746. | |
| 8 | Ezugwu E O, Arthur S J, Hines E L. Tool-wear prediction using artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1995, 49(3): 255-264. |
| 9 | 雷小宝, 廖文和, 谢峰, 等. 义齿用预烧结氧化锆高速铣削时刀具磨损及寿命预测[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2013, 37(4): 567-572, 578. |
| Lei Xiao-bao, Liao Wen-he, Xie Feng, et al. Predict on cutter wear and life in high-speed milling of pre-sintered zirconia used for denture[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2013, 37(4): 567-572, 578. | |
| 10 | Stephenson D A, Agapiou J S. Metal Cutting Theory and Practice[M].3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2016. |
| 11 | Alajmi M S, Almeshal A M. Estimation and optimization of tool wear in conventional turning of 709m40 alloy steel using support vector machine(SVM) with bayesian optimization[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 3773. |
| 12 | Quiza R, Figueira L, Davim J P. Comparing statistical models and artificial neural networks on predicting the tool wear in hard machining D2 AISI steel[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2008, 37(7/8): 641-648. |
| 13 | Ramamoorthy K. Tool wear evaluation by stereo vision and prediction by artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 112(1): 43-52. |
| 14 | Xu L, Huang C, Li C, et al. Prediction of tool wear width size and optimization of cutting parameters in milling process using novel ANFIS-PSO method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2020(3): 1-12. |
| 15 | Çelik Y H, Kilickap E, Güney M. Investigation of cutting parameters affecting on tool wear and surface roughness in dry turning of Ti-6Al-4V using CVD and PVD coated tools[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2017, 39(6): 2085-2093. |
| 16 | 杨兆军, 陈传海, 陈菲, 等. 数控机床可靠性技术的研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(21): 130-139. |
| Yang Zhao-jun, Chen Chuan-hai, Chen Fei, et al. Progress in the research of reliability technology of machine tools[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(21): 130-139. | |
| 17 | Wu P, Wu J, Deng C. SVR-based degradation analysis and reliability assessment for CNC machine tools [C]∥Kota Kinabalu: Applied Computing,Computer Science, and Computer Engineering, Wuhan, 2011: 586-591. |
| 18 | Sun B, Xu B, He J, et al. Application of inverse gaussian model in mechanical product degradation model [C]∥2nd International Conference on System Reliability and Safety, Milan, 2017: 238-242. |
| 19 | Li S, Ran Y, Zhang G, et al. Accuracy degradation model and residual accuracy life prediction of CNC machine tools based on wiener process [C]∥2nd International Conference on Robotics and Mechantronics, Shaanxi, 2021: 032039. |
| 20 | 杨志伟, 任工昌, 孟勃敏. 基于性能退化数据的加工中心的可靠性评估[J]. 陕西科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 29(6): 43-46. |
| Yang Zhi-wei, Ren Gong-chang, Meng Bo-min. Reliability evaluation on machining center based on performance degradation data[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2011, 29(6): 43-46. | |
| 21 | 邓超, 钱有胜, 吴军, 等. BP网络在进给系统定位误差预测中的运用[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2017, 37(3): 449-455. |
| Deng Chao, Qian You-sheng, Wu Jun, et al. A forecasting method of positioning acurracy for CNC machine tools feed system based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement and Diagnosis, 2017, 37(3): 449-455. | |
| 22 | Duan C, Deng C, Li N. Reliability assessment for CNC equipment based on degradation data[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 100(1-4): 421-434. |
| 23 | Peng W, Li Y F, Yang Y J, et al. Bivariate analysis of incomplete degradation observations based on inverse gaussian processes and copulas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(2): 624-639. |
| 24 | 王刚, 陈捷, 洪荣晶, 等. 基于HMM和优化的PF的数控转台精度衰退模型[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(6): 7-13. |
| Wang Gang, Chen Jie, Hong Rong-jing, et al. Model for the positional accuracy degradation of NC rotary tables based on the hidden Markov model and optimized particle fitering[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(6): 7-13. | |
| 25 | 张云, 姜楠, 王立平. 基于Wiener过程的数控转台极小子样可靠性分析[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 59(2): 91-95. |
| Zhang Yun, Jiang Nan, Wang Li-ping. Relibility analysis of NC rotary table based on a wiener process for extremely small samples[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2019, 59(2): 91-95. | |
| 26 | Guo J, Zheng H, Li B, et al. A bayesian approach for degradation analysis with individual differences [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 175033-175040. |
| 27 | Li Z, Wang Y, Wang K. A data-driven method based on deep belief networks for backlash error prediction in machining centers[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2017(4): 1-13. |
| 28 | Wen J, Gao H, Liu Q, et al. A new method for identifying the ball screw degradation level based on the multiple classifier system[J]. Measurement, 2018, 130: 118-127. |
| 29 | Jiang R. A general proportional model and modelling procedure[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2012, 28(6): 634-647. |
| 30 | Jiang R. Introduction to Quality and Reliability Engineering[M]. Beijing:Science Press and Springer, 2015. |
| 31 | Guida M, Pulcini G. The inverse Gamma process: a family of continuous stochastic models for describing state-dependent deterioration phenomena[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2013, 120: 72-79. |
| 32 | Jiang R. An extended log-linear model for modeling wear processes[C]∥9th IMA International Conference on Modelling in Industrial Maintenance and Reliability, London, 2016: 84-89. |
| 33 | Jiang R, Jardine A. Health state evaluation of an item: a general framework and graphical representation[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2008, 93(1): 89-99. |
| 34 | Jiang R. A new NHPP model for modeling failure process with S-shaped mean cumulative function[C]∥the Proceedings of 2016 11th International Conference on Reliability Maintainability and Safety, Hangzhou, 2016: 17209315. |
| 35 | Akaike H T. A new look at the statistical model identification[J]. Automatic Control IEEE Transactions on, 1974, 19(6): 716-723. |
| 36 | Jiang R. A trade off BX life and its applications[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2013, 113: 1-6. |
| [1] | 邓飞跃,吕浩洋,顾晓辉,郝如江. 基于轻量化神经网络Shuffle⁃SENet的高速动车组轴箱轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. |
| [2] | 赵泓荀,杨兆军,陈传海,田海龙,王立平. 考虑参数权重的数控机床电主轴加速试验优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 409-416. |
| [3] | 于立娟,刘昂,杨兆军,田海龙,陈传海,高景文. 基于网络层次和数据包络的数控机床可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 400-408. |
| [4] | 董绍江,朱朋,裴雪武,李洋,胡小林. 基于子领域自适应的变工况下滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [5] | 李国发,王彦博,何佳龙,王继利. 机电装备健康状态评估研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 267-279. |
| [6] | 张根保,李浩,冉琰,李裘进. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
| [7] | 王倩, 赵丁选, 赵颖, 陈娜. 舰载直升机复杂舰面上的动力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1109-1113. |
| [8] | 张彪,赵克定,李阁强 . 被动力伺服系统摩擦非线性控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(06): 1348-1353. |
|
||