吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 396-404.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220453
城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略
- 长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
Resilience assessment and recovery strategy on urban rail transit network
Min MA( ),Da-wei HU(
),Da-wei HU( ),Lan SHU,Zhuang-lin MA
),Lan SHU,Zhuang-lin MA
- College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
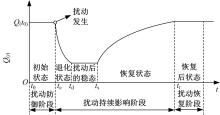
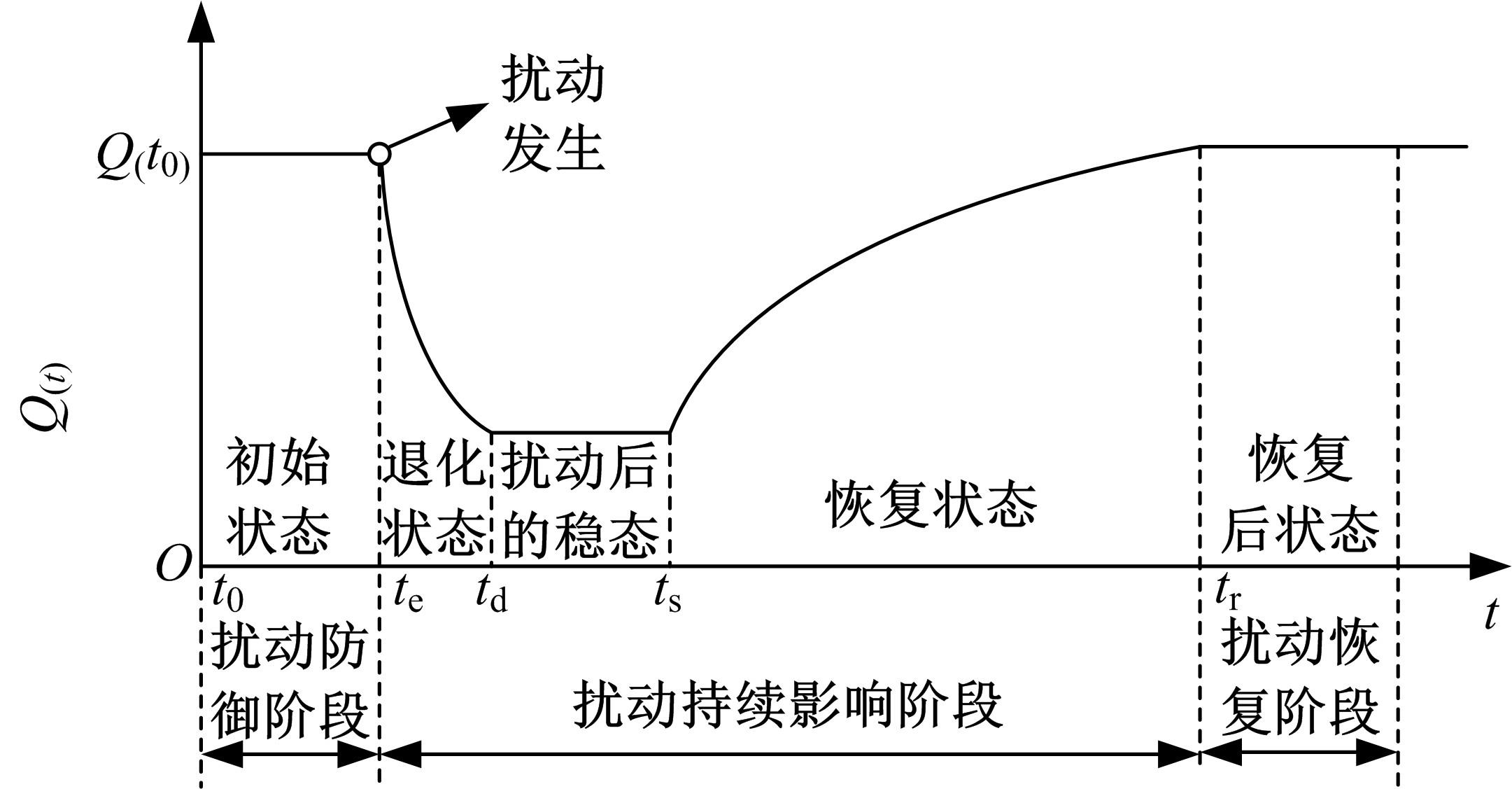
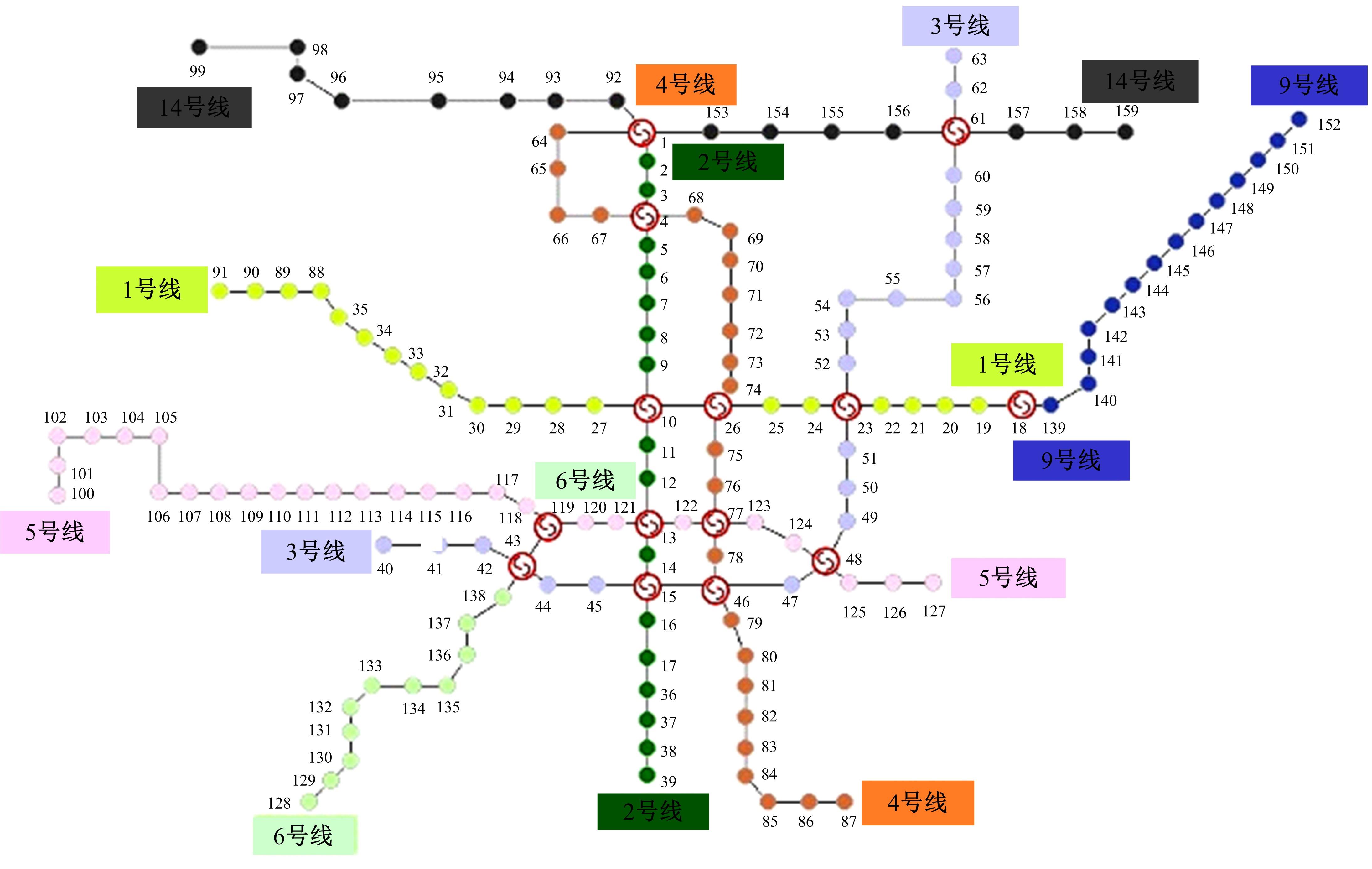
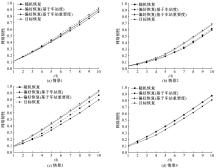
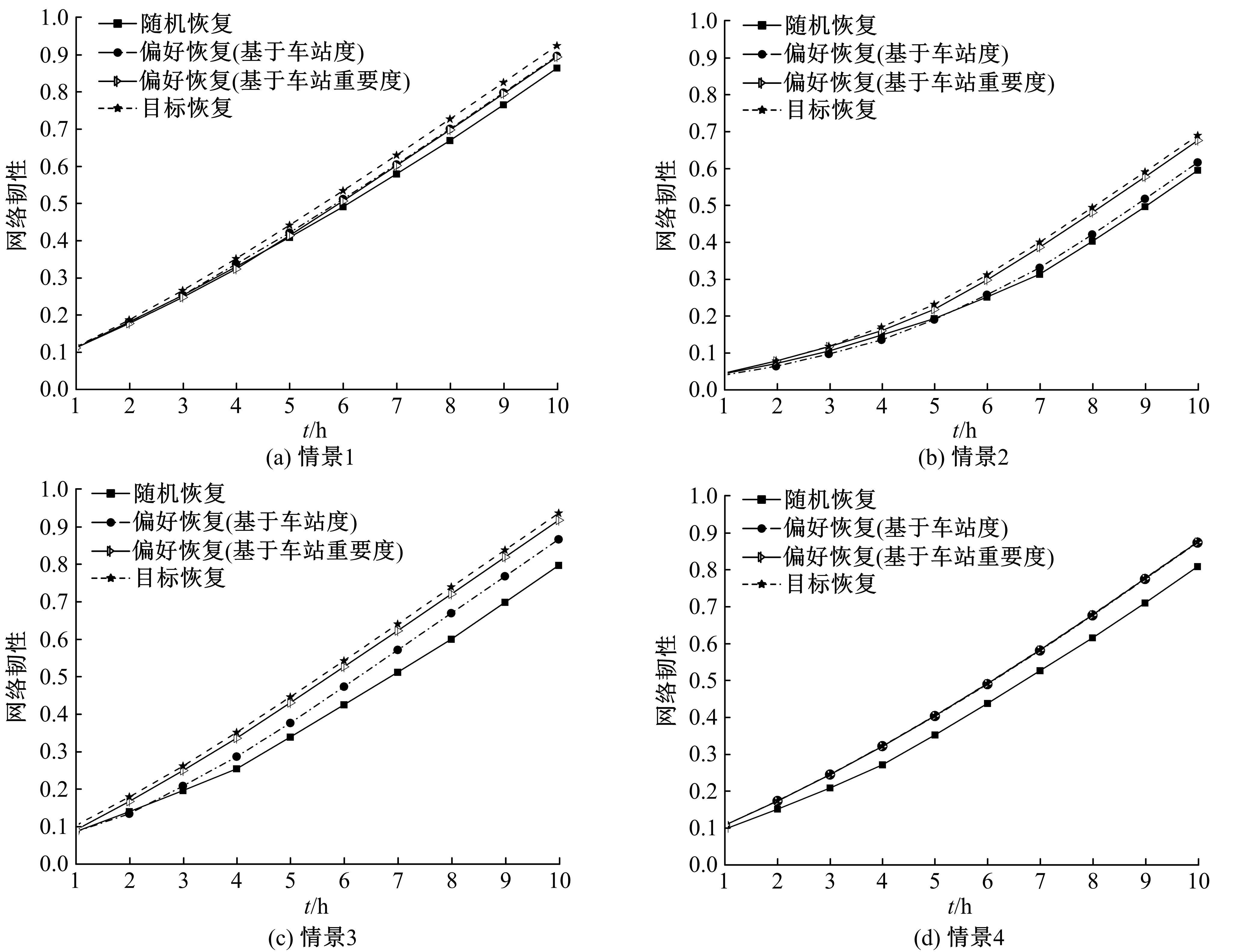
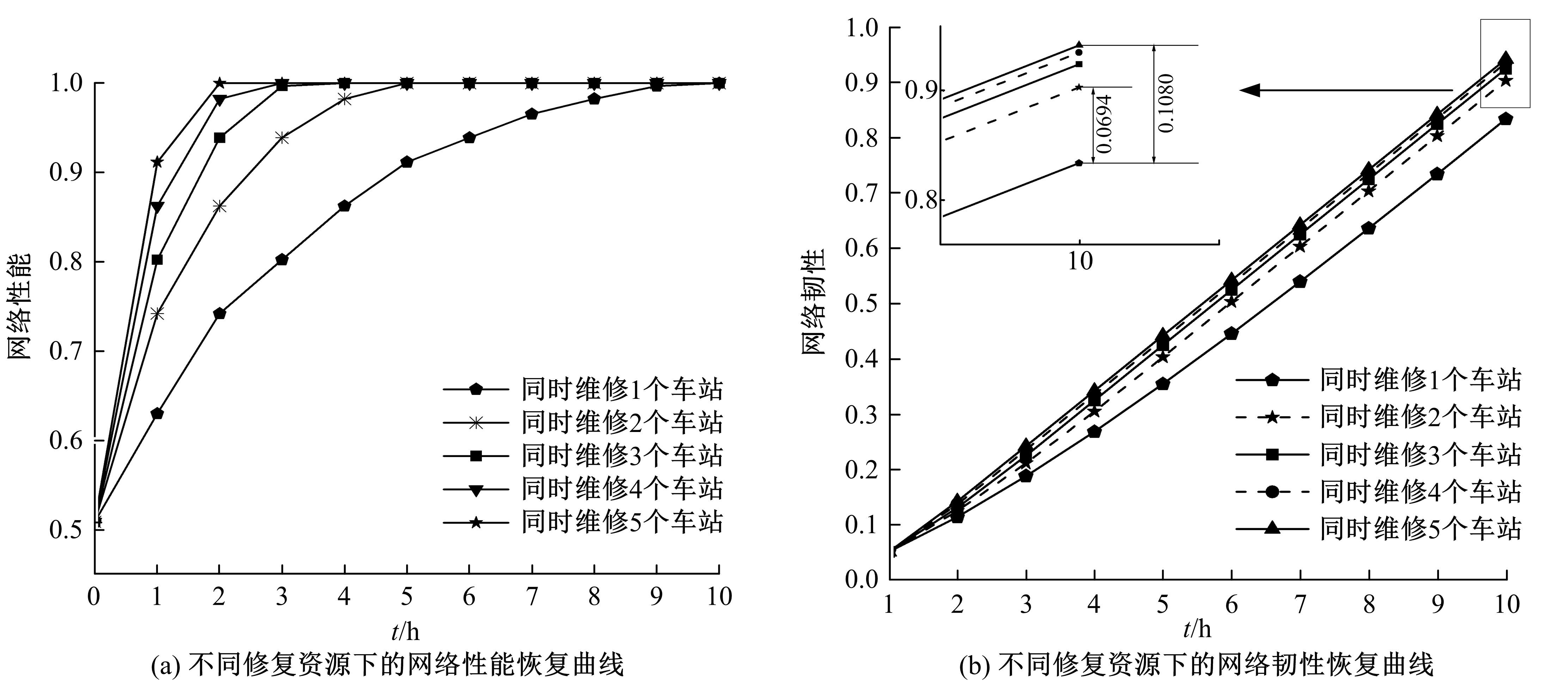
针对现有研究基于拓扑网络效率分析城市轨道交通网络韧性的不足,提出以网络性能响应函数为基础的韧性评估方法,提出的网络性能响应函数是OD客流损失率和网络服务效率损失率的加权求和,采用德尔菲-熵权法确定指标的综合权重,构建以网络韧性指标最大化为目标的恢复优化模型,采用自适应遗传算法进行求解。以西安市轨道交通网络为例,考虑随机攻击和蓄意攻击策略提出4种假设扰动情景,对比分析目标恢复策略与随机恢复策略、偏好恢复策略在4种假设扰动情景下对网络韧性修复效果的差异。结果表明:目标恢复策略对轨道交通网络的修复效果最好,其次是偏好恢复策略;与随机攻击策略相比,蓄意攻击时不同恢复策略得到的网络韧性差别较大;选择修复受损车站顺序时,不能仅考虑受损车站在网络拓扑结构中的重要性,还应当考虑受损车站客流量对网络性能的影响;增加修复资源可以缩短恢复时间和提高修复效率,但修复资源的增加与网络韧性的提升不成正比。研究结论可以为城市轨道交通网络的韧性评估与抢修恢复提供决策依据。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Derrible S, Kennedy C. Network analysis of world subway systems using updated graph theory[J] Transportation Research Record, 2009(2112): 17-25. |
| 2 | 冯国强,李菁.城市轨道交通减排治污效应评估[J].中国人口·资源与环境, 2019, 29(10): 143-151. |
| Feng Guo-qiang, Li Jing. Assessment of emission reduction effect of urban rail transit[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2019, 29(10): 143-151. | |
| 3 | 侯秀芳, 梅建萍, 左超. 2021年中国内地城轨交通线路概况[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2022, 35(1): 12-16. |
| Hou Xiu-fang, Mei Jian-ping, Zuo Chao. An overview of urban rail transit lines in the Chinese mainland in 2021[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2022, 35(1): 12-16. | |
| 4 | Holling C S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1973, 4: 1-23. |
| 5 | Berdica K. An introduction to road vulnerability: what has been done, is done and should be done[J]. Transport Policy, 2002, 9(2): 117-127. |
| 6 | 杨金顺,孙洪运,李林波,等.道路交通系统恢复力研究进展综述[J].交通信息与安全,2014,32(3): 87-93. |
| Yang Jin-shun, Sun Hong-yun, Li Lin-bo, et al. Review of road transportation system resilience research[J]. Journal of Transportation Information and Safety, 2014, 32(3): 87-93. | |
| 7 | Bruneau M, Chang S E, Eguchi R T, et al. A framework to quantitatively asses and enhance the seismic resilience of communities[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2003, 19(4): 733-752. |
| 8 | Ayyub B M. Practical resilience metrics for planning, design, and decision making[J]. ASCE-ASME Journal of Risk Uncertain Engineering Systems, Part A: Civil Engineering, 2015, 1(3): 04015008. |
| 9 | Zhang D, Du F, Huang H, et al. Resilience assessment of urban rail transit networks: Shanghai metro as an example[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 106: 230-243. |
| 10 | 张洁斐, 任刚, 马景峰, 等. 基于韧性评估的轨道交通网络修复时序决策方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 2(4): 14-20. |
| Zhang Jie-fei, Ren Gang, Ma Jing-feng, et al. Decision-making method of repair sequence for metro network based on resilience evaluation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 2(4): 14-20. | |
| 11 | 黄莺, 刘梦茹, 魏晋果, 等. 基于韧性曲线的城市轨道交通网络恢复策略研究[J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(1): 32-36. |
| Huang Ying, Liu Meng-ru, Wei Jin-guo, et al. Research on urban metro network recovery strategy based on resilience curve[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(1): 32-36. | |
| 12 | 吕彪,管心怡,高自强. 轨道交通网络服务韧性评估与最优恢复策略[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(5): 198-205, 221. |
| Lv Biao, Guan Xin-yi, Gao Zi-qiang. Evaluation and optimal recovery strategy of metro network service resilience[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(5): 198-205, 221. | |
| 13 | Nan C, Sansavini G. A quantitative method for assessing resilience of interdependent infrastructures[J]. Reliability Engineering&System Safety, 2017, 157: 35-53. |
| 14 | Ouyang M, Dueñas-Osorio L, Min X. A three-stage resilience analysis framework for urban infrastructure systems[J]. Structural Safety, 2012, 36/37: 23-31. |
| 15 | 张海涛, 靖继鹏. 制造企业综合信息竞争力测度模型的建立[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2005, 35(3): 339-342. |
| Zhang Hai-tao, Jing Ji-peng. Measure model for manufacturing enterprise integrated information competitive power[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2005, 35(3): 339-342. | |
| 16 | 朱天曈, 丁坚勇, 郑旭. 基于改进TOPSIS法和德尔菲——熵权综合权重法的电网规划方案综合决策方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(12): 91-99. |
| Zhu Tian-tong, Ding Jian-yong, Zheng Xu. A comprehensive decision-making method for power network planning schemes based on the combination of the improved TOPSIS method with Delphi-entropy weight method[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(12): 91-99. | |
| 17 | 陈国芳, 卫豪. 基于EW-AHP和未确知测度理论的隧道瓦斯风险评价[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(5): 89-95. |
| Chen Guo-fang, Wei Hao. Tunnel gas risk assessment based on EW-AHP and unascertained measurement theory[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(5): 89-95. | |
| 18 | 魏丽英, 李鸣君. 考虑诱导影响的公交优先信号配时模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(3): 777-784. |
| Wei Li-ying, Li Ming-jun. Bus priority signal timing model considering the influence of traffic guidance[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(3): 777-784. | |
| 19 | 阳光灿,熊禾根.改进遗传算法求解柔性作业车间调度问题[J].计算机仿真,2022,39(2):221-225, 292. |
| Yang Guang-can, Xiong He-gen.Improved genetic algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling problem[J]. Computer Simulation, 2022, 39(2): 221-225, 292. | |
| 20 | 徐力,刘云华,王启富.自适应遗传算法在机器人路径规划的应用[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(18): 36-41. |
| Xu Li, Liu Yun-hua, Wang Qi-fu. Application of adaptive genetic algorithm in robot path planning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(18): 36-41. | |
| 21 | 张超群, 郑建国, 钱洁. 遗传算法编码方案比较[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2011, 28(3): 819-822. |
| Zhang Chao-qun, Zheng Jian-guo, Qian Jie, Comparison of coding schemes for genetic algorithms[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(3): 819-822. | |
| 22 | 周伟, 李敏, 丘铭军, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的车身板件厚度优化[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 62(3): 523-532. |
| Zhou Wei, Li Min, Qiu Ming-jun, et al. Vehicle body panel thickness optimization by a genetical algorithm [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2022, 62(3): 523-532. |
| [1] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [2] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [3] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [4] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [5] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [6] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [7] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [8] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [9] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [10] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [11] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [12] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [13] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [14] | 程国柱,孙秋月,刘玥波,陈纪龙. 基于博弈论的城市道路变道切入行为模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2839-2844. |
| [15] | 李翠玉,胡雅梦,康亚伟,张德良. 应用自适应遗传算法的电动汽车充放电协同调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2508-2513. |
|