吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 474-482.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210644
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
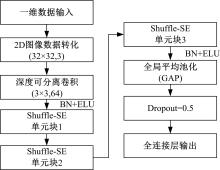
基于轻量化神经网络Shuffle⁃SENet的高速动车组轴箱轴承故障诊断方法
- 1.石家庄铁道大学 省部共建交通工程结构力学行为与系统安全国家重点实验室,石家庄 050043
2.石家庄铁道大学 机械工程学院,石家庄 050043
Fault diagnosis of high⁃speed train axle bearing based on a lightweight neural network Shuffle⁃SENet
Fei-yue DENG1,2( ), LYUHao-yang2,Xiao-hui GU1(
), LYUHao-yang2,Xiao-hui GU1( ),Ru-jiang HAO2
),Ru-jiang HAO2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Behavior in Traffic Engineering Structure and System Safety,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
摘要:
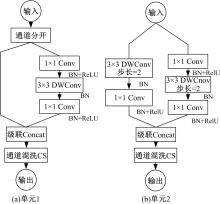
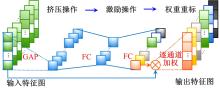
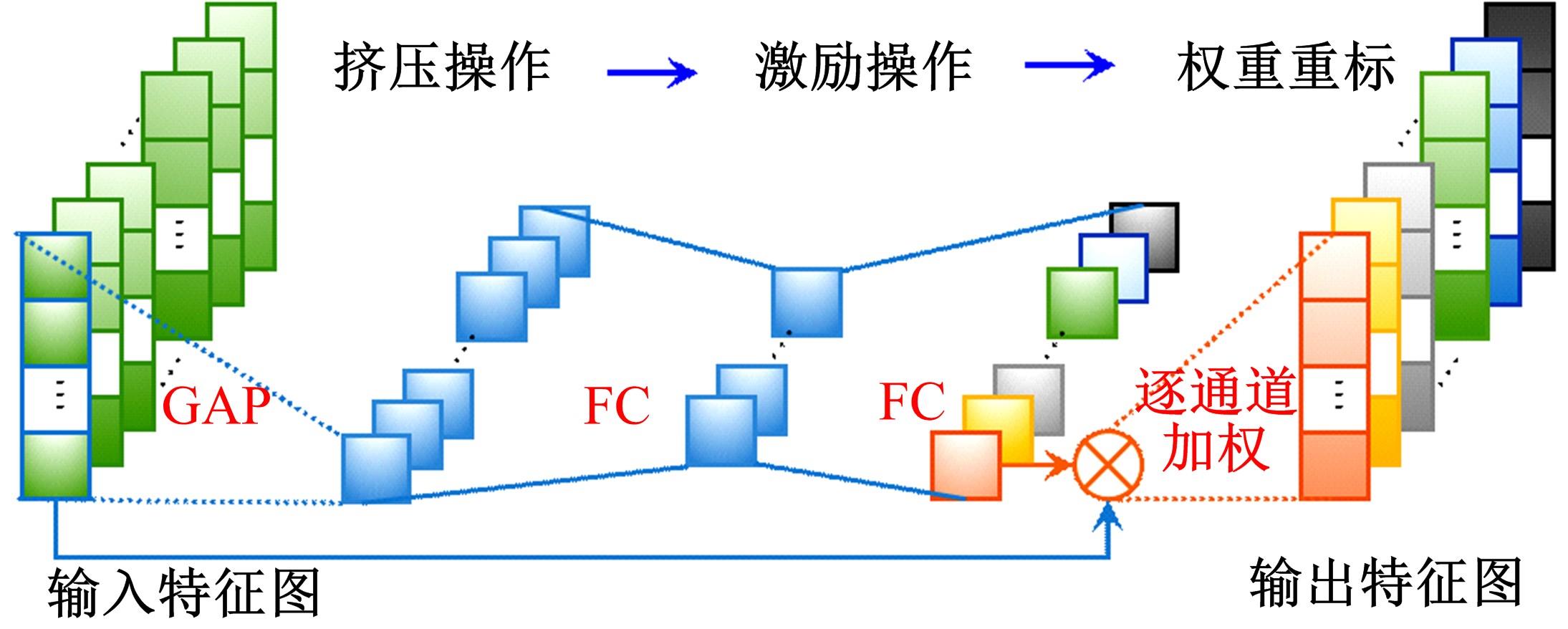
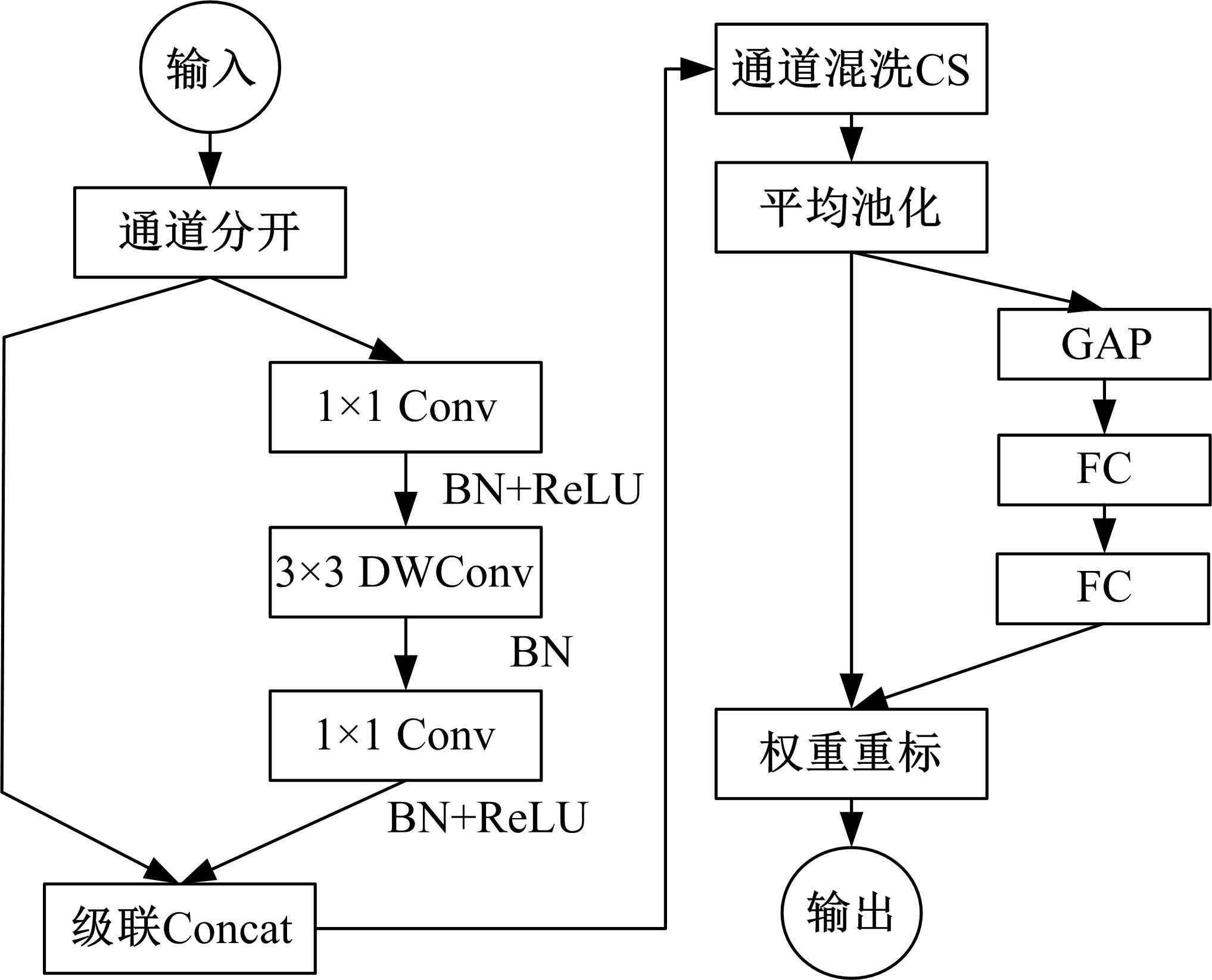
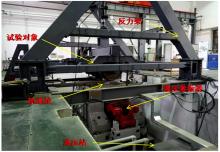
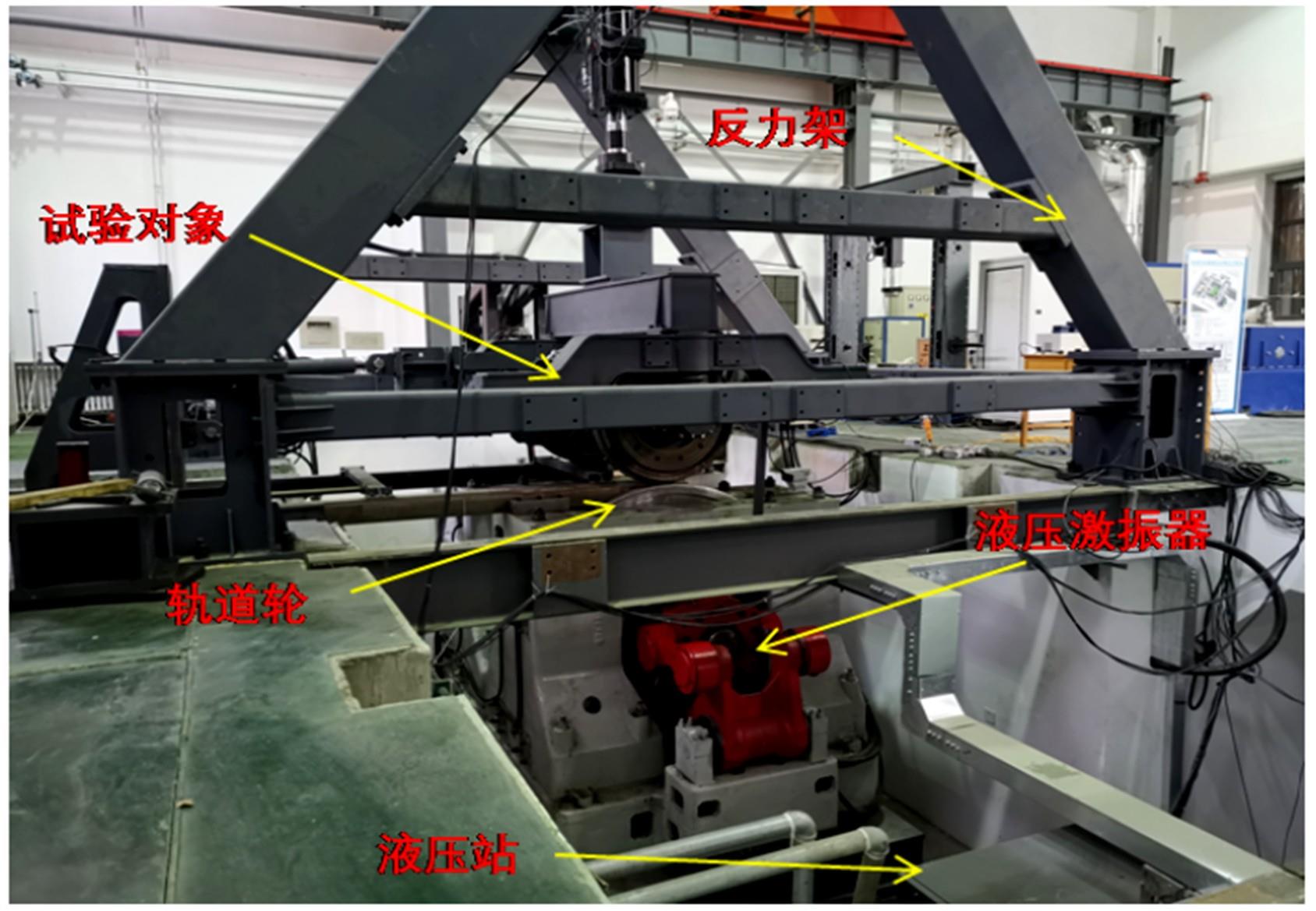
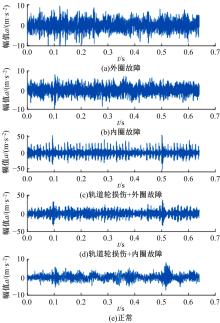
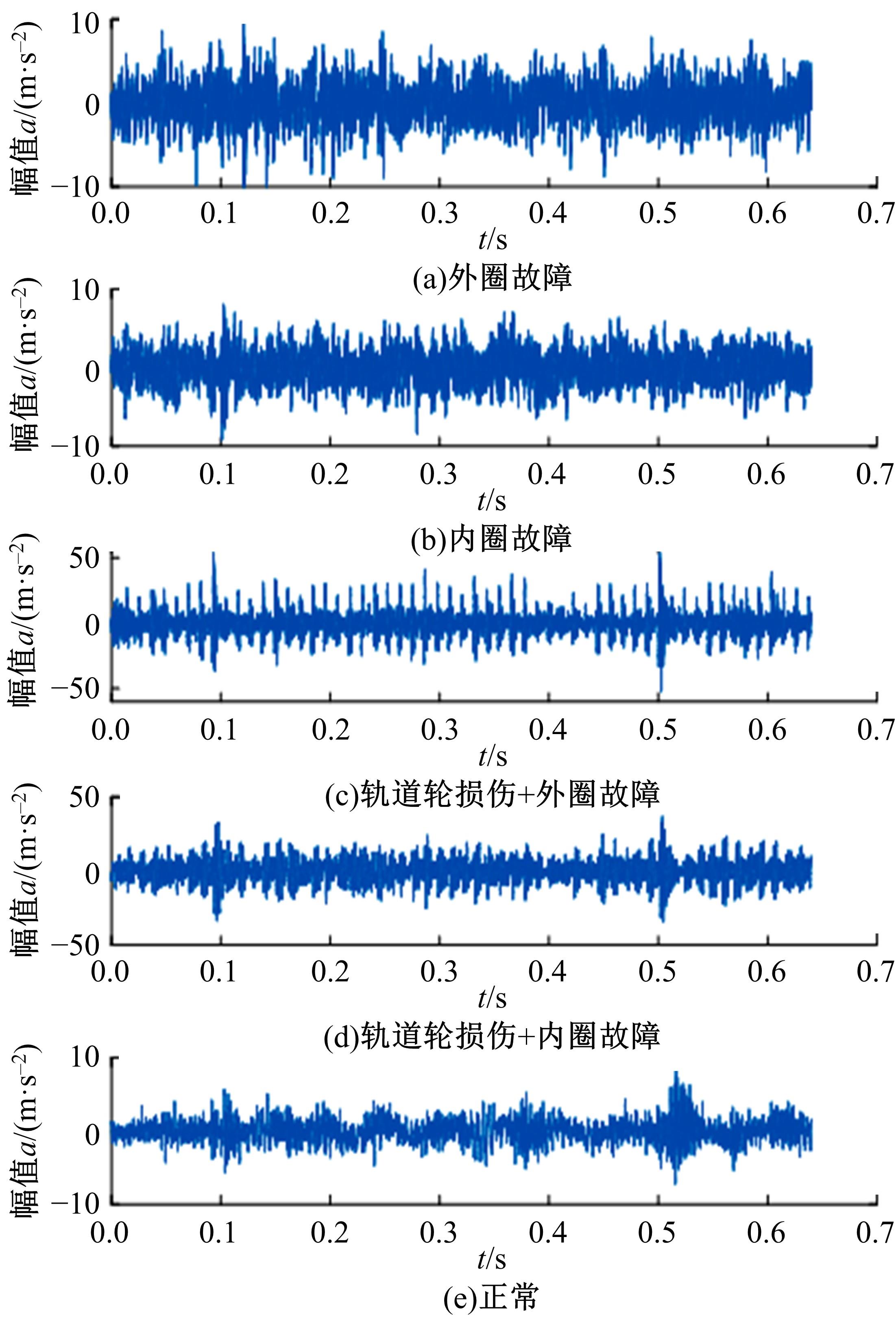
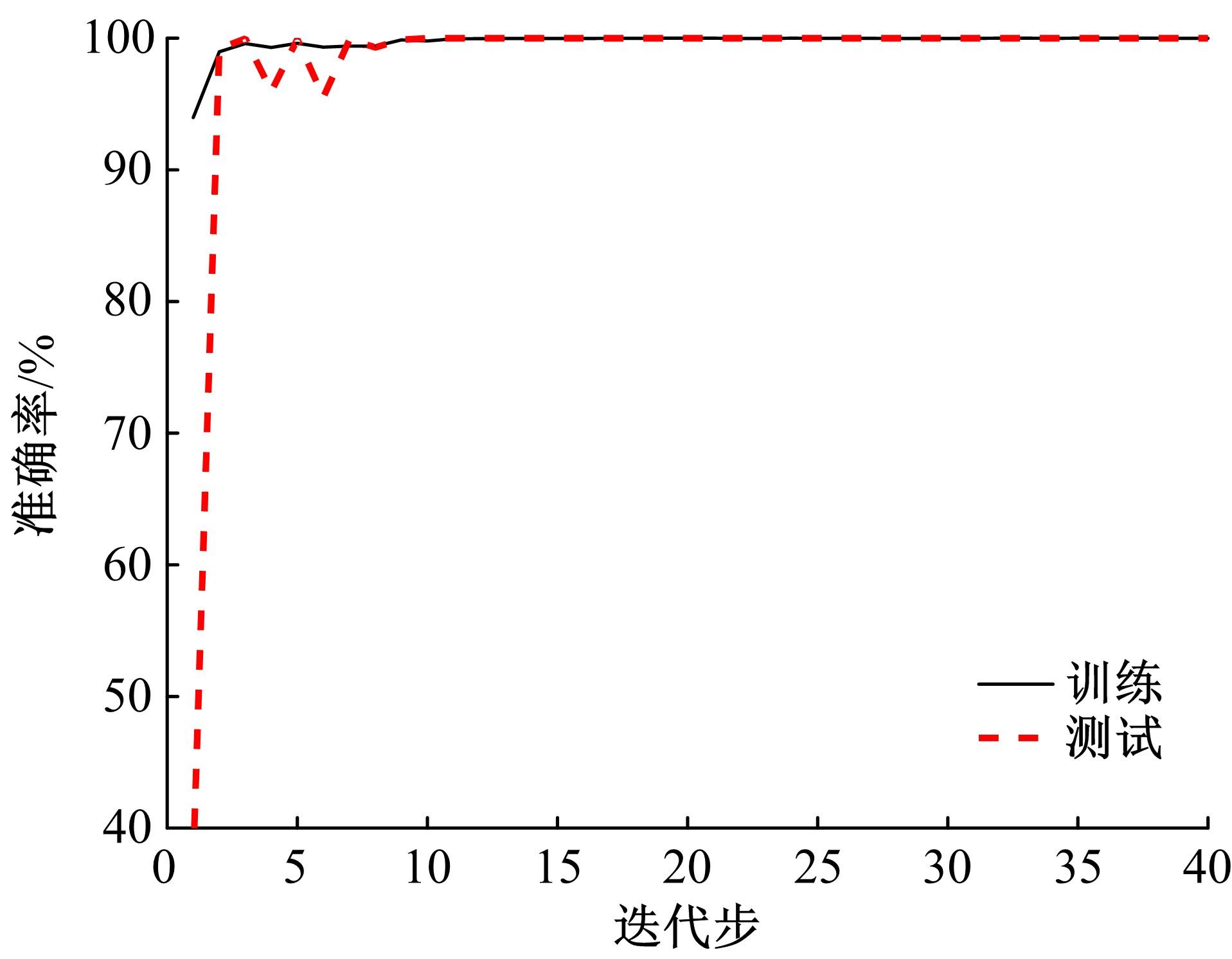
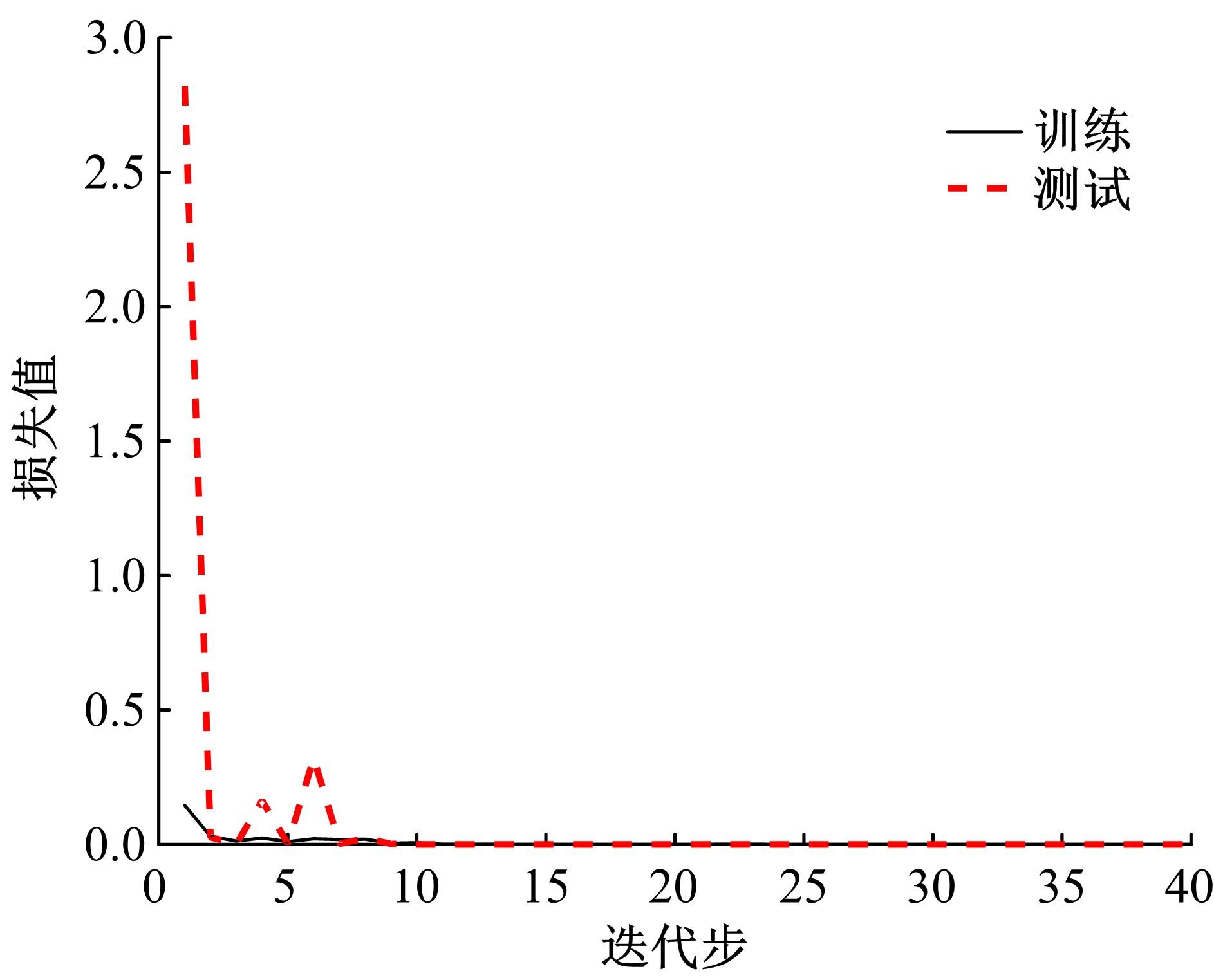
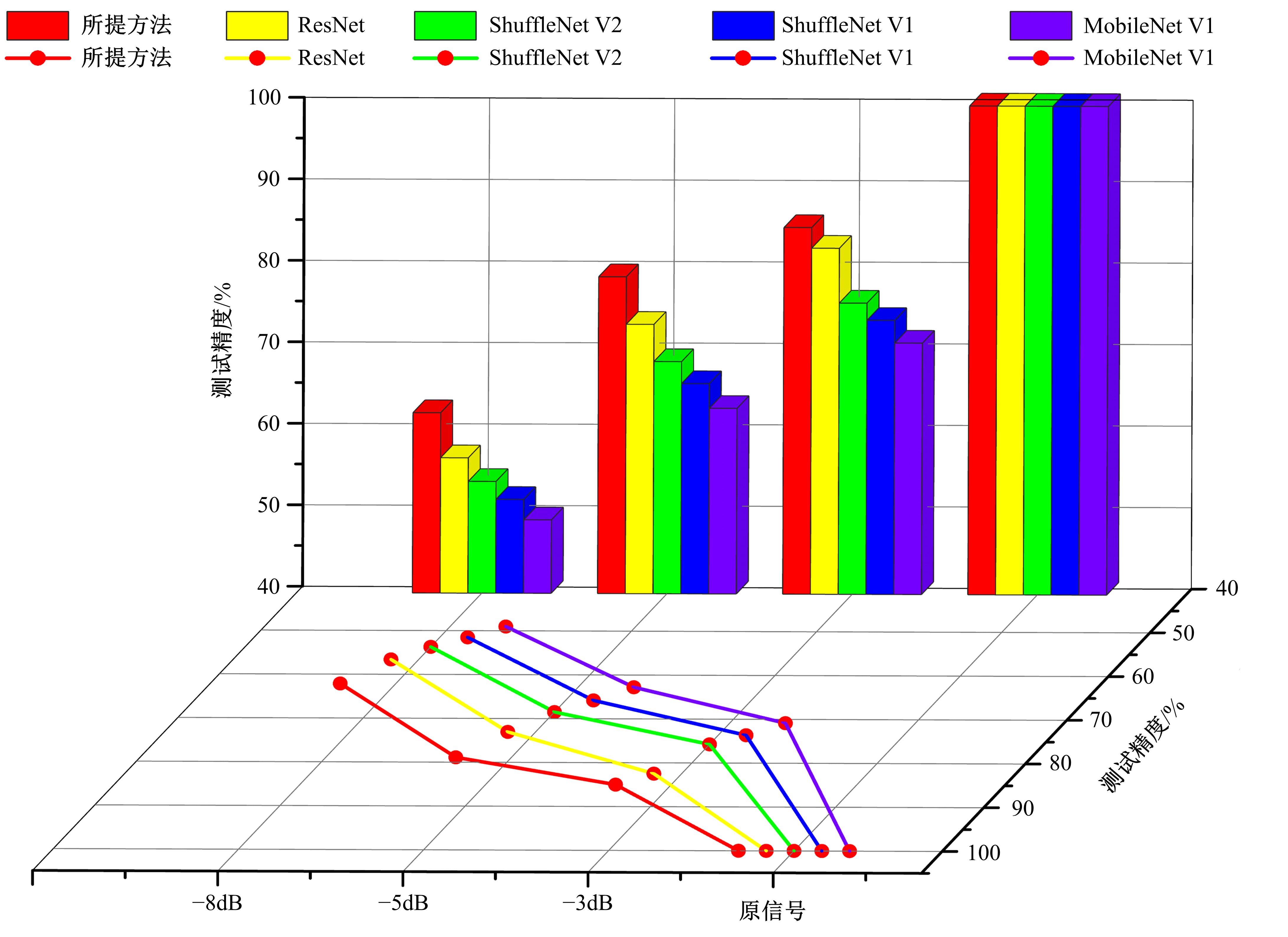
针对复杂工况下高速动车组轴箱轴承故障难以准确诊断的问题,提出了一种Shuffle-SE单元设计方法,并基于模块化思想建立了一种新的轻量化网络Shuffle-SENet用于高速列车轴箱轴承故障诊断。Shuffle-SE单元以ShuffleNet V2单元为基础,在保留网络轻量化的同时,对网络结构进行了局部优化,并进一步嵌入了Squeeze-and-excitation(SE)结构。所构建的轻量化网络模型在保证运算高效的同时,故障诊断精度明显提升。此外,本文对Shuffle-SE单元的数量及SE结构中降维系数对网络模型性能的影响进行了深入分析。实验分析结果表明:本文网络模型可有效用于多种复杂工况下高铁轴箱轴承故障诊断,相比MobileNet V2、ShuffleNet V1/V2、ResNets等目前较为流行的神经网络模型,本文模型在运行效率和故障诊断精度两方面均有较好表现。本文研究为深度学习技术走向工程实际应用,克服对计算机硬件配置较高的限制提供了一种新的解决方法。
中图分类号:
- TH17
| 1 | 院老虎, 连冬杉, 张亮, 等. 基于密集连接卷积网络和支持向量机的飞行器机械部件故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1635-1641. |
| Yuan Lao-hu, Lian Dong-shan, Zhang Lian, et al. Fault diagnosis of key mechanical components of aircraft based on densenet and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1635-1641. | |
| 2 | 张根保, 李浩, 冉琰, 等. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
| Zhang Gen-bao, Li Hao, Ran Yan, et al. A transfer learning model for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. | |
| 3 | Wang B, Lei Y G, Yan T, et al. Recurrent convolutional neural network: a new framework for remaining useful life prediction of machinery[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 379: 117-129. |
| 4 | Wang F, Jiang H, Shao H W, et al. An adaptive deep convolutional neural network for rolling bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28: 095005. |
| 5 | Jing L, Zhao M, Li P, et al. A convolutional neural network based feature learning and fault diagnosis method for the condition monitoring of gearbox[J]. Measurement, 2017, 111: 1-10. |
| 6 | Peng D, Liu Z L, Wang H. et al. A novel deeper one-dimensional CNN with residual learning for fault diagnosis of wheelset bearings in high-speed trains[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 10278-10293. |
| 7 | Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B, et al. Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: arXiv:. |
| 8 | Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, et al. Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 4510-4520. |
| 9 | Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, et al. Shufflenet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 6848-6856. |
| 10 | Ma N, Zhang X, Zheng H T, et al. Shufflenet v2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Cham, 2018: 122-138. |
| 11 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G I. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017: 84-90. |
| 12 | Jie H, Li S, Gang S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 42(8): 7132-7141. |
| 13 | Hoang D T, Kang H J. Rolling element bearing fault diagnosis using convolutional neural network and vibration image[J]. Cognitive Systems Research, 2019, 53: 42-50. |
| 14 | Deng F Y, Ding H, Yang S P, et al. An improved deep residual network with multiscale feature fusion for rotating machinery fault diagnosis[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 32(2): 024002. |
| 15 | Zhao M H, Kang M, Tang B P, et al. Deep residual networks with dynamicallyweighted wavelet coefficients for faultdiagnosis of planetary gearboxes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(5): 4290-4300. |
| 16 | Zhang W, Li C H, Peng G L, et al. A deep convolutional neural network with new training methods for bearing fault diagnosis under noisy environmentand different working load[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2017, 100: 439-453. |
| 17 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, 2016: 770-778. |
| [1] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [2] | 王进花,胡佳伟,曹洁,黄涛. 基于自适应变分模态分解和集成极限学习机的滚动轴承多故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 318-328. |
| [3] | 董绍江,朱朋,裴雪武,李洋,胡小林. 基于子领域自适应的变工况下滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [4] | 罗巍,卢博,陈菲,马腾. 基于PSO-SVM及时序环节的数控刀架故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [5] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [6] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [7] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [8] | 院老虎,连冬杉,张亮,刘义. 基于密集连接卷积网络和支持向量机的飞行器机械部件故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1635-1641. |
| [9] | 范以撒,那景新,上官林建. 基于剩余强度的高速动车侧窗粘接强度校核方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 840-846. |
| [10] | 李伟,陈剑,陶善勇. 自适应耦合周期势系统随机共振信号增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1091-1096. |
| [11] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [12] | 潘凤文,弓栋梁,高莹,徐明伟,麻斌. 基于锂离子电池线性化模型的电流传感器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 435-441. |
| [13] | 张根保,李浩,冉琰,李裘进. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
| [14] | 王德军, 魏薇郦, 鲍亚新. 考虑侧风干扰的电子稳定控制系统执行器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1548-1555. |
| [15] | 宋大凤, 李广含, 张琳, 潘冰, 曾小华, 彭宇君, 王庆年. 模糊逻辑在混合动力汽车电机故障检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 354-359. |
|
||