吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1810-1817.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181122
基于车辆响应的路面不平度识别方法
- 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Road roughness identification based on vehicle responses
Jie LI( ),Wen-cui GUO,Qi ZHAO,Sheng-feng GU
),Wen-cui GUO,Qi ZHAO,Sheng-feng GU
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
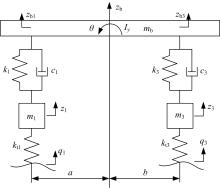
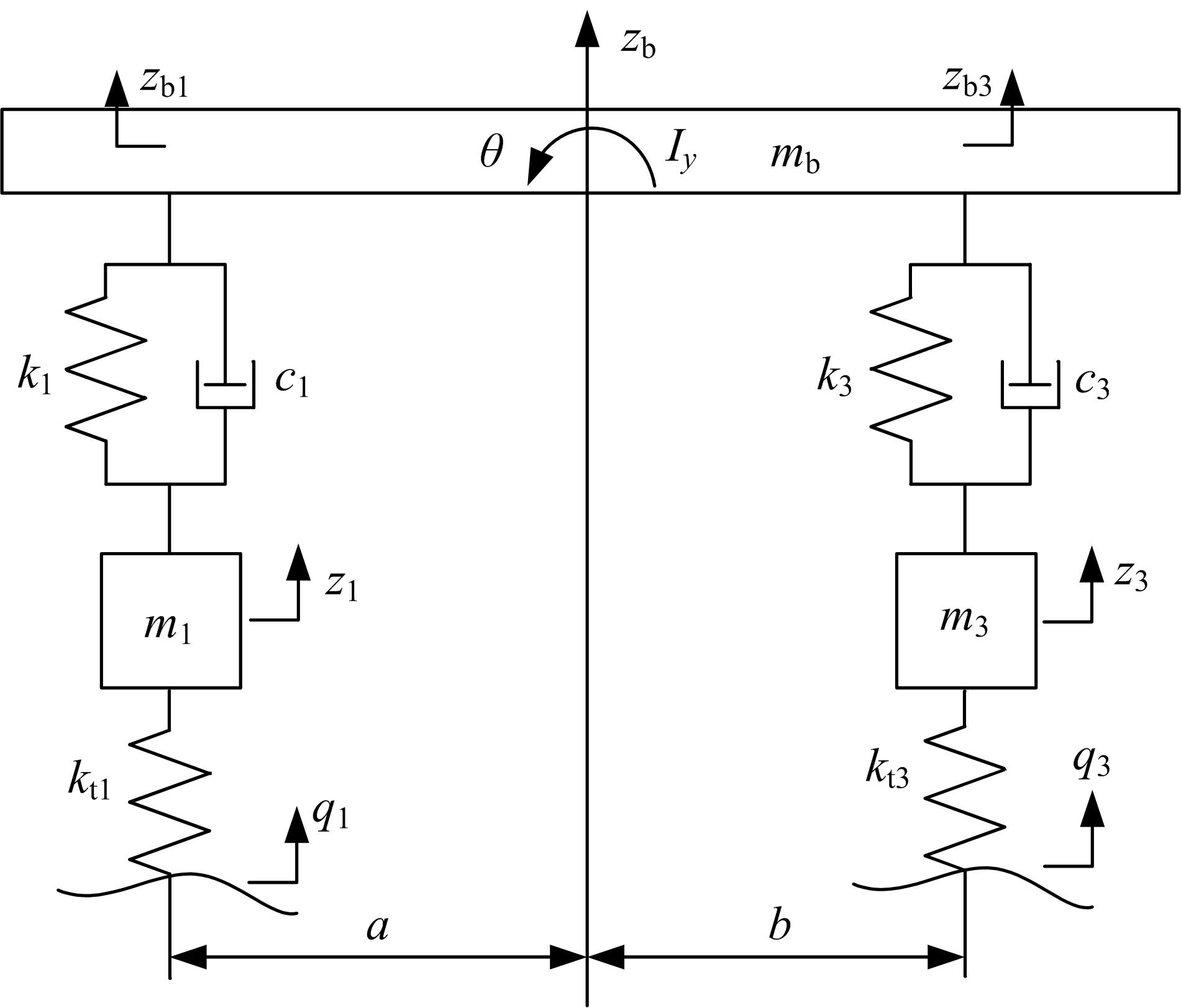
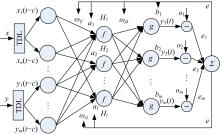
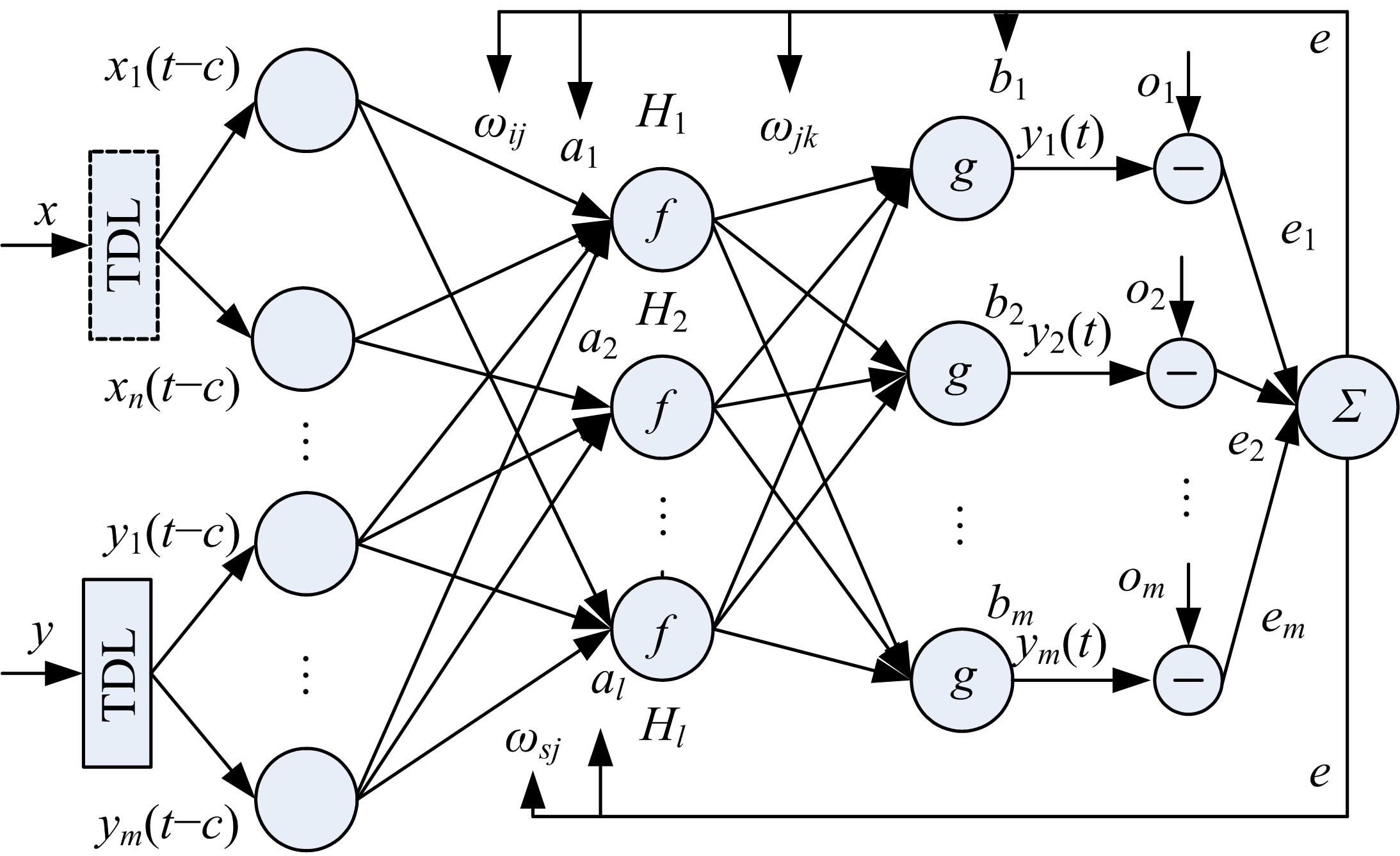
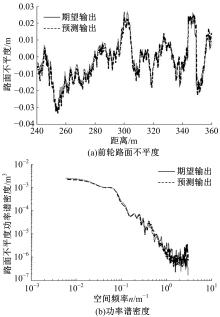
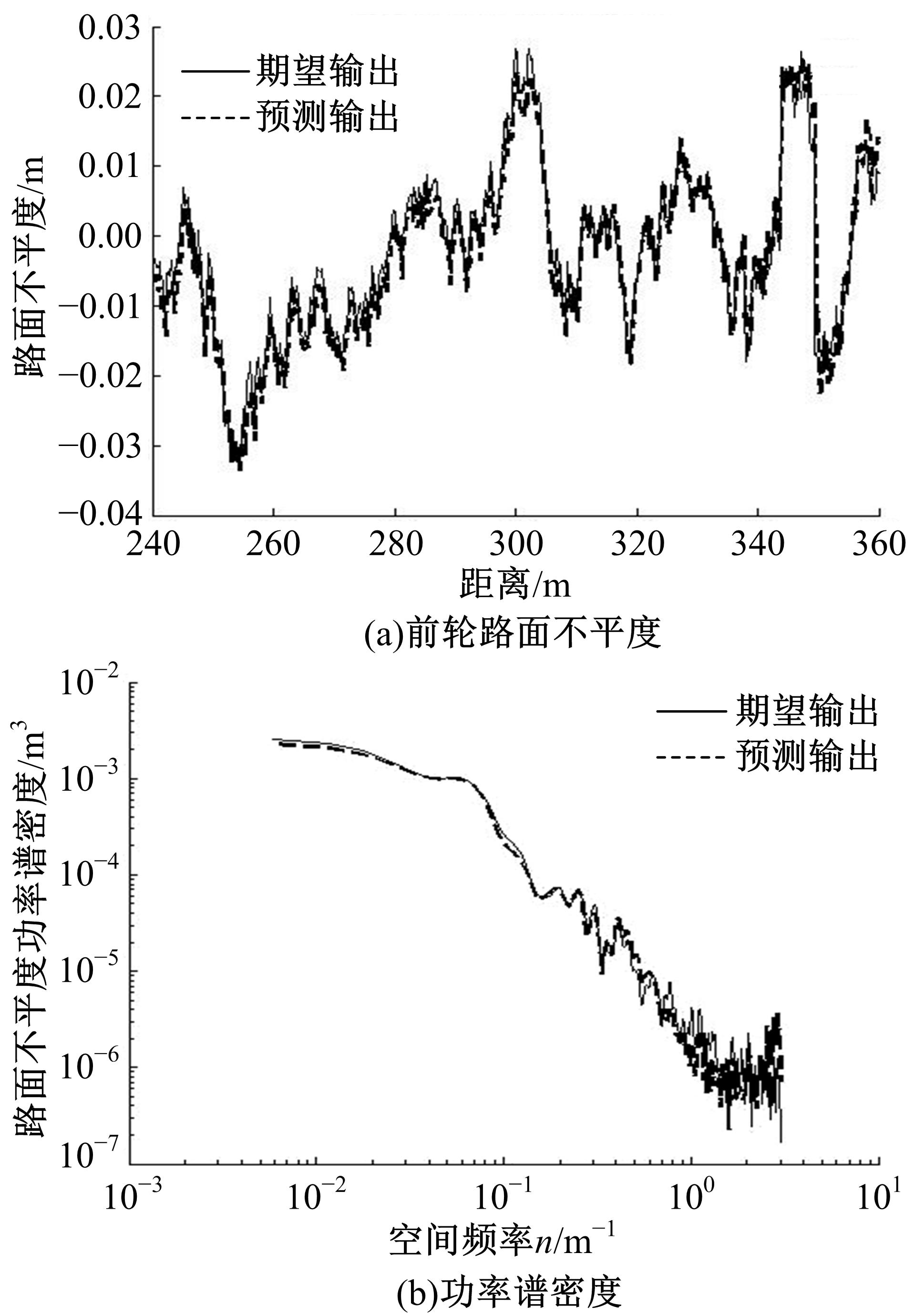
针对路面不平度识别的问题,研究了基于车辆响应的NARX神经网络识别方法及其适用性。建立了汽车振动系统4自由度平面模型,通过仿真获得车辆响应和车轮路面不平度。对于NARX神经网络及其应用选择、输入方案优化和评价指标进行了研究,提出了车辆响应选择和组合优化的解决方案。采用NARX神经网络识别了常用的B级路面和车速为60 km/h下某轿车的前轮路面不平度,其相关系数和均方根误差分别达到96.75%和0.003 3。考虑了训练采样点数、车辆响应随机噪声、车速和路面等级的变化对训练完成的NARX神经网络效果的影响,说明了基于车辆响应识别路面不平度的NARX神经网络方法的适用性。研究结果表明,采用正交试验设计确定NARX神经网络优化输入方案和基于车辆响应识别路面不平度取得了满意的结果,两者具有良好的适用性。
中图分类号:
- U461.4
|
| [1] | 陈鑫,阮新建,李铭,王宁,王佳宁,潘凯旋. 基于大涡模拟的离散格式改进方法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1756-1763. |
| [2] | 何仁,涂琨. 基于温度补偿气隙宽度的电磁制动器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1777-1785. |
| [3] | 靳立强, 田端洋, 田浩, 刘蒙蒙. 汽车电子稳定系统制动增力辅助技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1764-1776. |
| [4] | 管欣,金号,段春光,卢萍萍. 汽车行驶道路侧向坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. |
| [5] | 王杨,宋占帅,郭孔辉,庄晔. 转动惯量试验台的惯性参数测量[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1795-1801. |
| [6] | 刘巧斌,史文库,陈志勇,骆联盟,苏志勇,黄开军. 混合可靠性模型参数的核密度和引力搜索估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1818-1825. |
| [7] | 庄蔚敏,刘洋,王鹏跃,施宏达,徐纪栓. 钢铝异质自冲铆接头剥离失效仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1826-1835. |
| [8] | 陈百超,邹猛,党兆龙,黄晗,贾阳,石睿杨,李建桥. CE-3月球车筛网轮月面沉陷行为试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. |
| [9] | 马芳武,倪利伟,吴量,聂家弘,徐广健. 轮腿式全地形移动机器人位姿闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| [10] | 马芳武,韩露,周阳,王世英,蒲永锋. 采用聚乳酸复合材料的汽车零件多材料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1385-1391. |
| [11] | 高振海,孙天骏,何磊. 汽车纵向自动驾驶的因果推理型决策[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. |
| [12] | 张博,张建伟,郭孔辉,丁海涛,褚洪庆. 路感模拟用永磁同步电机电流控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1405-1413. |
| [13] | 王鹏宇,赵世杰,马天飞,熊晓勇,程馨. 基于联合概率数据关联的车用多传感器目标跟踪融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1420-1427. |
| [14] | 胡兴军,惠政,郭鹏,张扬辉,张靖龙,王靖宇,刘飞. 基于流固耦合的汽车气动特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1414-1419. |
| [15] | 韩小健,赵伟强,陈立军,郑宏宇,刘阳,宗长富. 基于区域采样随机树的客车局部路径规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1428-1440. |
|