吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1222-1229.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200321
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
随机振动环境下液压直管道设计方法
- 1.中南大学 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
2.中南大学 机电工程学院,长沙 410083
Design method of hydraulic straight pipe under random vibration
Wei LI1,2( ),Huai-liang ZHANG1,2(
),Huai-liang ZHANG1,2( ),Wei QU1,2
),Wei QU1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of High Performance and Complex Manufacturing,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China
2.College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China
摘要:
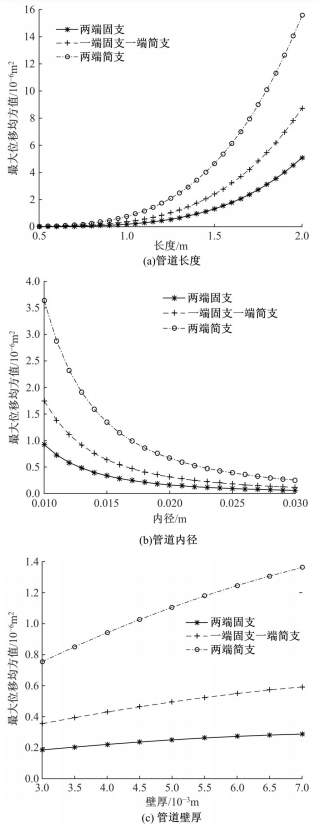
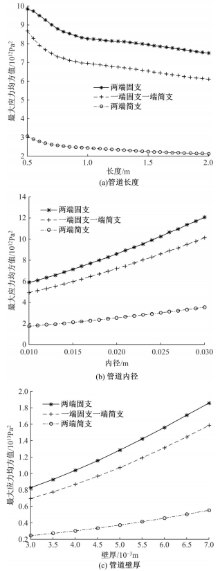
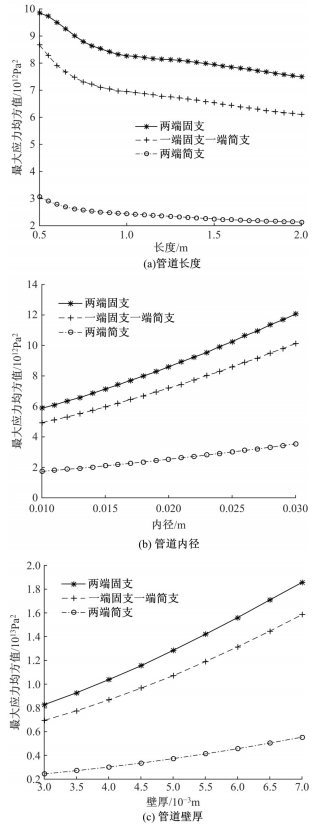
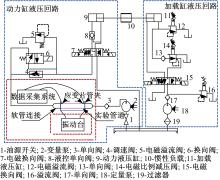
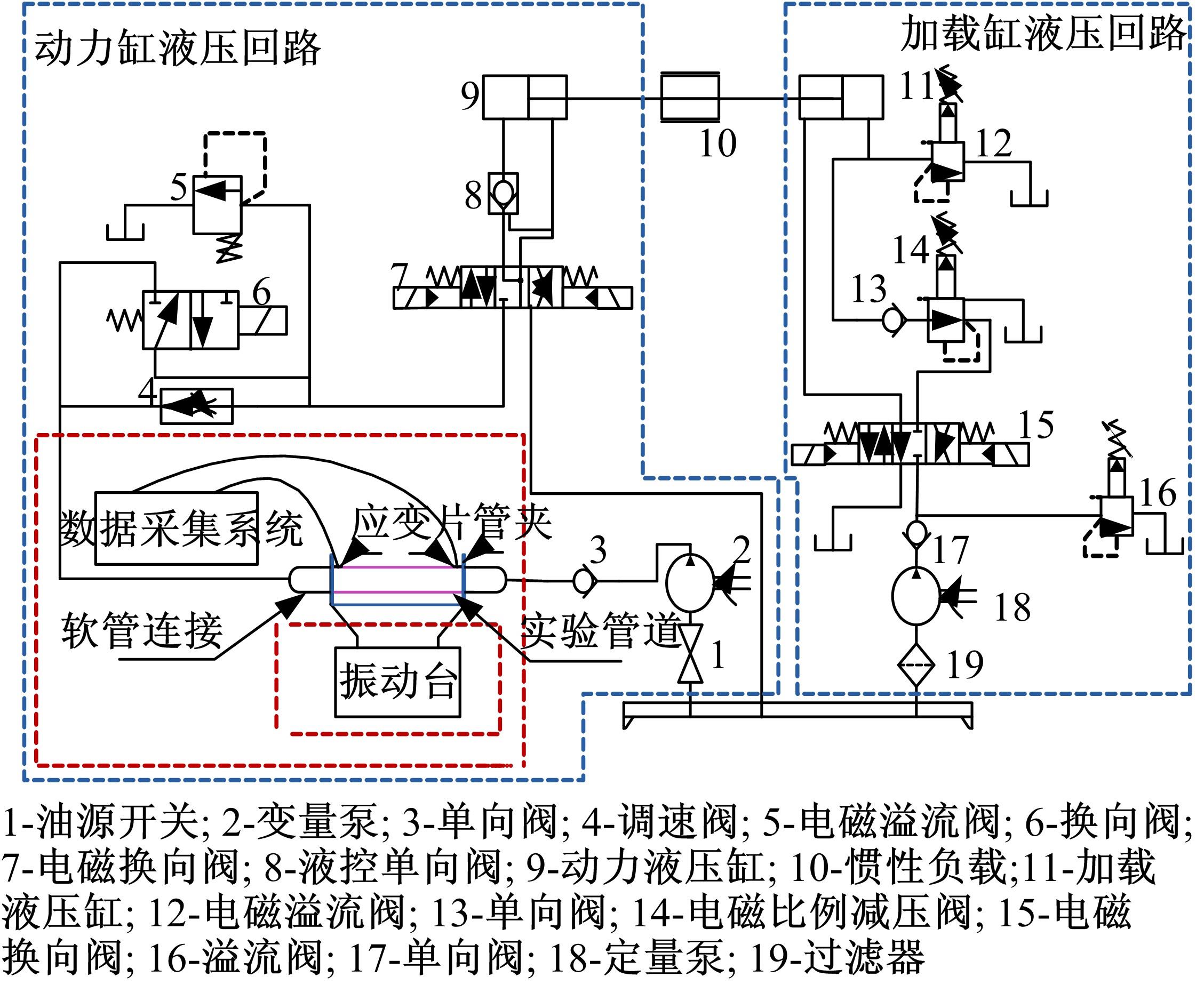
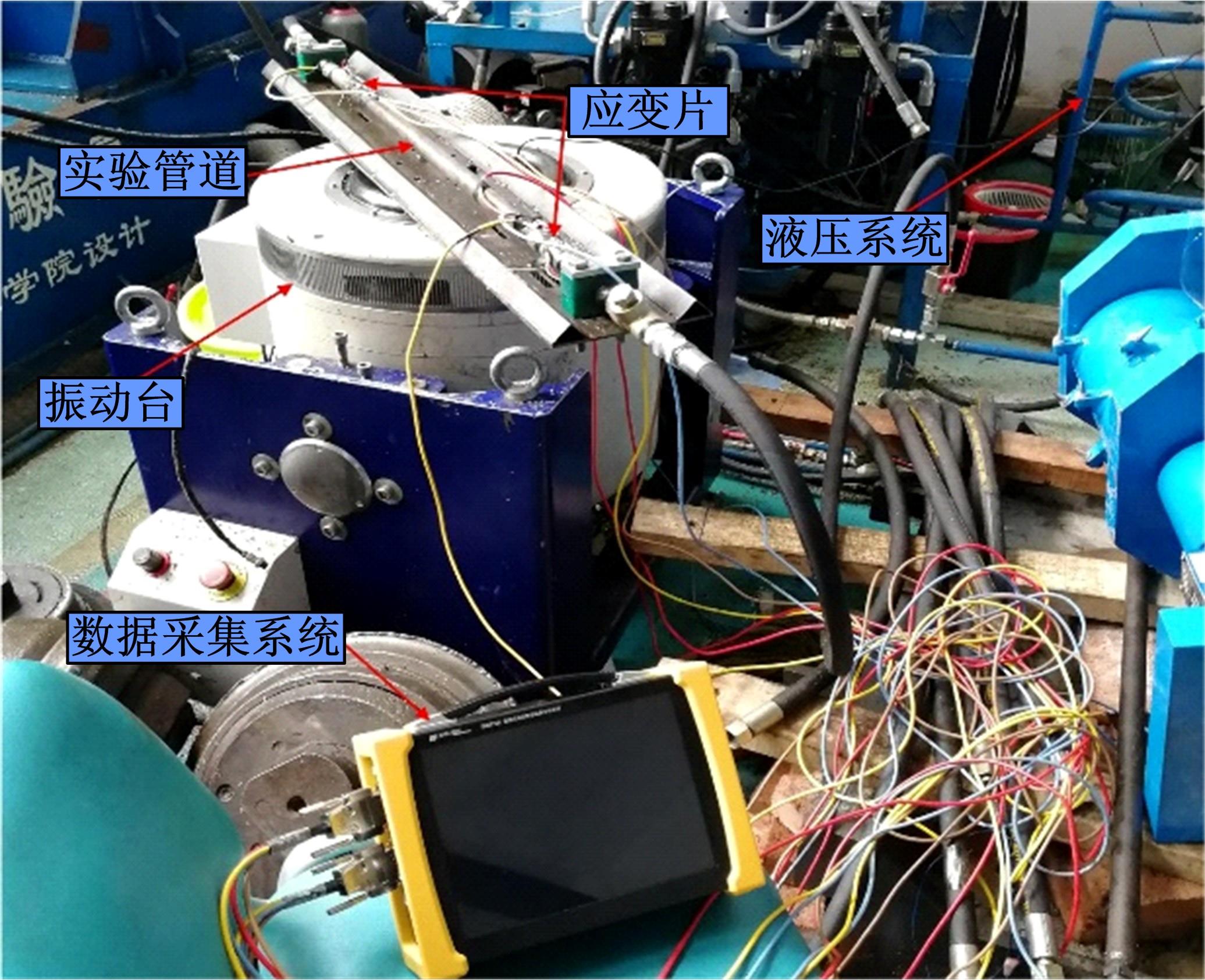
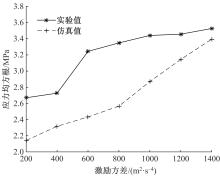
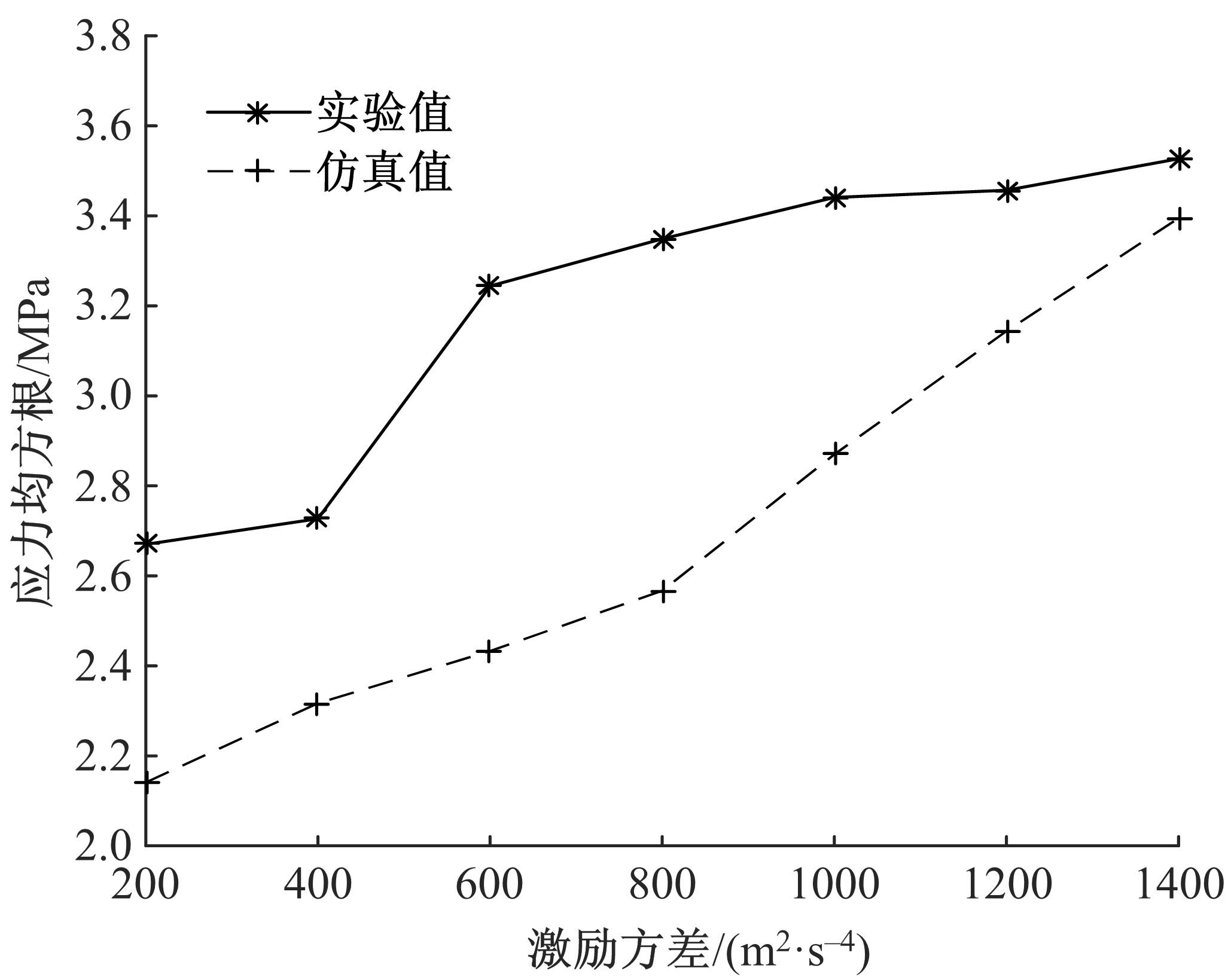
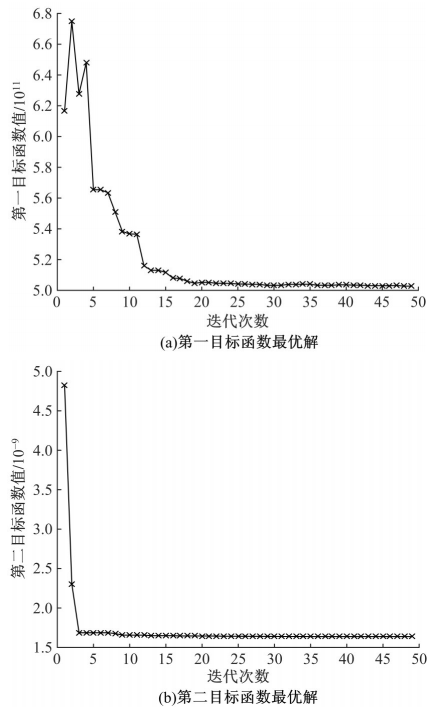
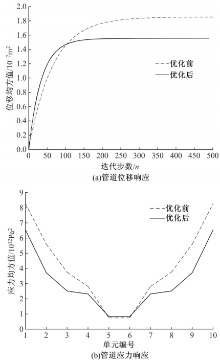
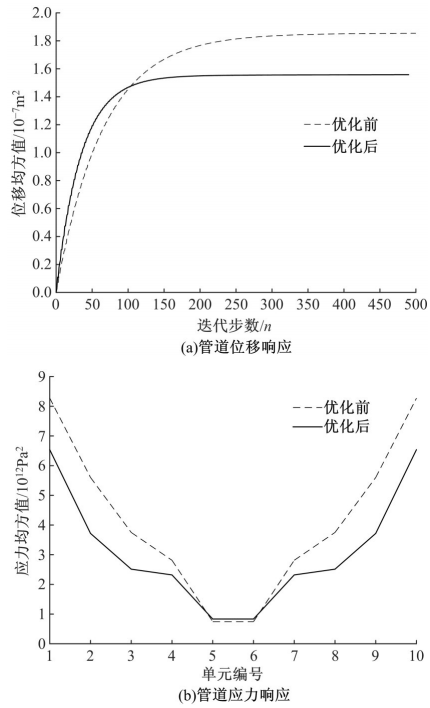
为了减小硬岩掘进机(TBM)工作过程中产生的随机振动对其液压系统中的液压直管道位移和应力的影响,建立了随机振动环境下液压直管道设计模型,并采用实验验证了模型的正确性。分析了管道结构参数对液压直管道应力响应和位移响应的影响规律,发现液压直管道应力响应和位移响应随管道内径和管道长度的变化趋势是相反的,而随着管道壁厚的增大,管道最大位移响应和最大应力响应均增大。采用基于遗传算法的多目标优化算法对随机振动环境下两端固支液压直管道的结构参数进行优化设计,对比分析了设计前后管道的应力响应和位移响应,结果表明,设计后的管道最大位移均方值降低了约16.21%,最大应力均方值降低了21.04%。研究结果可为随机振动环境中液压管道的抗振设计与选型提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
- TH137.5
| 1 | 刘森,张怀亮,彭欢. 基础振动诱发的流体-管道轴向耦合振动特性[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016,42(3):610-618. |
| Liu Sen, Zhang Huai-liang, Peng Huan. Fluid-pipeline coupling vibration characteristics induced by foundation vibration[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(3):610-618. | |
| 2 | 瞿维,张怀亮,宁海辉,等. TBM液压弯管动态特性分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018,54(1):82-89. |
| Qu Wei, Zhang Huai-liang, Ning Hai-hui, et al. Dynamic characteristics of the hydraulic bend pipe on the TBM[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018,54(1):82-89. | |
| 3 | Khudayarov B A, Turaev F J. Mathematical simulation of nonlinear oscillations of viscoelastic pipelines conveying fluid[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2019,66:662-679. |
| 4 | Dai H L, Abdelkefi A, Wang L. Modeling and nonlinear dynamics of fluid-conveying risers under hybrid excitations[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2014, 81:1-14. |
| 5 | Heshmati M, Amini Y, Daneshmand F. Vibration and instability analysis of closed-cell poroelastic pipes conveying fluid[J]. European Journal of Mechanics A—Solids, 2019, 73:356-365. |
| 6 | Naji Abhari M, Ghodsian M, Ghodsian M,et al. Experimental and numerical simulation of flow in a 90° bend[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2010,21(3):292-298. |
| 7 | Tan X, Mao X Y, Ding H, et al. Vibration around non-trivial equilibrium of a supercritical Timoshenko pipe conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 428:104-118. |
| 8 | Maalawi K Y, Abouel-Fotouh A M, El Bayoumi M, et al. Design of composite pipes conveying fluid for improved stability characteristics[J]. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 2016,11(12):7633-7639. |
| 9 | Borglund D. On the optimal design of pipes conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Fluids & Structures, 1998, 12(3):353-365. |
| 10 | Jung B S, Karney B. Fluid transients and pipeline optimization using GA and PSO: the diameter connection[J]. Urban Water Journal, 2004, 1(2):167-176. |
| 11 | Hiramoto Kazuhiko, Doki Hitoshi. Simultaneous optimal design of structural and control systems for cantilevered pipes conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004,274(3-5):685-699. |
| 12 | Wang Fa-cheng. Effective design of submarine pipe-in-pipe using finite element analysis[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 153:23-32. |
| 13 | Qu W, Zhang H, Li W, et al. Influence of support stiffness on dynamic characteristics of the hydraulic pipe subjected to basic vibration[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2018, 2018:1-8. |
| 14 | Lin Y H, Tsai Y K. Nonlinear vibrations of Timoshenko pipes conveying fluid[J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1997, 34(23):2945-2956. |
| 15 | Zhai H B, Wu Z Y, Liu Y S, et al. Dynamic response of pipeline conveying fluid to random excitation[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2011,241(8):2744-2749. |
| 16 | 谭东耀.随机振动离散分析方法[J].力学学报,1992,24(4):473-479. |
| Tan Dong-yao. Random vibration discrete analysis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 1992,24(4):473-479. |
| [1] | 叶辉,刘畅,闫康康. 纤维增强复合材料在汽车覆盖件中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 417-425. |
| [2] | 胡兴军,惠政,郭鹏,张扬辉,张靖龙,王靖宇,刘飞. 基于流固耦合的汽车气动特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1414-1419. |
| [3] | 郭昊添,徐涛,梁逍,于征磊,刘欢,马龙. 仿鲨鳃扰流结构的过渡段换热表面优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1793-1798. |
| [4] | 王扬, 王晓梅, 陈泽仁, 于建群. 基于离散元法的玉米籽粒建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1537-1547. |
| [5] | 于繁华, 刘仁云, 张义民, 张晓丽, 孙秋成. 机械零部件动态可靠性稳健优化设计的群智能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1903-1908. |
| [6] | 王靖宇, 于旭涛, 胡兴军, 郭鹏, 辛俐, 郭峰, 张扬辉. 汽车外后视镜流致振特性及其流动机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1669-1676. |
| [7] | 江海, 李敏姣, 顾守东, 张莎莎, 张凯, 焦晓阳, 刘建芳. 谐振管对驻波悬浮特性的理论分析及实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 151-156. |
| [8] | 袁哲, 徐东, 刘春宝, 李雪松, 李世超. 基于热流固耦合过程的液力缓速器叶片强度分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1506-1512. |
| [9] | 于繁华, 刘仁云, 张义民, 孙秋成, 张晓丽. 机械结构动态可靠性设计的智能计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1269-1275. |
| [10] | 齐龙, 梁仲维, 蒋郁, 马旭, 武涛, 芦玉龙, 赵柳霖. 轻型水田除草机的设计及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 1004-1012. |
| [11] | 杨一洋, 许男, 郭孔辉, 陈平. 轮胎滑水机理在钢带式高速轮胎试验台上的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 1-7. |
| [12] | 陈书明, 彭登志, 王登峰, 梁杰. 车内低频噪声声固耦合及试验优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1550-1556. |
| [13] | 武彬, 李骏, 李康, 侯福建, 蒋文虎. 发动机低摩擦优化设计及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 81-85. |
| [14] | 谭越, 马文星, 卢秀泉. 基于流固耦合的冲焊型液力变矩器焊接强度分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 928-932. |
| [15] | 焦晓阳, 刘建芳, 刘晓论, 孙旭光. 超声驻波悬浮能力特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 340-345. |
|
||