吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 585-595.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200799
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.华东交通大学 土木建筑学院,南昌 330013
3.华东交通大学 道路工程研究所,南昌 330013
4.新疆交通投资(集团)有限责任公司,乌鲁木齐 830057
Optimal design on recycled hot⁃mix asphalt mixture based on performance⁃cost model
Yu-quan YAO1( ),Jian-gang YANG1,2,3(
),Jian-gang YANG1,2,3( ),Jie GAO1,2,3,Liang SONG4
),Jie GAO1,2,3,Liang SONG4
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
3.Institute of Road Engineering,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
4.Xinjiang Communications Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Urumqi 830057,China
摘要:
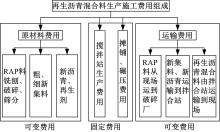
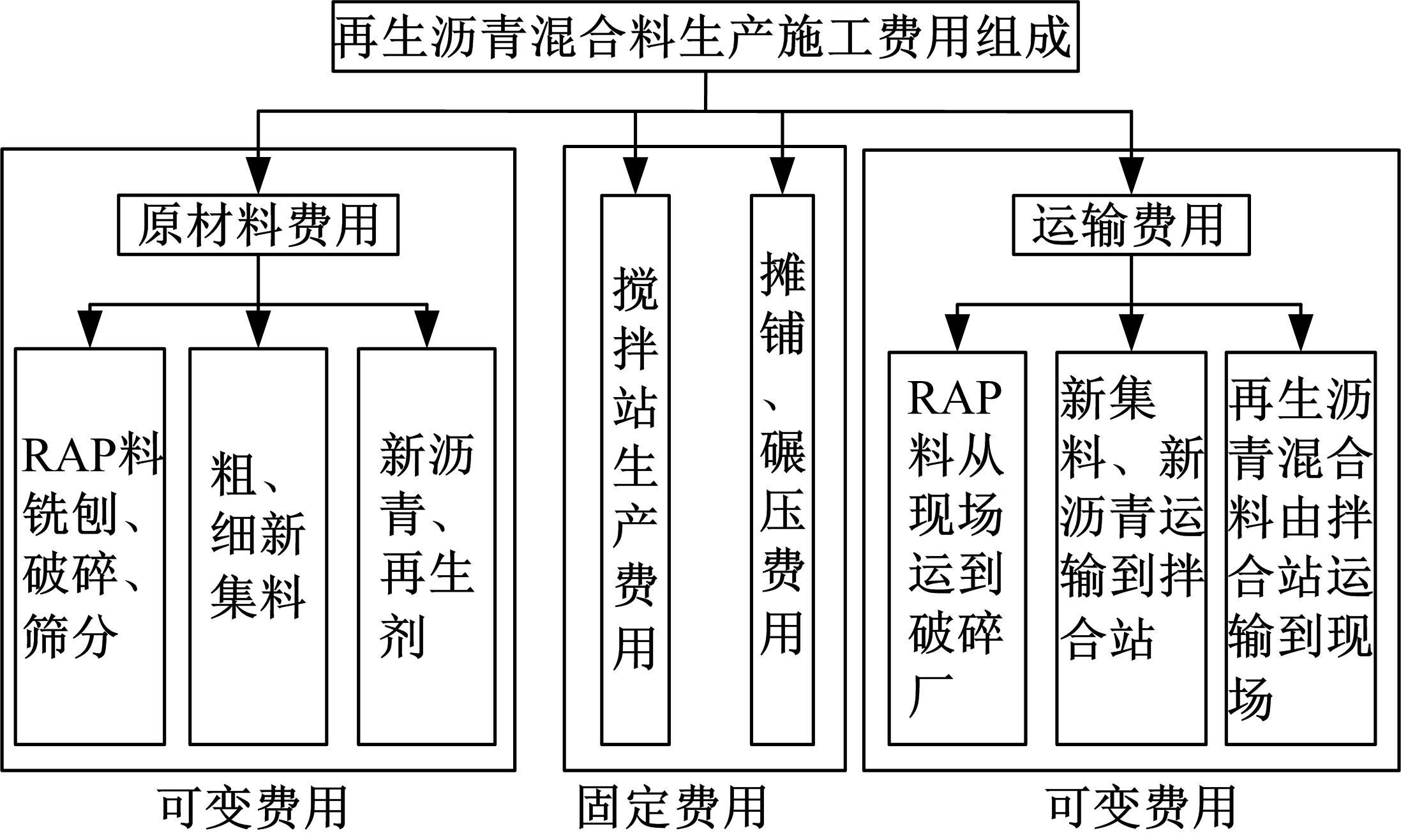
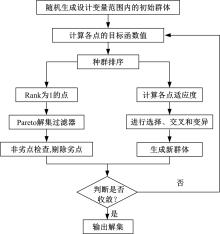
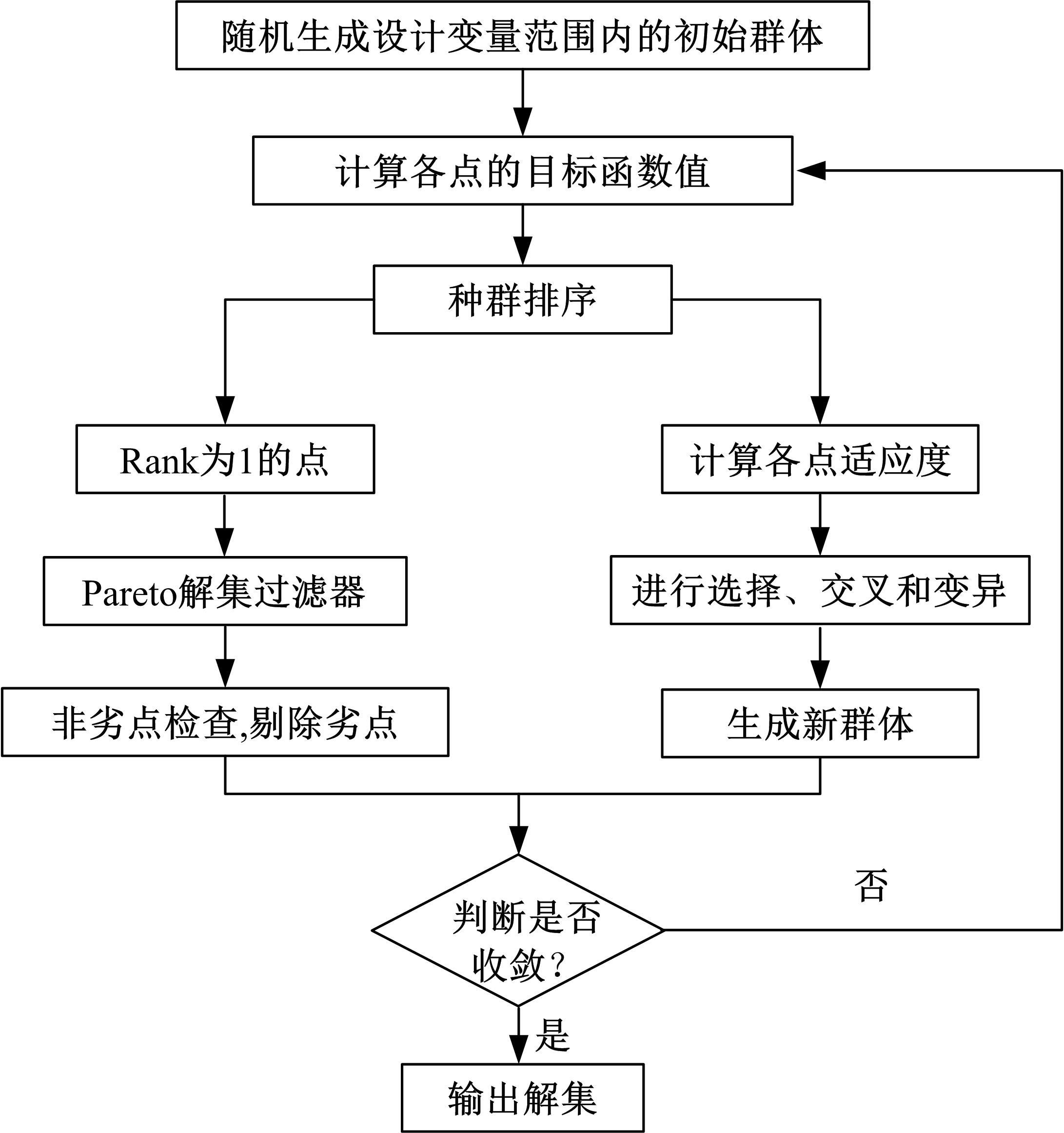
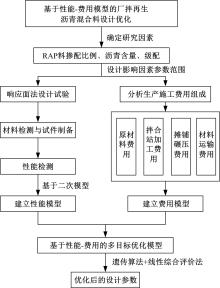
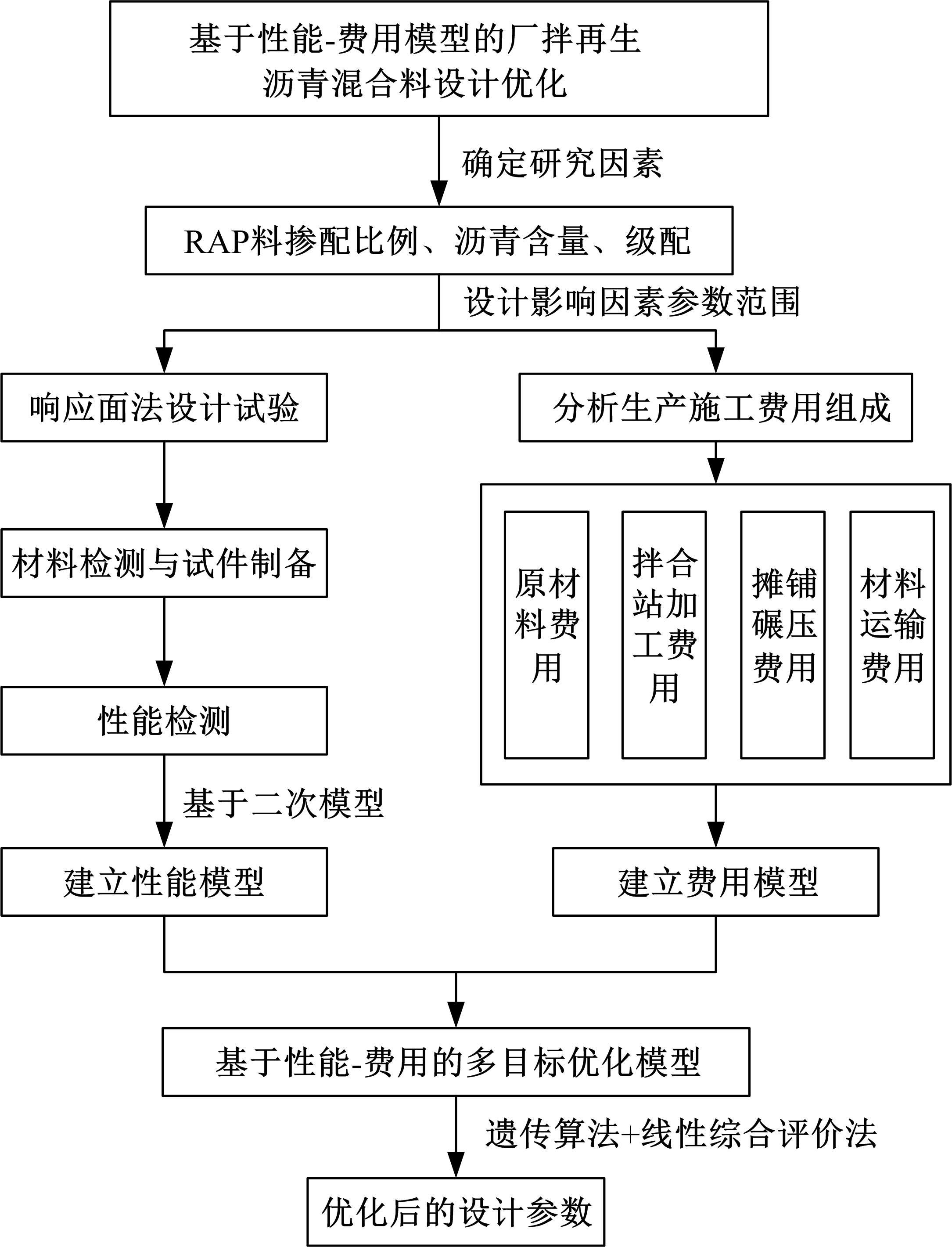
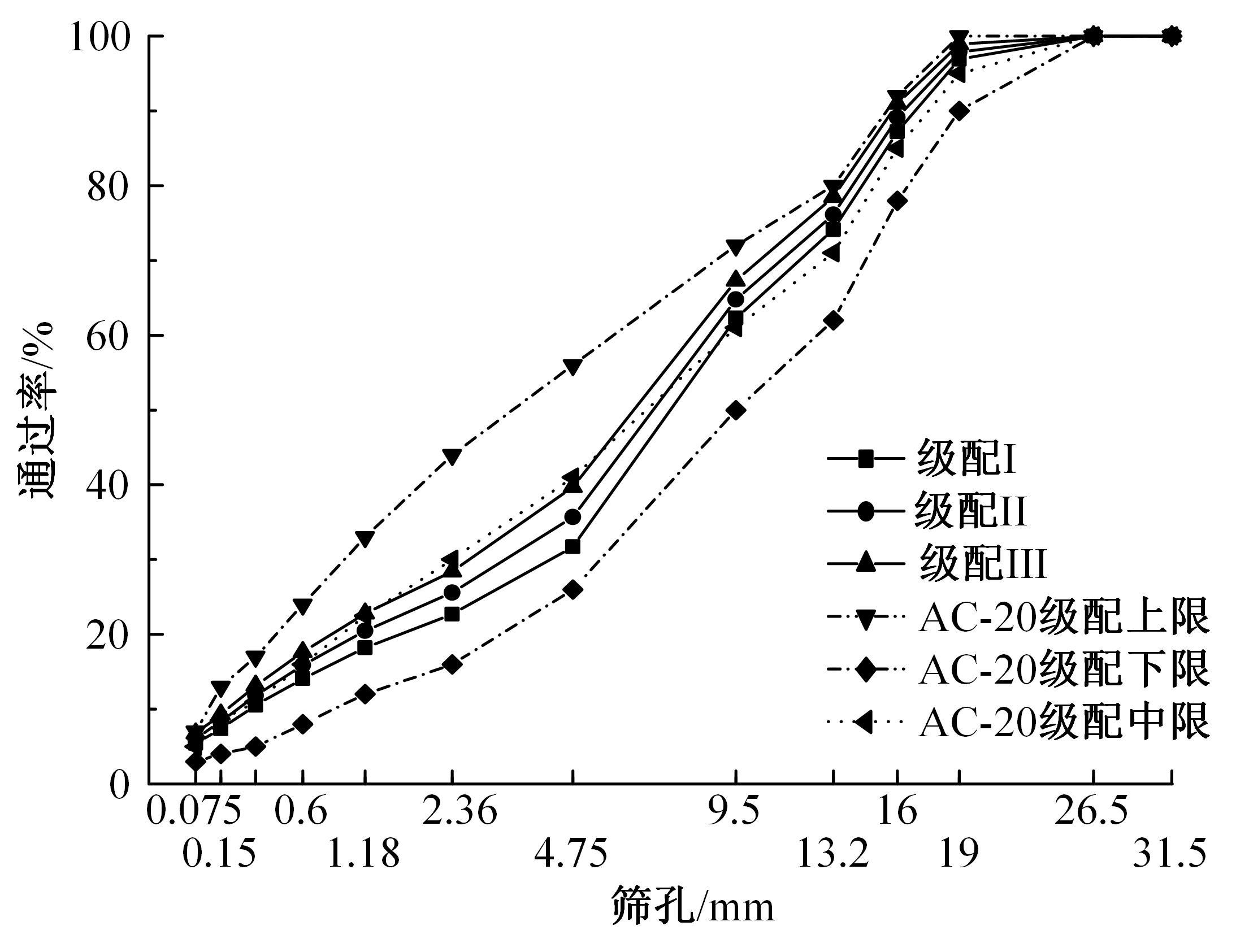
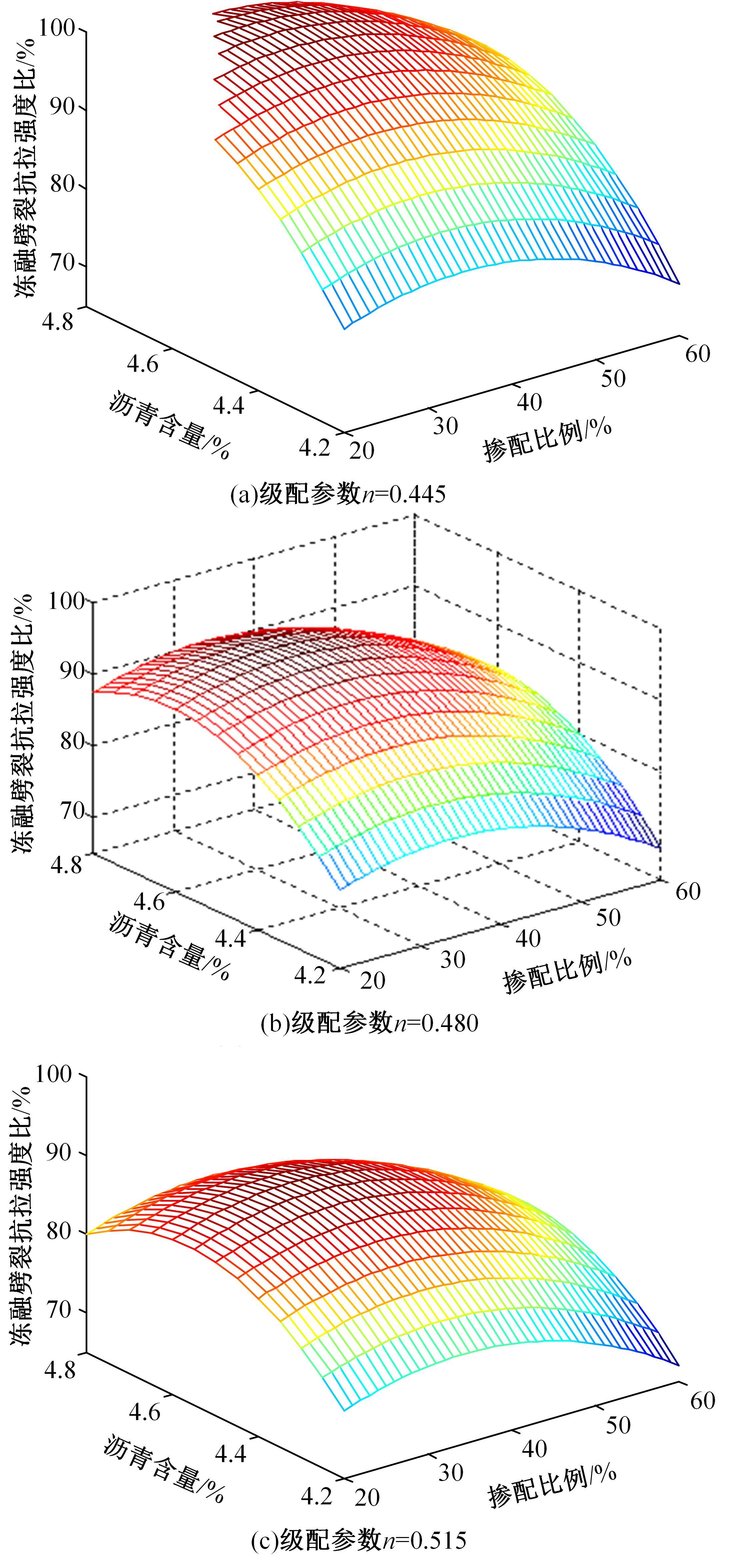
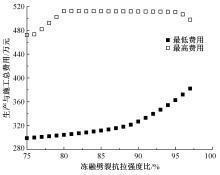
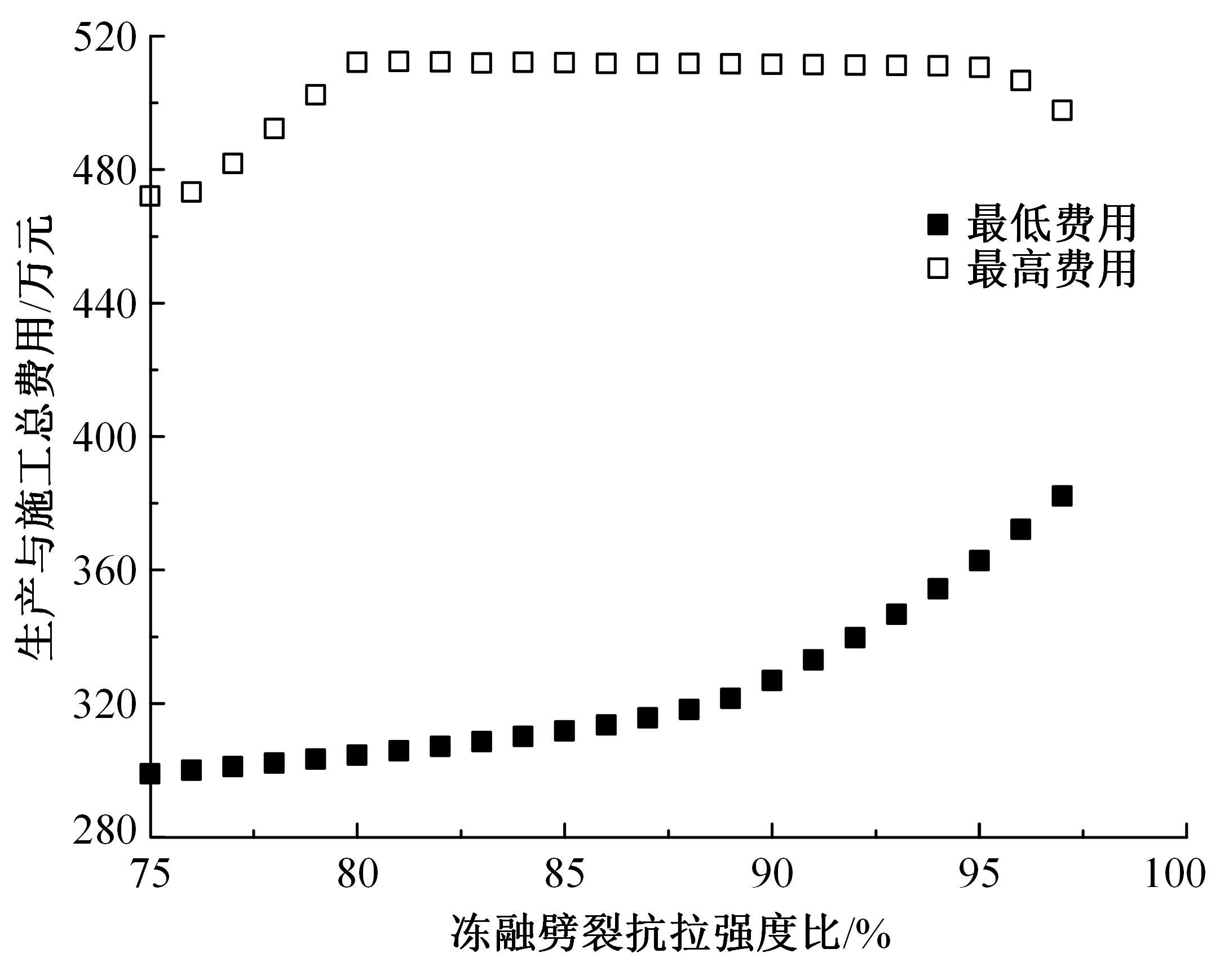
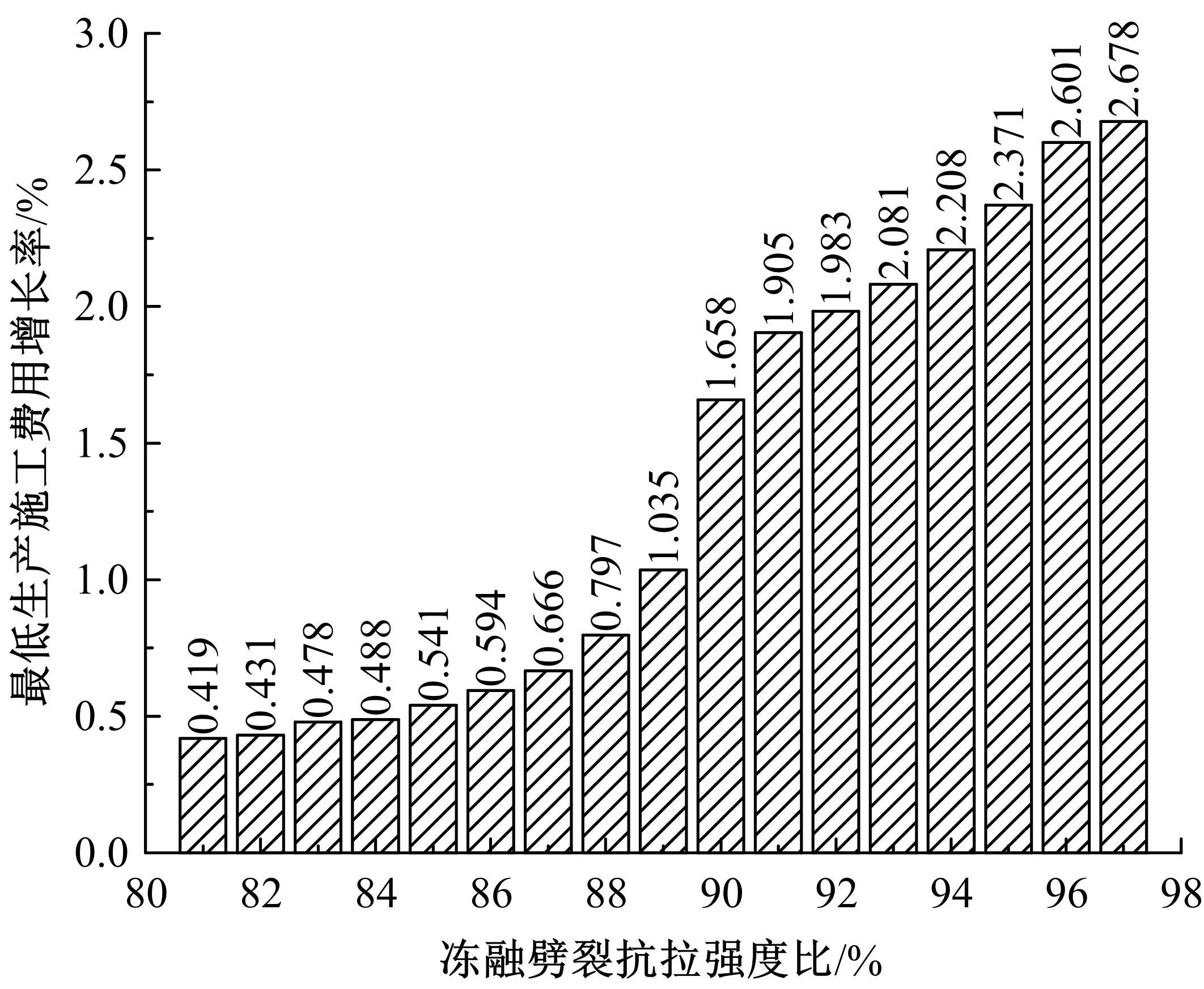
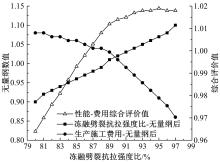
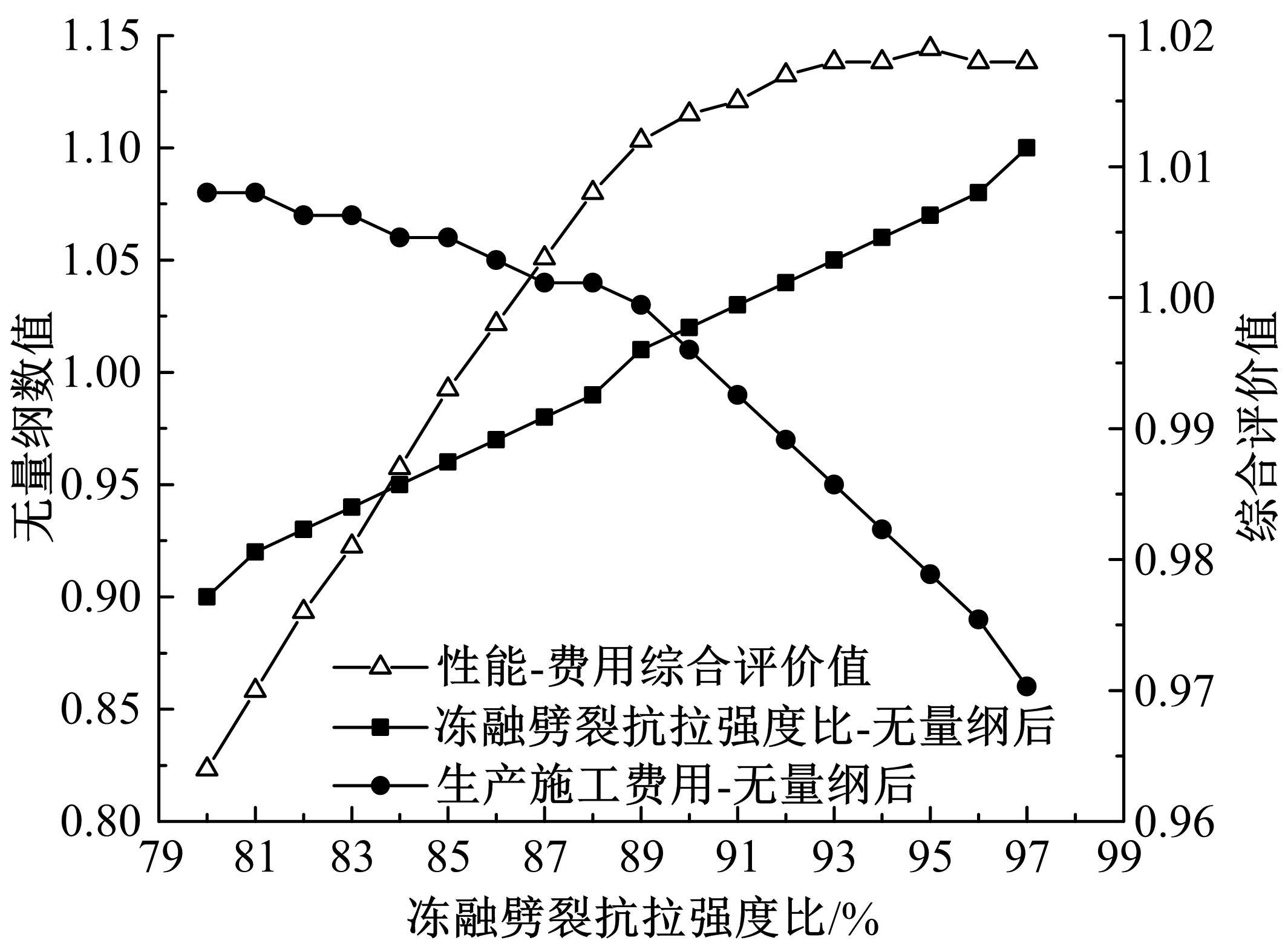
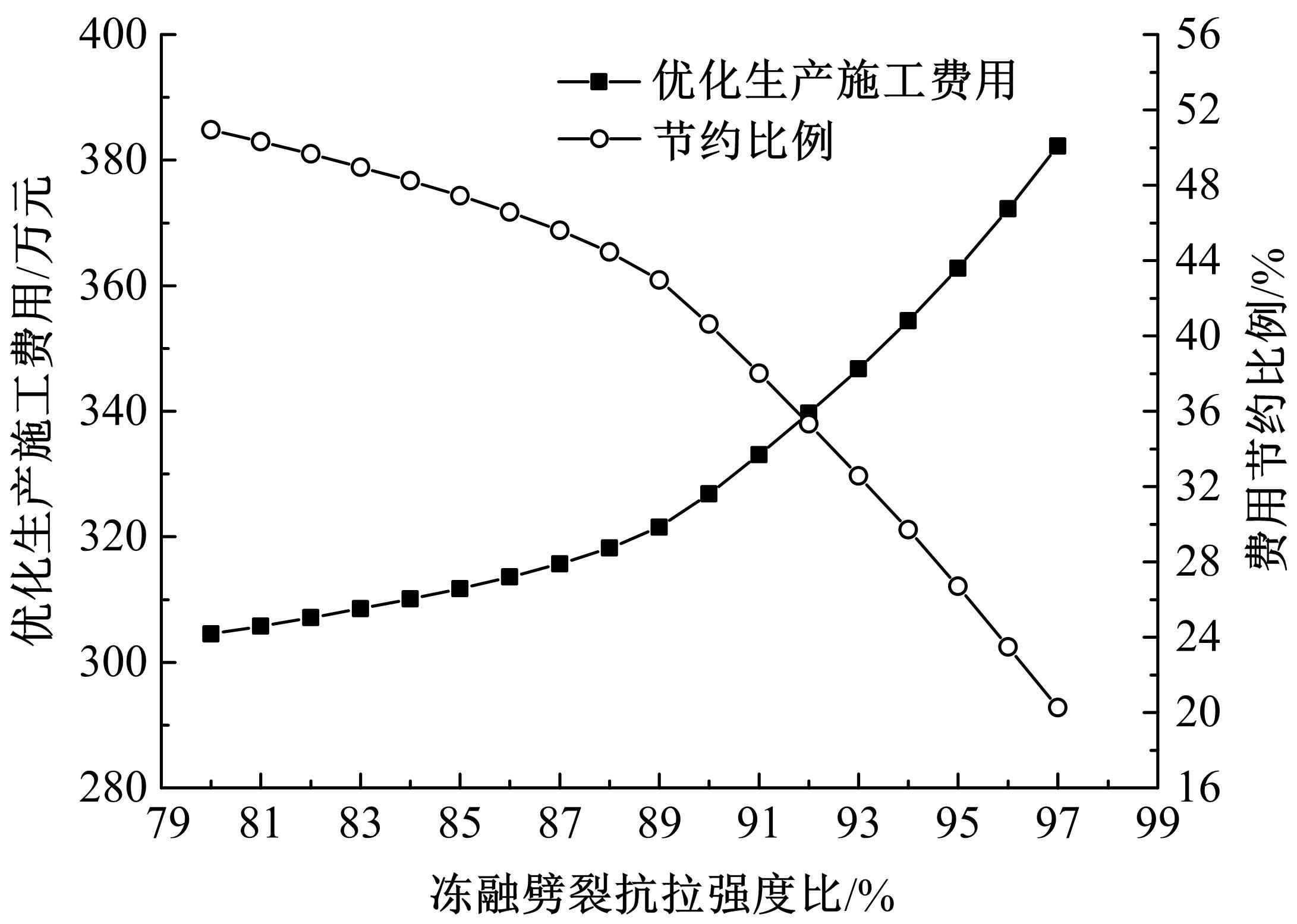
为了克服厂拌热再生沥青路面水稳定性不足的风险,以水稳定为控制指标,在性能-费用模型的基础上优化其材料设计。首先,采用响应面法建立了沥青混合料回收料掺量、沥青含量、矿料级配与水稳定性的二次回归模型,构建了厂拌热再生施工全过程的生产施工费用模型,提出了基于性能-费用的再生沥青混合料材料优化设计模型。然后,结合遗传算法、线性综合评价方法,求取了优化的材料设计参数。结果表明:响应面法可以有效解决多因素影响规律的建模分析问题;沥青混合料回收料掺量、沥青含量、矿料级配对再生沥青混合料的水稳定性具有显著影响;以福银高速三明段为算例,相同水稳定性控制目标下的优化后费用较实际降低了26.7%,优化后的材料参数如下:沥青混合料回收料掺量为51%、沥青含量为4.61%、级配参数为0.445。
中图分类号:
- U416.2
| 1 | Gao Jie, Yang Jian-gang, Yu Di, et al. Reducing the variability of multi-source reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: a practice in China[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 278:No.122389. |
| 2 | 仰建岗,姚玉权,孙晨.不同工况对就地热再生沥青混合料性能的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(10):14-24. |
| Yang Jian-gang, Yao Yu-quan, Sun Chen. Influence of different working conditions on hot in-place recycled asphalt mixture performance[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(10):14-24. | |
| 3 | Yang Jian-gang, Tao Wen-jie, Gao Jie, et al. Measurement of particle agglomeration and aggregate breakdown of reclaimed asphalt pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 296:No.123681. |
| 4 | Madrigal D P, Lannone A, Martinez A H, et al. Effect of mixing time and temperature on cracking resistance of bituminous mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement material[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(8):No.04017058. |
| 5 | 左锋,叶奋,宋卿卿. RAP掺量对再生沥青混合料路用性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(4):1403-1410. |
| Zuo Feng, Ye Fen, Song Qing-qing. Influence of RAP content on road performance of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4):1403-1410. | |
| 6 | Farooq M A, Mir M S, Sharma A. Laboratory study on use of RAP in WMA pavements using rejuvenator[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 168(20):61-72. |
| 7 | Zhu Yue-feng, Li Yan-wei, Si Chun-di, et al. Laboratory evaluation on performance of fiber-modified asphalt mixtures containing high percentage of RAP[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020(4):1-9. |
| 8 | Lu D X, Saleh M, Nguyen N H T. Effect of rejuvenator and mixing methods on behaviour of warm mix asphalt containing high RAP content[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 197(10):792-802. |
| 9 | Zhou Zhou, Gu Xing-yu, Li Qiang, et al. Use of rejuvenator, styrene-butadiene rubber latex, and warm-mix asphalt technology to achieve conventional mixture performance with 50% reclaimed asphalt pavement[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2016, 2575(1):160-167. |
| 10 | Kusam A, Malladi H, Tayebali A A, et al. Laboratory evaluation of workability and moisture susceptibility of warm-mix asphalt mixtures containing recycled asphalt pavements[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2016, 29(5):No.04016276. |
| 11 | 周刚,李培国,陈天泉,等. 聚酯纤维及沥青对高RAP掺量沥青混合料路用性能的研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版,2016,35(4):40-46, 105. |
| Zhou Gang, Li Pei-guo, Chen Tian-quan, et al. Polyester fiber content and asphalt content's impact on the road performance of high RAP content asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Sciences),2016, 35(4):40-46, 105. | |
| 12 | Jahanbakhsh H, Karimi M M, Naseri H, et al. Sustainable asphalt concrete containing high reclaimed asphalt pavements and recycling agents: Performance assessment, cost analysis, and environmental impact[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 244: No.118837. |
| 13 | 单景松,李峰,杜贝贝. 基于价值工程的国省道沥青路面结构决策[J]. 公路交通科技, 2014, 31(1):26-31. |
| Shan Jing-song, Li Feng, Du Bei-bei. Decision-making of asphalt pavement structure of national and provincial highways based on value engineering[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2014, 31(1):26-31. | |
| 14 | Bressi S, Pittet M, Dumont A G, et al. A framework for characterizing RAP clustering in asphalt concrete mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 106: 564-574. |
| 15 | 靳卫东, 梁春雨. 公路施工组织与概预算[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020. |
| 16 | 马涛, 赵永利, 黄晓明. 沥青路面厂拌热再生关键技术[M]. 南京:东南大学出版社, 2015. |
| 17 | 张文修, 梁怡. 遗传算法的数学基础[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2003. |
| 18 | 熊颖,陈维,姚玉权,等. 基于马歇尔指标的就地热再生沥青混合料再生剂用量分析[J]. 公路交通科技:应用技术版,2019,15(8):80-84. |
| Xiong Ying, Chen Wei, Yao Yu-quan, et al. Analysis on the amount of regenerant in hot recycling asphalt mixture based on Marshall index[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (Application Technology Edition), 2019, 15(8): 80-84. | |
| 19 | . 公路工程集料试验规程 [S]. |
| 20 | . 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程 [S]. |
| 21 | . 公路沥青路面再生技术规范 [S]. |
| 22 | 樊旭英,李印冬,李章珍,等. 再生沥青混合料级配优化设计[J]. 公路与汽运,2018(4):62-65. |
| Fan Xu-ying, Li Yin-dong, Li Zhang-zhen, et al. Gradation optimization design of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Highways & Automotive Applications,2018(4):62-65. | |
| 23 | Concha J L, Norambuena-Contreras J. Thermophysical properties and heating performance of self-healing asphalt mixture with fibres and its application as a solar collector[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 178: No.115632. |
| 24 | . 公路沥青路面施工技术规范 [S]. |
| [1] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [2] | 张立杰,阿喜塔,田笑,李稳. 基于Gamma过程的加速退化试验多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 361-367. |
| [3] | 赵泓荀,杨兆军,陈传海,田海龙,王立平. 考虑参数权重的数控机床电主轴加速试验优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 409-416. |
| [4] | 章子玲,胡雄,亓寅,王微,陶志强,刘志峰. 基于向量投影响应面的数控机床几何误差分配方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 384-391. |
| [5] | 董伟智,张爽,朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [6] | 冉武平,陈慧敏,李玲,冯立群. 干湿循环下粗粒土回弹模量演变规律及模型预估和修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2079-2086. |
| [7] | 文畅平,任睆遐. 基于Lade模型的生物酶改良膨胀土双屈服面本构关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1716-1723. |
| [8] | 许哲谱,杨群. 基于实时路况地图的短期养护作业开始时间优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1763-1774. |
| [9] | 李卫,张怀亮,瞿维. 随机振动环境下液压直管道设计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1222-1229. |
| [10] | 王元元,孙璐,刘卫东,薛金顺. 测量路面三维纹理双目重构算法的约束改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. |
| [11] | 彭勇,杨汉铎,陆学元,李彦伟. 基于离散元法的空隙特征对沥青混合料虚拟剪切疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [12] | 朱伟刚,朱超,张亚球,魏海斌. 基于卷积格网曲面拟合滤波算法的数字高程模型构建及质量评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [13] | 程永春,李赫,李立顶,王海涛,白云硕,柴潮. 基于灰色关联度的矿料对沥青混合料力学性能的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [14] | 宫亚峰,逄蕴泽,王博,谭国金,毕海鹏. 基于吉林省路况的新型预制装配式箱涵结构的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [15] | 阳恩慧,徐加秋,唐由之,李奥,邱延峻. 温拌剂对沥青断裂和老化性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
|
||