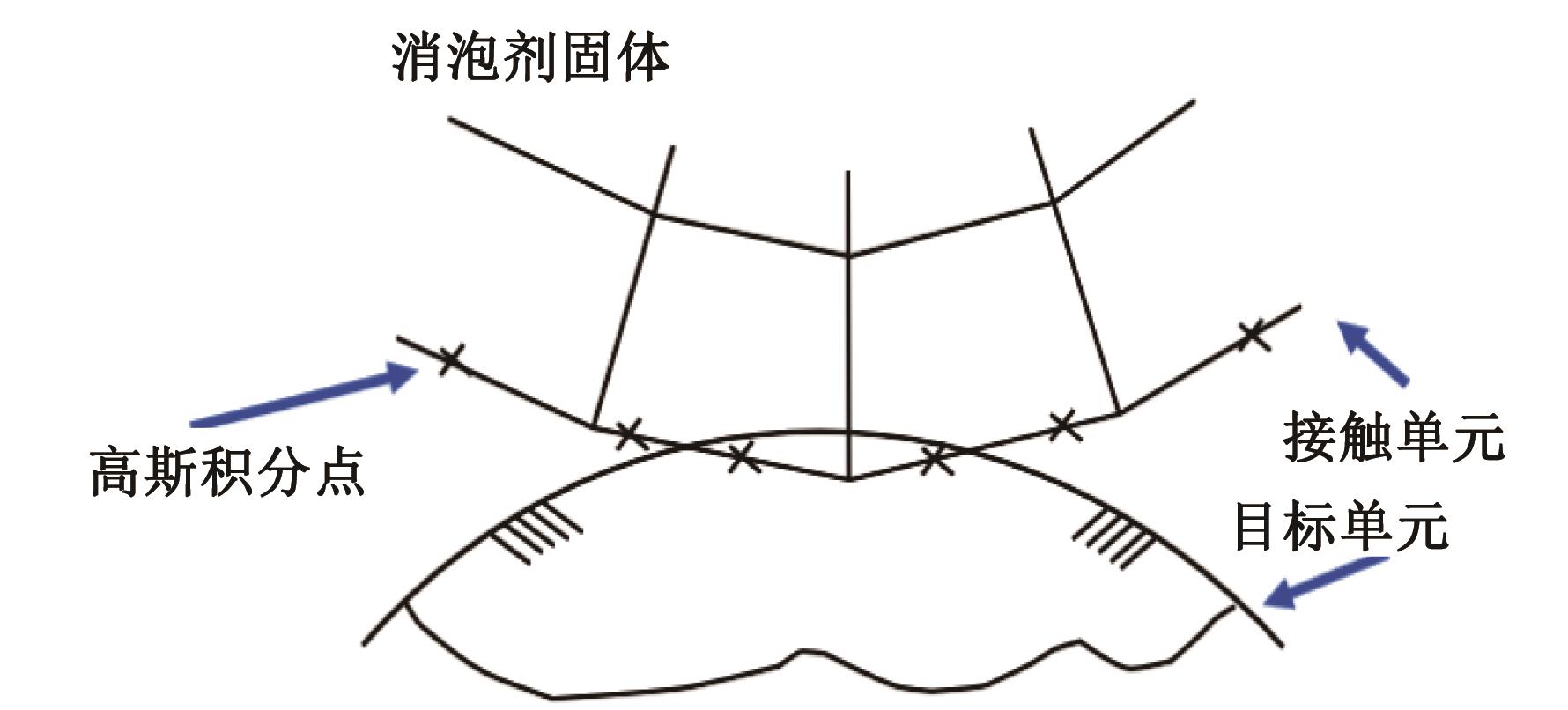
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 392-400.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230234
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
仿清道夫下唇结构除污性能分析
王淑坤1( ),冯育泽1,2,张景然1,张心明1,郑龙2,3(
),冯育泽1,2,张景然1,张心明1,郑龙2,3( )
)
- 1.长春理工大学 机电工程学院,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 威海仿生研究院,山东 威海 264207
3.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
Analysis on decontamination performance of lower lip structure of imitation scavenger
Shu-kun WANG1( ),Yu-ze FENG1,2,Jing-ran ZHANG1,Xin-ming ZHANG1,Long ZHENG2,3(
),Yu-ze FENG1,2,Jing-ran ZHANG1,Xin-ming ZHANG1,Long ZHENG2,3( )
)
- 1.College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.Weihai Institute for Bionics,Jilin University,Weihai 264207,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
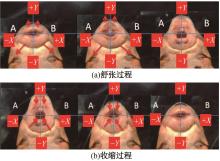
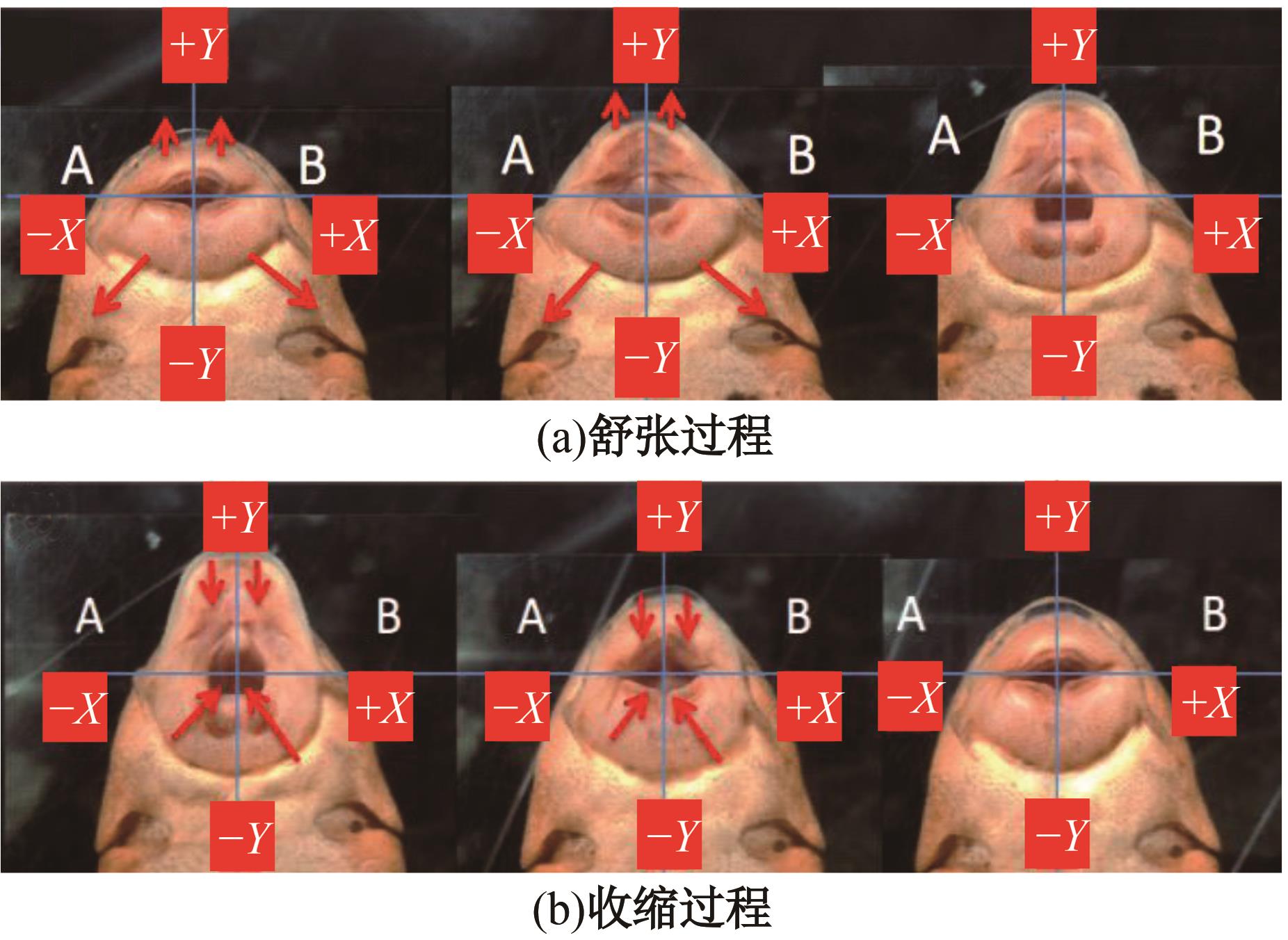
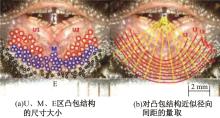
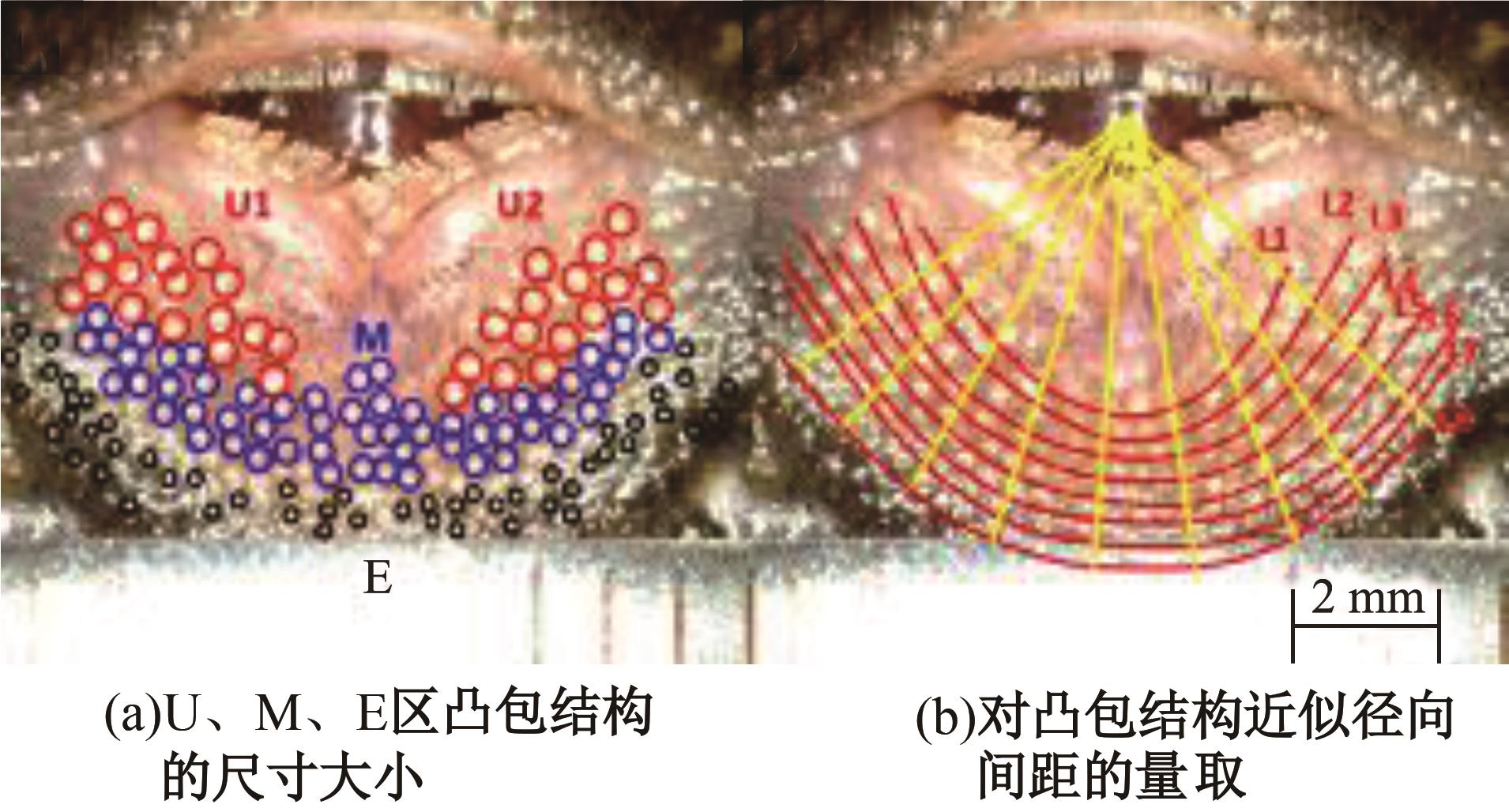
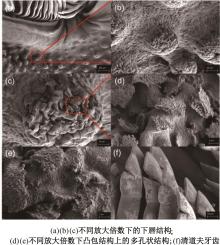
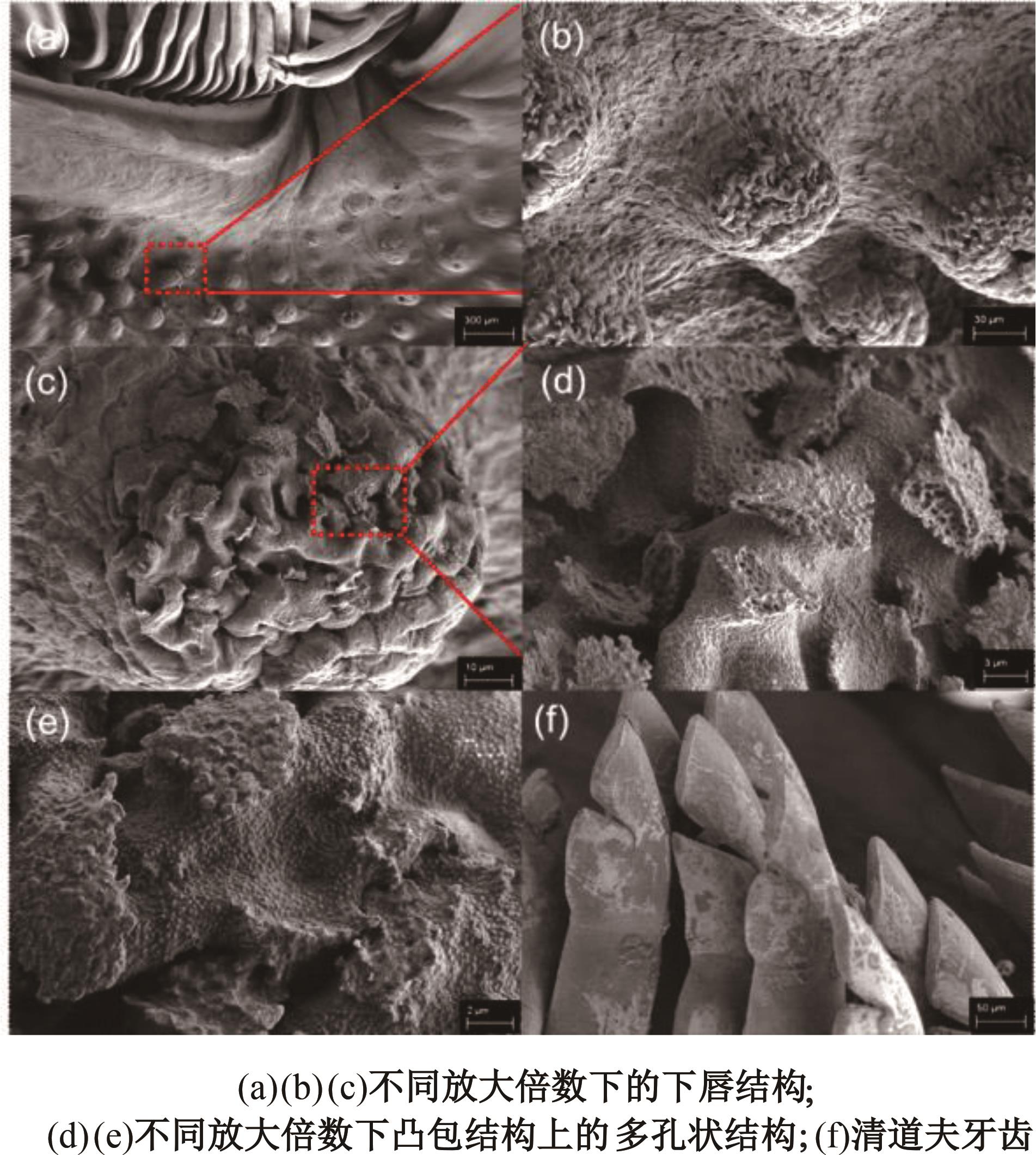
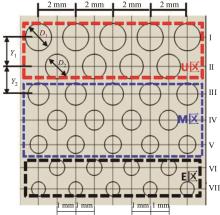
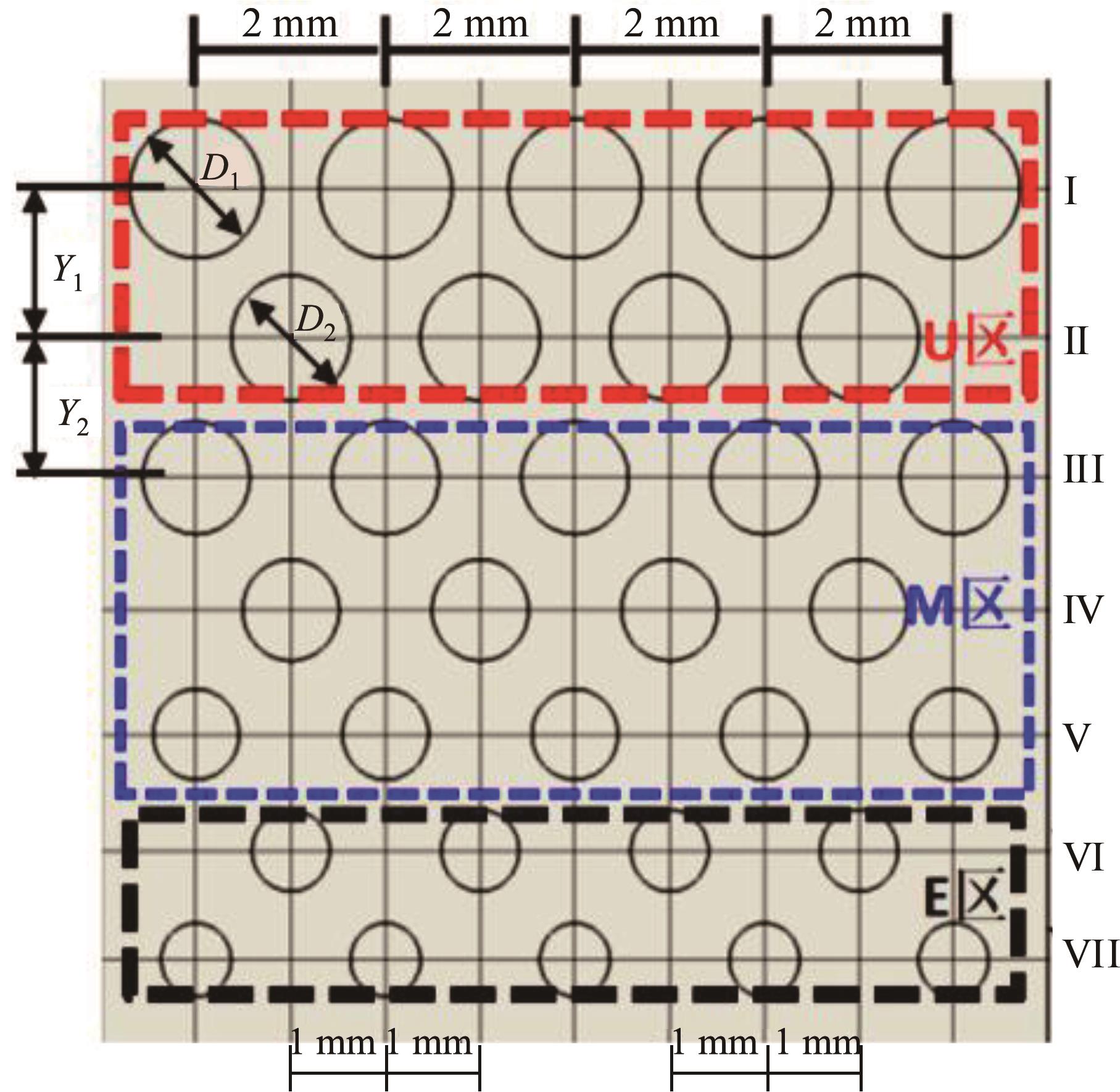
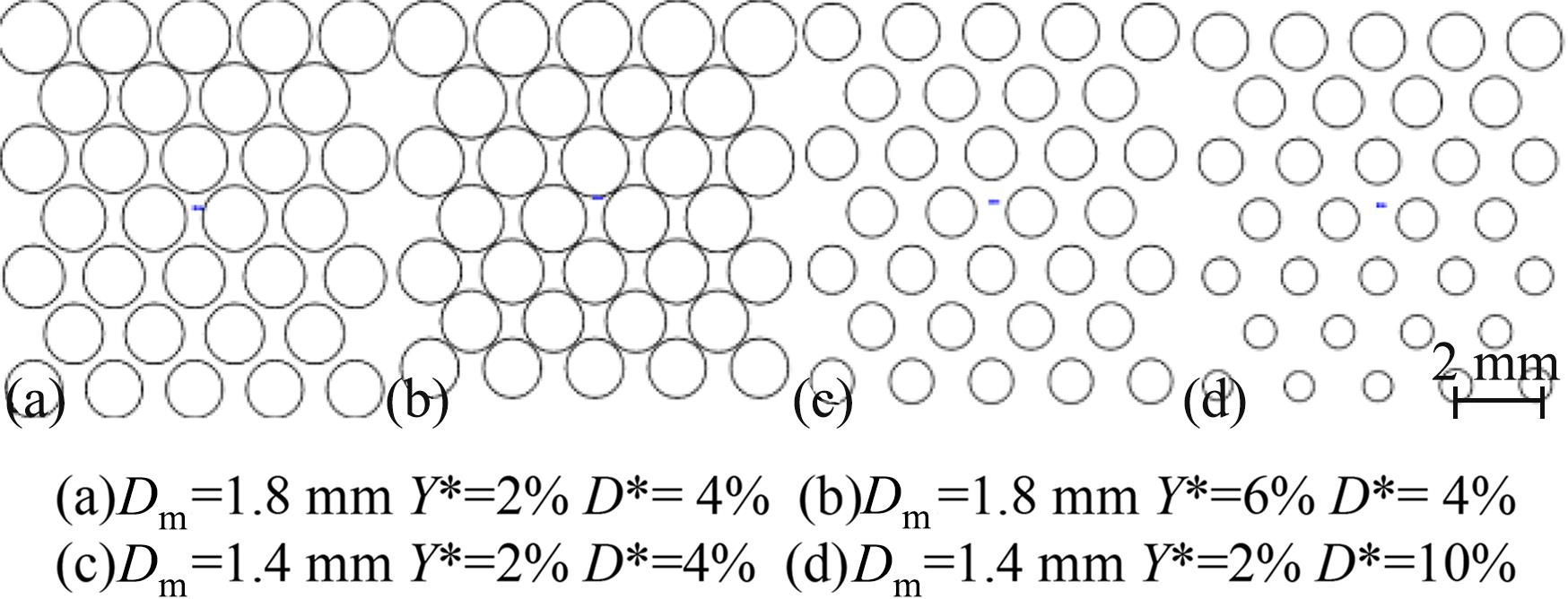
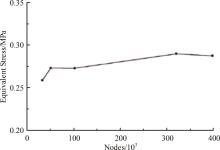
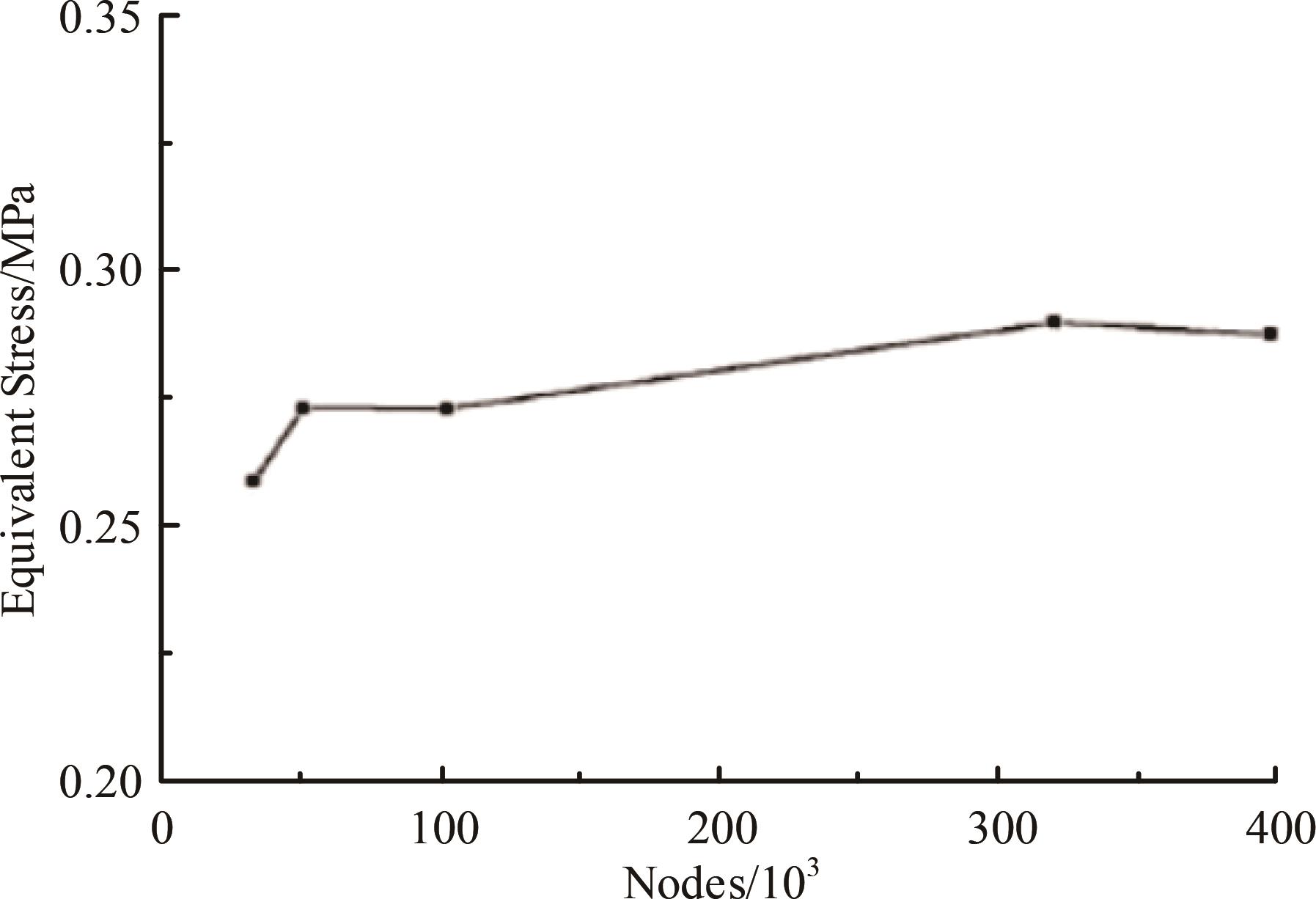
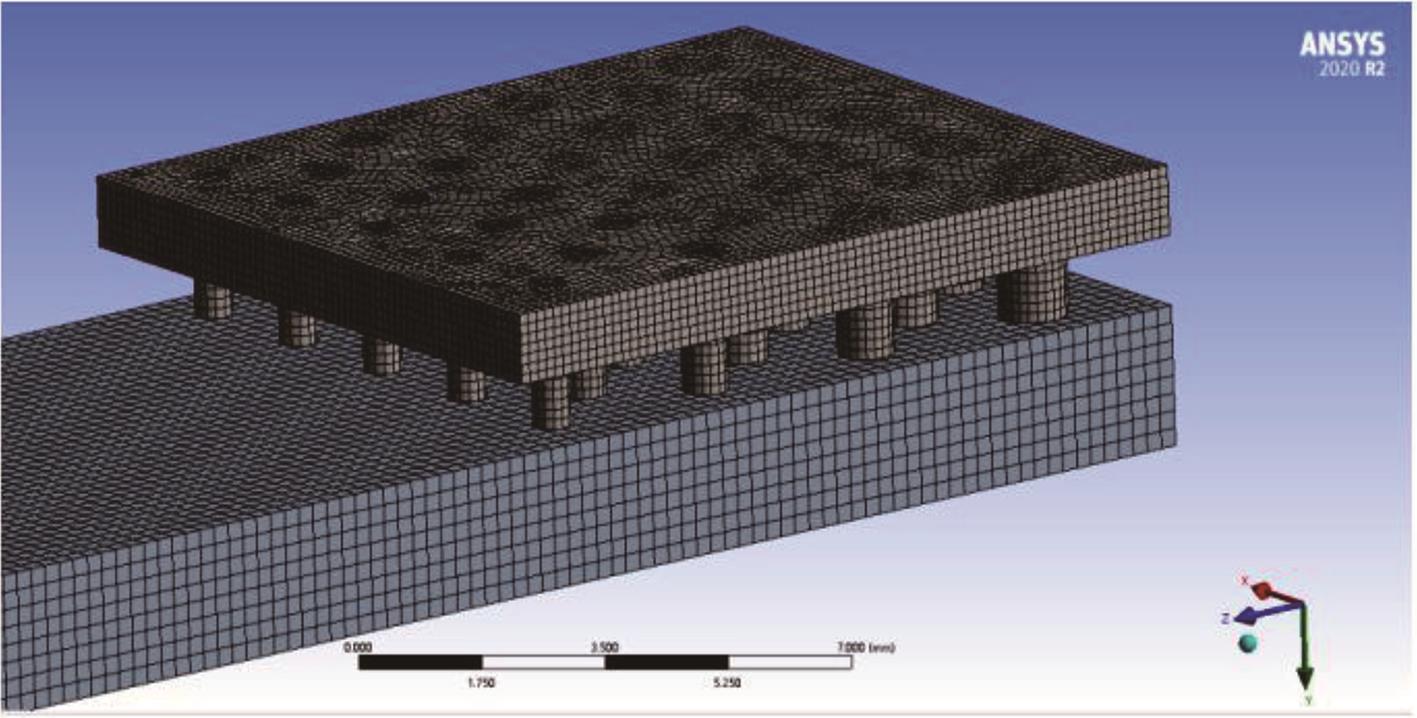
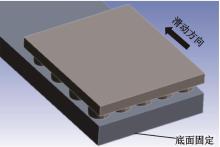
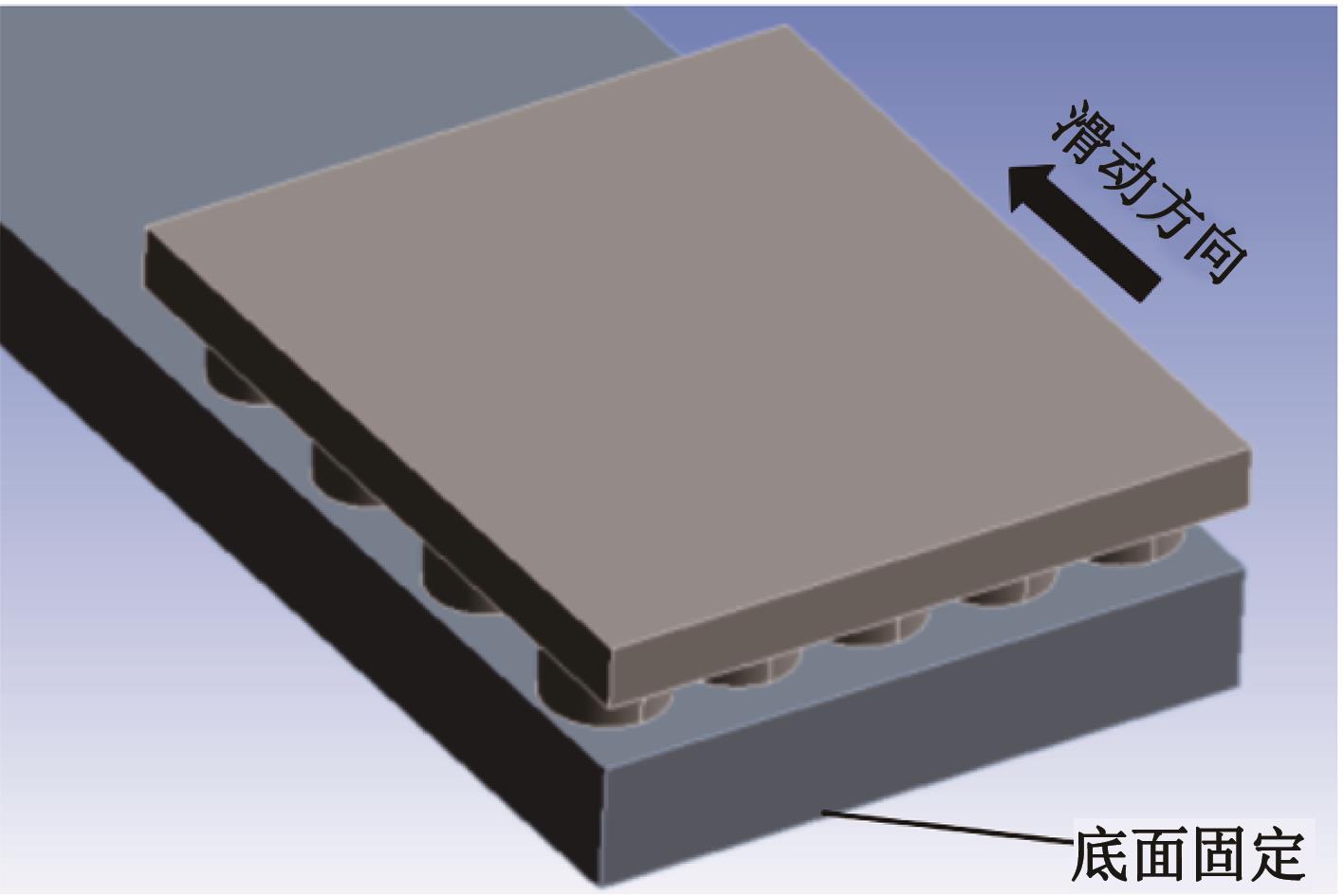
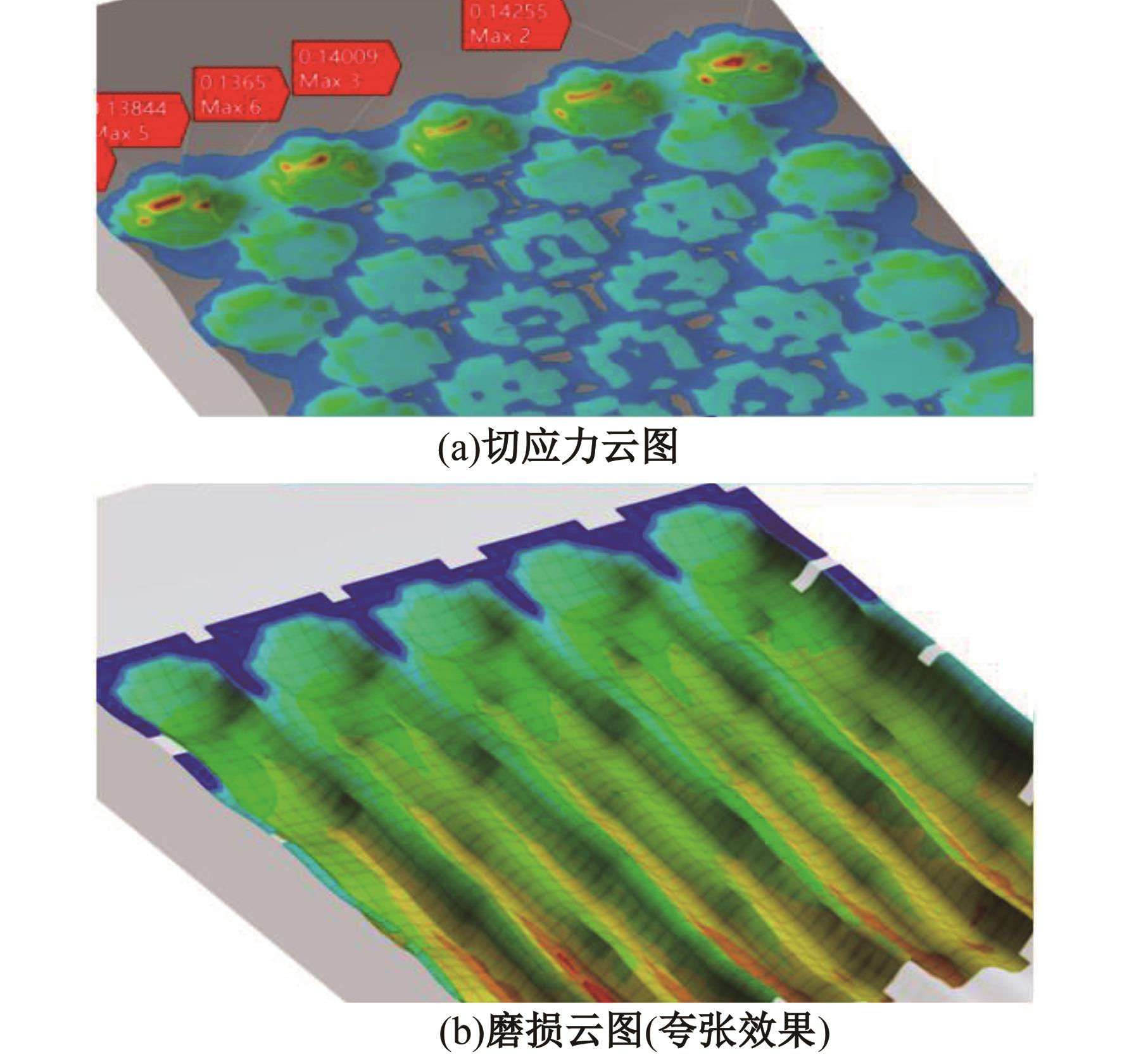
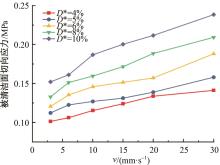
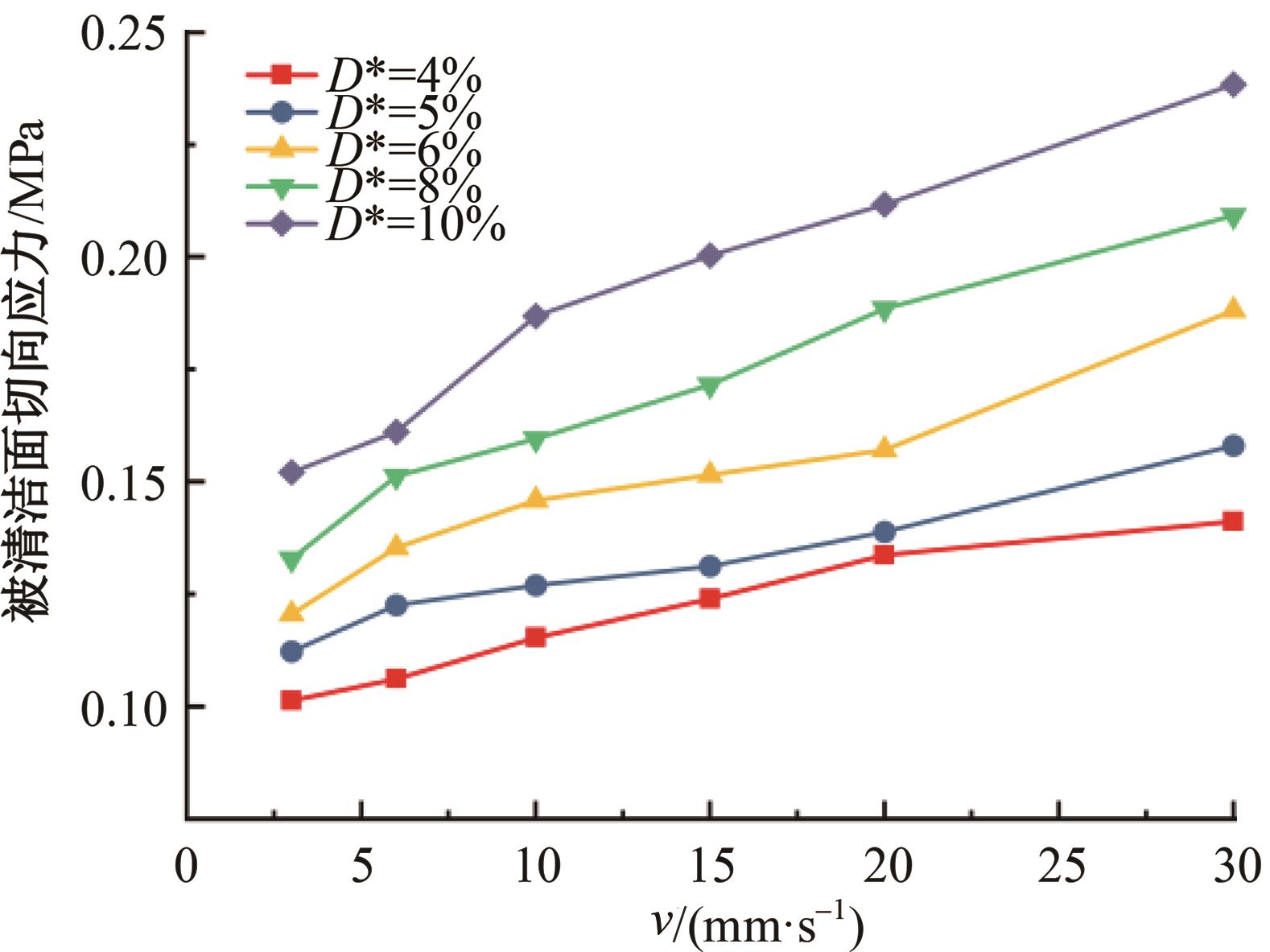
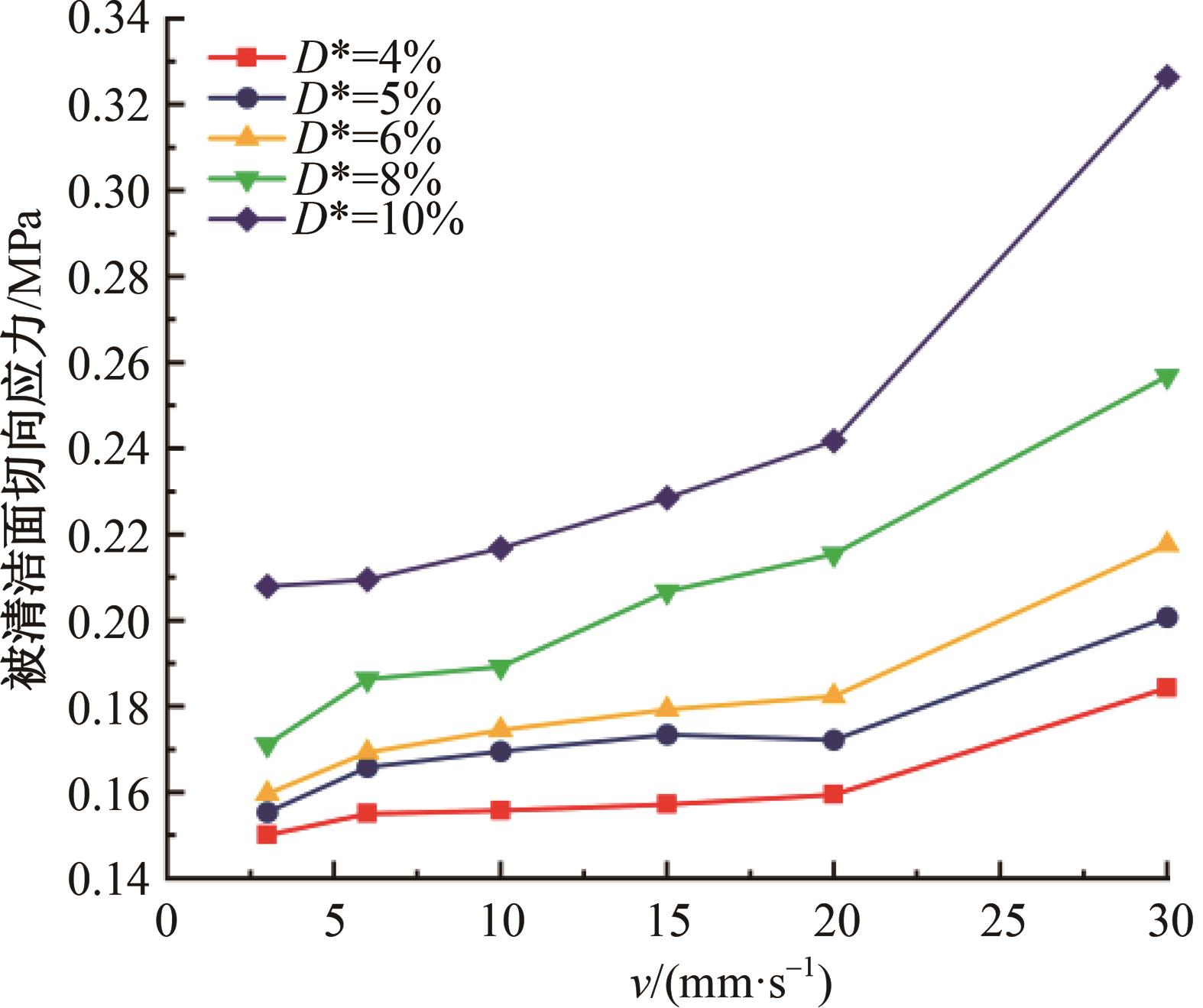
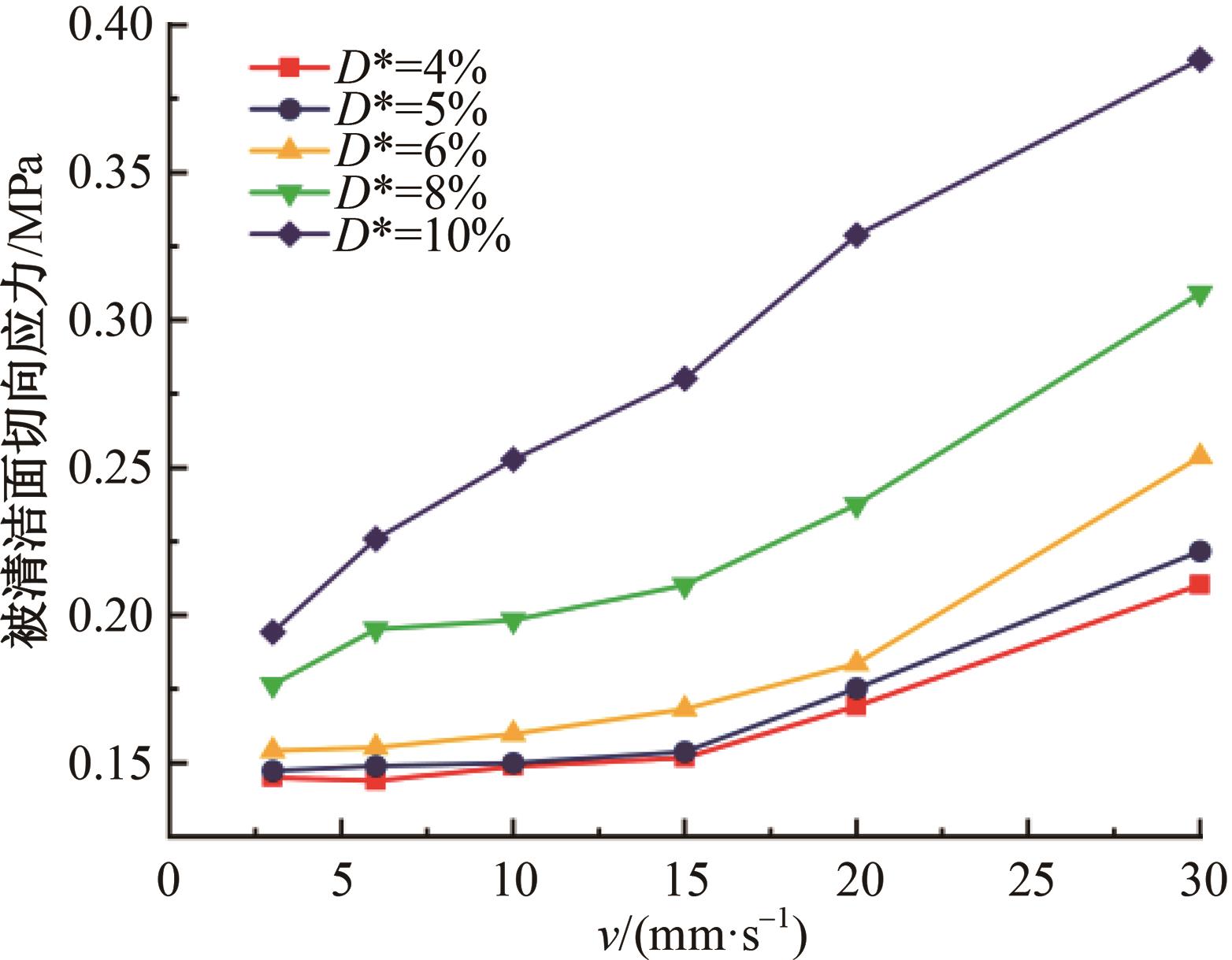
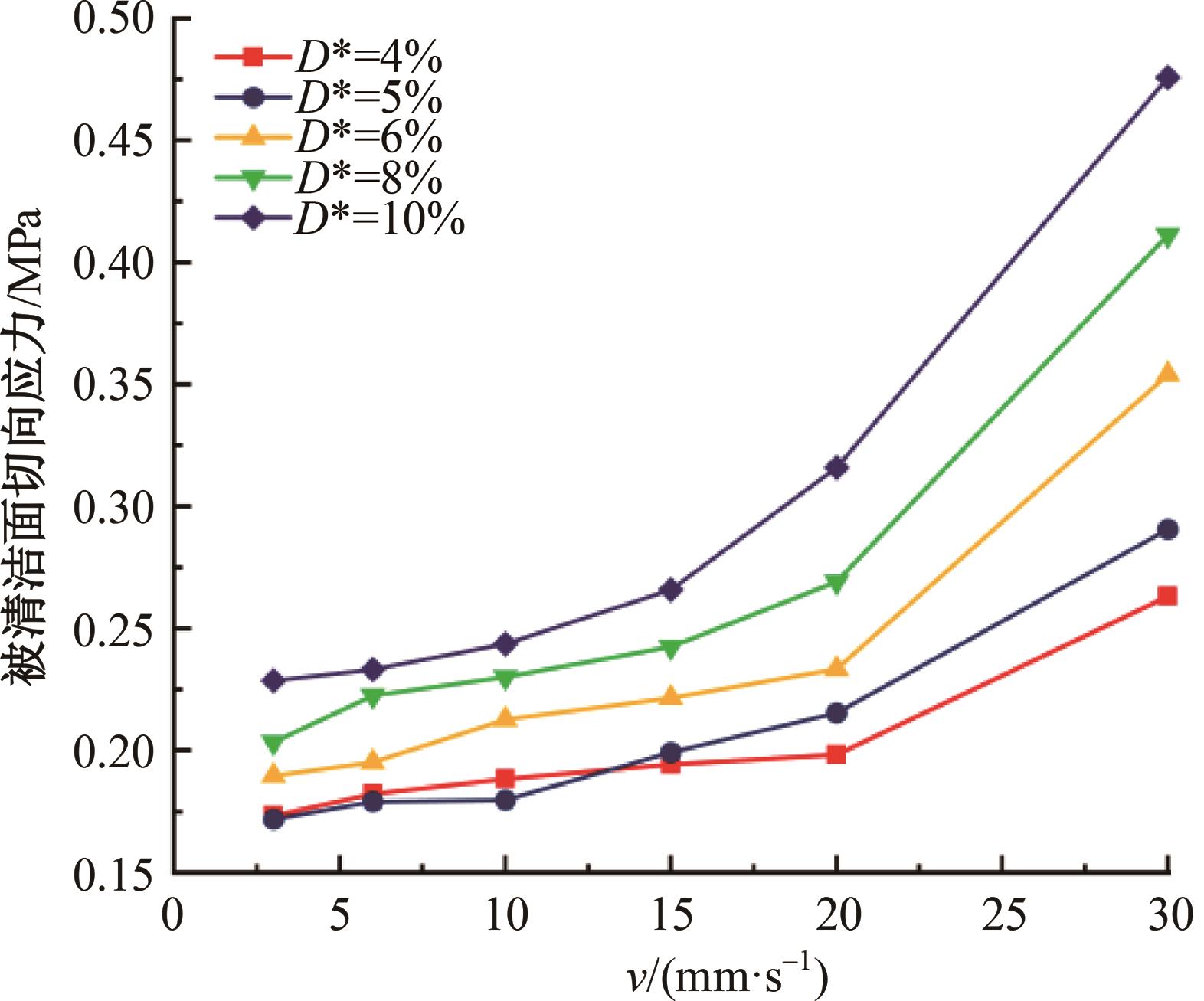
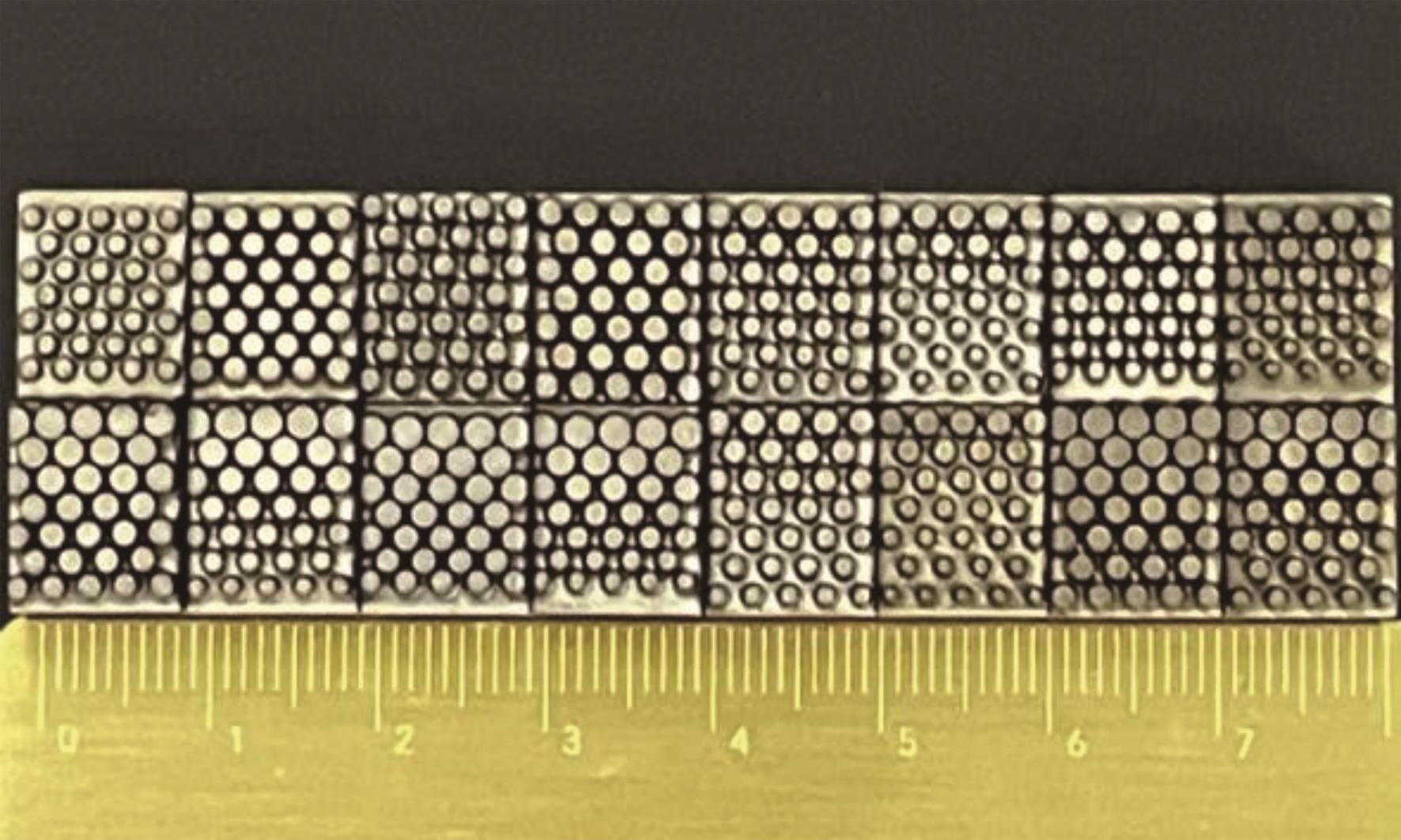
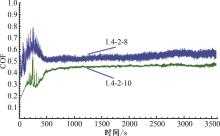
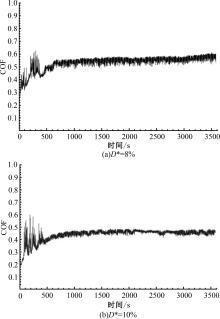
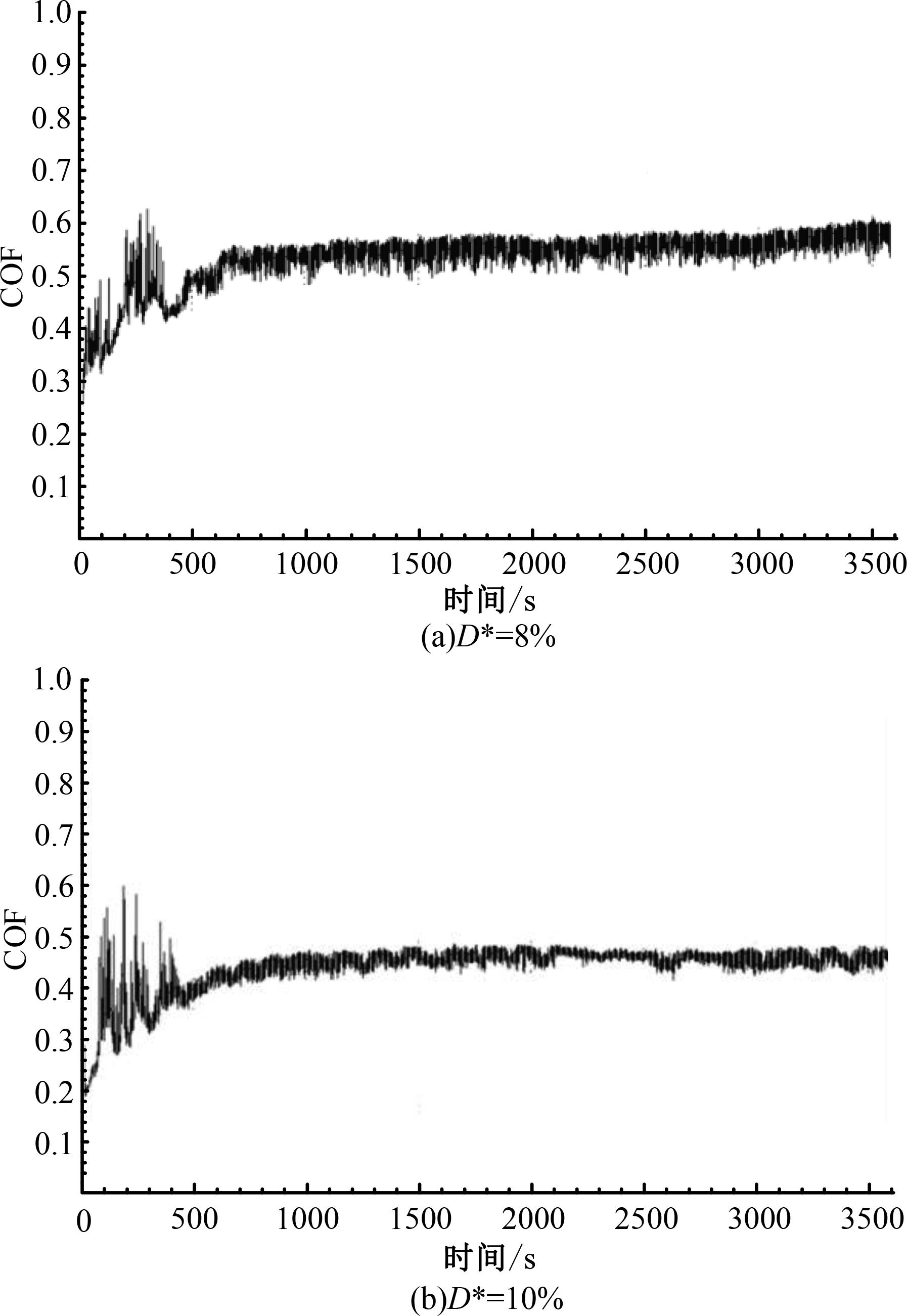
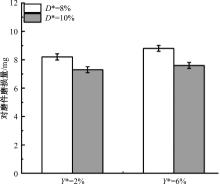
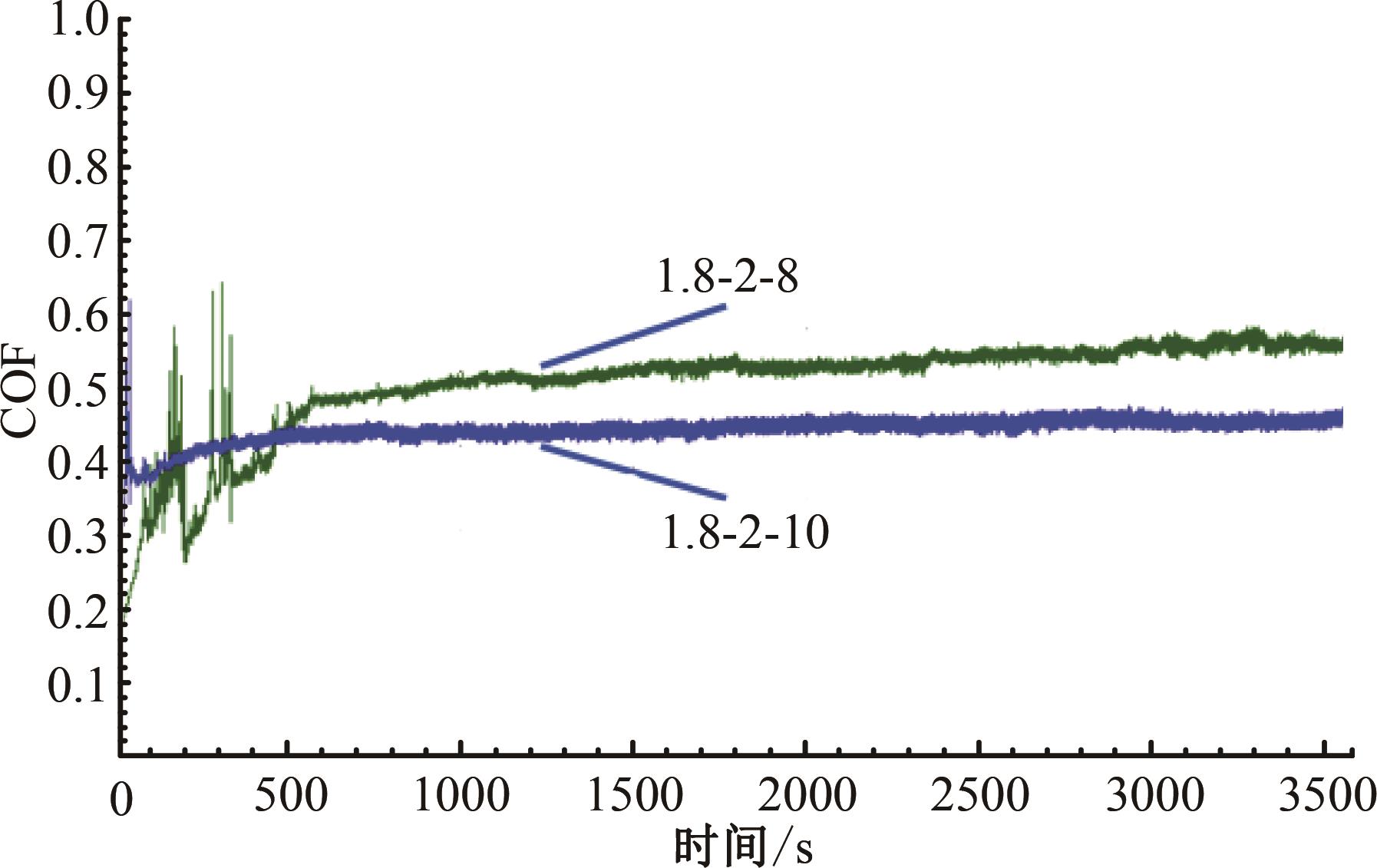
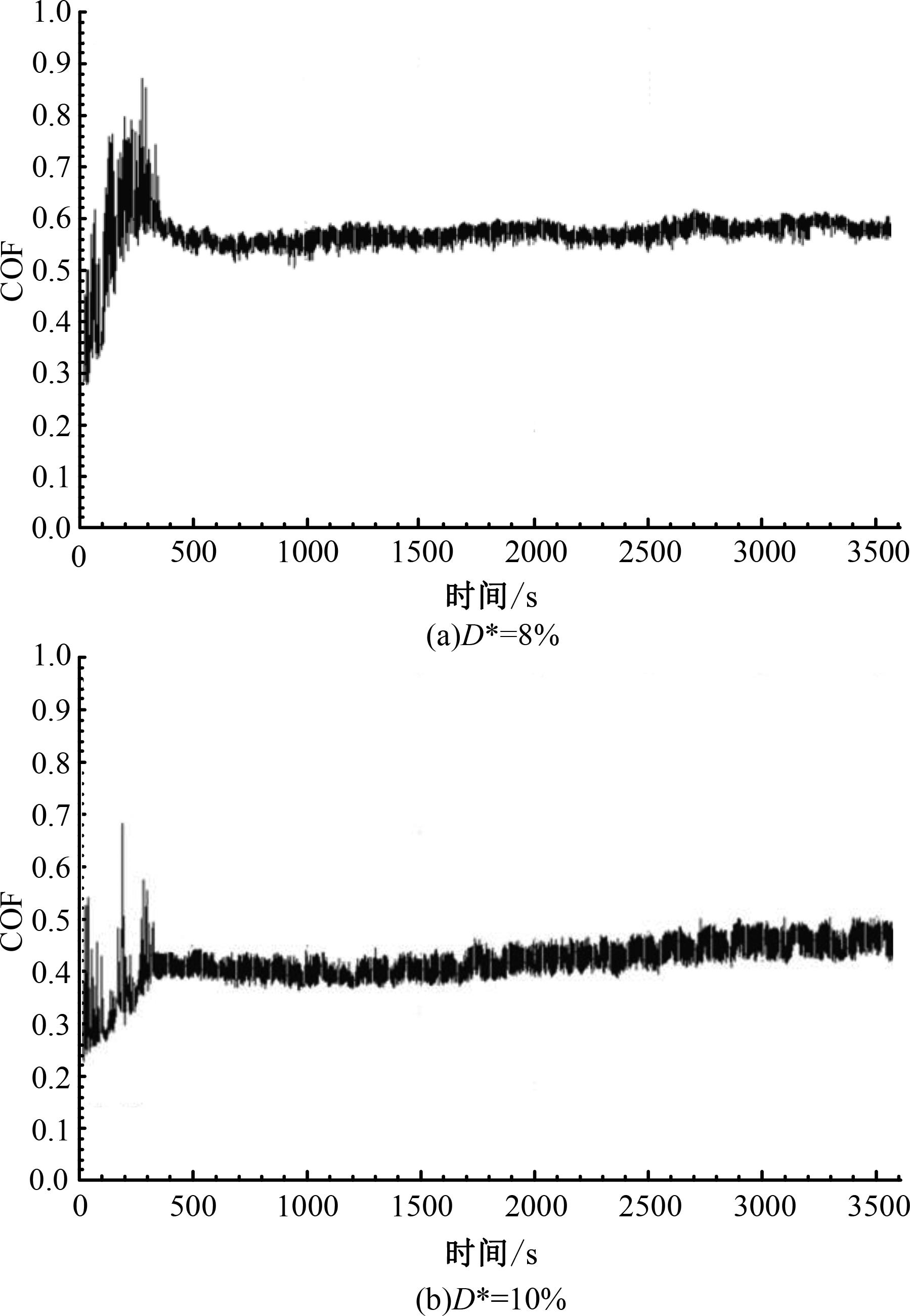
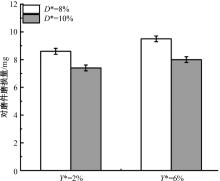
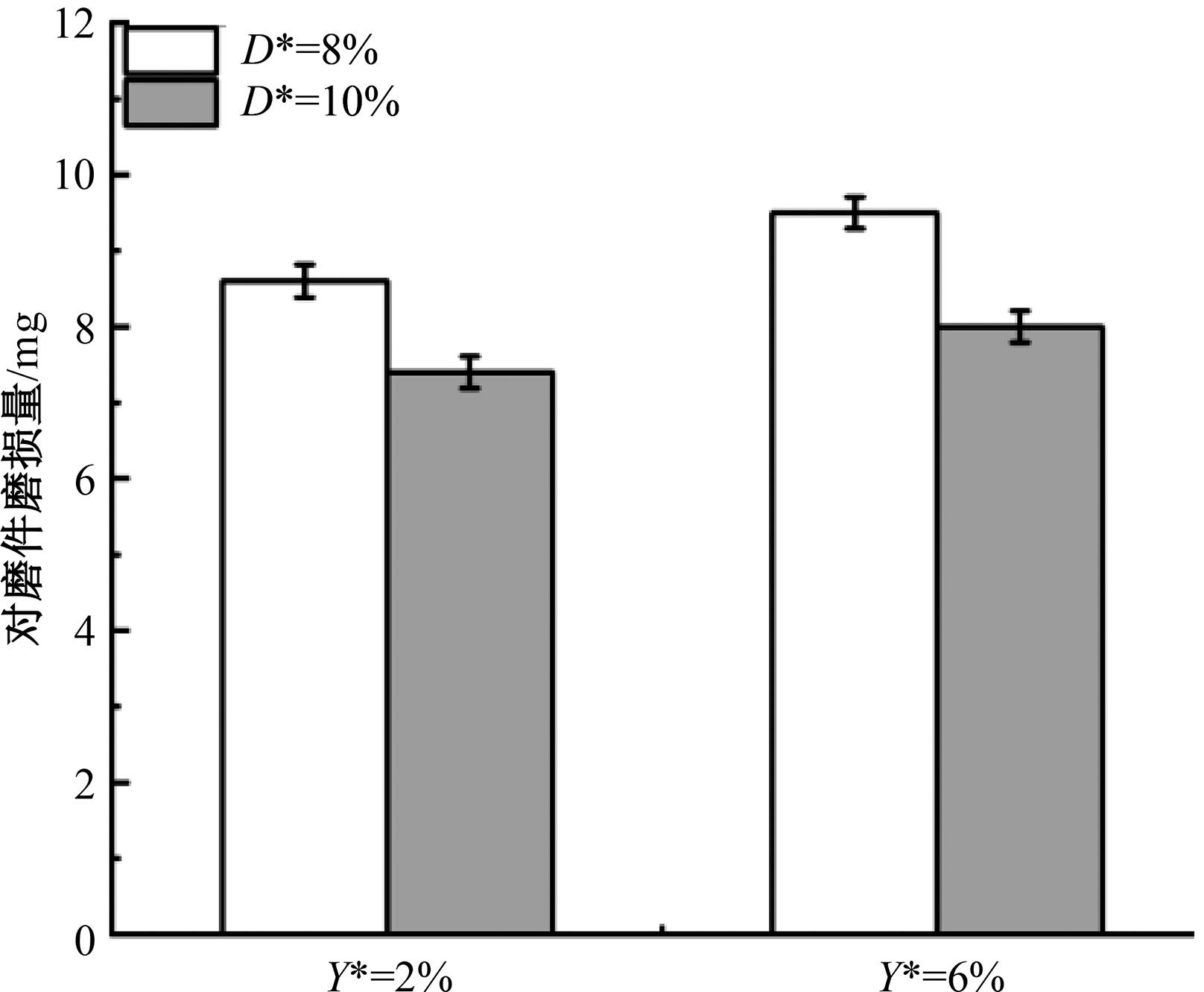
针对海洋设施表面的硬质海洋污损物设计了一种接触式仿生除污结构,通过理论模型及实际试验对不同结构的除污性能进行了测试,并根据试验结果对其除污机理做出了分析。结果表明:最大直径(Dm)和纵向缩减率(Y*)相同时,直径缩减率(D*)在6%~8%的结构具有更好的除污性能,而在Dm和D*相同时,随着Y*增大,除污性能随之提高。分析其原因,D*和Y*是影响除污过程中切向刮擦力的主要仿生结构参数,对D*和Y*进行适当设计,可以提升仿生除污结构的除污性能。结合仿真模拟和实际试验可知,D*=8%的结构具有最佳除污性能。
中图分类号:
- TH117.1
| 1 | Schultz M P, Bendick J A, Holm E R, et al. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship[J]. Biofouling, 2011, 27(1): 87-98. |
| 2 | Townsin R L. The ship hull fouling penalty[J]. Biofouling, 2003, 19(Sup.1): 9-15. |
| 3 | Swain G. Redefining antifouling coatings[J]. Journal of Protective Coatings & Linings, 1999, 16(9): 26-33. |
| 4 | Jin H, Tian L, Bing W, et al. Bioinspired marine antifouling coatings: status, prospects, and future[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 124:No.100889. |
| 5 | 薛静静. 高附着型有机硅涂层的构建及其生物污损防护性能的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学化学学院,2022. |
| Xue Jing-jing. Fabrication of mechanically enhanced organic silicone coatings and its anti-biofouling performance[D].Changchun: College of Chemistry,Jilin University,2022. | |
| 6 | Wong T S, Kang S H, Tang S K, et al. Bioinspired self-repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity[J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7365): 443-447. |
| 7 | Tian L, Yin Y, Bing W, et al. Antifouling technology trends in marine environmental protection[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(2): 239-263. |
| 8 | 陈彦臻, 胡以怀. 船体表面附着物清洗技术的研究及应用[J]. 表面技术, 2017, 46(10): 60-71. |
| Chen Yan-zhen, Hu Yi-huai.Research and application of ship hull fouling cleaning technologies[J].2017,46(10):60-71. | |
| 9 | 全玉臣. 船舶清洗市场趋势[J]. 清洗世界, 2007, 143(1): 35-38. |
| Quan Yu-chen.Shiooing cleaning market trend[J].Cleaning World,2007,143(1):35-38. | |
| 10 | 孟庆鑫,王丽慧,王立权,等.水下船体表面清刷机器人方案研究[J]. 船舶工程, 2002 (1): 44-46. |
| Meng Qing-xin, Wang Li-hui, Wang Li-quan,et al.Study of design of underwater robot for brushing hull exterior[J].Ship Engineering,2002 (1):44-46. | |
| 11 | Tribou M, Swain G. Grooming using rotating brushes as a proactive method to control ship hull fouling [J]. Biofouling, 2015, 31(4): 309-319. |
| 12 | Nassiraei A, Sonoda T, Ishii K. Development of ship hull cleaning underwater robot[C]∥Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering & Technology, Himeji, Japan, 2012: No.2012.74. |
| 13 | 杨兴宇. 船体水下除海生物机器人结构设计及关键技术研究[D]. 天津:河北工业大学机械工程学院, 2019. |
| Yang Xing-yu.Structure design and key technology research of hull underwater clear sea creature robot[D]. Tianjin: College of Mechanical Engineering,Hebei University of Technology,2019. | |
| 14 | Abd-Elhafeez H H, Mokhtar D M. Comparative morphological study of lips and associated structures of two algal grazer fish[J]. Journal of Advanced Microscopy Research, 2014, 9(4): 275-284. |
| 15 | 赵立新, 章宝玲, 刘洋, 等. 基于表面织构技术改善摩擦学性能的研究进展 [J]. 摩擦学学报, 2022, 42(1): 202-224. |
| Zhao Li-xin, Zhang Bao-ling, Liu Yang,et al.State of the art for improving tribological performance based on of surface texturing technology[J].Tribology,2022,42(1):202-224. | |
| 16 | 史航, 王鲁民. 海洋污损生物藤壶的附着机理及防除[J]. 广东农业科学, 2006(6): 72-73, 81. |
| Shi Hang, Wang Lu-min.Adhesion mechanism and prevention of marine biofouling barnacle[J].GuangDong Agricultural Science,2006(6):72-73, 81. |
| [1] | 刘洋. 橡胶鞋底弹性打磨仿真及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2167-2173. |
| [2] | 王琛,雒特,惠倩倩,王忠昊,王方方. 面向分体式飞行汽车对接锁定的机电系统设计与验证[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2130-2140. |
| [3] | 刘洋,江涛. 计及安装角的六自由度平台虎克铰干涉计算模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1519-1527. |
| [4] | 谭晓丹,王勇澎,Hall Robert,徐天爽,黄庆学. 面向电铲自主装卸的矿用自卸车斗型优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1227-1236. |
| [5] | 孙伟,杨俊. 等角贴敷压电分流片圆柱壳有限元建模及减振分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 365-374. |
| [6] | 胡斌,蔡一全,罗昕,毛自斌,李俊伟,郭孟宇,王剑. 基于种群胁迫的有限齿侧空间高速充种理论与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 574-588. |
| [7] | 刘洋. 动臂塔机防后倾缓冲力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2785-2794. |
| [8] | 赵洋,肖洋,孙皓,霍文浩,冯松,廖勇. 基于围道积分的润滑接触齿轮微点蚀损伤特征模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 799-810. |
| [9] | 邹猛,郭子琦,陈朕,曹洪涛,朱建中,徐丽涵. 模拟月尘与典型金属材料摩擦磨损特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2307-2315. |
| [10] | 郑伟,孙见君,马晨波,於秋萍,张玉言,牛韬. 汽车轮毂加工夹具的研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 25-36. |
| [11] | 陈魏,雷雨龙,李兴忠,付尧,扈建龙,侯利国. 低速工况下渐开线圆柱直齿轮齿面粘着磨损计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1628-1634. |
| [12] | 佟金,高子博,霍超,王子阳,马云海,常志勇. 低温下铜纳米颗粒对UHMWPE复合材料摩擦磨损性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 493-500. |
| [13] | 郭震,于红英,滑忠鑫,赵娣. 刚性折纸机构运动分析及折叠过程仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 66-76. |
| [14] | 朱伟,王传伟,顾开荣,沈惠平,许可,汪源. 一种新型张拉整体并联机构刚度及动力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1777-1786. |
| [15] | 毛宇泽, 王黎钦. 鼠笼支撑一体化结构对薄壁球轴承承载性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
|
||