吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1364-1371.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220767
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址
李艳波1( ),柳柏松1,姚博彬1(
),柳柏松1,姚博彬1( ),陈俊硕1,渠开发2,武奇生1,曹洁宁1
),陈俊硕1,渠开发2,武奇生1,曹洁宁1
- 1.长安大学 能源与电气工程学院,西安 710064
2.山东省交通规划设计院有限公司,济南 250031
Location of electrical changing station of expressway considering stochastic characteristics of road network
Yan-bo LI1( ),Bai-song LIU1,Bo-bin YAO1(
),Bai-song LIU1,Bo-bin YAO1( ),Jun-shuo CHEN1,Kai-fa QU2,Qi-sheng WU1,Jie-ning CAO1
),Jun-shuo CHEN1,Kai-fa QU2,Qi-sheng WU1,Jie-ning CAO1
- 1.School of Energy and Electrical Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Shandong Transportation Planning and Design Institute Co. ,Ltd,Jinan 250031,China
摘要:
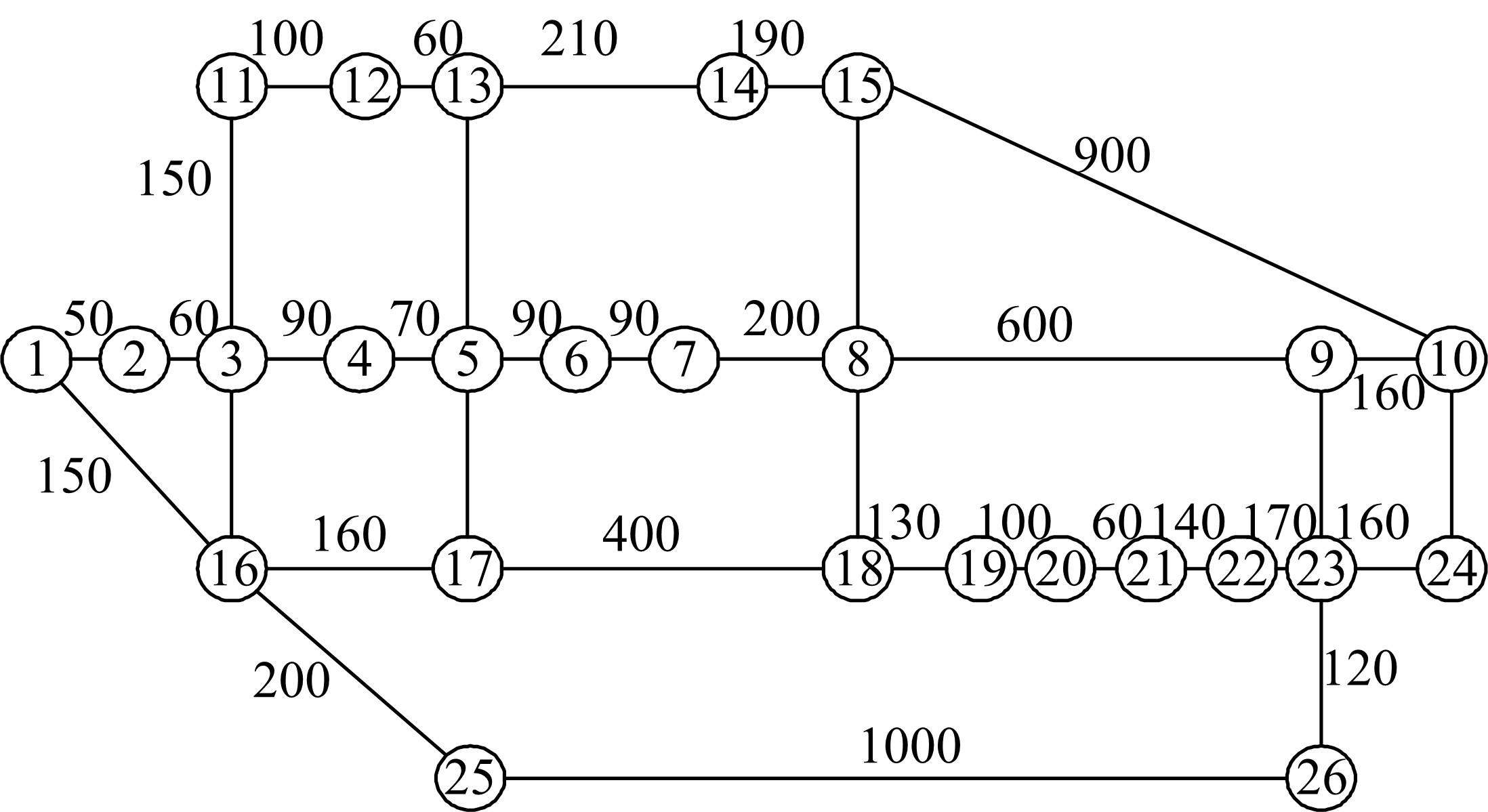
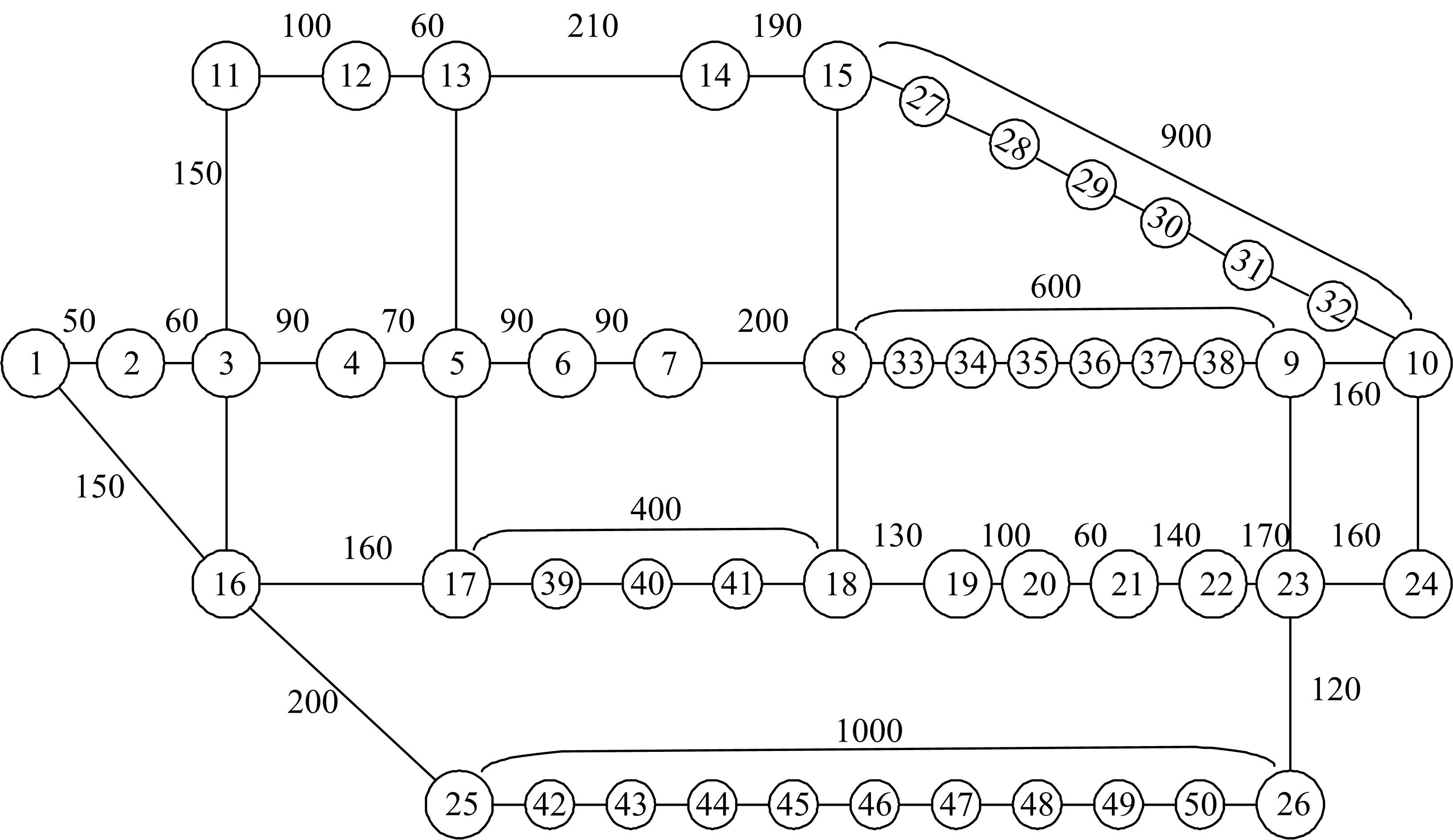
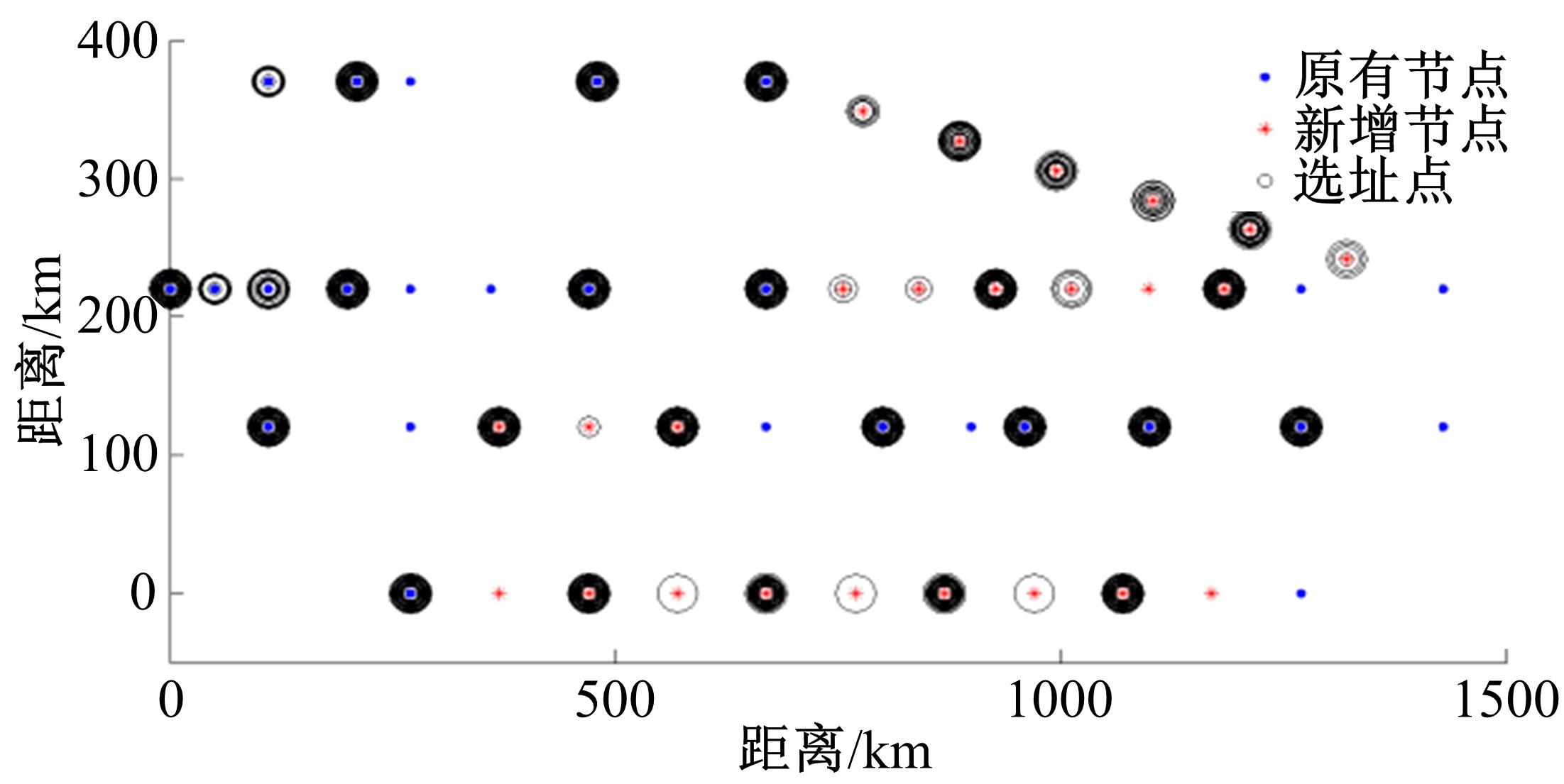
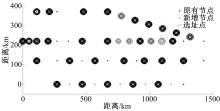
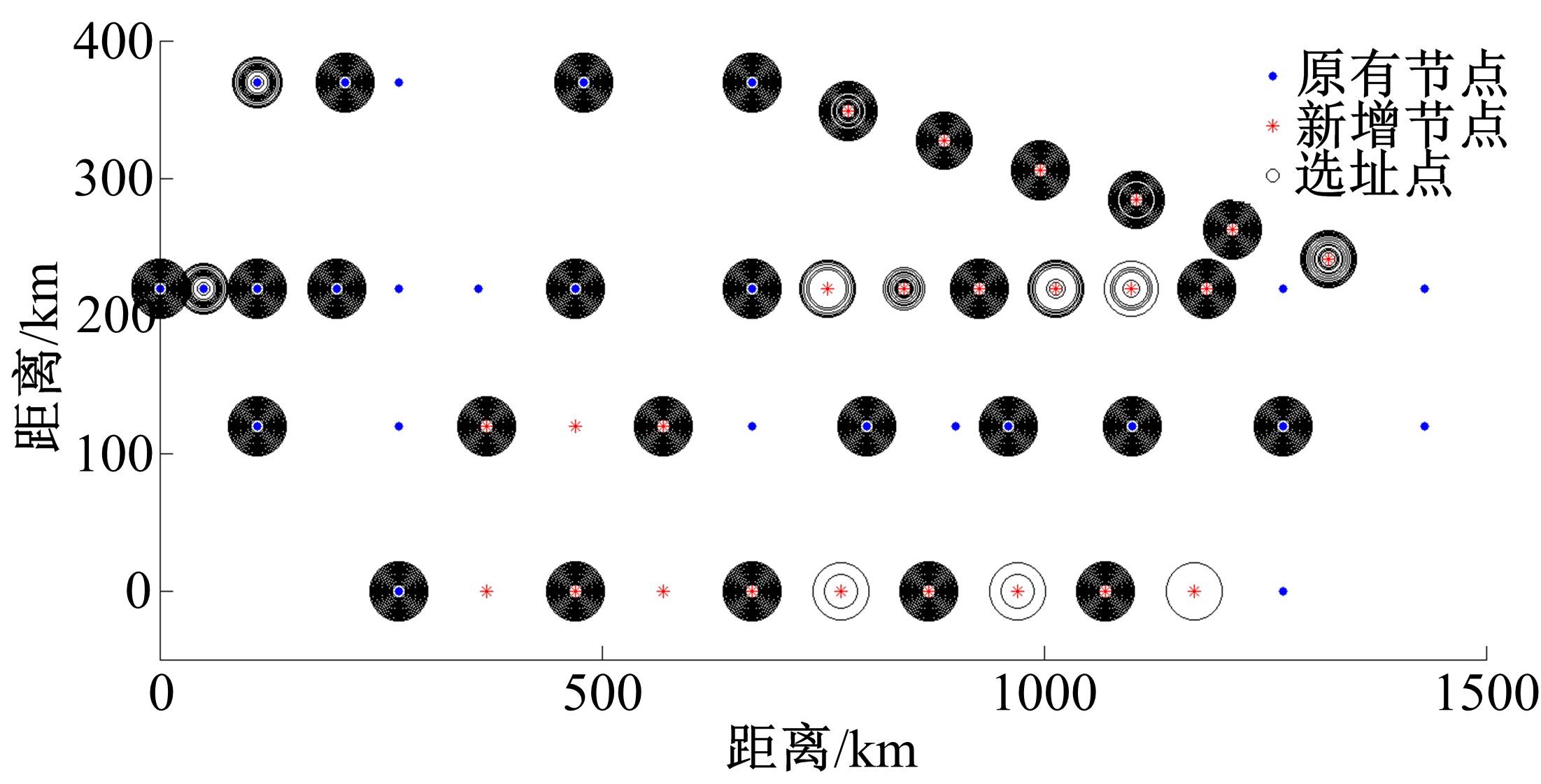
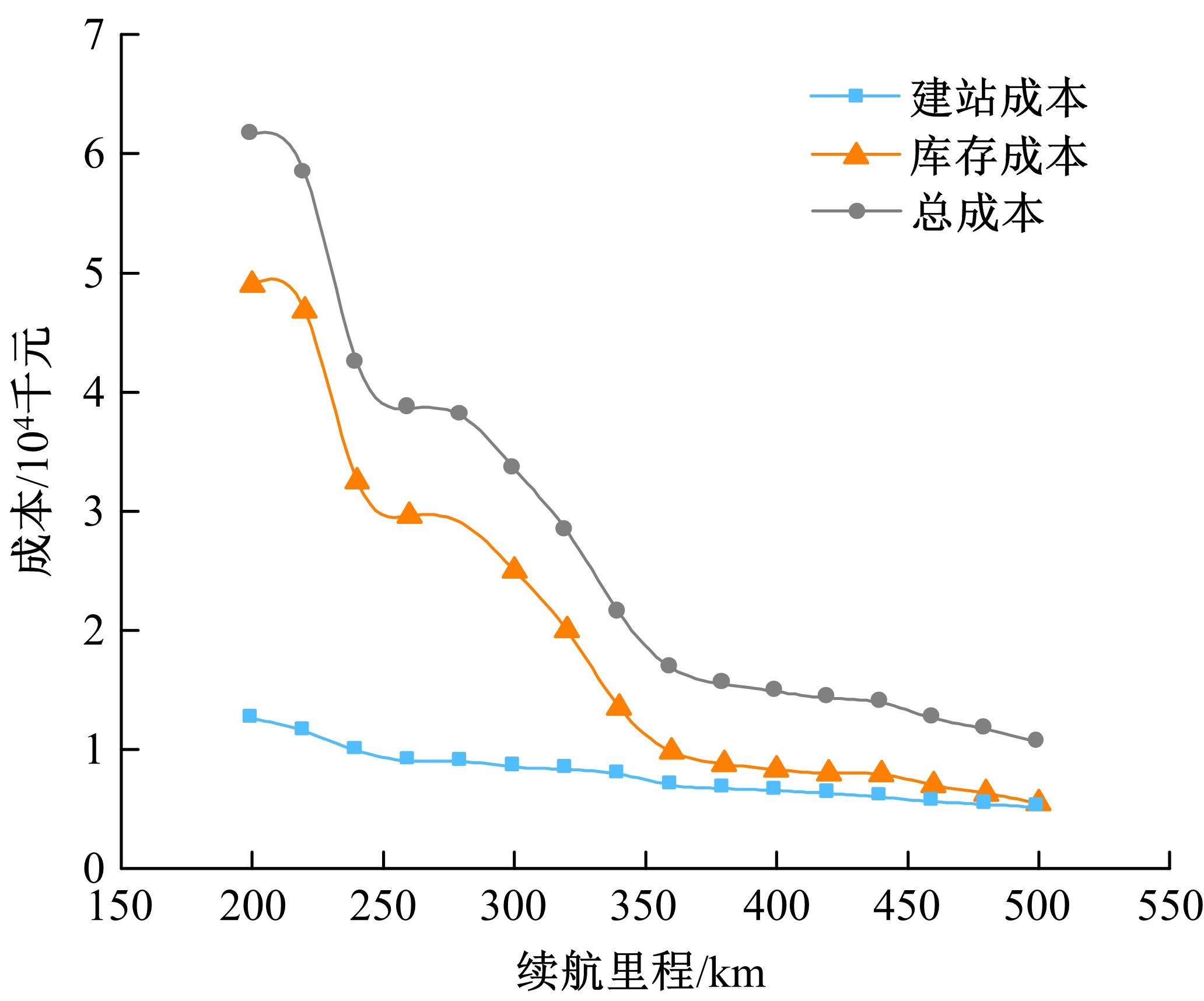
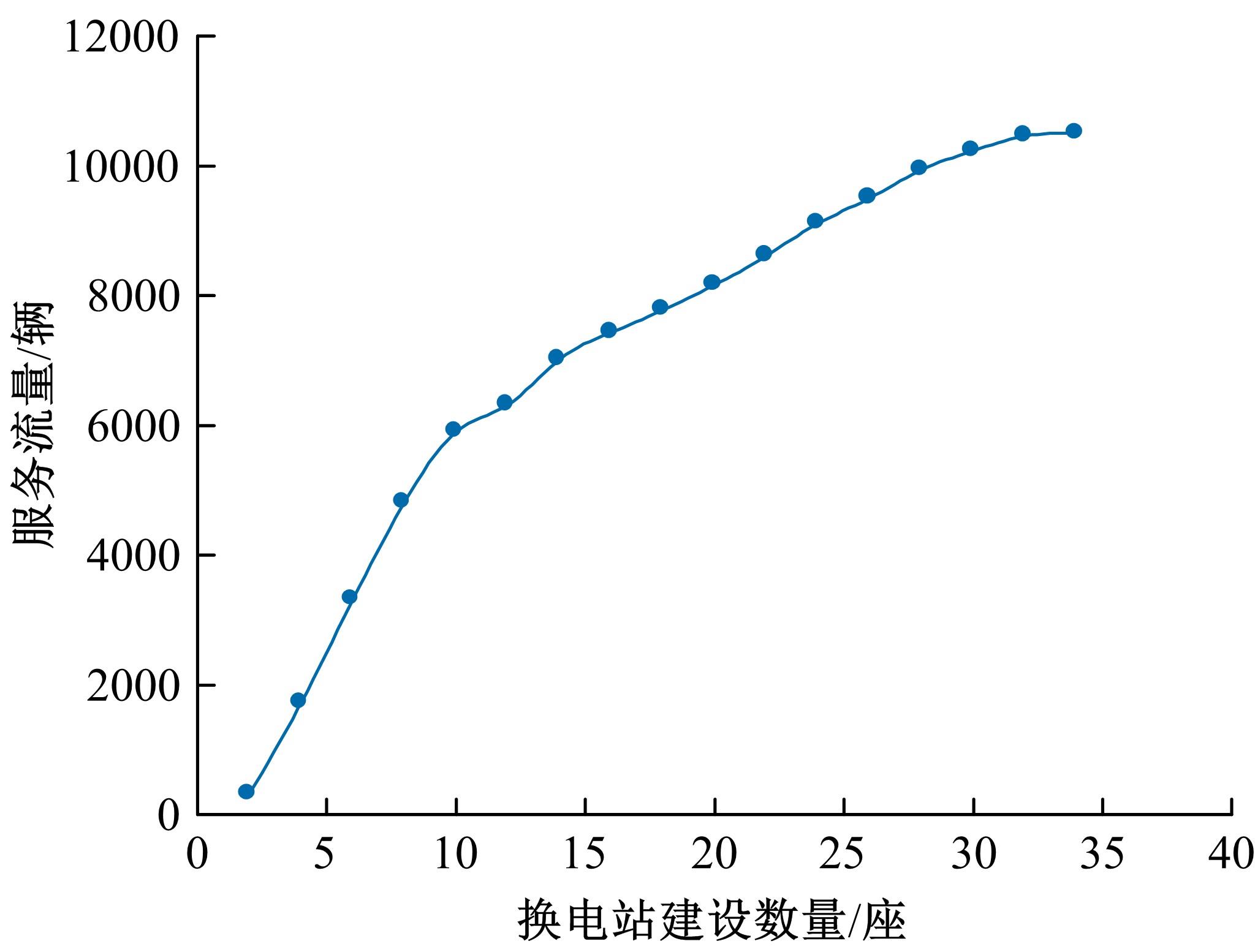
综合考虑路径上电动汽车流量和初始剩余电量的随机特性,引入扩张网络理论,构建了多路径条件下潜在的换电站选址数学模型。并结合“精英主义”,利用遗传算法对选址模型进行求解,获取选址初始解。最后,利用统计分析的方法对初始解进行筛选得到最终的最优选址点。在此基础上对电动车续航里程与建站成本关系及换电站数量与服务流量关系进行了分析,通过比较,“精英主义”的引进可明显降低换电站初始建设成本及求解时间,而统计分析法的运用使换电站既可满足高速路网中绝大多数车主的用电需求,又能有效降低建站所需初始成本。
中图分类号:
- U49
| 1 | 杨天宇, 郭庆来, 盛裕杰, 等.系统互联视角下的城域电力-交通融合网络协同[J].电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(11): 1-9. |
| Yang Tian-yu, Guo Qing-lai, Sheng Yu-jie, et al. Coordination of urban integrated electric power and traffic network from perspective of system interconnection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(11): 1-9. | |
| 2 | 崔岩, 胡泽春, 段小宇.考虑充电需求空间灵活性的电动汽车运行优化研究综述[J].电网技术, 2022, 46(3): 981-994. |
| Cui Yan, Hu Ze-chun, Duan Xiao-yu. Review on the electric vehicles operation optimization considering the spatial flexibility of electric vehicles charging demands[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(3): 981-994. | |
| 3 | 谌微微, 许茂增, 邢青松.考虑续航能力的新能源汽车充电站递阶延时布局研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(6): 156-162. |
| Chen Wei-wei, Xu Mao-zeng, Xing Qing-song. A hierarchical delay layout model for electric vehicle charging stations considering cruising capability[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(6): 156-162. | |
| 4 | 张玮, 张树培, 罗江鹏, 等.电动汽车充电桩排队服务动态优化模型[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(5): 1045-1051. |
| Zhang Wei, Zhang Shu-pei, Luo Jiang-peng, et al. Dynamic optimization model of queuing service for electric vehicle charging piles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(5): 1045-1051. | |
| 5 | 盛裕杰, 郭庆来, 刘梦洁, 等.多源数据融合的用户充电行为分析与充电设施规划实践[J].电力系统自动化, 2022, 22(6): 1-24. |
| Sheng Yu-jie, Guo Qing-lai, Liu Meng-jie, et al. User charging behavior analysis and charging facility planning practice based on multi-source data fusion[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 22(6): 1-24. | |
| 6 | Zhang H C, Moura S J, Hu Z C, et al. PEV fast-charging station siting and sizing on coupled transportation and power networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(4): 2595-2605. |
| 7 | 陈维新. 基于电动汽车充电需求的高速公路充电站布局研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2021. |
| Chen Wei-xin. Research on the highway charging station layout based on charging demand of electric vehicles[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| 8 | Zhang H C, Moura S J, Hu Z C, et al. A second-order cone programming model for planning PEV fast-charging stations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33(3): 2763-2777. |
| 9 | 吴赋章, 杨军, 林洋佳, 等.考虑用户有限理性的电动汽车时空行为特性[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(7): 1563-1574. |
| Wu Fu-zhang, Yang Jun, Lin Yang-jia, et al. Research on spatiotemporal behavior of electric vehicles considering the users' bounded rationality[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(7): 1563-1574. | |
| 10 | 龙雪梅, 杨军, 吴赋章, 等.考虑路网-电网交互和用户心理的电动汽车充电负荷预测[J].电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(14): 86-93. |
| Long Xue-mei, Yang Jun, Wu Fu-zhang, et al. Prediction of electric vehicle charging load considering interaction between road network and power grid and user's psychology[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(14): 86-93. | |
| 11 | 邹云程, 刘昊翔, 龙建成. 考虑出行者异质的多类型充电设施部署优化[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2020, 40(11): 2946-2957. |
| Zou Yun-cheng, Liu Hao-xiang, Long Jian-cheng. Optimizing the location of multi-type charging facilities considering heterogeneous travelers[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory &Practice, 2020, 40(11): 2946-2957. | |
| 12 | 葛少云, 李荣, 韩俊, 等.考虑电动出租车随机概率行为特性的充电站规划[J].电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(4): 50-58. |
| Ge Shao-yun, Li Rong, Han Jun, et al. Charging Station planning considering probability behavior characteristic of electric tax[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(4): 50-58. | |
| 13 | Giuseppe N, Antonio P, Salvatore M, et al. Optimal allocation of electric vehicle charging stations in a highway network: Part 1. Methodology and test application[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 27: 101102. |
| 14 | Cui Q, Weng Y, Tan C W, et al. Electric vehicle charging station placement method for urban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(6): 6552-6565. |
| 15 | Wu Y H, Ribberink H. Methodology to estimate the need for direct-current fast-charging stations along highways in canada[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(10): 04020108. |
| 16 | 邱荷婷. 基于交通流分配的充电站布局优化研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学经济管理学院, 2020. |
| Qiu He-ting. Research on the layout optimization of charging station based on traffic flow assignment[D]. Beijing: School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 17 | Ammous M, Belakaria S, Sorour S.Joint delay and cost optimization of in-route charging for on-demand electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2020, 5(1): 149-164. |
| 18 | 惠迎新, 陈嘉伟. 基于改进遗传算法下的挤扩支盘群桩优化方法[J/OL]. [2022-06-20]. |
| 19 | Li M X, Yang G L, Li X Q, et al. Variable universe fuzzy control of adjustable hydraulic torque converter based on multi-population genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 18526655. |
| 20 | Luan Y, Tang J. An improved gravity model for passenger flow distribution prediction of new urban rail transit lines[C]∥5th International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation, Nanchang, China, 2020: 487-491. |
| [1] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [2] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [3] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [4] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [5] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于某二级减速齿轮系统的齿面修形优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1541-1551. |
| [6] | 姜斌祥,姜彤彤,王永雷. 基于文化遗传算法的毒品检验区块链共识算法优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 684-692. |
| [7] | 刘兴涛,林思源,武骥,何耀,刘新天. 计及电池功率状态的再生制动优化策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2796-2805. |
| [8] | 朱思峰,赵明阳,柴争义. 边缘计算场景中基于粒子群优化算法的计算卸载[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2698-2705. |
| [9] | 李翠玉,胡雅梦,康亚伟,张德良. 应用自适应遗传算法的电动汽车充放电协同调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2508-2513. |
| [10] | 李晗,杜鹏,杜颖,李晓会. 基于遗传算法的无线体域网多路径路由选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2706-2711. |
| [11] | 张必达,闫强,张琳,张海瑞. 基于实时交通信息的电动汽车充换电路径规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2333-2342. |
| [12] | 陈传海,姚国祥,金桐彤,申桂香,于立娟,田海龙. 基于响应面与遗传算法的主轴系统动力学建模及参数修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2278-2286. |
| [13] | 赵又群,李宇昊,邓汇凡,林涛,林棻. 基于Popov超稳定性的分布式电动汽车稳定性控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2225-2233. |
| [14] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [15] | 冯建鑫,王强,王雅雷,胥彪. 基于改进量子遗传算法的超声电机模糊PID控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1990-1996. |
|
||