吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 2010-2018.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181037
TiC颗粒对铸态球墨铸铁组织和力学性能的影响
王金国1,2( ),任帅1,2,闫瑞芳1,2,黄恺1,2,王志强1,2
),任帅1,2,闫瑞芳1,2,黄恺1,2,王志强1,2
- 1. 吉林大学 汽车材料教育部重点实验室, 长春 130022
2. 吉林大学 材料科学与工程学院, 长春 130022
Effect of TiC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of as cast ductile iron
Jin-guo WANG1,2( ),Shuai REN1,2,Rui-fang YAN1,2,Kai HUANG1,2,Zhi-qiang WANG1,2
),Shuai REN1,2,Rui-fang YAN1,2,Kai HUANG1,2,Zhi-qiang WANG1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory of Automotive Materials, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
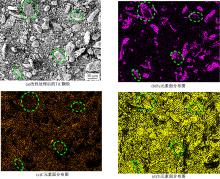
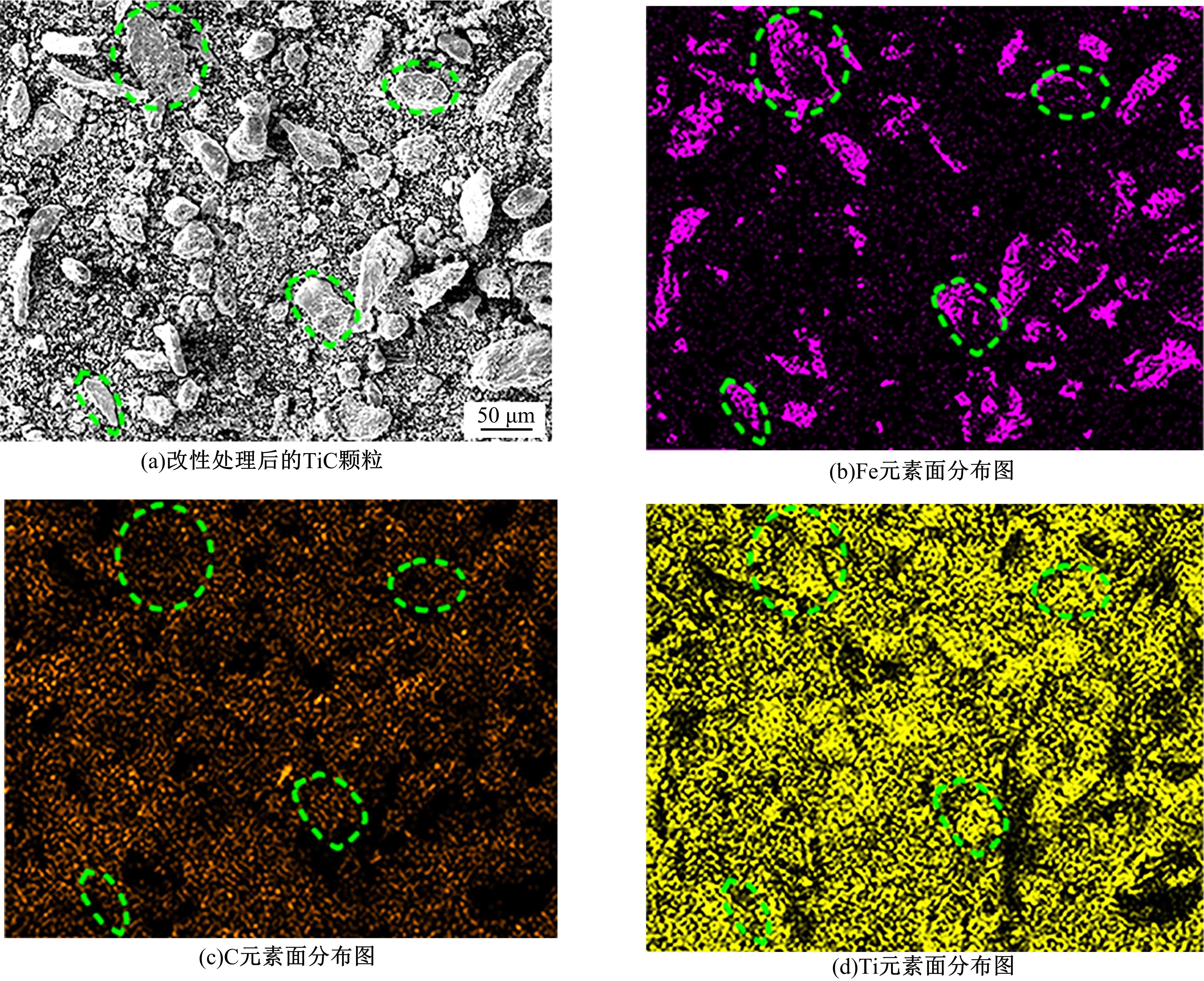
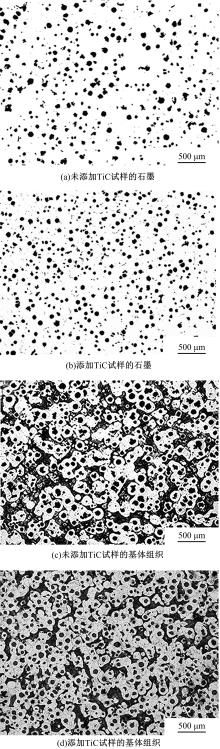
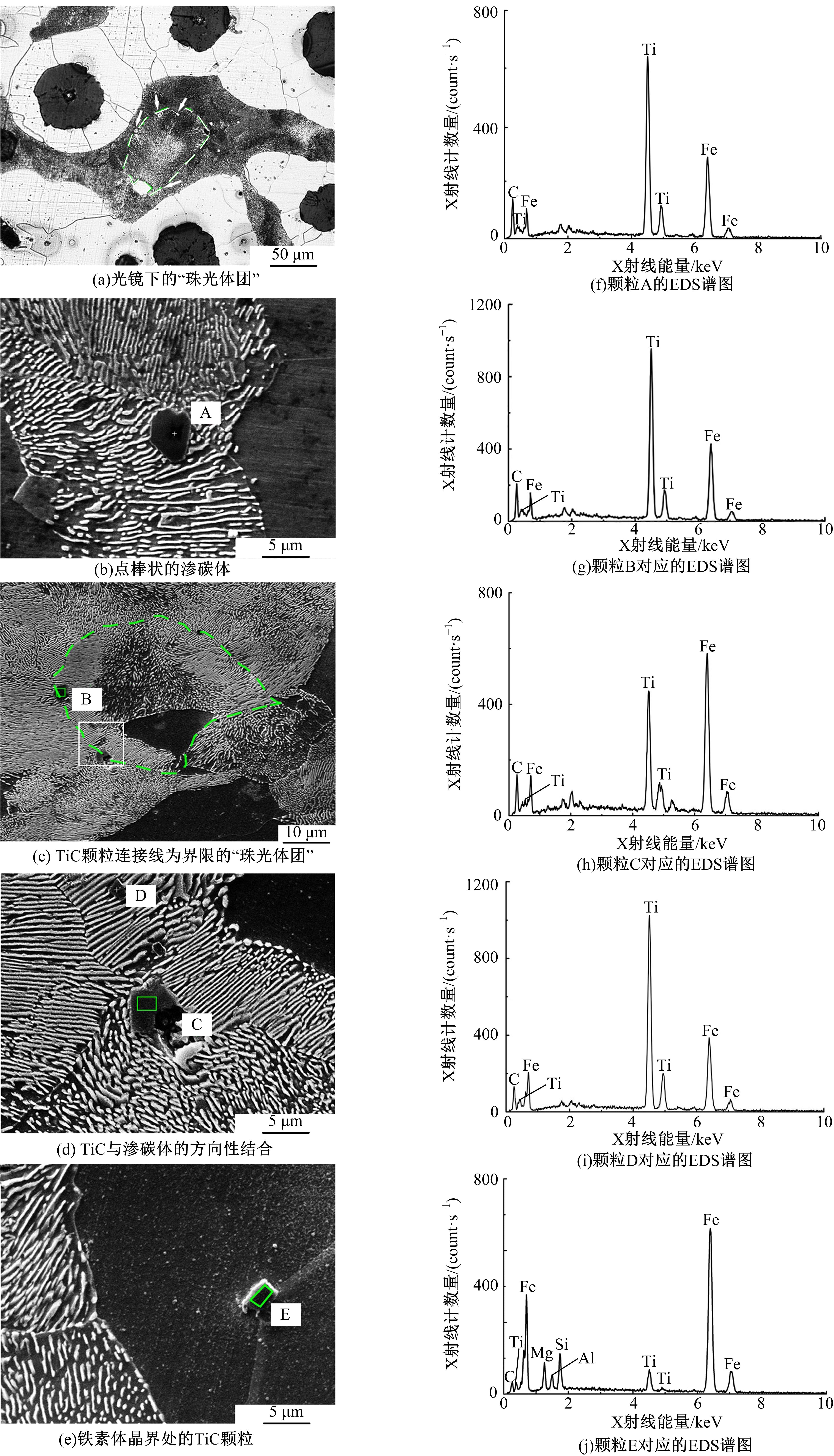
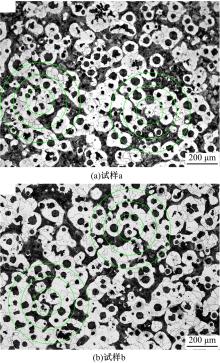
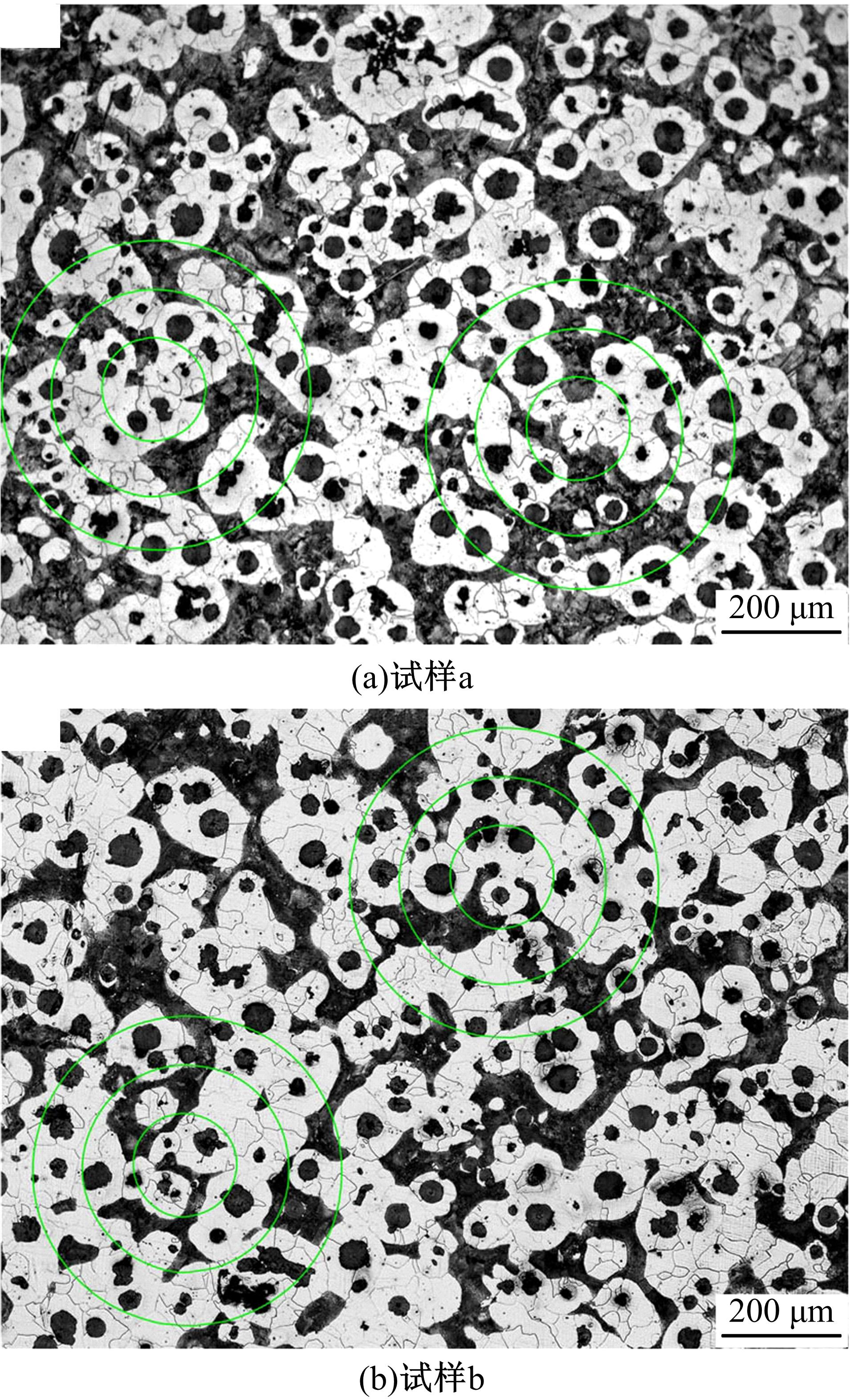
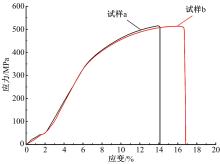
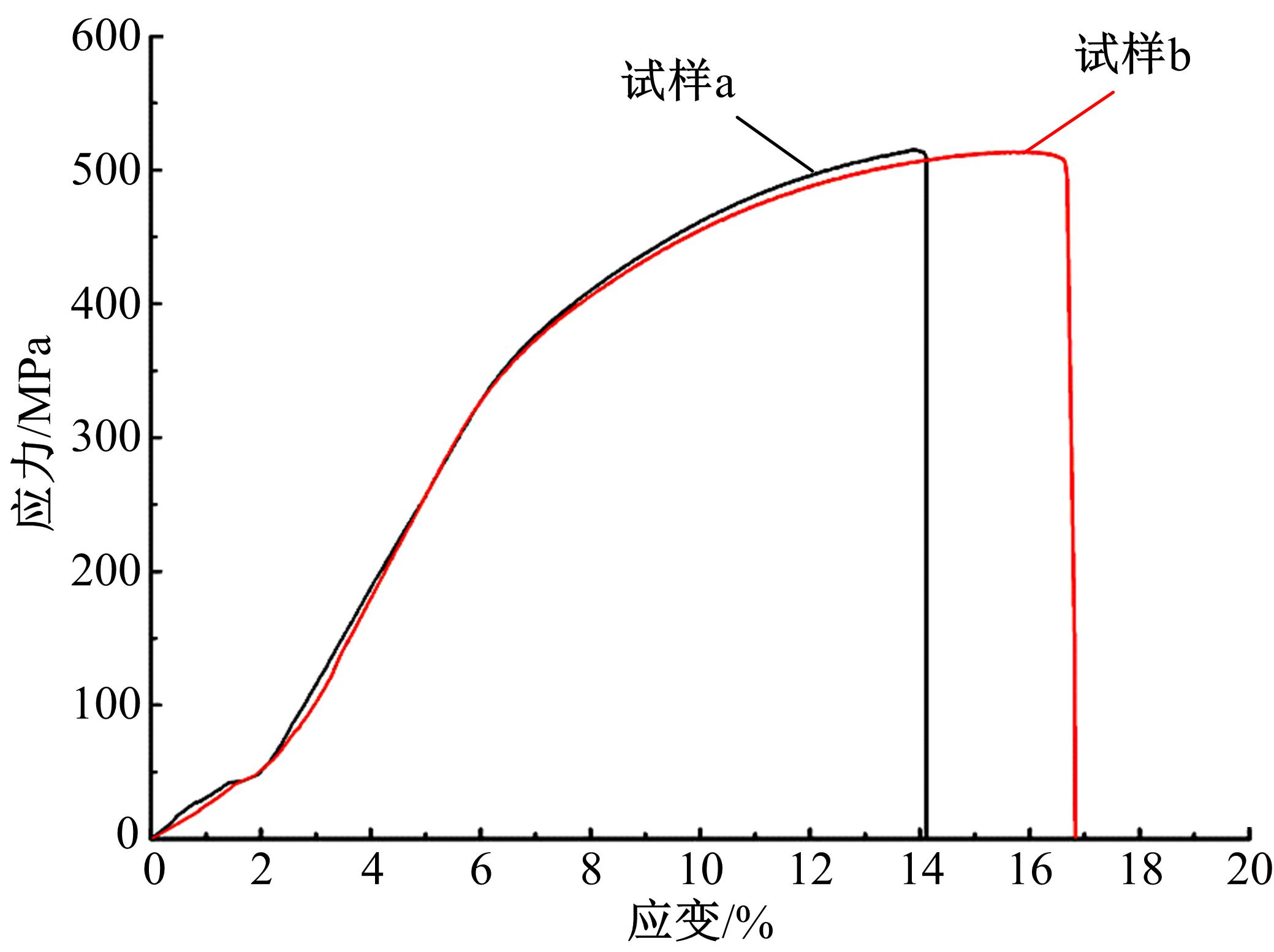
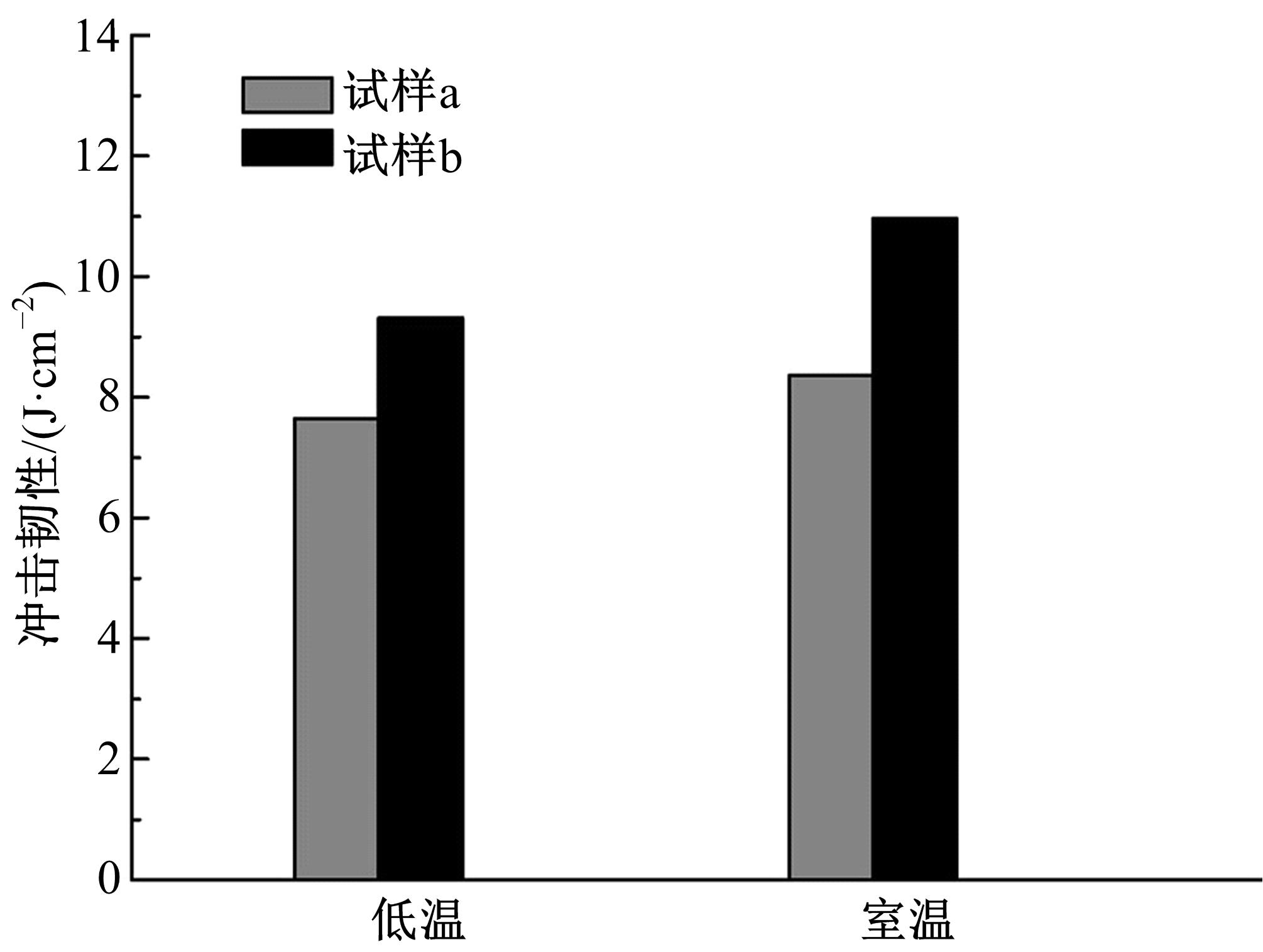
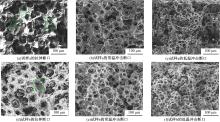
采用高能球磨方法对TiC粉末进行改性,并加入到球墨铸铁熔体。使用光镜、扫描电镜、能谱仪对其组织进行分析。结果表明,球墨铸铁的石墨和基体组织均得到改善。一部分TiC颗粒作为石墨异质核心,促进了石墨形核,使石墨球数目增加40.5%,石墨球尺寸细化,铁素体含量升高了4.5%,球化率提高了9.1%。另一部分进入基体的TiC颗粒,不仅改变了周围的渗碳体形貌,甚至形成独特的“珠光体团”结构;而且能阻碍晶界运动进而细化铁素体晶粒。采用拉伸试验机和冲击试验机对铸态球墨铸铁进行力学性能测试,结果表明,外加少量TiC颗粒使球墨铸铁的断裂总伸长率提高了19.1%,室温冲击韧性提高了31.1%,低温(-20 ℃)冲击韧性提高了21.8%。
中图分类号:
- TG143.5
|
| [1] | 段春争,张方圆,寇文能,魏斌. 高速硬切削表面白层马氏体相变[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1575-1583. |
| [2] | 谷晓燕,刘东锋,刘婧,孙大千,马会峰. 焊接能量对Cu/Al超声波焊接接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1600-1607. |
| [3] | 赵金钢,张明,占玉林,谢明志. 基于塑性应变能密度的钢筋混凝土墩柱损伤准则[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1124-1133. |
| [4] | 徐戊矫,刘承尚,鲁鑫垚. 喷丸处理后6061铝合金工件表面粗糙度的模拟计算及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
| [5] | 李于朋,孙大千,宫文彪. 6082⁃T6铝合金薄板双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊温度场[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [6] | 关庆丰,张福涛,彭韬,吕鹏,李姚君,许亮,丁佐军. 含硼、钴9%Cr耐热钢的热变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1799-1805. |
| [7] | 关庆丰, 董书恒, 郑欢欢, 李晨, 张从林, 吕鹏. 强流脉冲电子束作用下45#钢表面Cr合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1161-1168. |
| [8] | 赵宇光, 杨雪慧, 徐晓峰, 张阳阳, 宁玉恒. Al-10Sr变质剂状态、变质温度及变质时间对ZL114A合金组织的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
| [9] | 付文智, 刘晓东, 王洪波, 闫德俊, 刘晓莉, 李明哲, 董玉其, 曾振华, 刘桂彬. 关于1561铝合金曲面件的多点成形工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1822-1828. |
| [10] | 杨越东, 陈吉清, 兰凤崇, 周云郊. 基于焊点参数识别的白车身动态特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
| [11] | 汤华国, 马贤锋, 赵伟, 刘建伟, 赵振业. 高性能金属铝的制备、微观结构及其热稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1542-1547. |
| [12] | 关庆丰, 张远望, 孙潇, 张超仁, 吕鹏, 张从林. 强流脉冲电子束作用下铝钨合金的表面合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1171-1178. |
| [13] | 杨晓红, 杭文先, 秦绍刚, 刘勇兵, 刘利萍. H13钢激光熔覆钴基复合涂层的组织及耐磨性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 891-899. |
| [14] | 关庆丰, 黄尉, 李怀福, 龚晓花, 张从林, 吕鹏. 强流脉冲电子束诱发的Cu-C扩散合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1967-1973. |
| [15] | 张学广, 刘纯国, 郑愿, 江仲海, 李湘吉. 基于延性损伤和剪切损伤的铝合金成形极限预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1558-1566. |
|