吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1716-1723.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200383
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于Lade模型的生物酶改良膨胀土双屈服面本构关系
- 中南林业科技大学 土木工程学院,长沙 410018
Constitutive relation with double yield surfaces of bioenzyme⁃treated expansive soil based on Lade model
- School of Civil Engineering,Central South University of Forestry and Technology,Changsha 410018,China
摘要:
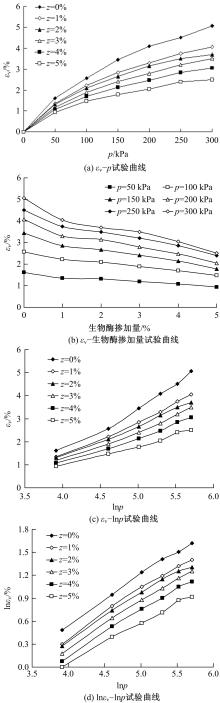
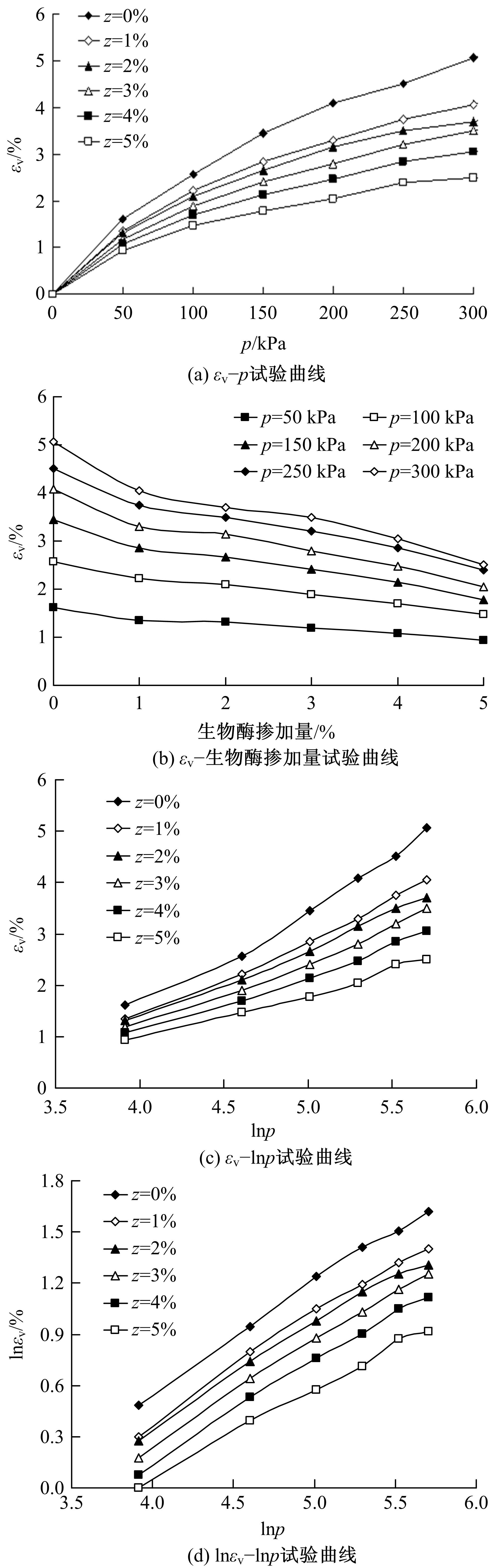
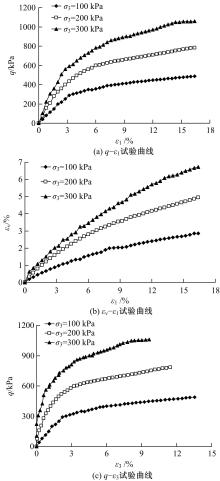
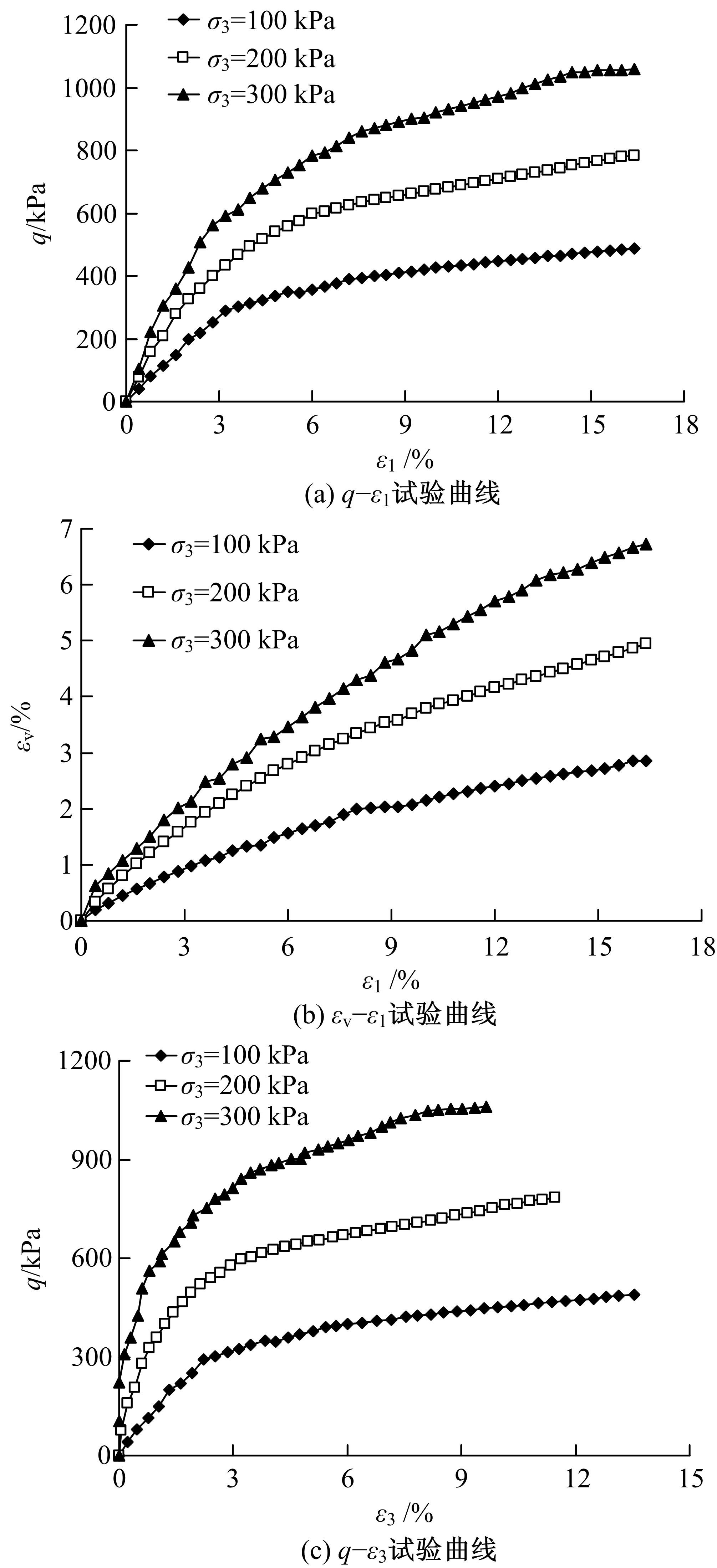
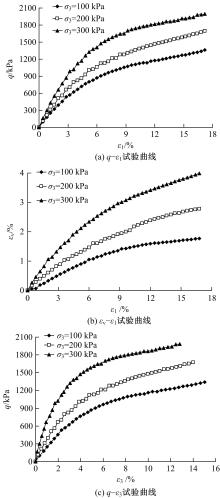
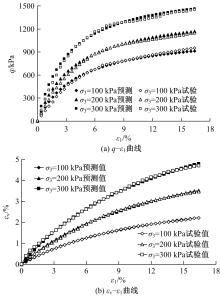
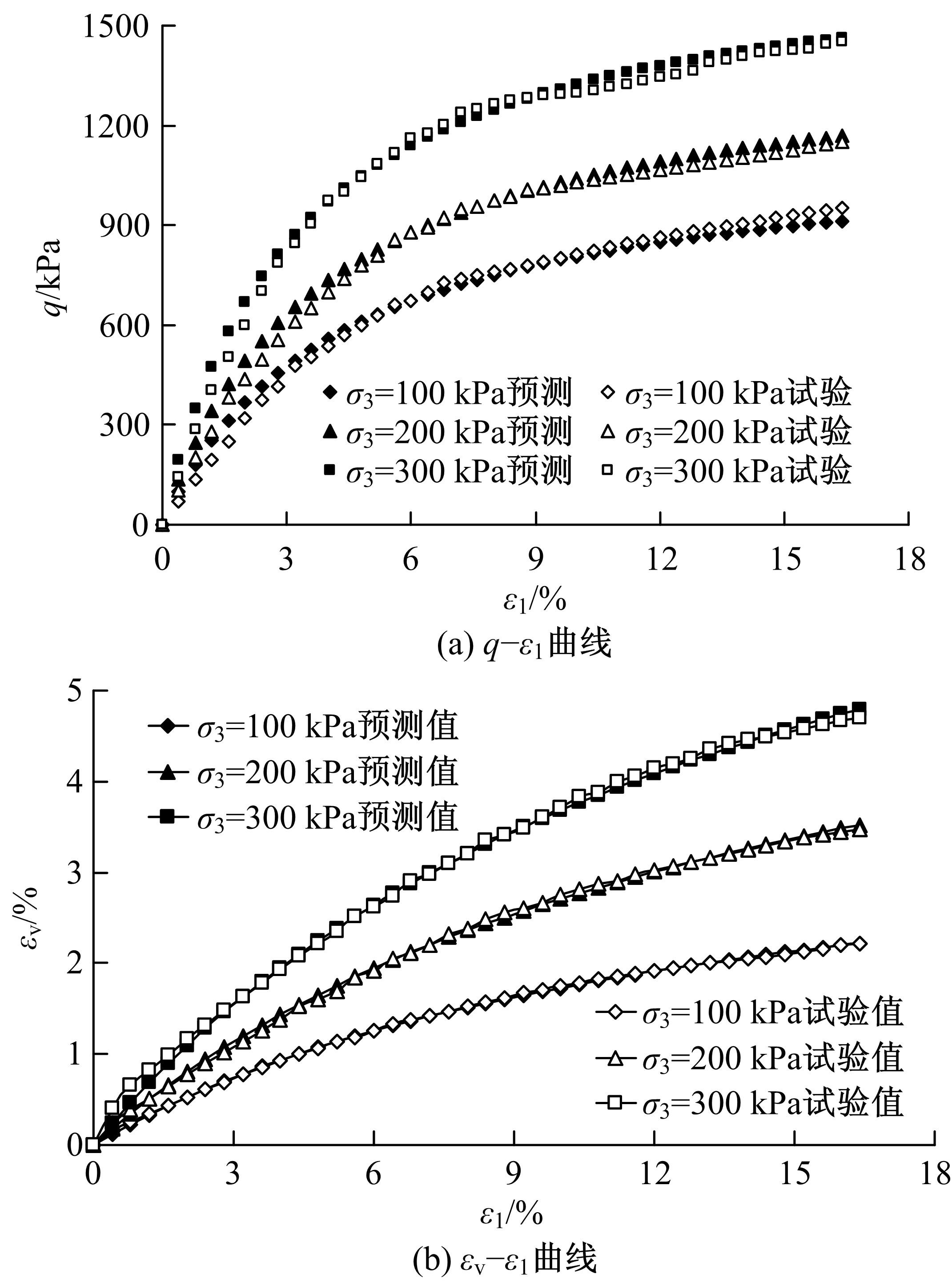
基于Lade模型,研究了生物酶改良膨胀土的双屈服面弹塑性应力-应变关系。首先,开展一系列不同生物酶掺量下改良膨胀土的等向固结排水试验、三轴固结排水剪切试验;然后,根据试验结果拟合Lade模型中的各参数与生物酶掺量之间的关系表达式;最后,建立基于生物酶掺量的Lade模型。研究表明:①体积应变
中图分类号:
- U416.1
| 1 | 戴文亭, 司泽华, 王振, 等. 剑麻纤维水泥加固土的路用性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 589-593. |
| Dai Wen-ting, Si Ze-hua, Wang Zhen, et al. Test on road performance of soils stabilized by sisal fiber and ionic soil stabilizer with cement[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 589-593. | |
| 2 | 宫亚峰, 申杨凡, 谭国金, 等. 不同孔隙率下纤维土无侧限抗压强度[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| Gong Ya-feng, Sheng Yang-fan, Tan Guo-jin, et al. Unconfined compressive strength of fiber soil with different porosity[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. | |
| 3 | Venkatasubramanian C, Dhinakran G. Effect of bio-enzymatic soil stabilization on unconfined compressive strength and California bearing ratio[J]. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2011, 6(5): 295-298. |
| 4 | dos Santos L R, Crispim F A, del Paulo P R. Estabilização de solos com um aditivo a base de Enzimas para fins rodoviários[J]. Engineering and Science, 2018, 7(3): 2-11. |
| 5 | Mukesh T S, Bharath K J, Gokulraja B, et al. Comparitive analysis on soil properties by adding conventional stabilizer with enzymatic stabilizer[J]. International Journal of Advanced Science and Engineering Research, 2018, 3(1): 30-36. |
| 6 | Naagesh S, Gangadhara S. Swelling behaviour of bio-enzyme treated expansive soil[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences and Engineering, 2011, 4(3): 555-560. |
| 7 | 戴北冰, 徐锴, 杨峻, 等. 基于生物酶的固土技术在香港的应用研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(6): 1735-1742. |
| Dai Bei-bing, Xu Kai, Yang Jun, et al. An investigation into application of bio-enzyme-based soil stabilization technology to Hong Kong[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(6): 1735-1742. | |
| 8 | 曾娟娟, 文畅平, 苏伟, 等. 基于生物酶改良膨胀土的试验研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2017, 33(5): 69-73. |
| Zeng Juan-juan, Wen Chang-ping, Su Wei, et al. Experiment research of bio-enzyme expansive soil modified[J]. Building Science, 2017, 33(5): 69-73. | |
| 9 | 曾娟娟, 文畅平, 包嘉邈, 等. 生物酶改性膨胀土室内三轴试验研究[J]. 中国科技论文, 2017, 12(6): 660-665. |
| Zeng Juan-juan, Wen Chang-ping, Bao Jia-miao, et al. Study on bio-enzyme-treated expansive soil by laboratory triaxial test[J]. China Science Paper, 2017, 12(6): 660-665. | |
| 10 | 曾娟娟, 文畅平, 刘子健. 生物酶改良膨胀土的压缩特性[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2018, 40(3): 133-138. |
| Zeng Juan-juan, Wen Chang-ping, Liu Zi-jian. Characteristics of compressibility of bio-enzyme expansive soil modified[J]. Journal of Civil,Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2018, 40(3): 133-138. | |
| 11 | Lade P V, Duncan J M. Elasto-plastic stress-strain theory for cohesionless soil[J]. ASCE Journal of Geotechnical Engineering Division, 1975, 101: 1037-1053. |
| 12 | Lade P V. Elasto-plastic stress-strain theory for cohesionless soil with curved yield surfaces[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1977, 13(11): 1019-1035. |
| 13 | 陈晓平, 杨光华, 杨雪强. 土的本构关系[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2011. |
| 14 | Kondner R L. Hyperbolic stress-strain response:cohesive soils[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1963, 89(1): 115-143. |
| 15 | Janbu N. Soil compressibility as determined by odometer and triaxial tests[C]∥Proceedings of European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Wiesbaden, Germany, 1963: 19-25. |
| [1] | 王元元,孙璐,刘卫东,薛金顺. 测量路面三维纹理双目重构算法的约束改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. |
| [2] | 彭勇,杨汉铎,陆学元,李彦伟. 基于离散元法的空隙特征对沥青混合料虚拟剪切疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [3] | 朱伟刚,朱超,张亚球,魏海斌. 基于卷积格网曲面拟合滤波算法的数字高程模型构建及质量评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [4] | 程永春,李赫,李立顶,王海涛,白云硕,柴潮. 基于灰色关联度的矿料对沥青混合料力学性能的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [5] | 宫亚峰,逄蕴泽,王博,谭国金,毕海鹏. 基于吉林省路况的新型预制装配式箱涵结构的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [6] | 阳恩慧,徐加秋,唐由之,李奥,邱延峻. 温拌剂对沥青断裂和老化性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
| [7] | 戴文亭,司泽华,王振,王琦. 剑麻纤维水泥加固土的路用性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 589-593. |
| [8] | 方宇,孙立军. 基于生存分析的城市桥梁使用性能衰变模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 557-564. |
| [9] | 王芳,李晓光,郭慧,胡佳. 基于驾驶员视觉兴趣区的沙漠草原公路曲线间直线段线形指标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 114-120. |
| [10] | 王英,李萍,念腾飞,姜继斌. 基于动水冲刷作用的沥青混合料短期水损害特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [11] | 万平,吴超仲,马晓凤. 基于ROC曲线和驾驶行为特征的驾驶愤怒强度判别阈值[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [12] | 熊锐,乔宁,褚辞,杨发,关博文,盛燕萍,牛冬瑜. 掺盐沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| [13] | 朱春凤,程永春,梁春雨,肖波. 硅藻土⁃玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青混合料路用性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [14] | 狄胜同,贾超,乔卫国,李康,童凯. 橡胶集料混凝土细观损伤特性的加载速率效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [15] | 张云龙,周刘光,王静,吴春利,吕翔. 冻融对粉砂土力学特性及路堤边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
|
||