吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2773-2784.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211324
列车制动过程踏面温度场及应力⁃应变分布特性
宋剑锋1( ),黄鑫磊1,仪帅2,杨振熙3,董永刚1(
),黄鑫磊1,仪帅2,杨振熙3,董永刚1( ),李树林4
),李树林4
- 1.燕山大学 机械工程学院,河北 秦皇岛 066044
2.潍柴雷沃重工股份有限公司 收获机械研究院,山东 潍坊 261200
3.燕山大学 材料科学与工程学院,河北 秦皇岛 066044
4.太原重工轨道交通设备有限公司,太原 030022
Temperature field and stress-strain distribution of tread during train braking
Jian-feng SONG1( ),Xin-lei HUANG1,Shuai YI2,Zhen-xi YANG3,Yong-gang DONG1(
),Xin-lei HUANG1,Shuai YI2,Zhen-xi YANG3,Yong-gang DONG1( ),Shu-lin LI4
),Shu-lin LI4
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066044,China
2.Harvest Machinery Research Institute,Weichai Revo Heavy Industry Co. ,Ltd. ,Weifang 261200,China
3.School of Materials Science and Engineering,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066044,China
4.Taiyuan Heavy Industry Rail Transit Equipment Co. ,Ltd. ,Taiyuan 030022,China
摘要:
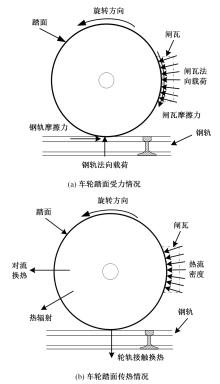
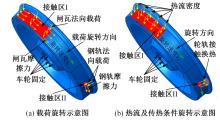
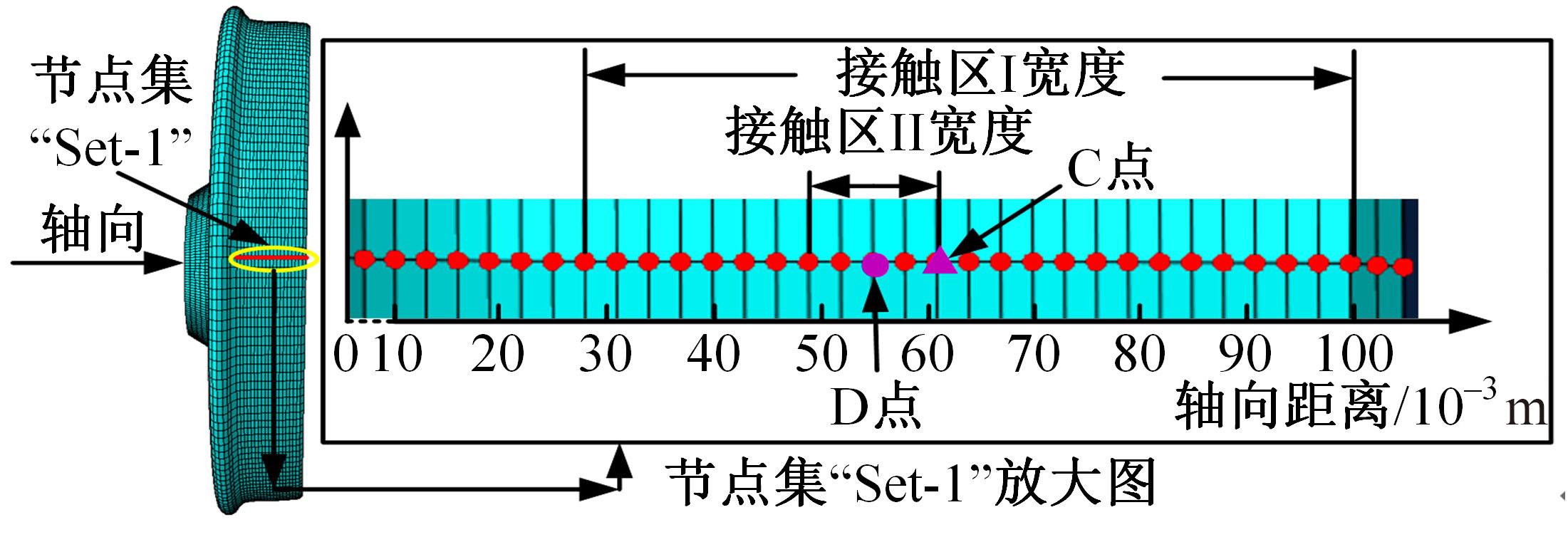
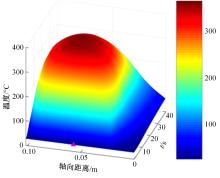
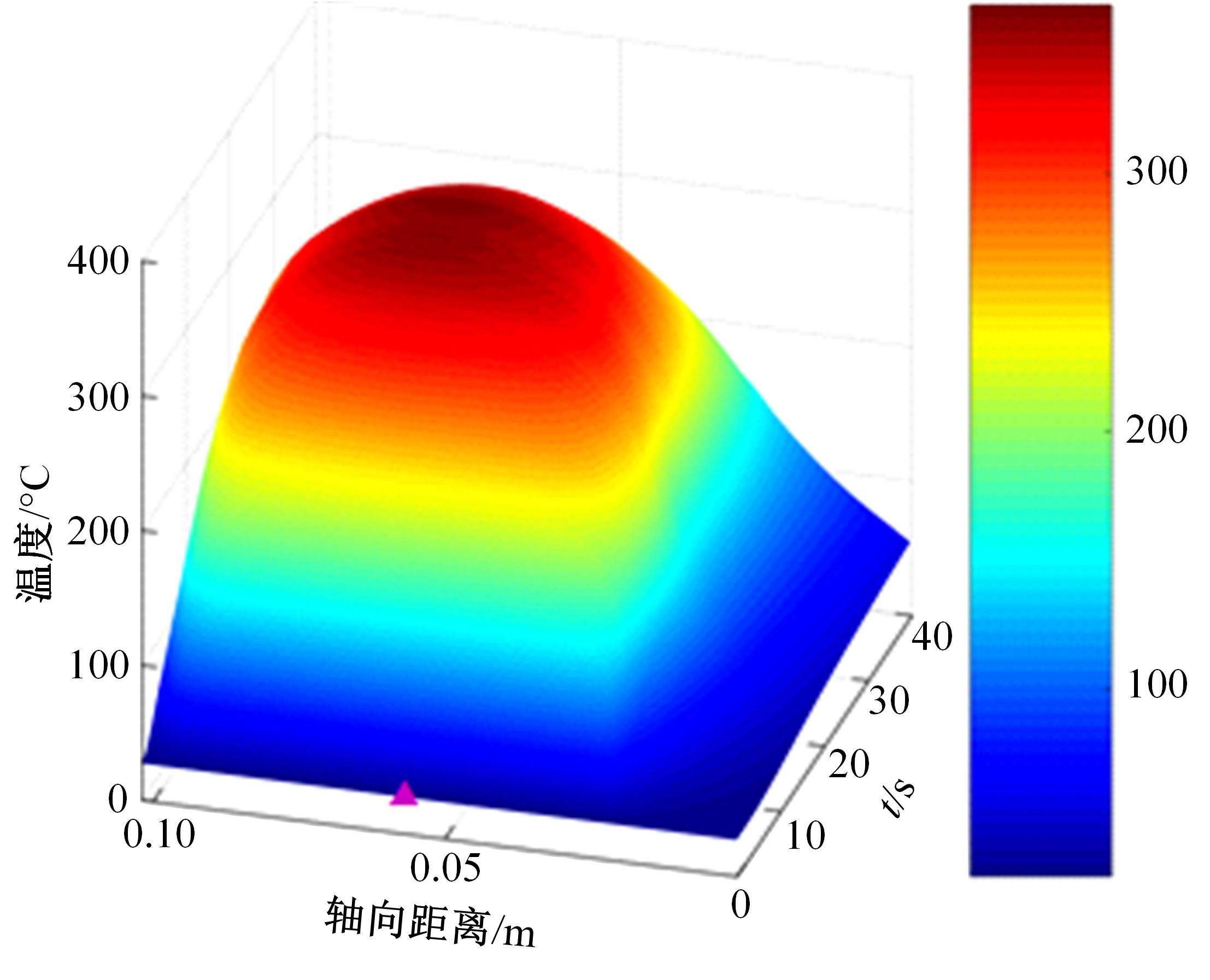
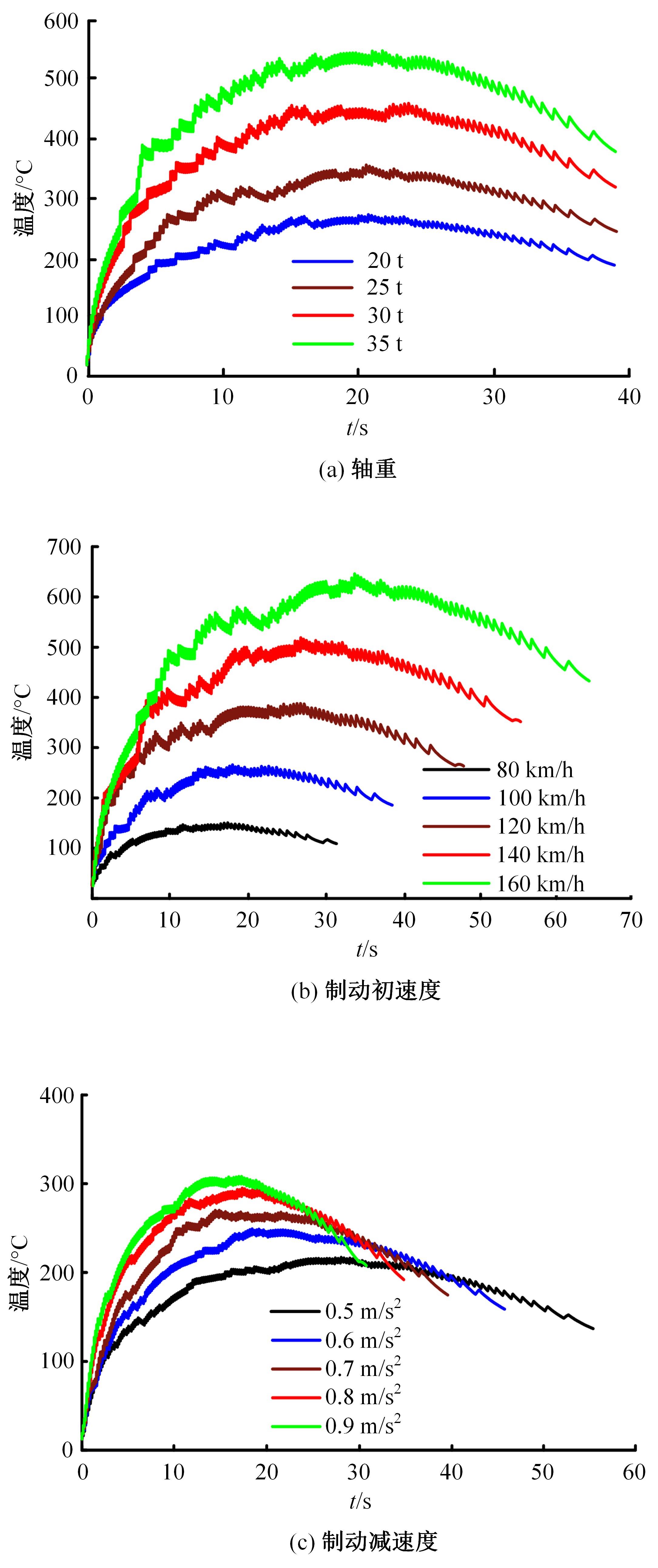
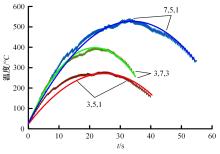
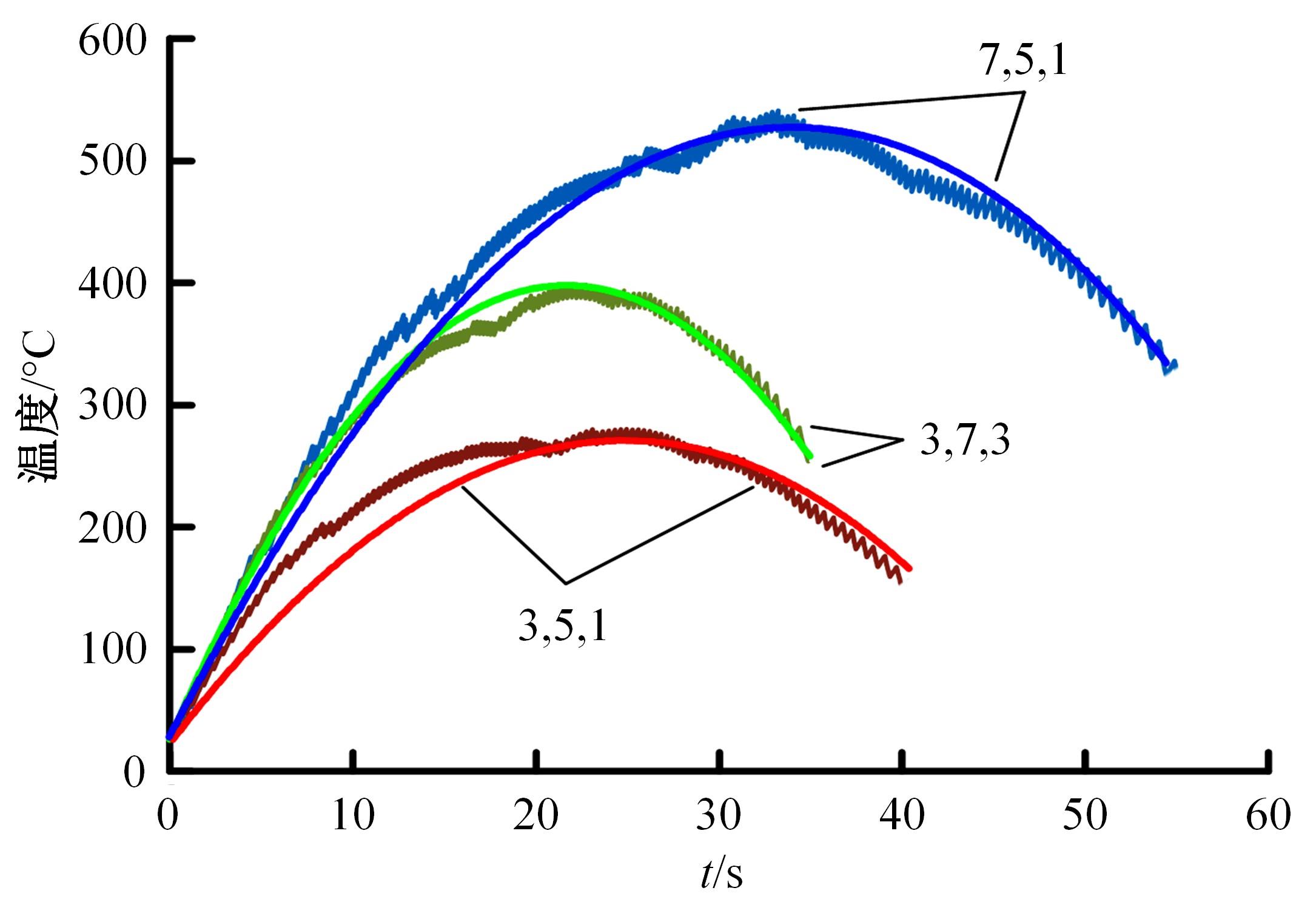
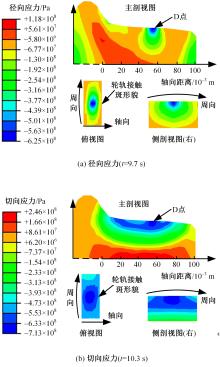
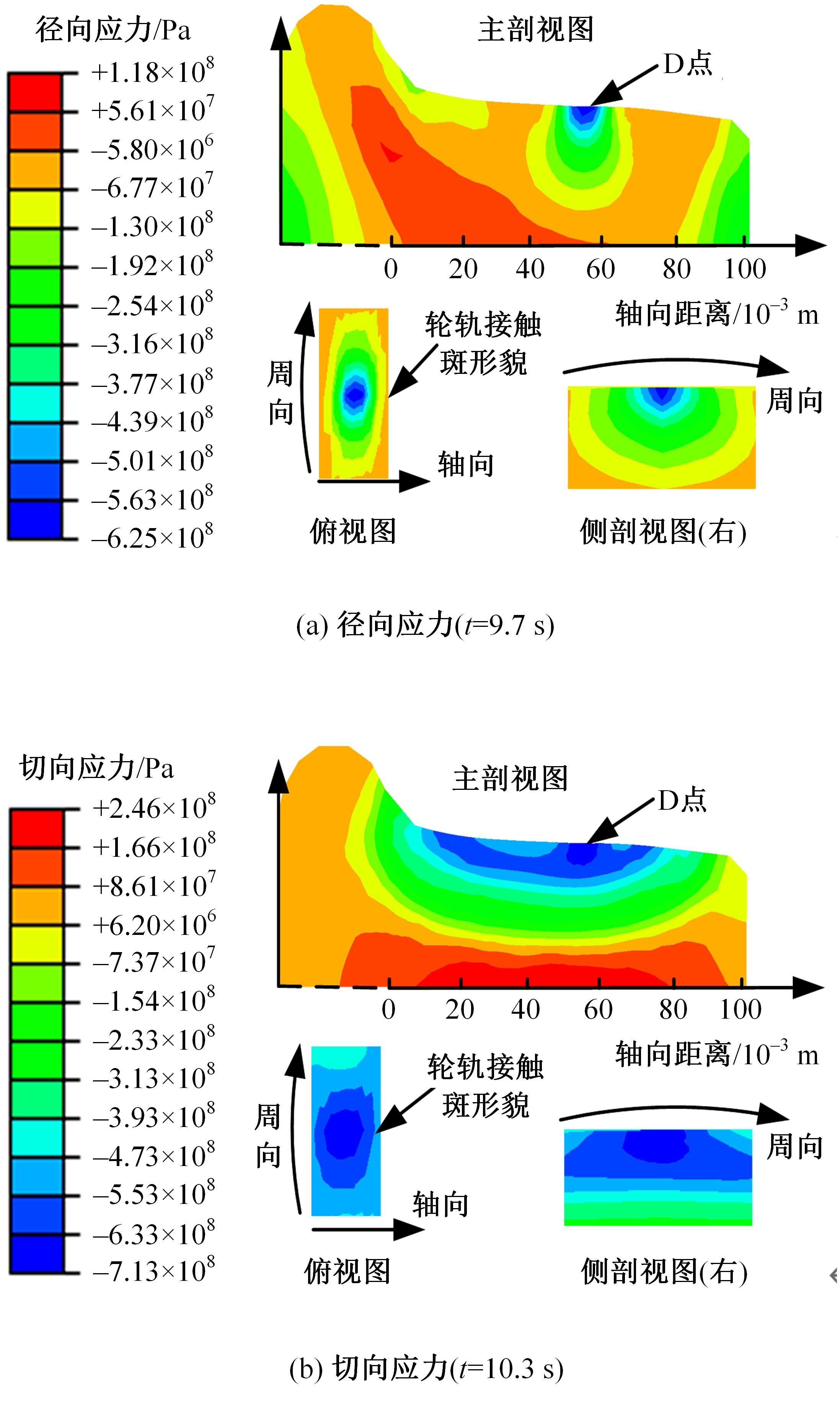
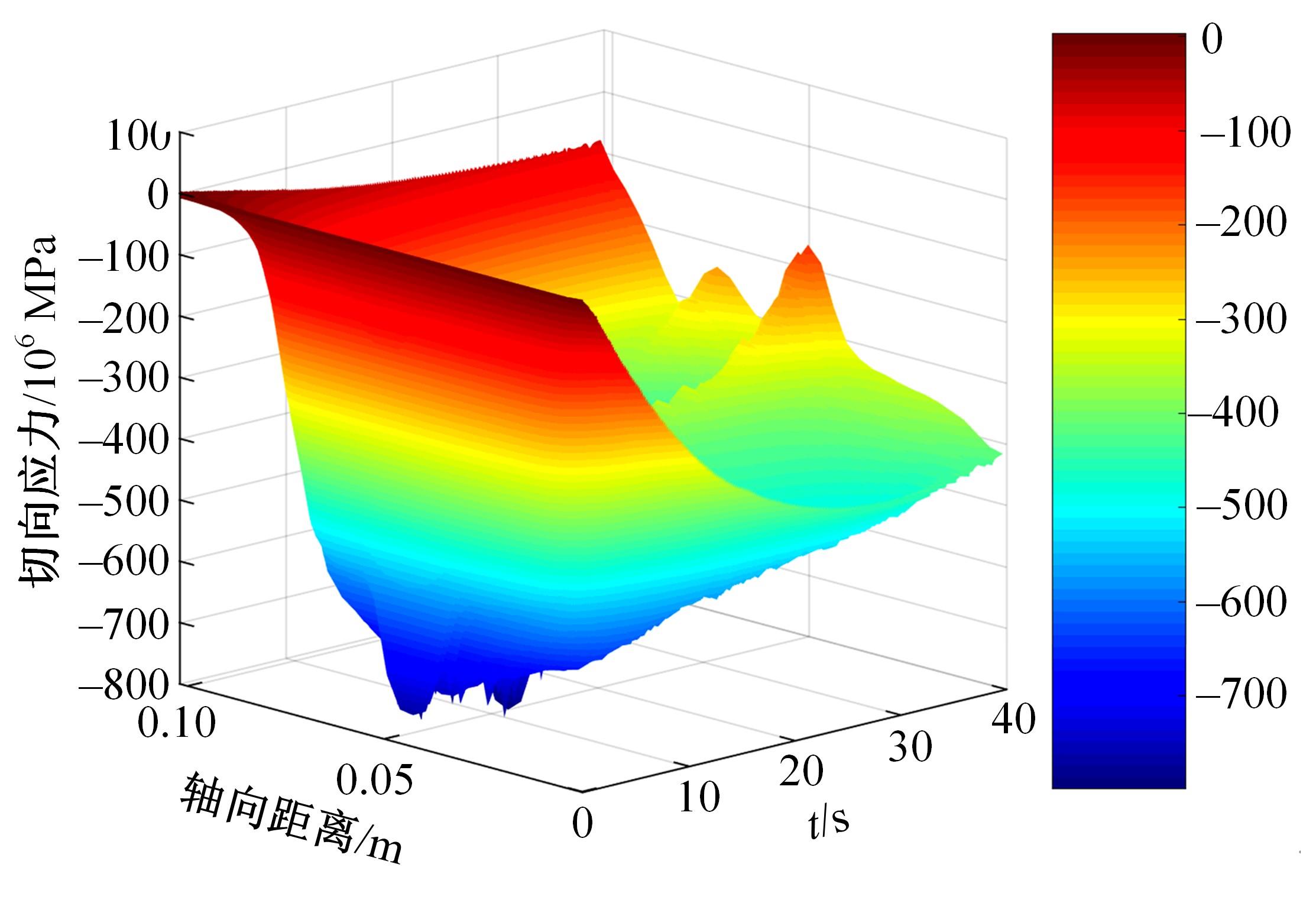
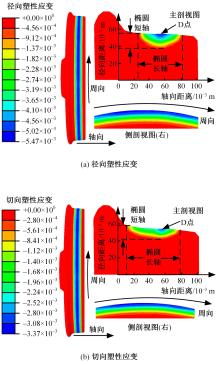
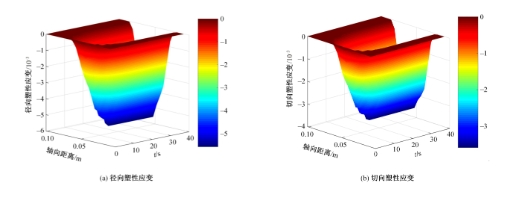
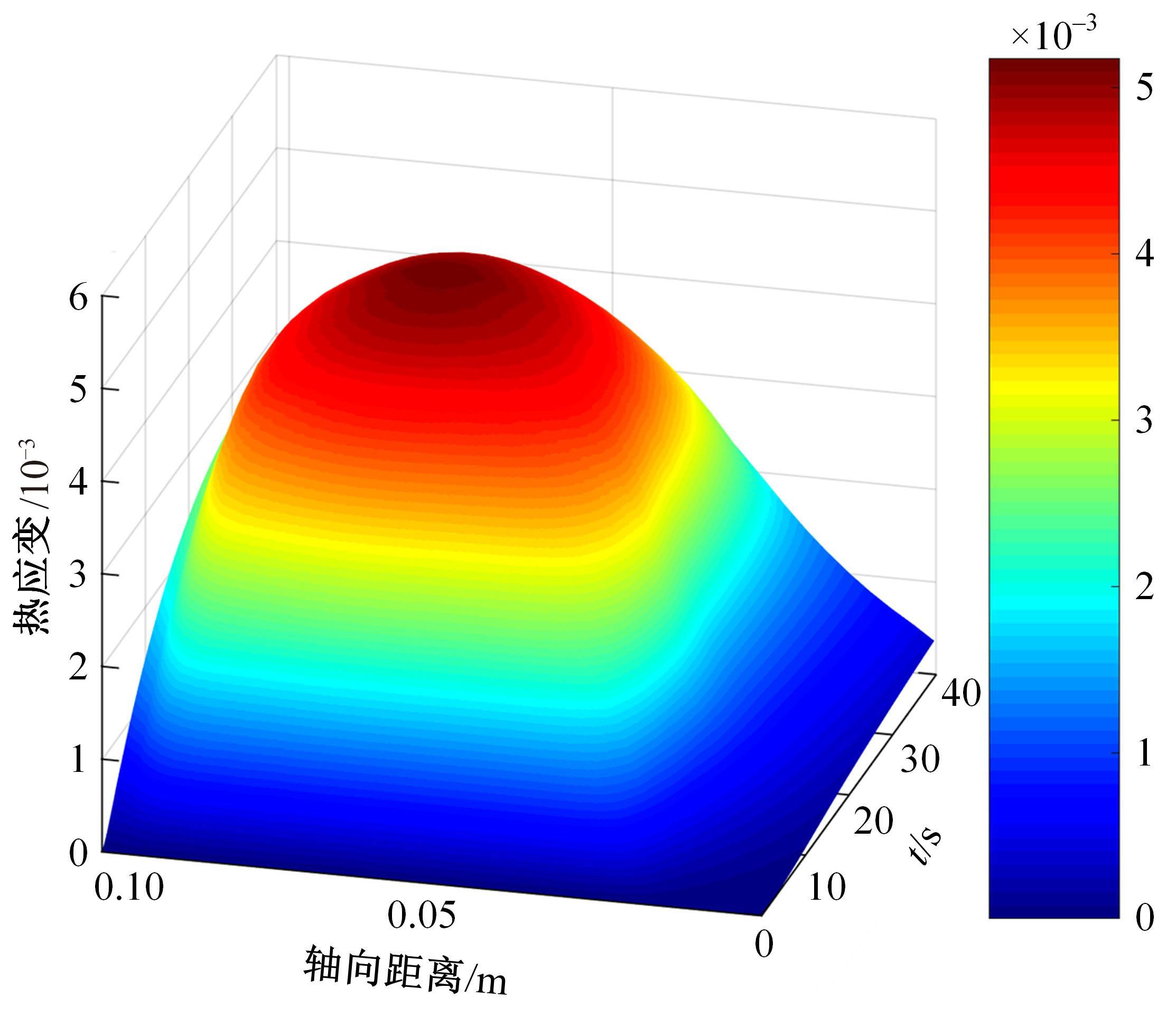
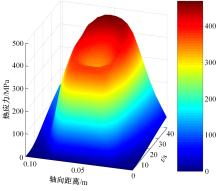
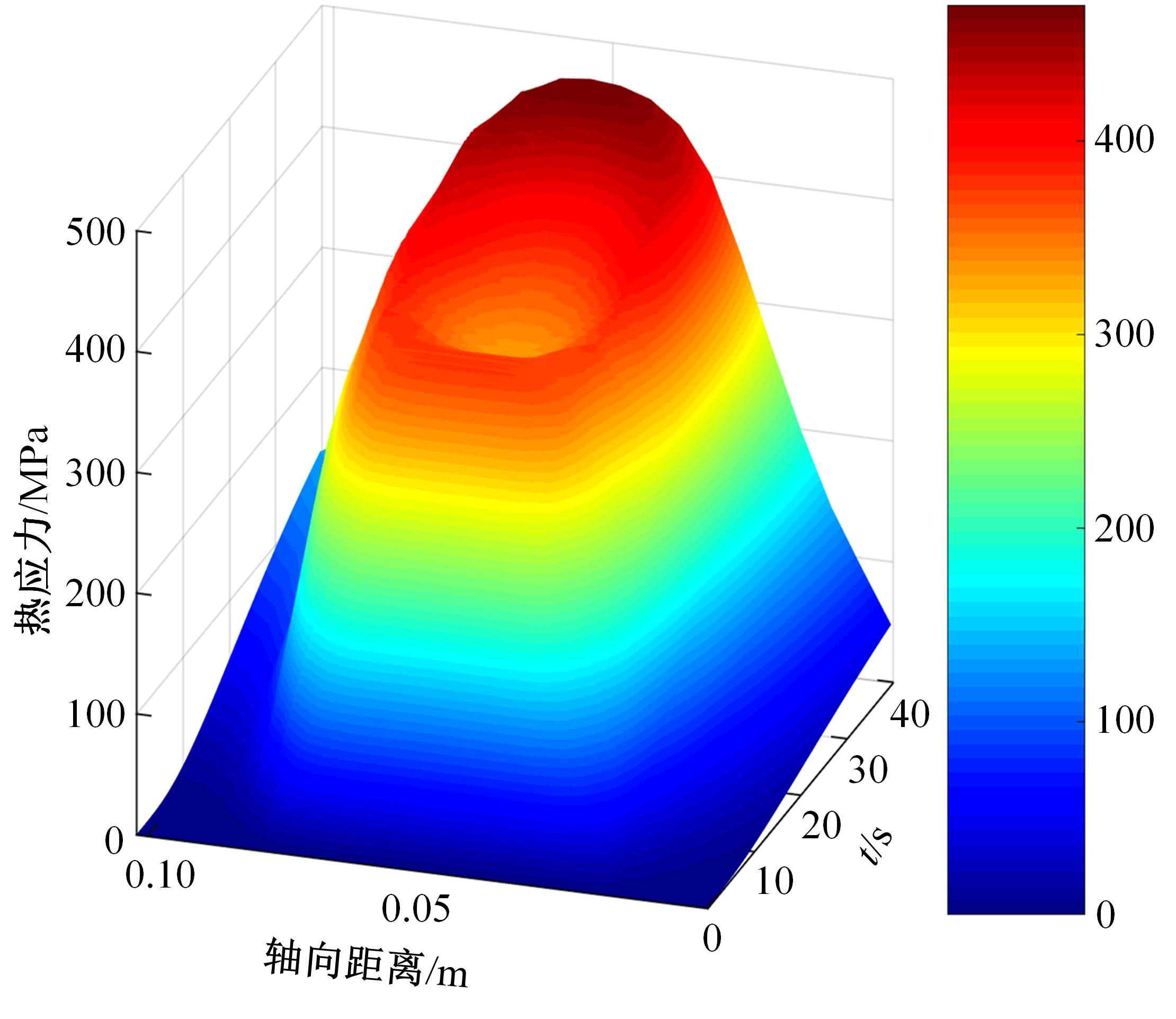
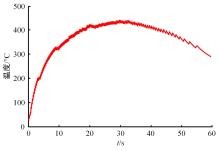
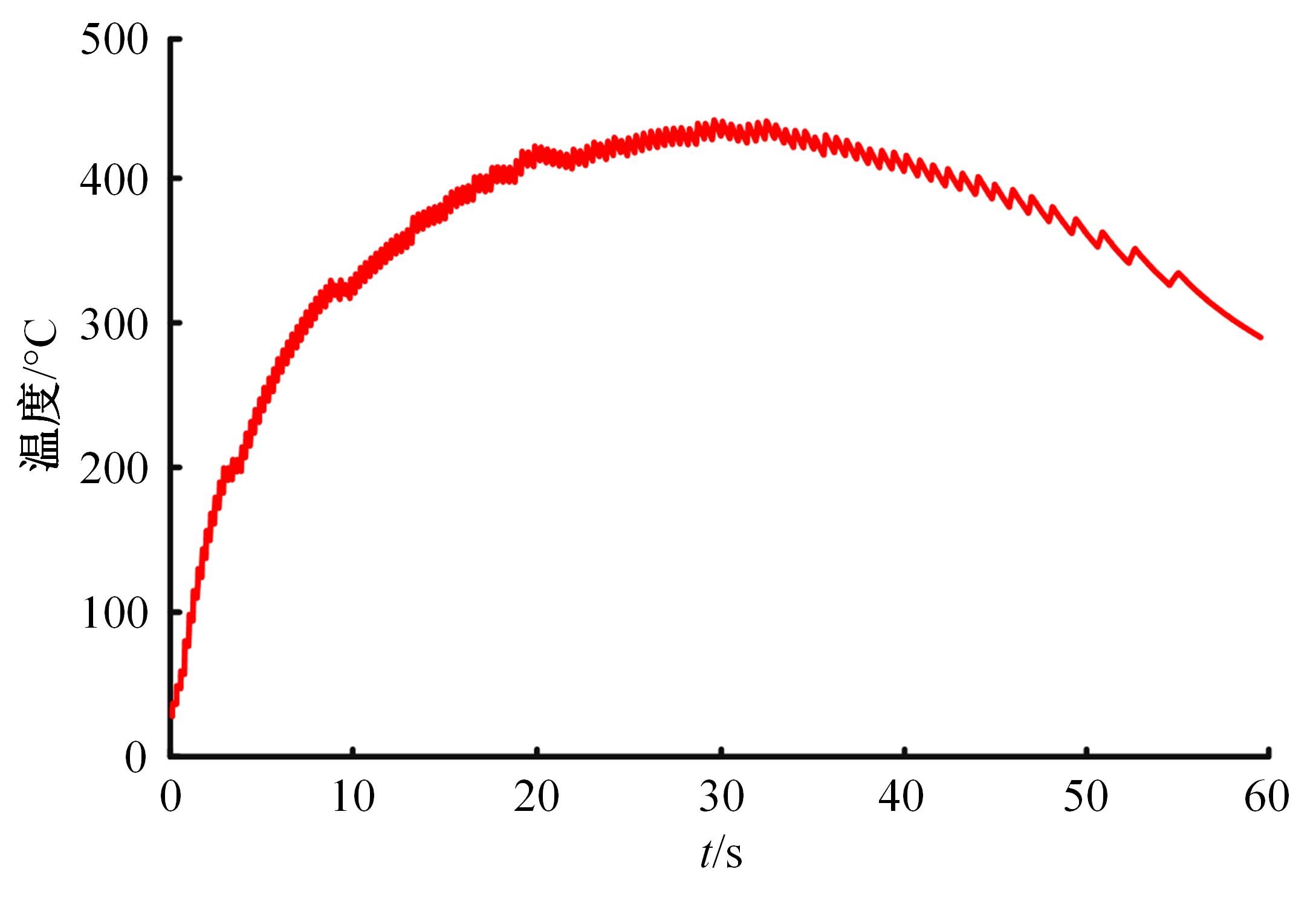
对Abaqus软件进行二次开发,采用旋转载荷法设置热流密度、法向载荷、切向载荷以及轮轨间的接触传热作用,在车轮表面设置对流换热和热辐射作用,基于热-机械耦合仿真得到了不同制动规程条件下踏面温度、应力和应变的动态变化及其分布特性,在此基础上回归得到了车轮踏面最高温度及制动结束温度与制动工况参数之间定量关系,并给出了制动过程踏面温度最高点温度变化曲线模型以及热应力预测模型。结果表明:轴重、制动初速度和减速度每增加5 t、20 km/h和0.1 m/s2,踏面的最高温度分别增加约90 ℃、120 ℃和26 ℃;25 t、100 km/h、0.7 m/s2制动工况下,径向应力辐达625 MPa,切向应力最大值为-713 MPa,最大径向、切向塑性应变分别为-5.47‰和-3.37‰,最大热应变为5.178‰,热应力范围为433 MPa。
中图分类号:
- U211.5
| 1 | Kato T, Fujimura T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Effect of wheel size and tread braking on subsurface crack initiation in heavy haul car wheel[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 19(7): 238-248. |
| 2 | Naeimi M, Li S G, Li Z L, et al. Thermomechanical analysis of the wheel-rail contact using a coupled modelling procedure[J]. Tribology International, 2018, 11(7): 250-260. |
| 3 | Akama M, Kimata T. Numerical simulation model for the competition between short crack propagation and wear in the wheel tread[J]. Wear, 2020, 20(5): 448-449. |
| 4 | Mazzu A, Ghidini A, Provezza L, et al. Study of the damage induced by thermomechanical load in ER7 tread braked railway wheels[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 25(6): 170-182. |
| 5 | 张金煜, 虞大联, 林鹏. 基于旋转热源法和均布热源法的列车踏面制动温度场分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(6): 94-100. |
| Zhang Jin-yu, Yu Da-lian, Lin Peng. Analysis of temperature field of train tread braking based on rotating heat source method and uniformly distributed heat source method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(6): 94-100. | |
| 6 | 毛保华, 龚超奇, 张桐, 等. 长大坡道货运列车周期性制动下车轮温升分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(4): 981-987. |
| Mao Bao-hua, Gong Chao-qi, Zhang Tong, et al. Analysis of wheel temperature rise of freight trains on long ramp under periodic braking[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(4): 981-987. | |
| 7 | 张野, 马晓杰, 朱绘丽. 基于ANSYS的车轮踏面紧急制动热分析[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2020, 40(3): 122-130. |
| Zhang Ye, Ma Xiao-jie, Zhu Hui-li. Thermal analysis of emergency braking of wheel tread based on ANSYS[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2020, 40(3): 122-130. | |
| 8 | Kazuyuki H, Katsuyoshi I, Fumiko M. Temperature-dependent wear of tread-braked railway wheels[J]. Wear, 2020, 28(6): 1-9. |
| 9 | Walia M S, Esmaeili A, Vernersson T, et al. Thermomechanical capacity of wheel treads at stop braking: a parametric study[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2018, 11(3): 407-415. |
| 10 | 陈帅, 吴磊, 张合吉, 等. 踏面制动温升对重载铁路车轮磨耗的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(2): 92-97. |
| Chen Shuai, Wu Lei, Zhang He-ji, et al. Influence of temperature rising of tread braking on wheel wear for heavy haul freight car[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(2): 92-97. | |
| 11 | 陈帅, 吴磊, 付青云, 等. 基于间隙热源法的车轮踏面制动摩擦温升研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2017, 42(5): 30-35. |
| Chen Shuai, Wu Lei, Fu Qing-yun, et al. Research on wheel temperature rising due to tread braking based on intermittent heat source method[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2017, 42(5): 30-35. | |
| 12 | 樊译璘. 重载铁路轮轨塑性匹配有限元分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学力学与工程学院, 2019. |
| Fan Yi-lin. Finite element analysis of wheel/rail plastic matching in heavy haul railway[D]. Chengdu: School of Mechanical and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 13 | 卢立丽. 货车车轮踏面制动热损伤研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2007. |
| Lu Li-li. Research on tread brake heat injury of freight wheel[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2007. | |
| 14 | 樊译璘, 阚前华, 康国政, 等. 热处理U71Mn钢轨钢的棘轮行为及其本构模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2019, 43(11): 62-72. |
| Fan Yi-lin, Kan Qian-hua, Kang Guo-zheng, et al. Ratcheting behavior and constitutive model of heat-treated U71Mn rail steel[J]. Material For Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 43(11): 62-72. | |
| 15 | 雷国军. 重载列车车轮表面对流传热特性的数值研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学车辆工程学院, 2020. |
| Lei Guo-jun. Numerical study on converctive heat transfer characteristics on the wheel surface of heavy-duty train[D]. Lanzhou: School of Vehicle Engineering, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 16 | Chen Shuai, Zhao Guo-tang, Wang Heng-yu, et al. Study of wheel wear influenced by tread temperature rising during tread braking[J]. Wear, 2019(20): 1-10. |
| 17 | 李辉平, 贺连芳, 赵国群, 等. 硼钢B1500HS界面传热系数与压力关系的研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(16): 78-82. |
| Li Hui-ping, He Lian-fang, Zhao Guo-qun, et al. Research on the surface heat transfer coefficient depending on surface pressure of boron steel B1500HS[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(16): 78-82. | |
| 18 | 包辰铭. 重载列车踏面制动车轮温度场分析及制动故障诊断研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2020. |
| Bao Chen-ming. Temperature field analysis of brake wheels on heavy-dutty train treads abd research on brake fault diagnosis[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 19 | 肖绯雄,陈旭. 恶劣工况下货车高摩合成闸瓦磨损分析[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2014, 38(4): 20-25. |
| Xiao Fei-xiong, Chen Xu. Wear analysis of the synthetic brake shoe with high friction of the freight train under harsh conditions[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2014, 38(4): 20-25. | |
| 20 | 王京波, 习年生, 常崇义, 等. 重载货车车轮制动热负荷的试验深化研究[R]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2012. |
| [1] | 程亚兵,杨泽宇,李岩,安立持,徐泽辉,曹鹏宇,陈璐翔. 基于混合动力汽车正时齿形链系统的振动噪声特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2465-2473. |
| [2] | 刘方成,王将,吴孟桃,补国斌,何杰. 土工格栅加筋橡胶砂应力-应变特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2542-2553. |
| [3] | 王佳怡,刘昕晖,王展,陈晋市,韩亚方,王禹琪. 基于AMESim的恒流量控制阀流量特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2499-2507. |
| [4] | 黄贤振,孙楷铂,栾晓刚,胡兵. 螺栓预紧连接可靠性灵敏度分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2219-2226. |
| [5] | 李新宇,凌贤长,曲娜. 考虑温度效应的冻结膨胀土统计损伤模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2339-2349. |
| [6] | 宫亚峰,吴树正,毕海鹏,谭国金. 基于现场监测技术的装配式箱涵温度场及冻胀分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2321-2331. |
| [7] | 张哲,付伟,张军辉,黄超. 循环荷载下冻融路基黏土长期塑性行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1790-1798. |
| [8] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [9] | 杨艳,侍玉青,张晓蓉,罗冠炜. 一类多刚性限幅振动系统的动态稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 364-375. |
| [10] | 朱劲松,秦亚婷,刘周强. 预应力UHPC-NC组合梁截面优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3151-3159. |
| [11] | 刘洋. 动臂塔机防后倾缓冲力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2785-2794. |
| [12] | 卢晓红,乔金辉,周宇,马冲,隋国川,孙卓. 搅拌摩擦焊温度场研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 1-17. |
| [13] | 王奎洋,何仁. 基于支持向量机的制动意图识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
| [14] | 王骏骋,吕林峰,李剑敏,任洁雨. 分布驱动电动汽车电液复合制动最优滑模ABS控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1751-1758. |
| [15] | 石忠华,宋权威,康振航,谢强,章继峰. 机翼结构超声除冰系统数值模拟与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1561-1573. |
|
||