吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 468-479.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211071
考虑时变交通拥堵的纯电动物流车路径规划模型
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Electric delivery vehicle routing problem optimization model with time⁃varying traffic congestion
Bao-feng SUN( ),Tian-zi YAO,Yu-qi CHEN
),Tian-zi YAO,Yu-qi CHEN
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
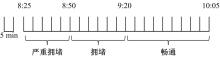
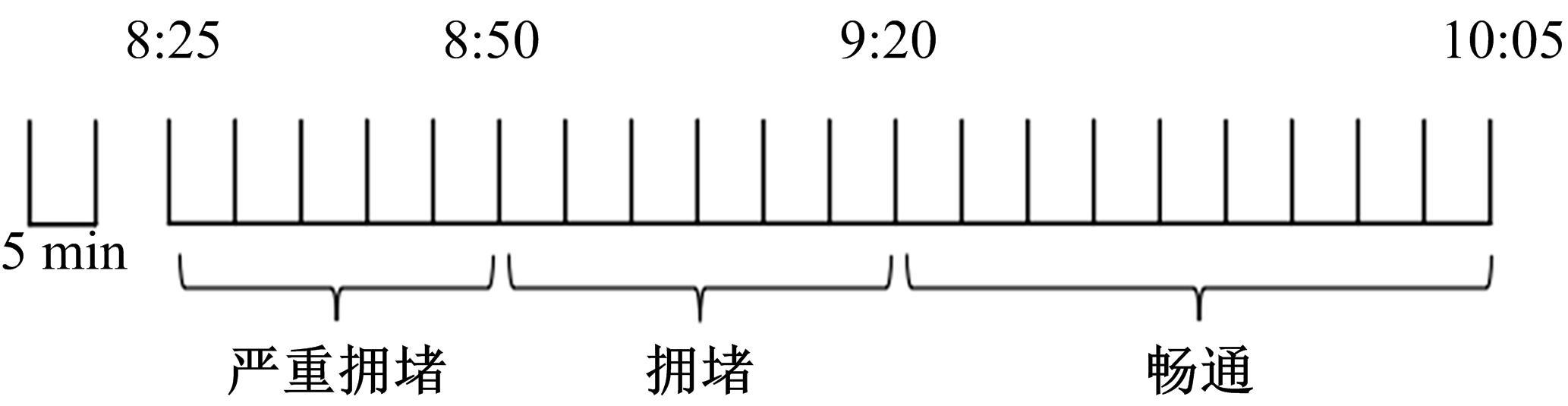
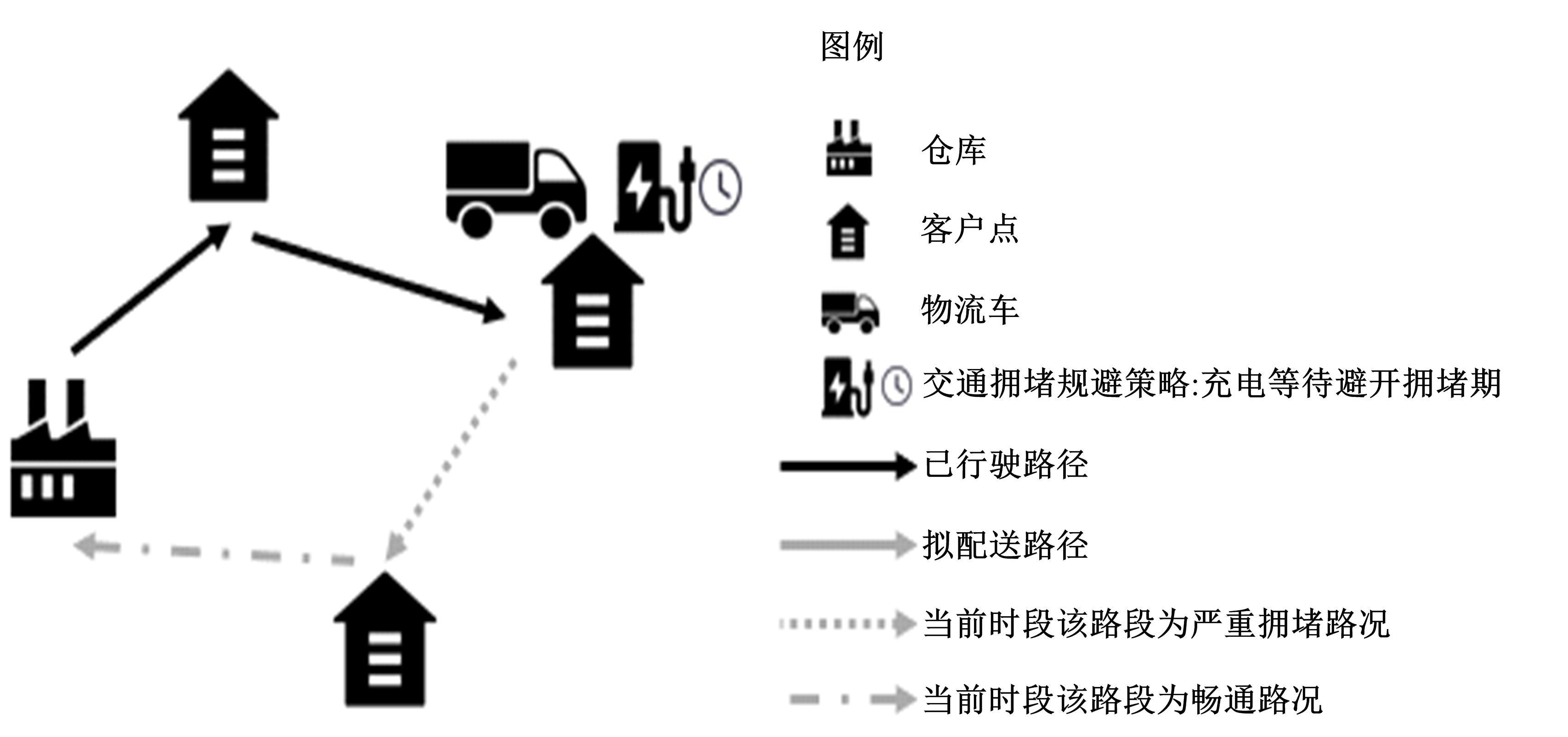
为通过合理规划车队出行方案,最大限度减少在交通拥堵时段车辆的能源消耗,同时缓解配送人员的电动车辆里程焦虑,本文研究了考虑时变交通拥堵的纯电动物流车路径规划问题。首先立足于EVRP扩展模型构建,建立了一个新的混合整数规划模型(TD-EVRP),尤其界定和表征了时变交通拥堵状态,并量化了电动物流车能源消耗,重新完善了客户时间窗、车辆载重以及车辆充电需求等约束条件。其次,引入了交通拥堵规避策略,允许车辆在交通高峰期在客户点停车充电,主动规避交通拥堵带来的不必要能源消耗。最后,使用改进的蚁群算法获得最优解,给出了交通拥堵规避策略下总能源消耗最小化的配送方案。有无对比分析表明,小规模实例下,带规避策略的TD-EVRP模型比无规避策略时能够显著减少能源消耗14.91%。
中图分类号:
- N945.15
| 1 | 国务院办公厅. 新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)[EB/OL][2020-10-20]. . |
| 2 | Desau; niers G, Errico F, Imich S, et al. Exact Algorithms for Electric Vehicle-Routing Problems with Time Windows[J]. Operations Research: The Journal of the Operations Research Society of America, 2016, 64(6): 1388-1405. |
| 3 | Schneider M, Stenger A, Goeke D. The electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and recharging stations [J]. Transportation Science, 2014, 48(4): 500-520. |
| 4 | 张书玮, 罗禹贡, 李克强. 动态交通环境下的纯电动车辆多目标出行规划[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 56(2): 130-136. |
| Zhang Shu-wei, Luo Yu-gong, Li Ke-qiang. Multi-Objective Trip Planning of Pure Electric Vehicles in Dynamic Traffic Environments[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2016, 56(2): 130-136. | |
| 5 | Qin H, Su X, Ren T, et al. A review on the electric vehicle routing problems: variants and algorithms[J]. Front Eng Manag, 2021, 8(3): 370-389. |
| 6 | Pelletier S, Jabali O, Laporte G. 50th anniversary invited article—goods distribution with electric vehicles: review and research perspectives[J]. Transportation Science, 2016, 50(1): 3-22. |
| 7 | Basso R, Kulcsárb B, Egardtb B, et al. Energy consumption estimation integrated into the electric vehicle routing problem[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2019, 69: 141-167. |
| 8 | Lu J, Chen Y, Hao J K, et al. The time-dependent electric vehicle routing problem: model and solution[J].Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 161: 113593. |
| 9 | Florio A M, Absi N, Feillet D. Routing Electric Vehicles on Congested Street Networks[J]. Transportation Science, 2020, 55(1): 238-256. |
| 10 | Jafari E, Boyles S D. Multicriteria stochastic shortest path problem for electric vehicles[J].Networks and Spatial Economics, 2017, 17(3): 1043-1070. |
| 11 | 柳开济. 纯电动物流配送车运营调度模型设计与实现[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学航空航天学院, 2016. |
| Liu Kai-ji. Design and implementation of operation dcheduling model for pure rlectric logistics delivery vehicle[D]. Chengdu: School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016. | |
| 12 | Kok A L, Hans E W, Schutten J. Vehicle routing under time-dependent travel times: The impact of congestion avoidance[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2012, 39(5): 910-918. |
| 13 | Xiao Y Y, Konak A. The heterogeneous green vehicle routing and scheduling problem with time-varying traffic congestion[J] Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2016, 88(C): 146-166. |
| 14 | 刘长石, 申立智, 盛虎宜,等. 考虑交通拥堵规避的低碳时变车辆路径问题研究[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(10): 2486-1496. |
| Liu Chang-shi, Shen Li-zhi, Sheng Hu-yi, et al. Research on low-carbon time-varying vehicle path problem considering traffic congestion avoidance[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(10): 2486-1496. | |
| 15 | 葛显龙, 冉小芬. 考虑时变交通拥堵的污染路径优化研究[J]. 工业工程与管理, 2020, 25(3): 75-85, 93. |
| Ge Xian-long, Ran Xiao-fen. Research on Pollution Path Optimization Considering Time-Varying Traffic Congestion[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2020, 25(3): 75-85, 93. | |
| 16 | Asamer J, Graser A, Heilmann B, et al. Sensitivity analysis for energy demand estimation of electric vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2016, 46: 182-199. |
| 17 | Demir E, Bektaş T, Laporte G. A review of recent research on green road freight transportation [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2014, 237(3): 775-793. |
| 18 | Goeke D, Schneider M. Routing a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 245(1): 81-99. |
| 19 | Li Y B, Soleimani H, Zohal M. An improved ant colony optimization algorithm for the multi-depot green vehicle routing problem with multiple objectives[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 227: 1161-1172. |
| 20 | Ropke S, Pisinger D. An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the pickup and delivery problem with time windows[J]. Transportation Science, 2006, 40(4): 455-472. |
| 21 | Zhang S, Gajpal Y, Appadoo S S, et al. Electric vehicle routing problem with recharging stations for minimizing energy consumption[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2018, 203: 404-413. |
| 22 | 陈宝文. 蚁群优化算法在车辆路径问题中的应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学航天学院, 2009. |
| Chen Bao-wen. Application of ant colony optimization in vehicle routing problems[D]. Harbin: School of Astronautics, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009. | |
| 23 | 宋稚雅. 基于纯电动物流车的城市配送车辆路径问题研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学经济与管理学院, 2019. |
| Song Zhi-ya. Study on urban distribution vehicle routing problem based on pure electric logistics vehicle[D]. Beijing: School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. |
| [1] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [2] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [3] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [4] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
| [5] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于静态半成套策略的多目标准时化物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 910-916. |
| [6] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [7] | 罗清玉,田万利,贾洪飞. 考虑通勤需求的电动汽车充电站选址与定容模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| [8] | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 曲大为. 基于马尔科夫链的长春市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| [9] | 孙宝凤, 高坤, 申琇秀, 梁婷. 基于能力平衡和变覆盖半径的加油站网络扩充选址模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 704-711. |
| [10] | 徐亮,程国柱. 基于车速离散度和经济车速的高速公路最低车速限制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
|