吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2761-2772.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211350
数控滚齿机工作台热-力变形分析及预测建模
- 1.重庆大学 机械与运载工程学院 重庆 400044
2.重庆大学 机械传动国家重点实验室 重庆 400044
Thermal-force deformation analysis and prediction modeling of CNC gear hobbing machine workbench
Si-bao WANG1,2( ),Zhong-zheng GUO1,2,Chi MA1,2,Shi-long WANG1,2
),Zhong-zheng GUO1,2,Chi MA1,2,Shi-long WANG1,2
- 1.College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmissions,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
摘要:
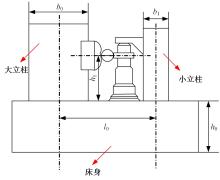
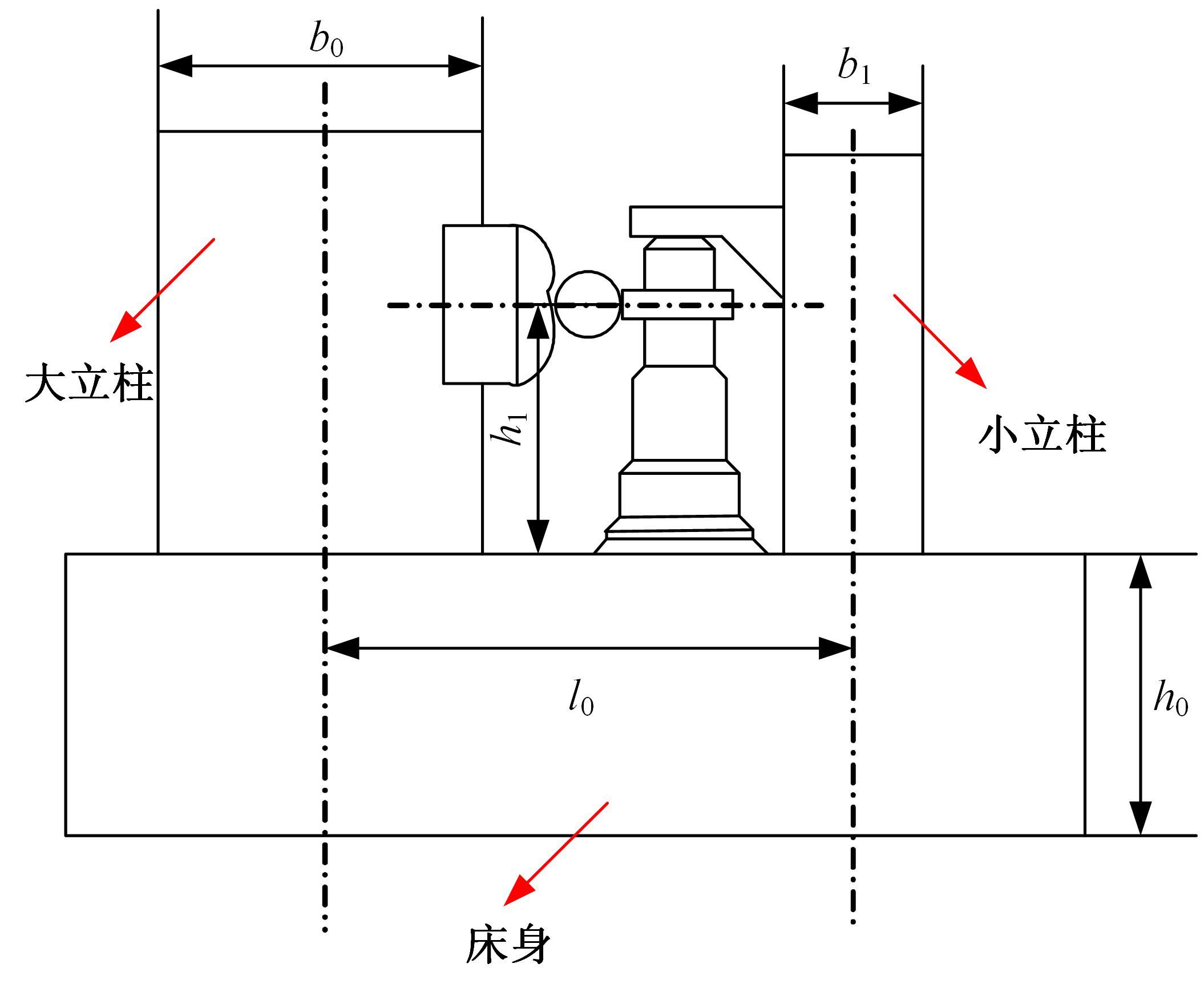
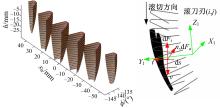
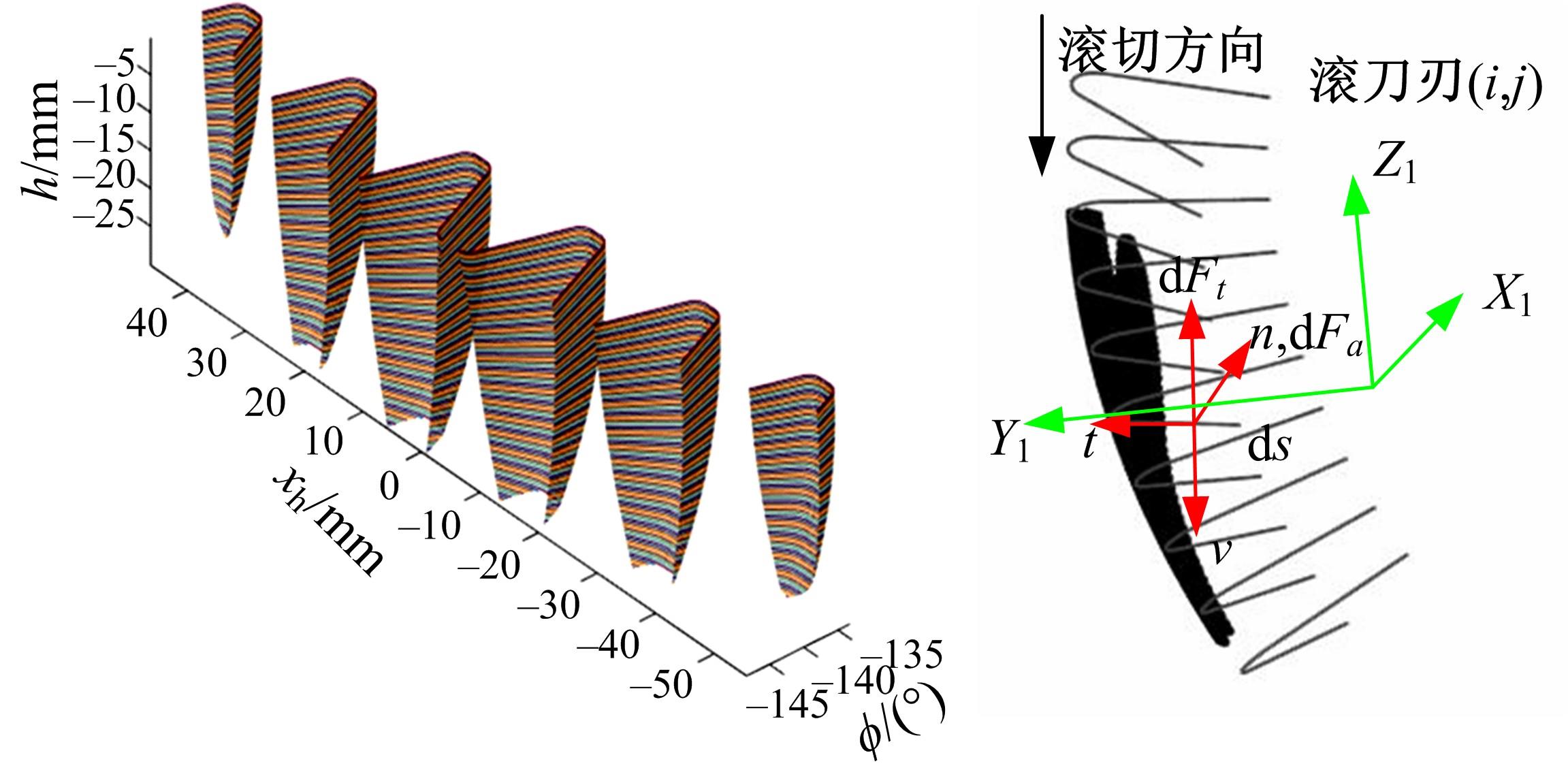
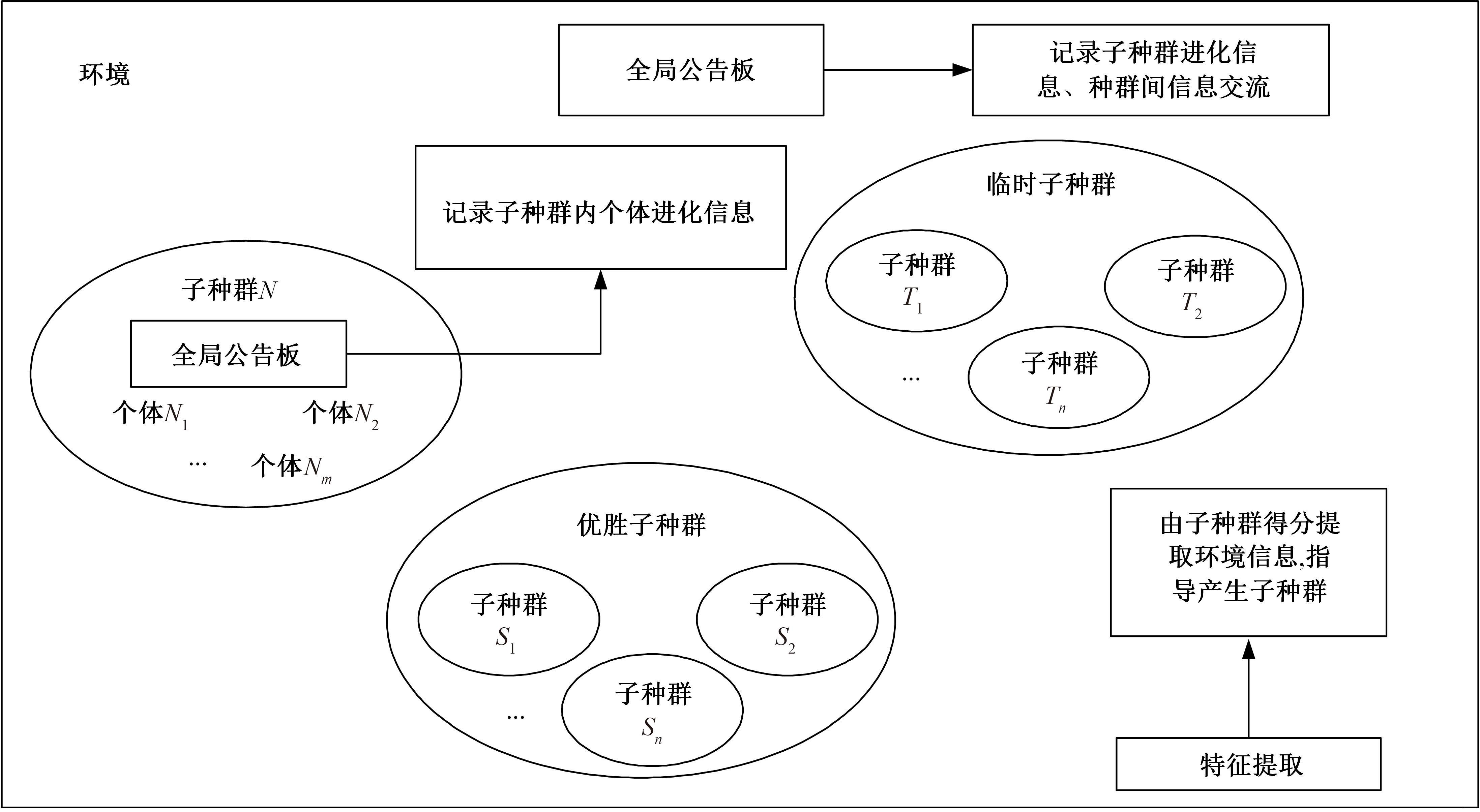
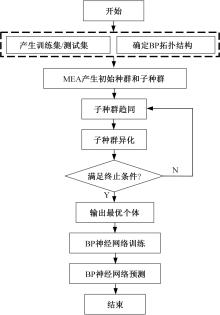
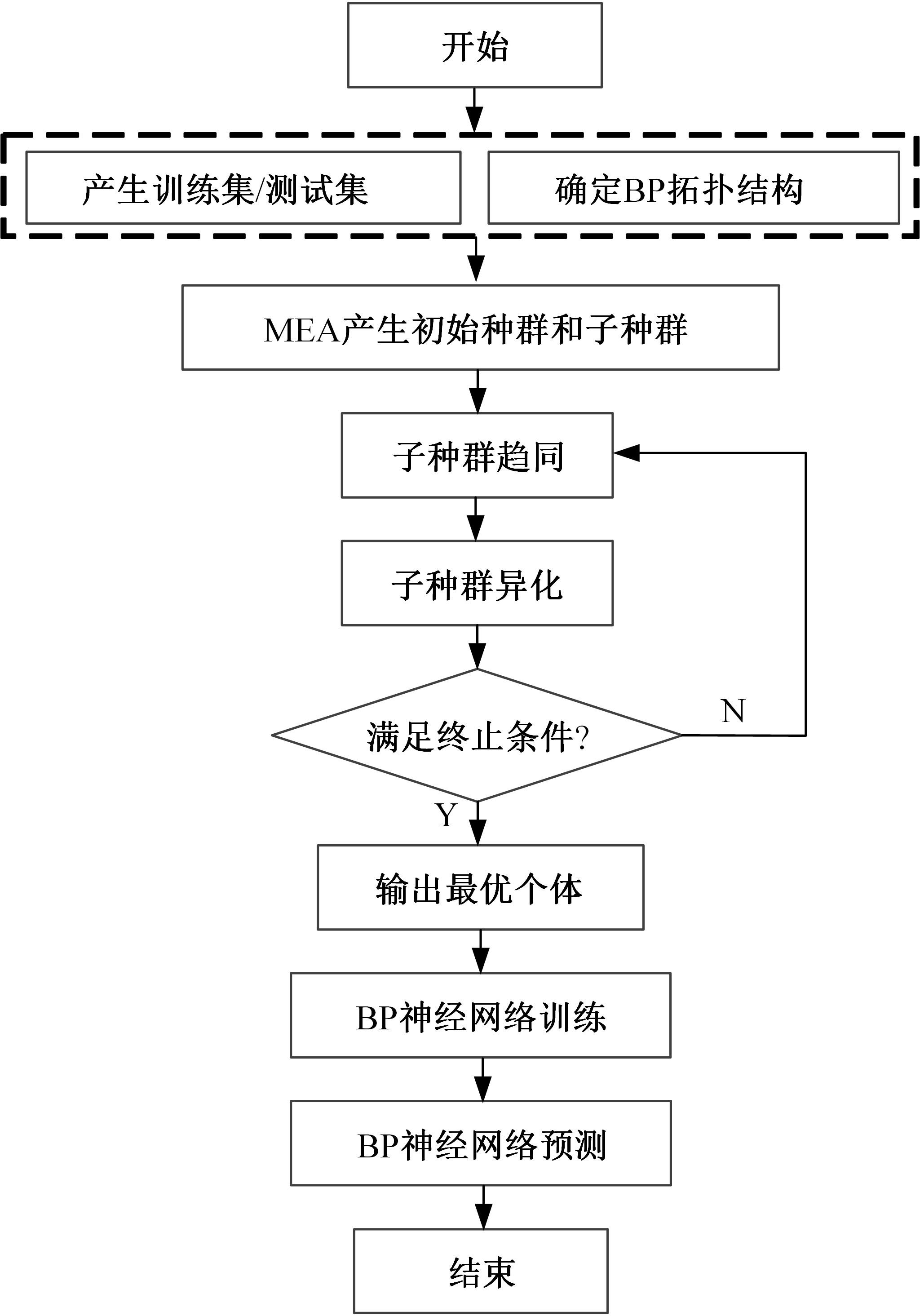
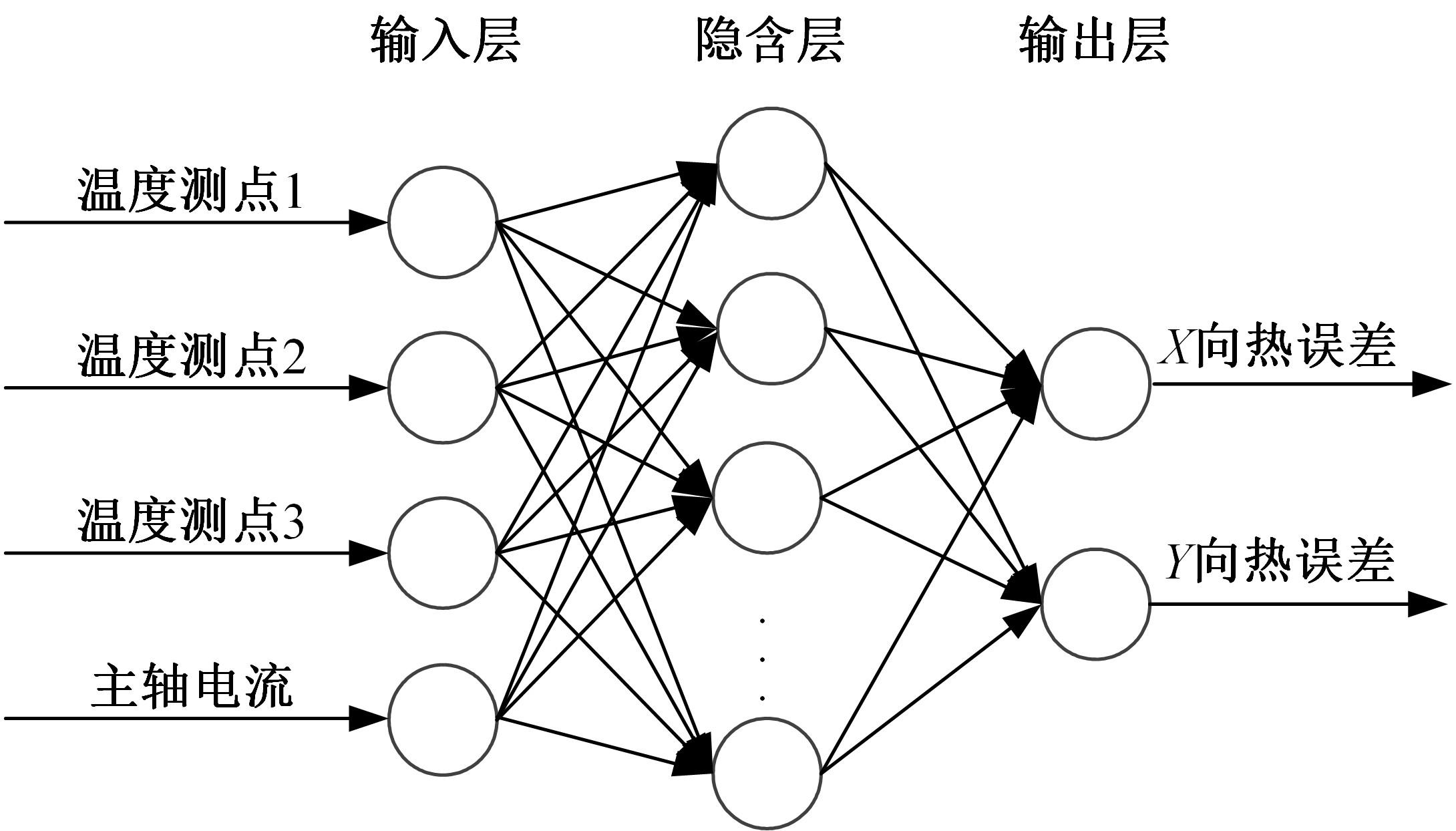
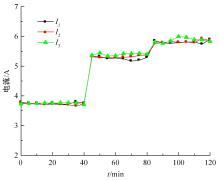
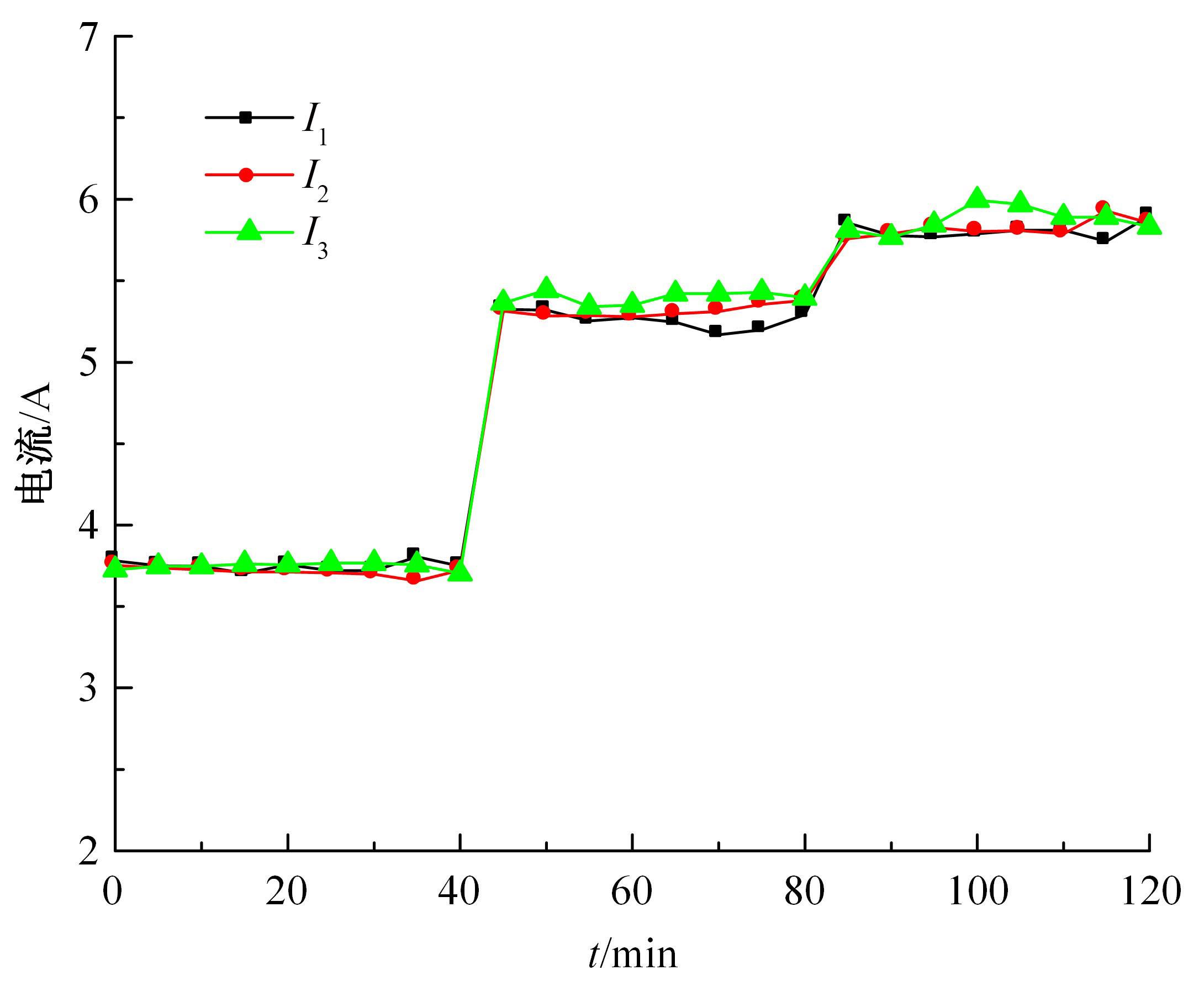
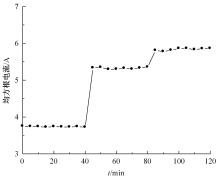
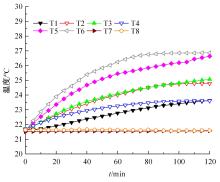
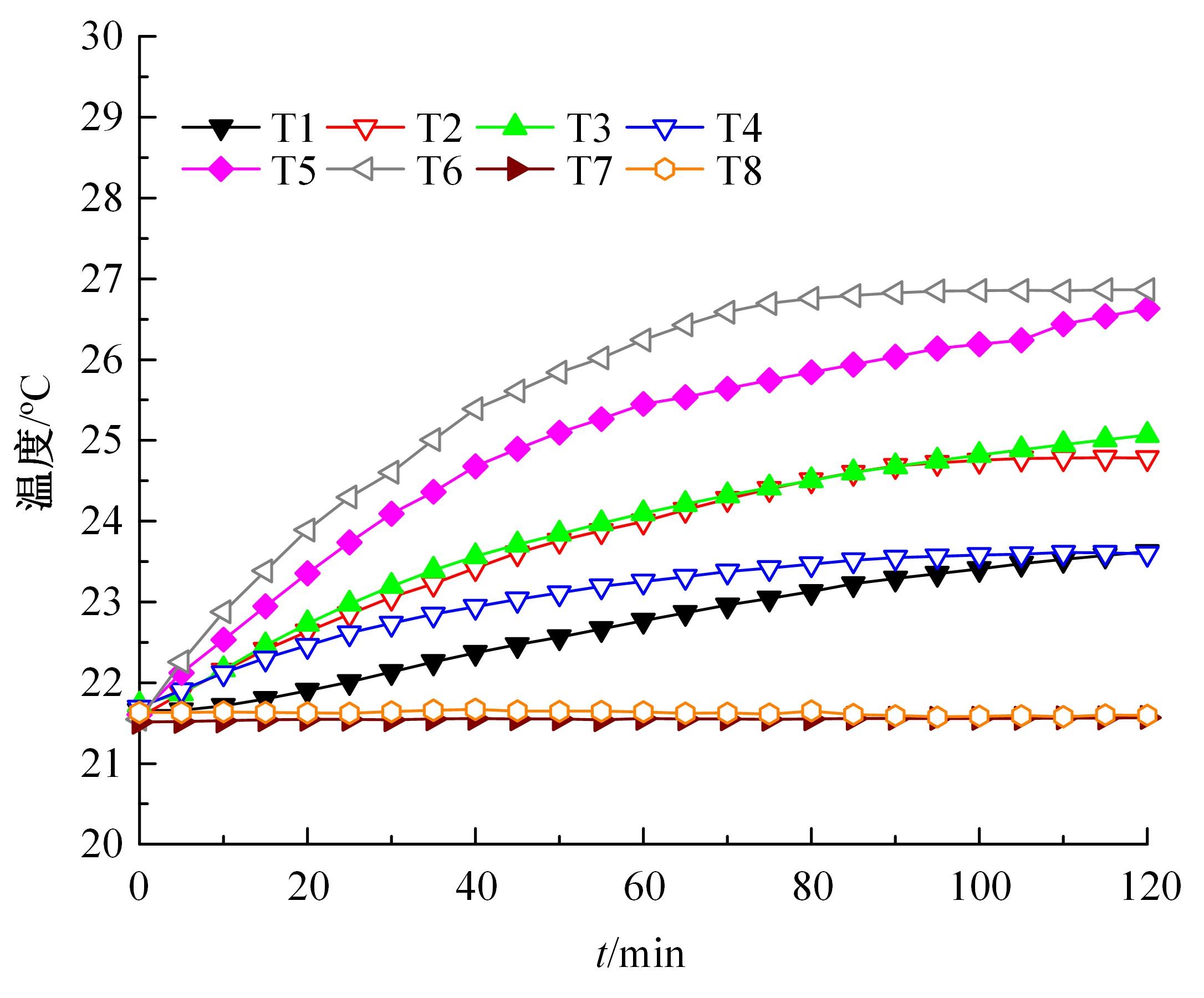
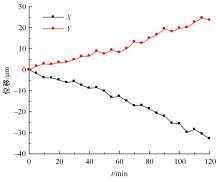
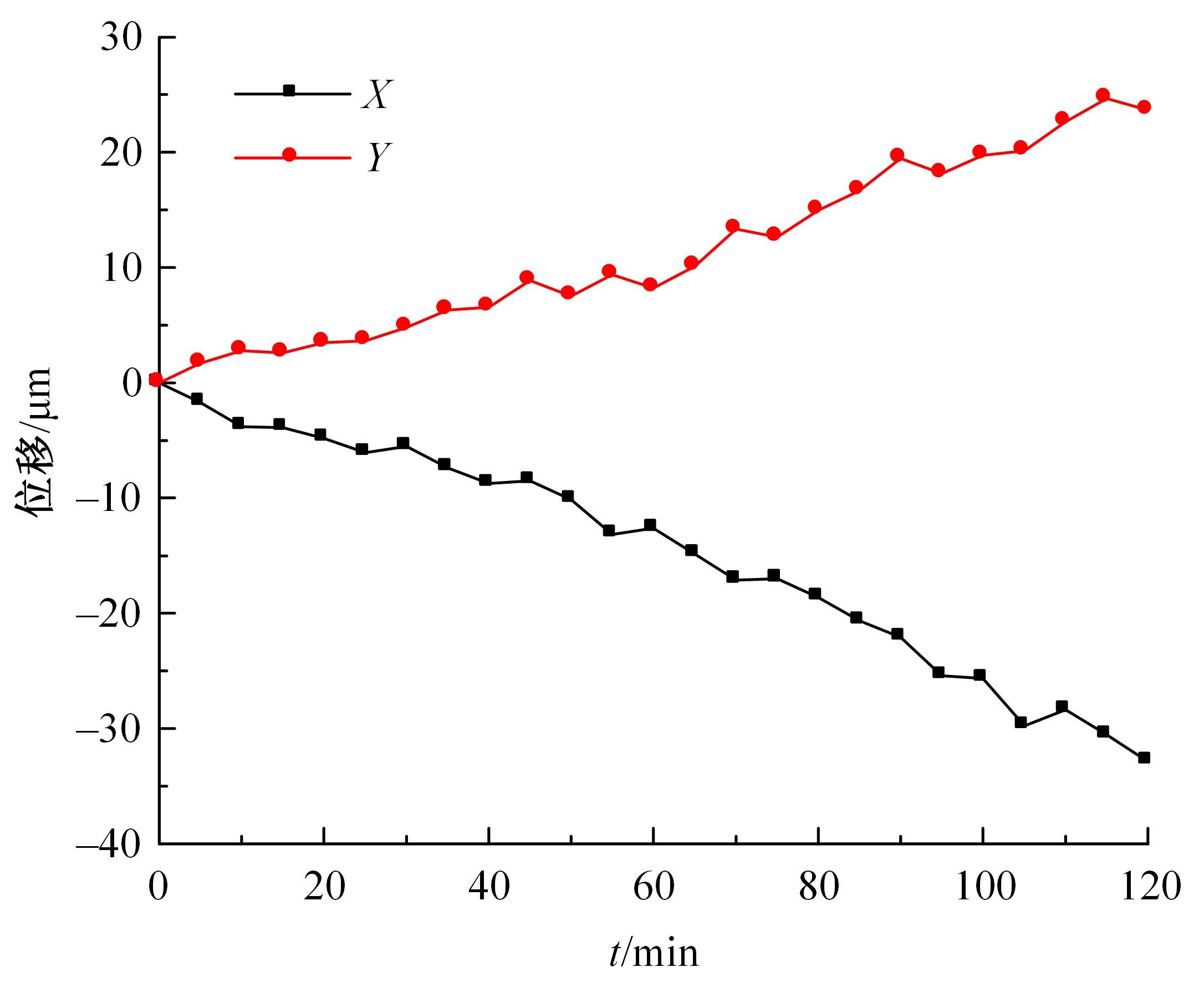
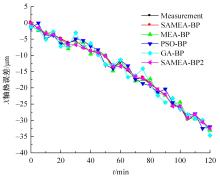
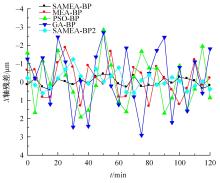
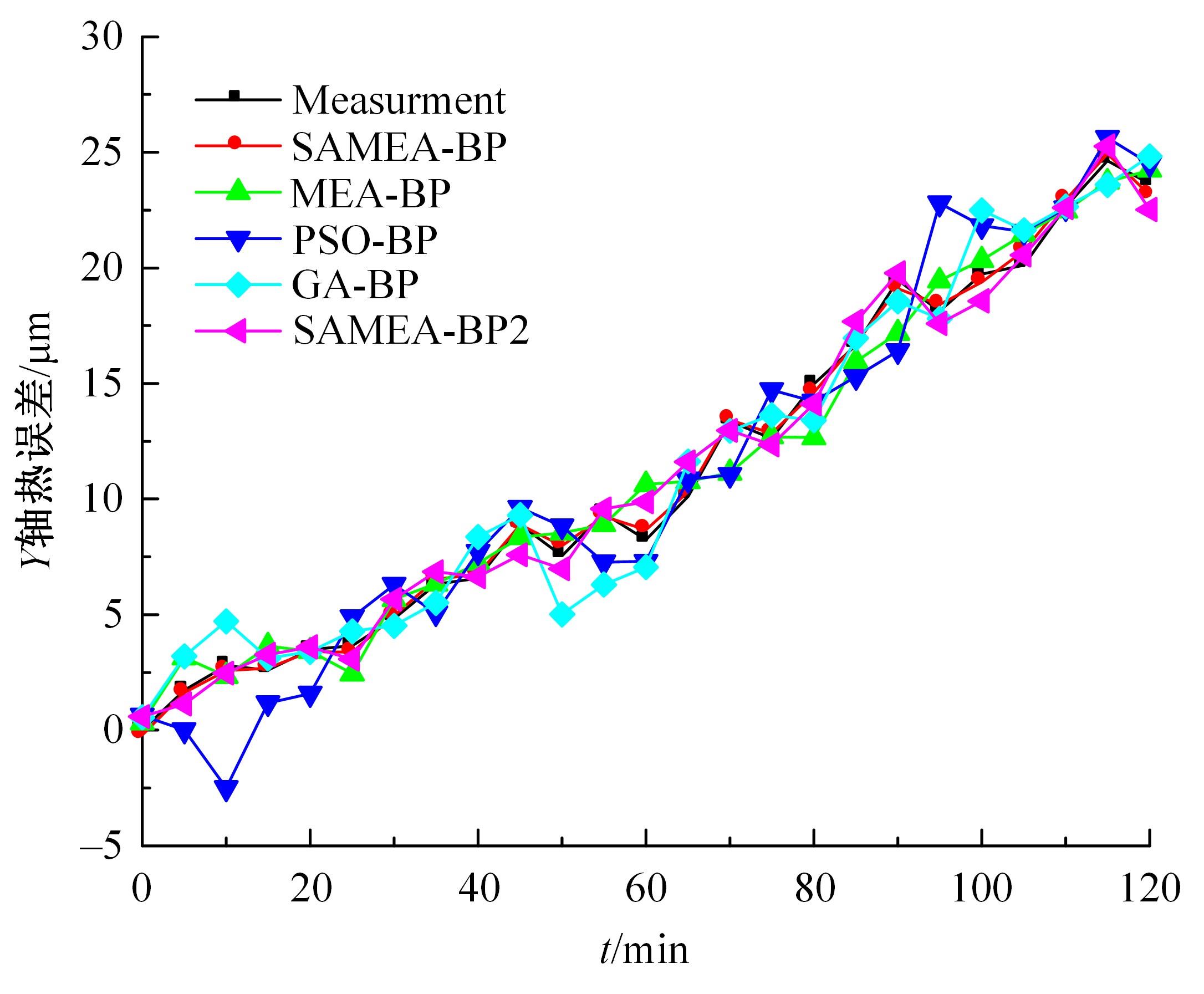
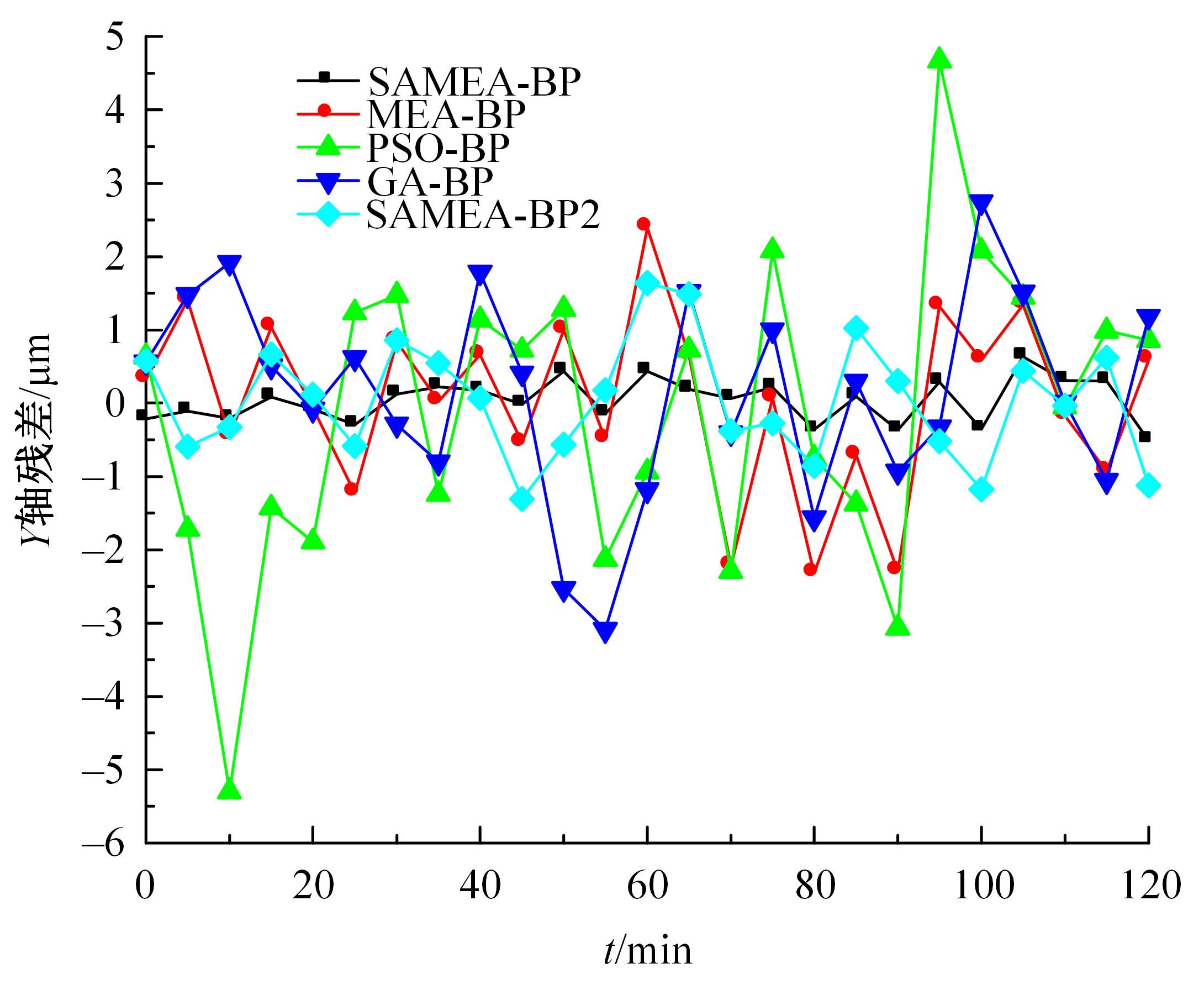
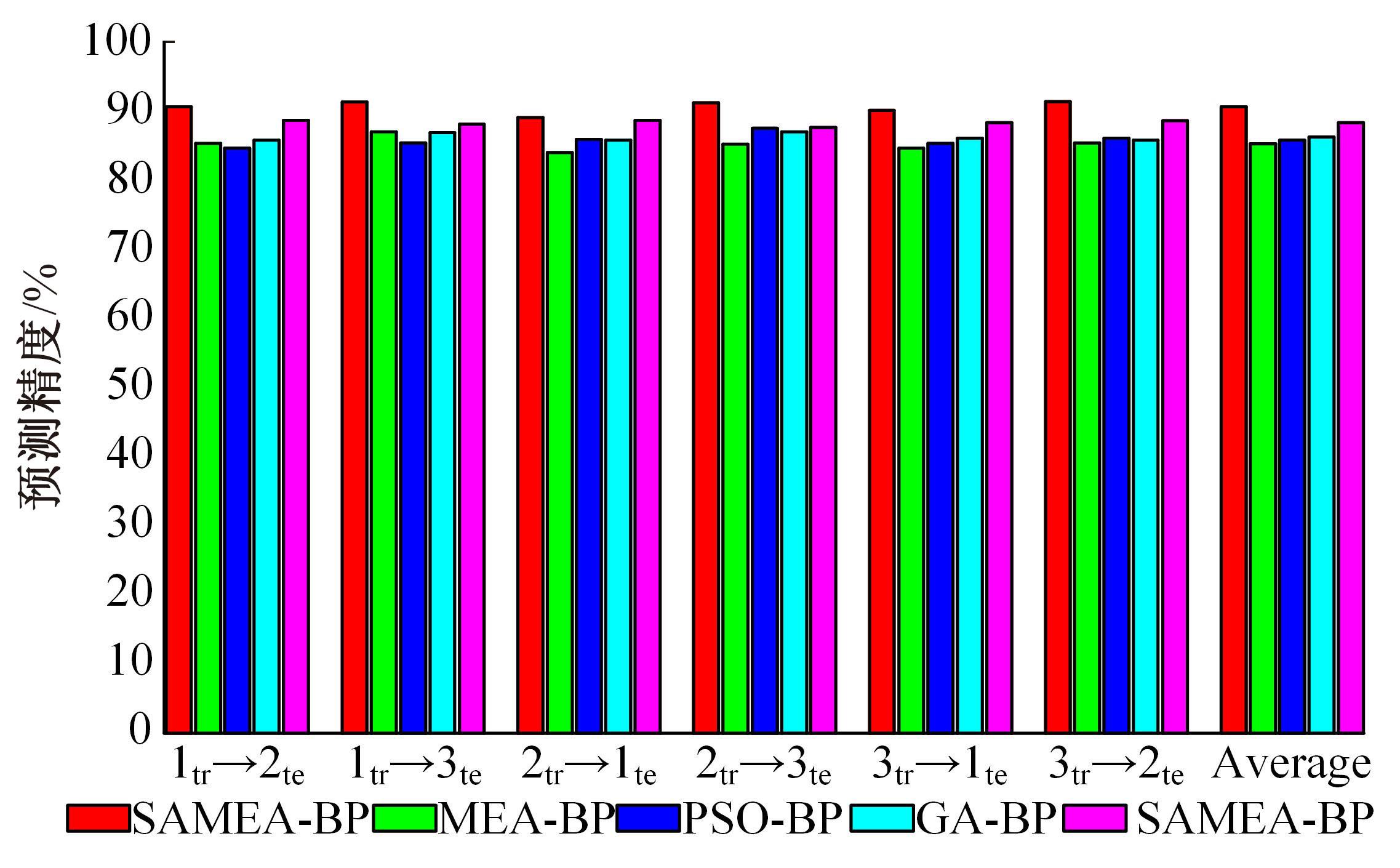
为了减小滚齿机工作台变形对加工精度的影响,对工作台热、力变形进行了研究,提出一种基于子种群自适应思维进化算法优化反向传播(SAMEA-BP)神经网络的滚齿机工作台热-力变形预测方法。通过SAMEA对BP神经网络的初始值、权重和阈值等参量进行调整,有效提升了基于神经网络的热-力变形预测准确度。结合K均值聚类策略和灰色关联分析(GRA)对影响热误差的温度测点进行耦合性和关联度分析,将热误差输入变量从8个测点减少到3个;针对滚齿加工中切削力导致的工作台变形,利用机床主轴电流表征切削力,并作为预测模型的输入变量。试验结果表明:本文模型平均预测精度为95.1%,与其他模型进行的对比分析验证了本文SAMEA-BP模型的有效性和泛化性。
中图分类号:
- TH161
| 1 | 李国龙, 陶小会, 徐凯, 等. 数控机床转台位置相关几何误差的快速测量与辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(2): 458-467. |
| Li Guo-long, Tao Xiao-hui, Xu Kai,et al. Rapid measurement and identification of position dependent geometric errors of CNC machine tool turntable[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 458-467. | |
| 2 | 李彬, 张云, 王立平, 等. 基于遗传算法优化小波神经网络数控机床热误差建模[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(21): 215-220. |
| Li Bin, Zhang Yun, Wang Li-ping,et al. Modeling for CNC machine tool thermal error based on genetic algorithm optimization wavelet neural networks[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(21): 215-220. | |
| 3 | 郭世杰, 张学炜, 张楠, 等. 机床主轴热关键点选择与典型转速热误差预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 1-10. |
| Guo Shi-jie, Zhang Xue-wei, Zhang Nan, et al. Thermal key point select and error prediction under typical speed of machine tool spindle[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 1-10. | |
| 4 | Liang Y, Su H, Lu L, et al. Thermal optimization of an ultra-precision machine tool by the thermal displacement decomposition and counteraction method[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 76(1-4): 635-645. |
| 5 | Grama S N, Mathur A, Aralaguppi R, et al. Optimization of high speed machine tool spindle to minimize thermal distortion[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2017, 58:457-462. |
| 6 | 谢杰, 黄筱调, 方成刚, 等. 磨齿机电主轴热特性及热误差建模[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 52(2): 247-254. |
| Xie Jie, Huang Xiao-diao, Fang Cheng-gang, et al. Thermal characteristics and thermal error modeling analysis for motorized spindle of gear grinding machine tool[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2018, 52(2): 247-254. | |
| 7 | Liu Y, Wang X F, Zhu X G, et al. Thermal error prediction of motorized spindle for five-axis machining center based on analytical modeling and BP neural network[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2021, 35(1): 281-292. |
| 8 | Miao E-M, Gong Y-Y, Niu P-C, et al. Robustness of thermal error compensation modeling models of CNC machine tools[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 69(9-12): 2593-2603. |
| 9 | Lei M, Jiang G, Yang J, et al. Thermal error modeling with dirty and small training sample for the motorized spindle of a precision boring machine[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 93(1-4): 571-586. |
| 10 | Xiang S, Yang J. Error map construction and compensation of a NC lathe under thermal and load effects[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 79(1-4): 645-655. |
| 11 | Tang Xian-kang, Zhao Jun, Zhang Zi-jian. Model of cutting forces prediction for gear milling considering the three-dimensional undeformed chip thickness, penetration curve and working angles[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 118(5/6): 1659-1671. |
| 12 | Umasai K, Venkata M, Pbgsn M. Mechanistic models for prediction of cutting forces and power consumption considering chip geometry[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 235(2): 479-488. |
| 13 | 陈永鹏. 高速干切滚齿多刃断续切削空间成形模型及其基础应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学机械与运载学院, 2015. |
| Chen Yong-peng. Spatial forming model of high-sppeed dry hobbong by interrupted cutting with multiple-cutting-edge and its application[D]. Chongqing: College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering, Chongqing University, 2015. | |
| 14 | Sabkhi N, Pelaingre C, Barlier C, et al. Characterization of the cutting forces generated during the gear hobbing process: spur gear[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2015, 31: 411-416. |
| 15 | Jomaa W, Songmene V, Bocher P. Predictive analytical modeling of cutting forces generated by high-speed machining of ductile and hard metals[J]. Machining Science and Technology, 2017, 21(3): 335-361. |
| 16 | 黄颖旭, 李波, 田锡天. 基于主轴电流的铣削力间接监测方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2022, 28(1): 93-101. |
| Huang Ying-xu, Li Bo, Tian Xi-tian. Indirect monitoring method of milling force based on spindle current[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 28(1): 93-101. | |
| 17 | Mostaghimi H, Park C I, Kang G, et al. Reconstruction of cutting forces through fusion of accelerometer and spindle current signals[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 68: 990-1003. |
| 18 | Panagiotis S, Harry B, Thanassis S, et al. A method for cutting force estimation through joint current signals in robotic machining[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2021, 55: 124-131. |
| 19 | Yamada Y, Kakinuma Y. Mode decoupled cutting force monitoring by applying multi encoder based disturbance observer[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 57:643-648. |
| 20 | 王国权. 数控滚齿机动态误差补偿技术研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学机械工程学院, 2015. |
| Wang Guo-quan.The Dynamic Error Compensating Technology Research of CNC Gear Hobbing Machine[D]. Hefei: College of Mechanical Engineering,Hefei University of Technology, 2015. | |
| 21 | 李根, 李文辉. 基于思维进化算法的人脸特征点跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2015, 45(2): 606-612. |
| Li Gen, Li Wen-hui. Facial feature tracking on mind evolutionary algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 606-612. |
| [1] | 杨海吉,何佳龙,李国发,王立鼎,王思远. 改进失效模式和影响分析方法在加工中心主轴系统风险分析中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 345-352. |
| [2] | 许博,李传习. 基于灰色理论的大跨度钢管混凝土拱桥承载能力检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2360-2366. |
| [3] | 邱小明, 王银雪, 姚汉伟, 房雪晴, 邢飞. 基于灰色关联的DP1180/DP590异质点焊接头工艺参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1147-1152. |
| [4] | 刘仁云,于繁华,刘军. 基于小波神经网络的简支梁桥损伤识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 413-0416. |
| [5] | 陶敏,李建桥,杨印生,李洪伟,潘燕. 金属基仿生减阻材料元素与性能量化分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(03): 367-0370. |
| [6] | 于繁华,赵宏伟,臧雪柏,刘仁云,王立江. 基于小波神经网络的变参数振动钻削仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2005, 35(03): 297-300. |
|
||