吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1227-1236.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220814
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
面向电铲自主装卸的矿用自卸车斗型优化
谭晓丹1( ),王勇澎2,Hall Robert3,徐天爽1(
),王勇澎2,Hall Robert3,徐天爽1( ),黄庆学4
),黄庆学4
- 1.吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
2.太原重型机械集团有限公司 矿山采掘装备及智能制造国家重点实验室,太原 030024
3.南达科他州矿业理工大学 采矿工程与管理学院,拉皮德城 57701
4.太原理工大学 机械与运载工程学院,太原 030024
Haul truck dump body optimization for autonomous shovel loading
Xiao-dan TAN1( ),Yong-peng WANG2,Robert Hall3,Tian-shuang XU1(
),Yong-peng WANG2,Robert Hall3,Tian-shuang XU1( ),Qing-xue HUANG4
),Qing-xue HUANG4
- 1.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Mining Equipment and Intelligent Manufacturing,Taiyuan Heavy Industry Co. ,Ltd. ,Taiyuan 030024,China
3.Department of Mining Engineering and Management,South Dakota School of Mines and Technology,Rapid City 57701,USA
4.College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering,Taiyuan University of Technology,Taiyuan 030024,China
摘要:
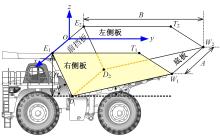
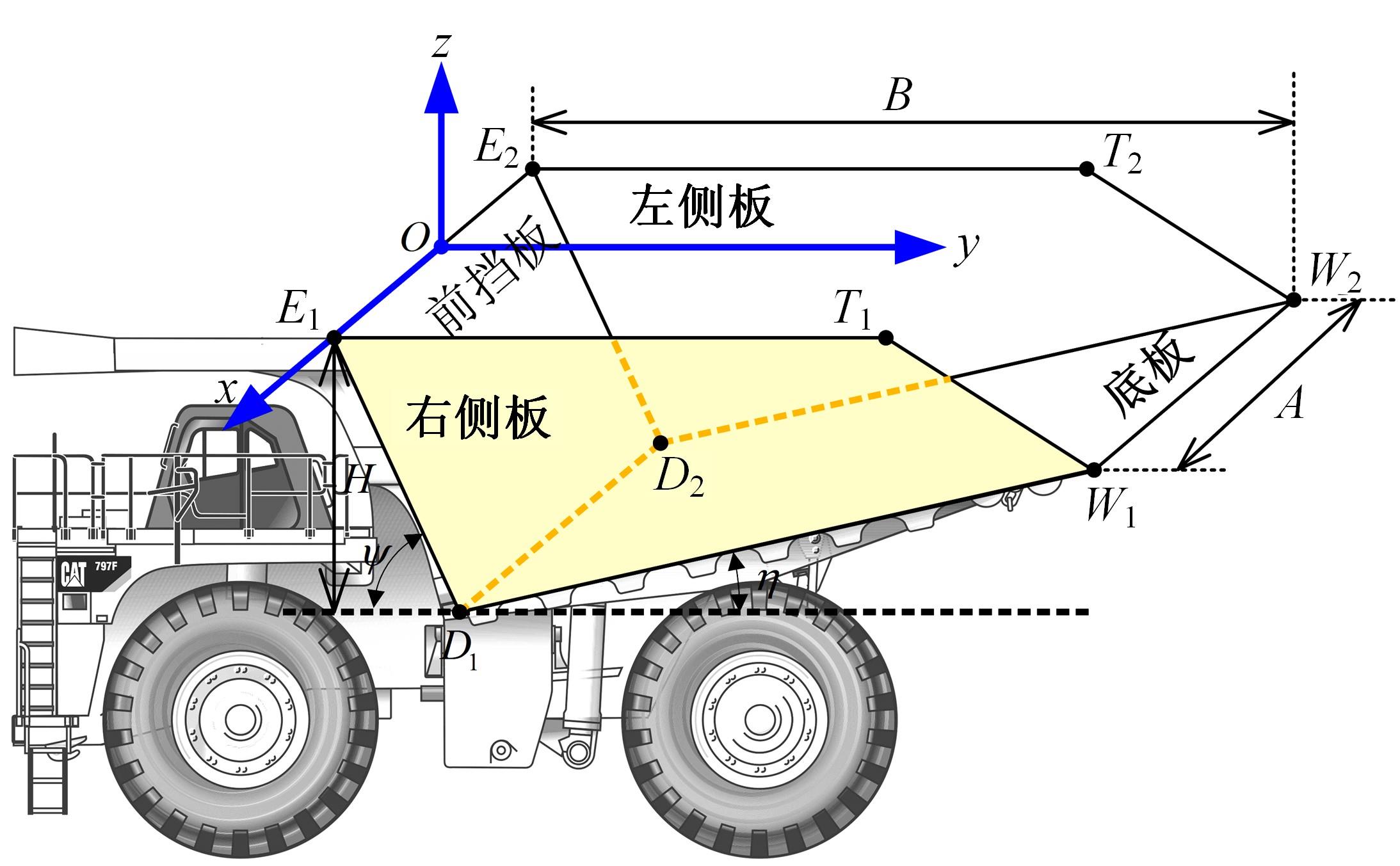
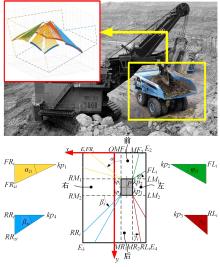
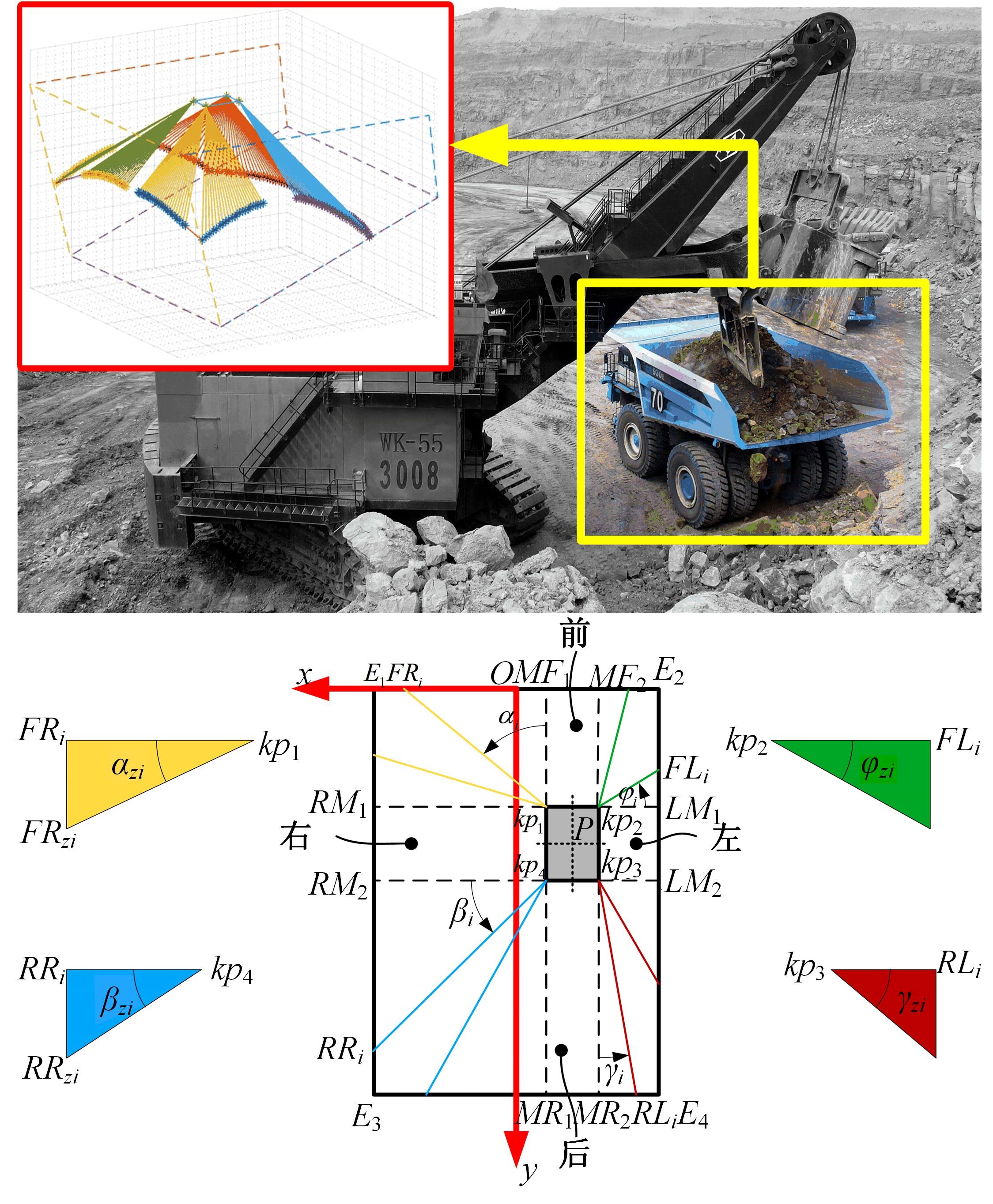
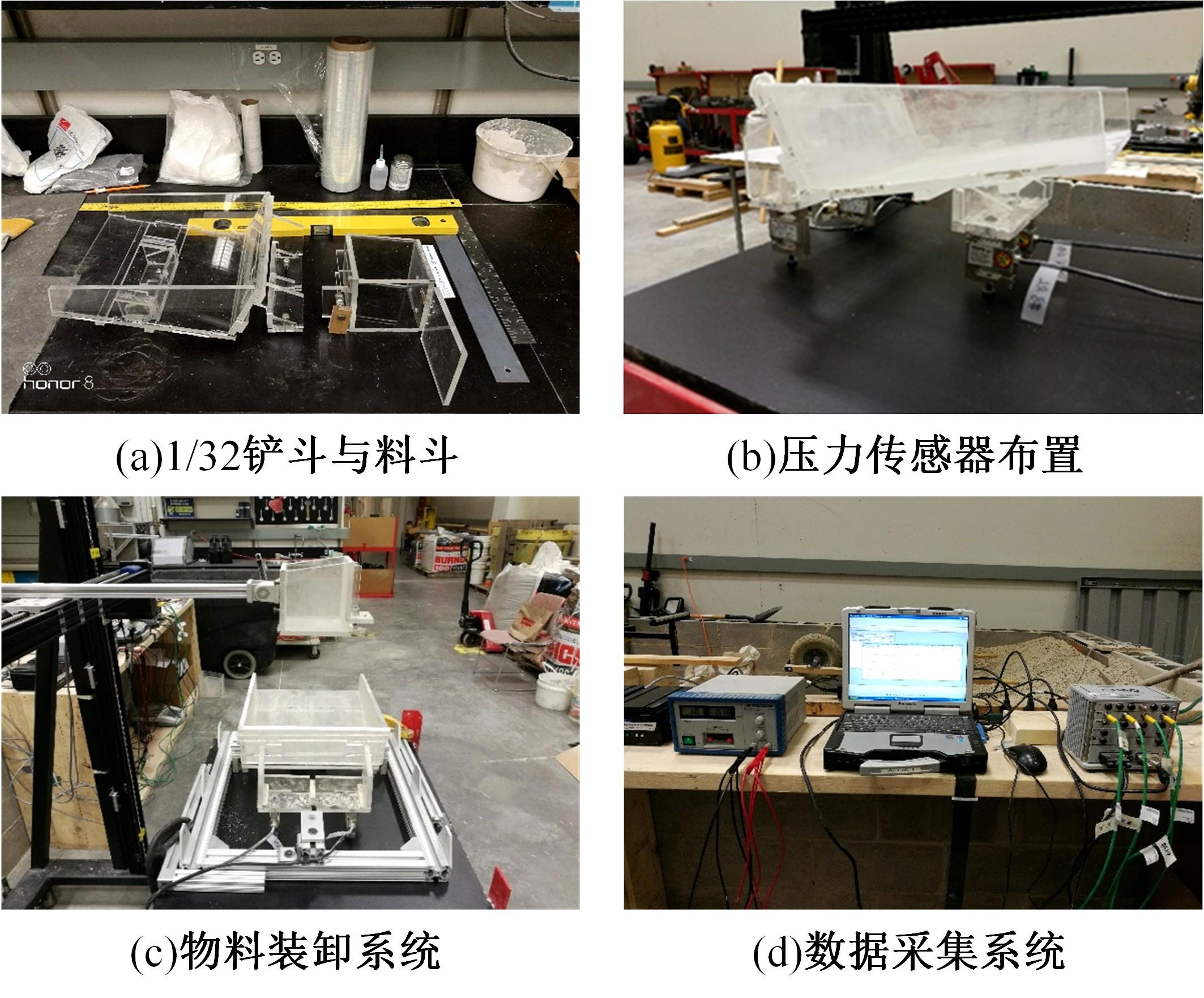
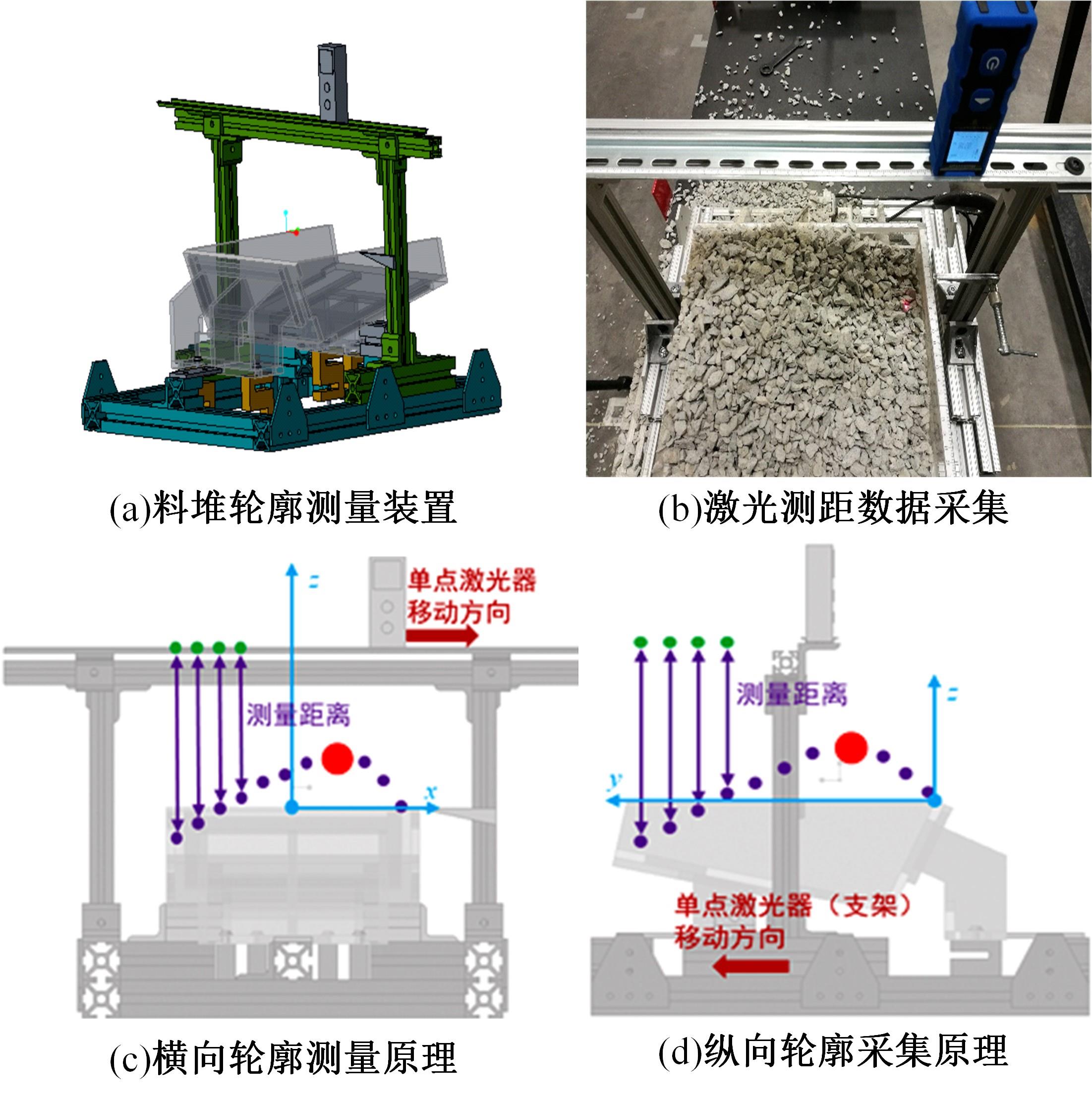
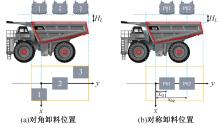
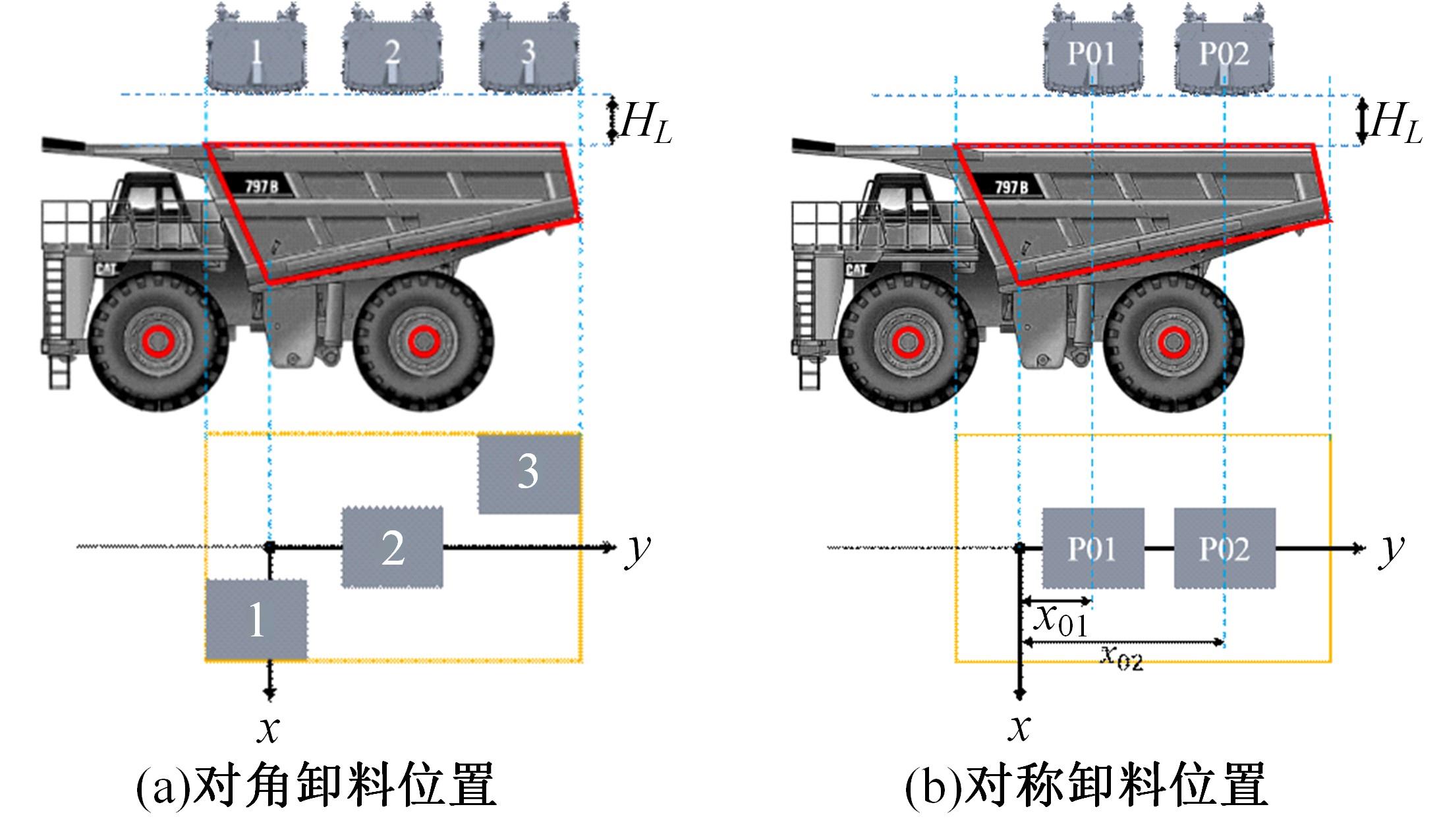
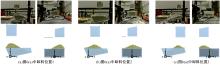
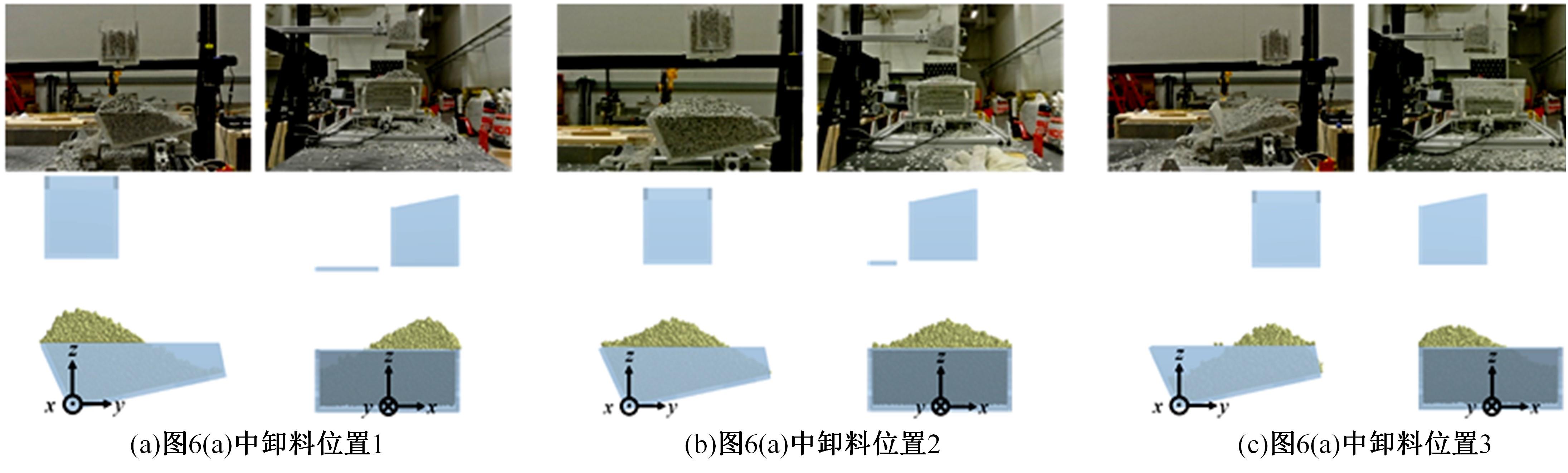
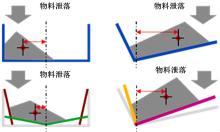
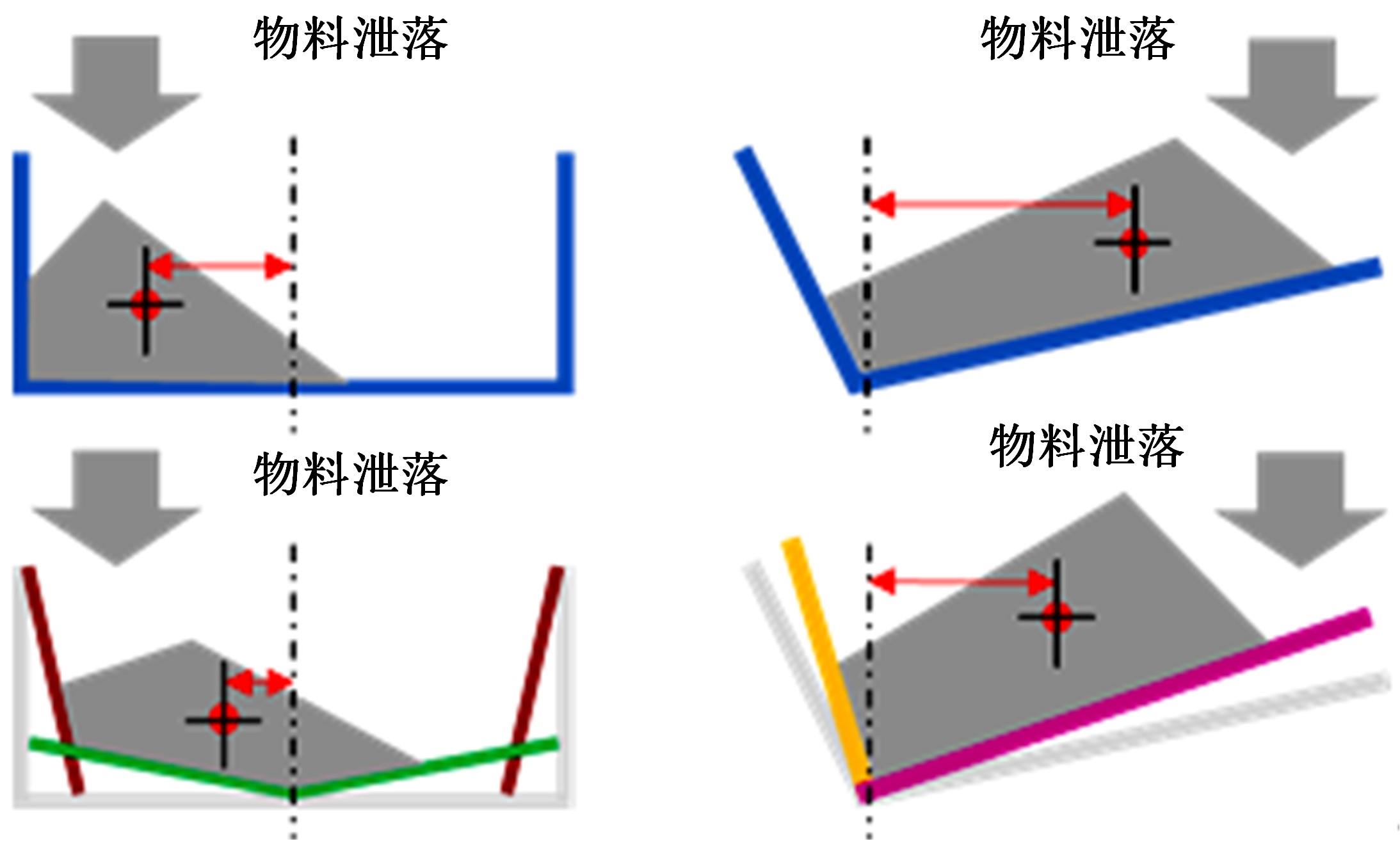
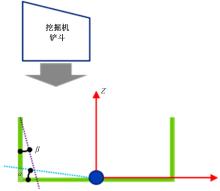
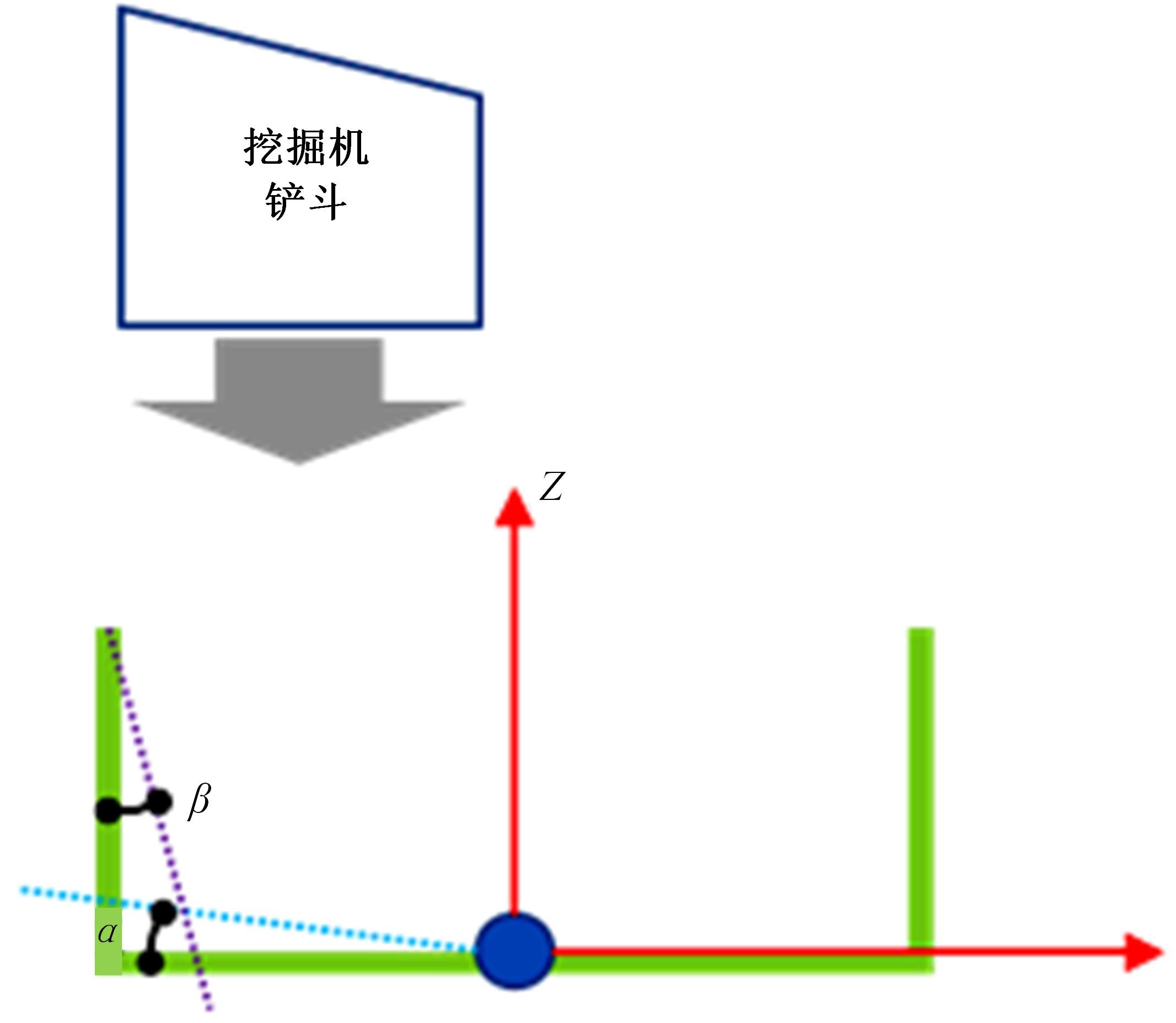
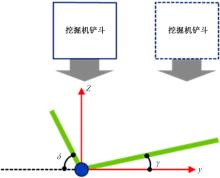
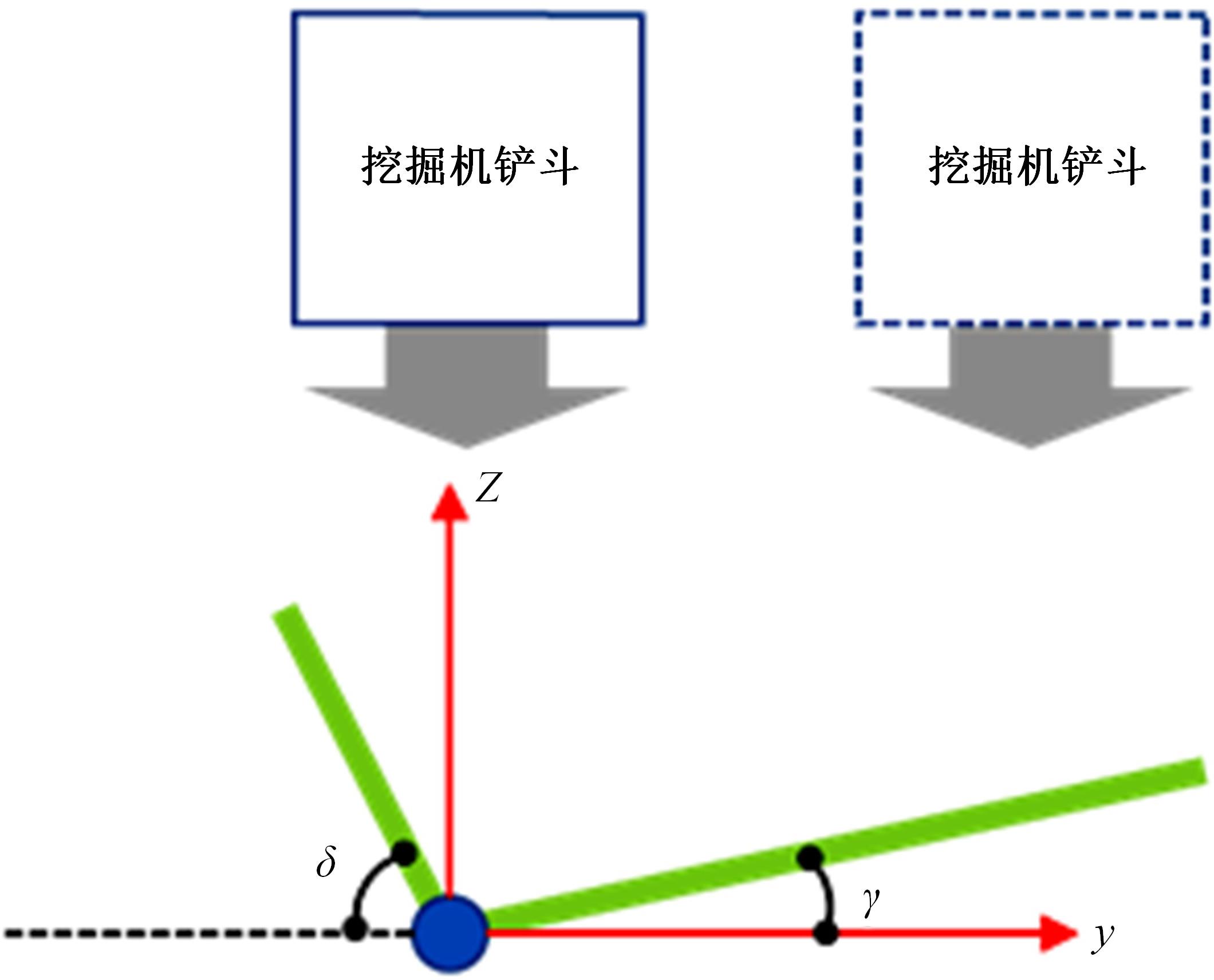
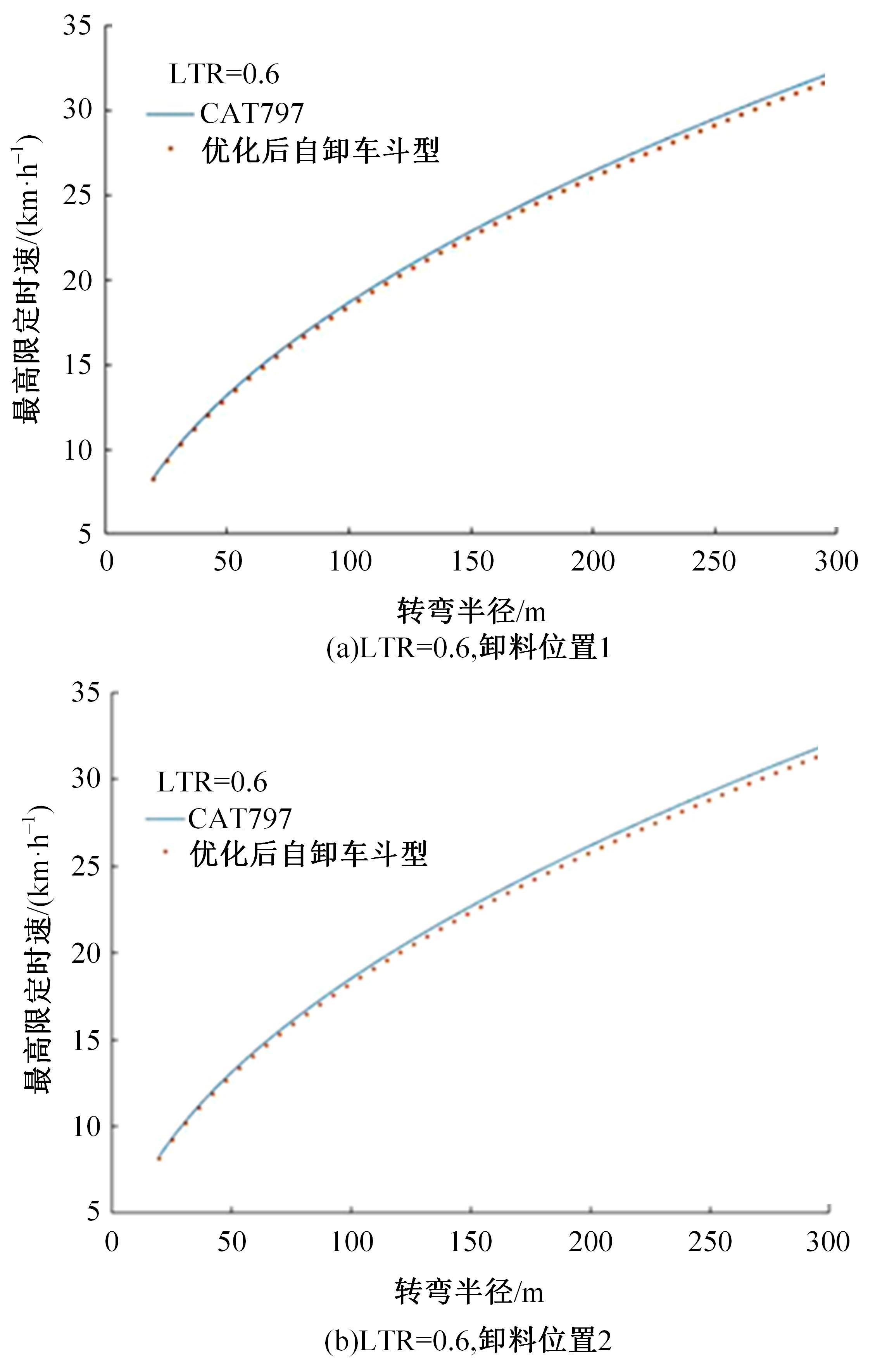
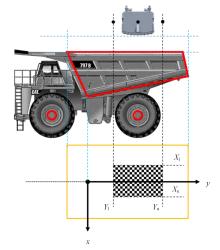
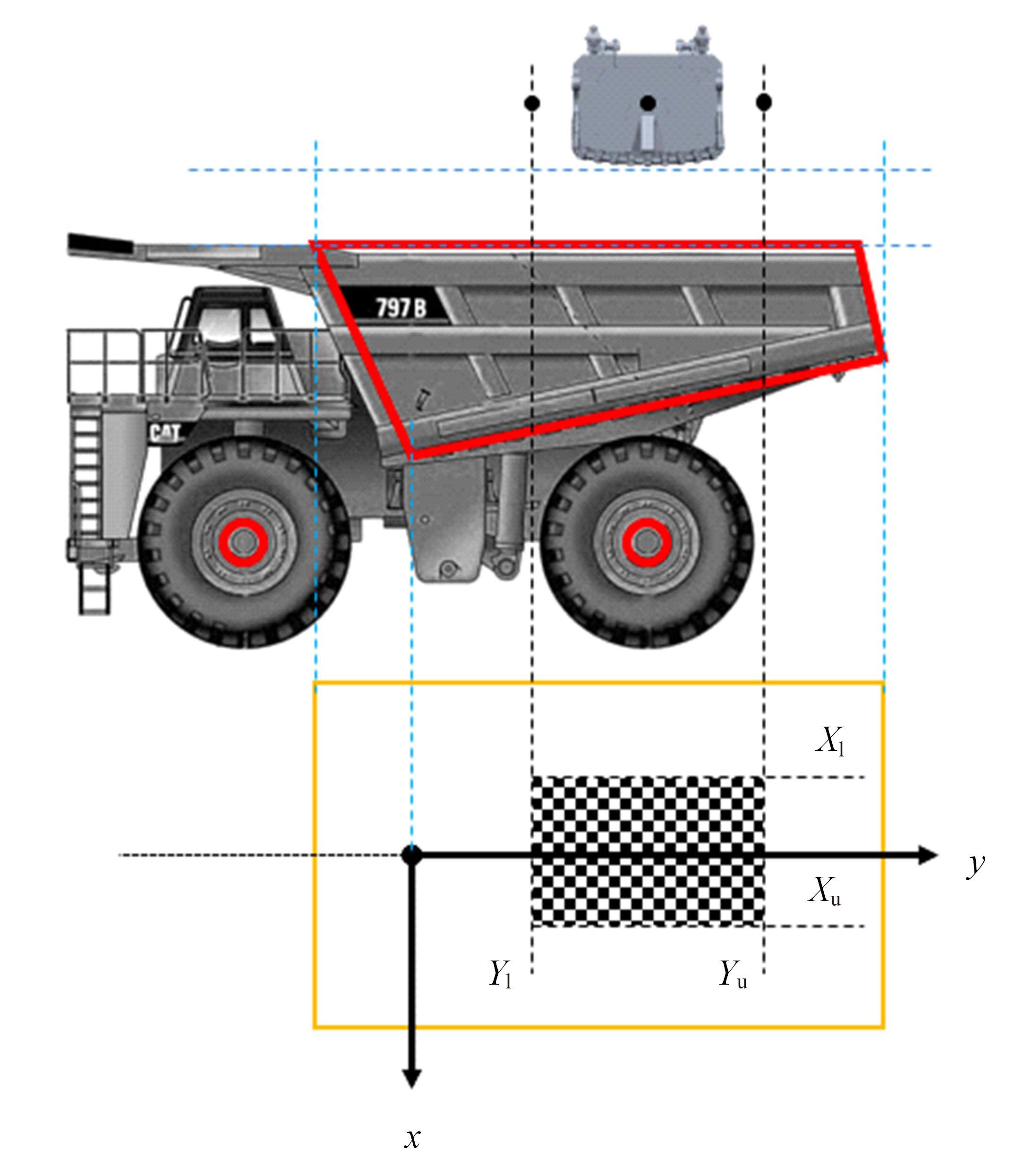
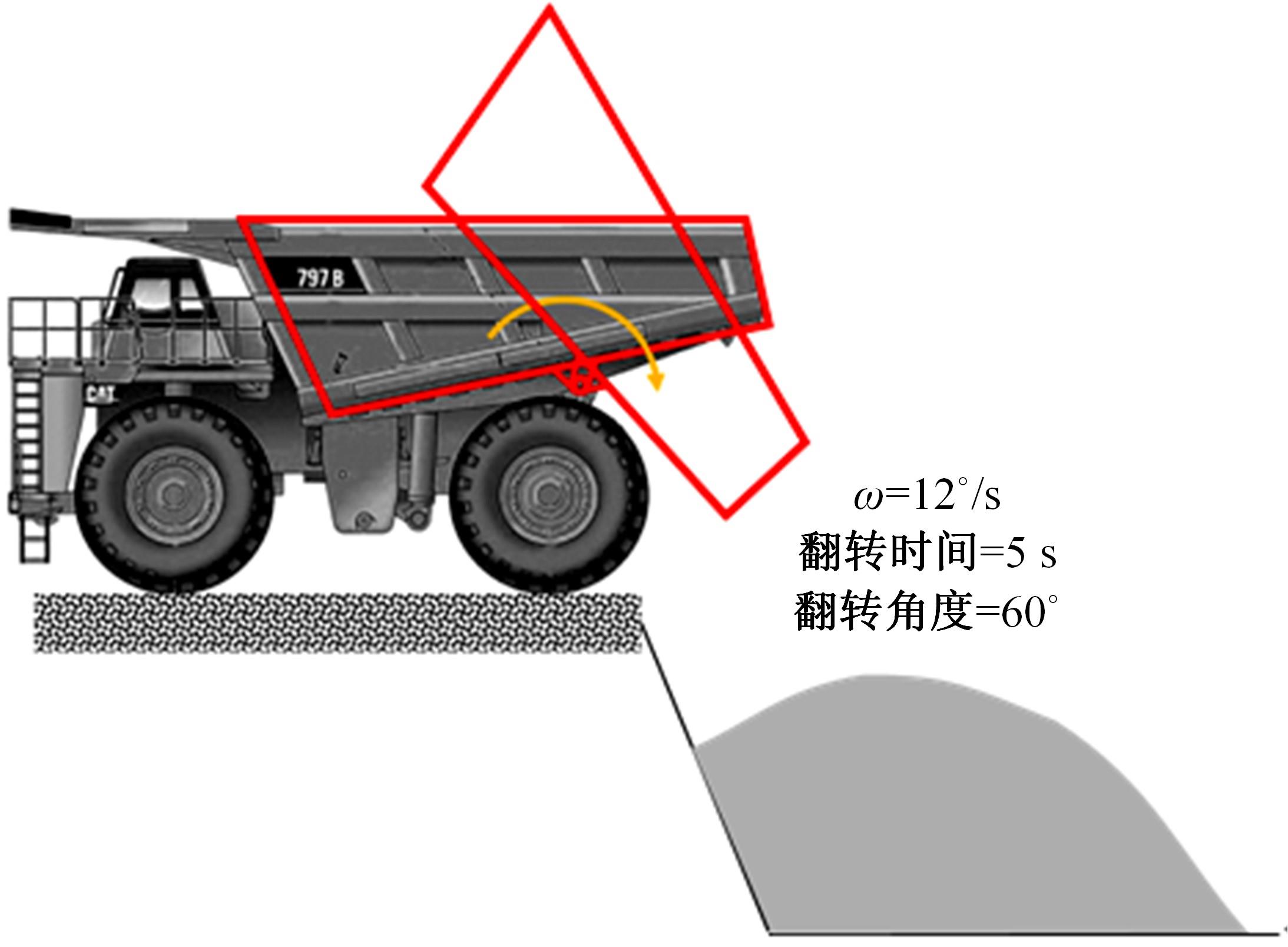
针对现有电铲自主装卸功能在料堆重构、环境感知、目标识别等领域存在技术难度的现状,从降低自主装卸作业任务难度的角度出发,本文提出了一种以载荷均衡分布为目标的矿用自卸车斗型优化方法。首先,构建了一种基于差分迭代的装卸后自卸车斗内料堆的轮廓重构方法,并对料堆质心位置进行计算;其次,建立并验证了模拟电铲装卸过程的离散元仿真方法;再次,利用离散元仿真实验,研究了不同斗型结构参数对斗内料堆质心位置的影响;最后,以横向载荷均布为目标,以纵向载荷分布、行驶安全性、斗容变化为约束对斗型进行优化。结果表明:优化后的斗型与原斗型相比,在保持装载能力和行驶安全性的前提下,极端装卸位置时的载荷分布均匀性显著提升,并具有更大的合理装卸面积和更高的作业效率。
中图分类号:
- U469.4
| 1 | 王继新, 季景方, 张英爽, 等. 基于小波分形理论的工程车辆时域载荷信号降噪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2011, 41(): 221-225. |
| Wang Ji-xin, Ji Jing-fang, Zhang Ying-shuang, et al. Denoising method of time domain load signals of engineering vehicles based on wavelet and fractal theory[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(Sup.2): 221-225. | |
| 2 | Duff E. Automated volume estimation of haul-truck loads[C]. ACRA 2000, Melbourne, Australia, 2000: 179-184. |
| 3 | LeRoy G, Philip T. Process for three-dimensional modeling and design of off-highway dump bodies[P]. United States Patent: US008113763B2, 2012-02-14. |
| 4 | LeRoy G. Method of estimating the volumetric carrying capacity of a truck body[P]. United States Patent: USOO8280596B2, 2012-10-02. |
| 5 | SAE J1363. Capacity rating—dumper body and trailer body [S]. |
| 6 | LeRoy G. Adapting the off-highway truck body volumetric process to real world conditions[C]∥SAE International Off-Highway and Powerplant Congress and Exposition, Milwaukee USA, 2000. |
| 7 | Joshua C. Haul truck payload modelling using strut pressures[D]. Edmonton: School of Mining & Petroleum Engineering, University of Alberta, 2015. |
| 8 | Sun X, Li X, Xiao D, et al. A method of mining truck loading volume detection based on deep learning and image recognition[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(2): 635. |
| 9 | Yao Z, Huang Q, Ji Z, et al. Deep learning-based prediction of piled-up status and payload distribution of bulk material[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 121: 103424. |
| 10 | Javier G, Tito A, Francisco Y, et al. Point cloud-based estimation of effective payload volume for earthmoving loaders[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 117: 103207. |
| 11 | Mi C, Gu Z, Zhang Y, et al. Frame weight and anti-fatigue co-optimization of a mining dump truck based on Kriging approximation model[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 66: 99-109. |
| 12 | Mi C, Gu Z, Yang Q, et al. Frame fatigue life assessment of a mining dump truck based on finite element method and multibody dynamic analysis[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2012, 23: 18-26. |
| 13 | 申焱华,魏福林,石博强. 基于退化过程的矿用自卸车货箱磨损预测分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2016, 27(21): 2846-2850, 2854. |
| Shen Yan-hua, Wei Fu-lin, Shi Bo-qiang. Wear prediction analysis of mining dump truck body based on degradation processes[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 27(21): 2846-2850, 2854. | |
| 14 | 邓阳庆,王登峰,王建华, 等. 面向用户的重型自卸车节油研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2009, 39(): 74-77. |
| Deng Yang-qing, Wang Deng-feng, Wang Jian-hua, et al. User-oriented fuel economy study on heavy-duty tipper[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(Sup.1): 74-77. | |
| 15 | Soofastaei A, Aminossadati S M, Kizil M S,et al. A comprehensive investigation of loading variance influence on fuel consumption and gas emissions in mine haulage operation[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2016, 26(6): 995-1001. |
| 16 | Chamanara A. Enhancing mine haul truck KPIs via payload balance[D]. Edmonton: School of Mining & Petroleum Engineering, University of Alberta, 2013. |
| 17 | 郑宏宇, 杨硕, 文良浒, 等. 基于电控制动系统的客车防侧翻控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1038-1043. |
| Zheng Hong-yu, Yang Shuo, Wen Liang-hu, et al. Anti-rollover control strategy of bus based on electronically controlled braking system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016,46(4): 1038-1043. | |
| 18 | 陈东辉, 吕建华, 龙刚, 等. 基于ADAMS的半悬挂式农业机组静侧翻稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2018,48(4): 1176-1183. |
| Chen Dong-hui, Jian-hua Lyu, Long Gang, et al. Static rollover stability of semi-mounted agricultural machinery based on ADAMS[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(4): 1176-1183. |
| [1] | 孙伟,杨俊. 等角贴敷压电分流片圆柱壳有限元建模及减振分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 365-374. |
| [2] | 胡斌,蔡一全,罗昕,毛自斌,李俊伟,郭孟宇,王剑. 基于种群胁迫的有限齿侧空间高速充种理论与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 574-588. |
| [3] | 刘洋. 动臂塔机防后倾缓冲力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2785-2794. |
| [4] | 赵洋,肖洋,孙皓,霍文浩,冯松,廖勇. 基于围道积分的润滑接触齿轮微点蚀损伤特征模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 799-810. |
| [5] | 郑伟,孙见君,马晨波,於秋萍,张玉言,牛韬. 汽车轮毂加工夹具的研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 25-36. |
| [6] | 陈魏,雷雨龙,李兴忠,付尧,扈建龙,侯利国. 低速工况下渐开线圆柱直齿轮齿面粘着磨损计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1628-1634. |
| [7] | 郭震,于红英,滑忠鑫,赵娣. 刚性折纸机构运动分析及折叠过程仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 66-76. |
| [8] | 朱伟,王传伟,顾开荣,沈惠平,许可,汪源. 一种新型张拉整体并联机构刚度及动力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1777-1786. |
| [9] | 毛宇泽, 王黎钦. 鼠笼支撑一体化结构对薄壁球轴承承载性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
| [10] | 王继新, 翟新婷, 毕野虹天, 李莺莺. 基于AIC-K-means的载荷分段混合分布估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1092-1098. |
| [11] | 赵春江, 梁波, 葛世东, 黄庆学. 求解高速球轴承载荷分布的简化矩阵模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1595-1598. |
|
||