吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 1951-1961.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211061
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型
- 浙江大学 智能交通研究所,杭州 310058
Dynamic road resistance model of intermittent flow on urban roads based on BPR function
Dian-hai WANG( ),You-wei HU,Zheng-yi CAI,Jia-qi ZENG,Wen-bin YAO
),You-wei HU,Zheng-yi CAI,Jia-qi ZENG,Wen-bin YAO
- Intelligent Transportation Research Institute,Zhejing University,Hangzhou 310058,China
摘要:
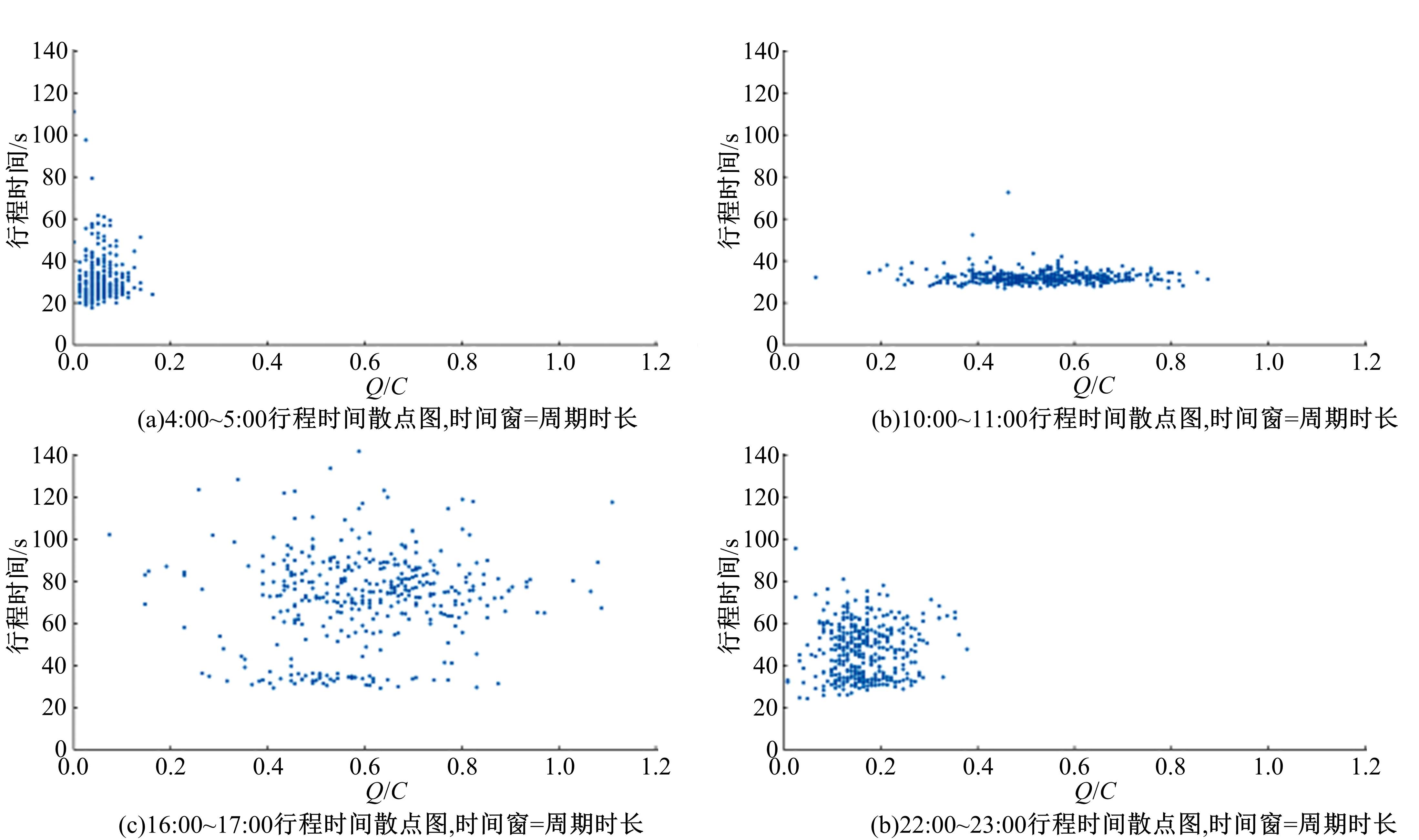
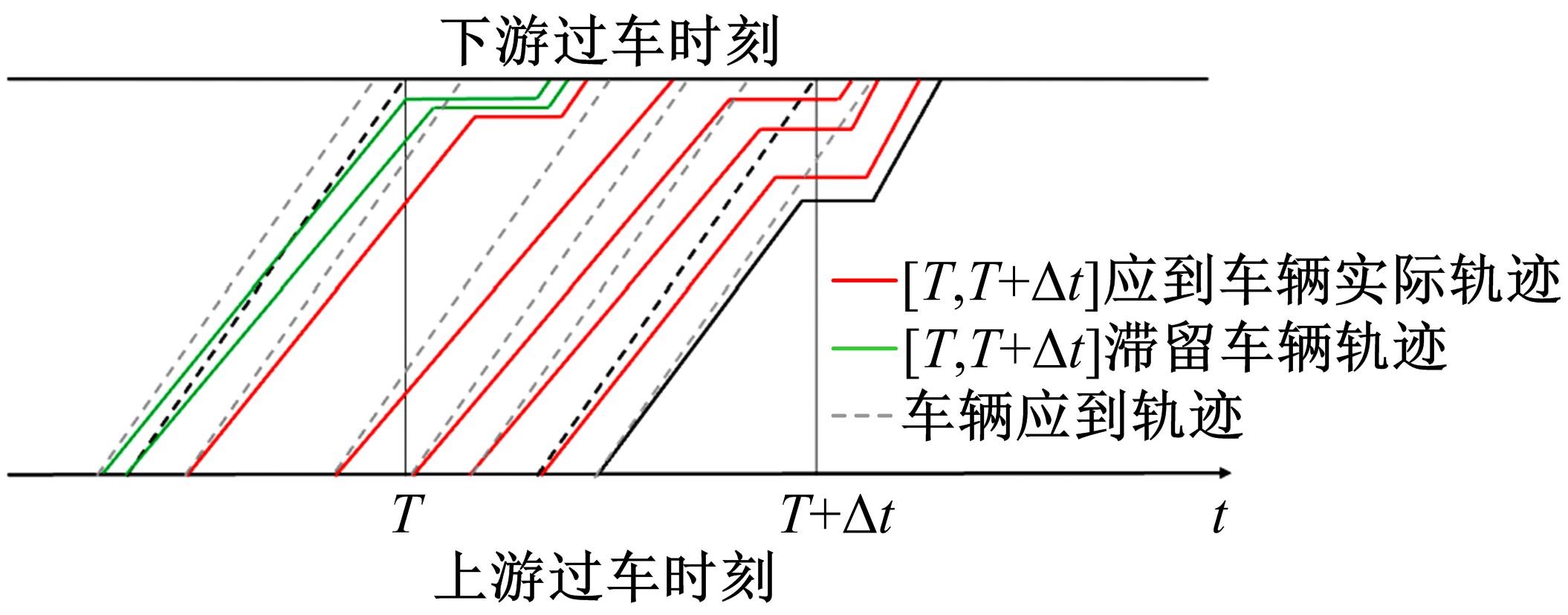
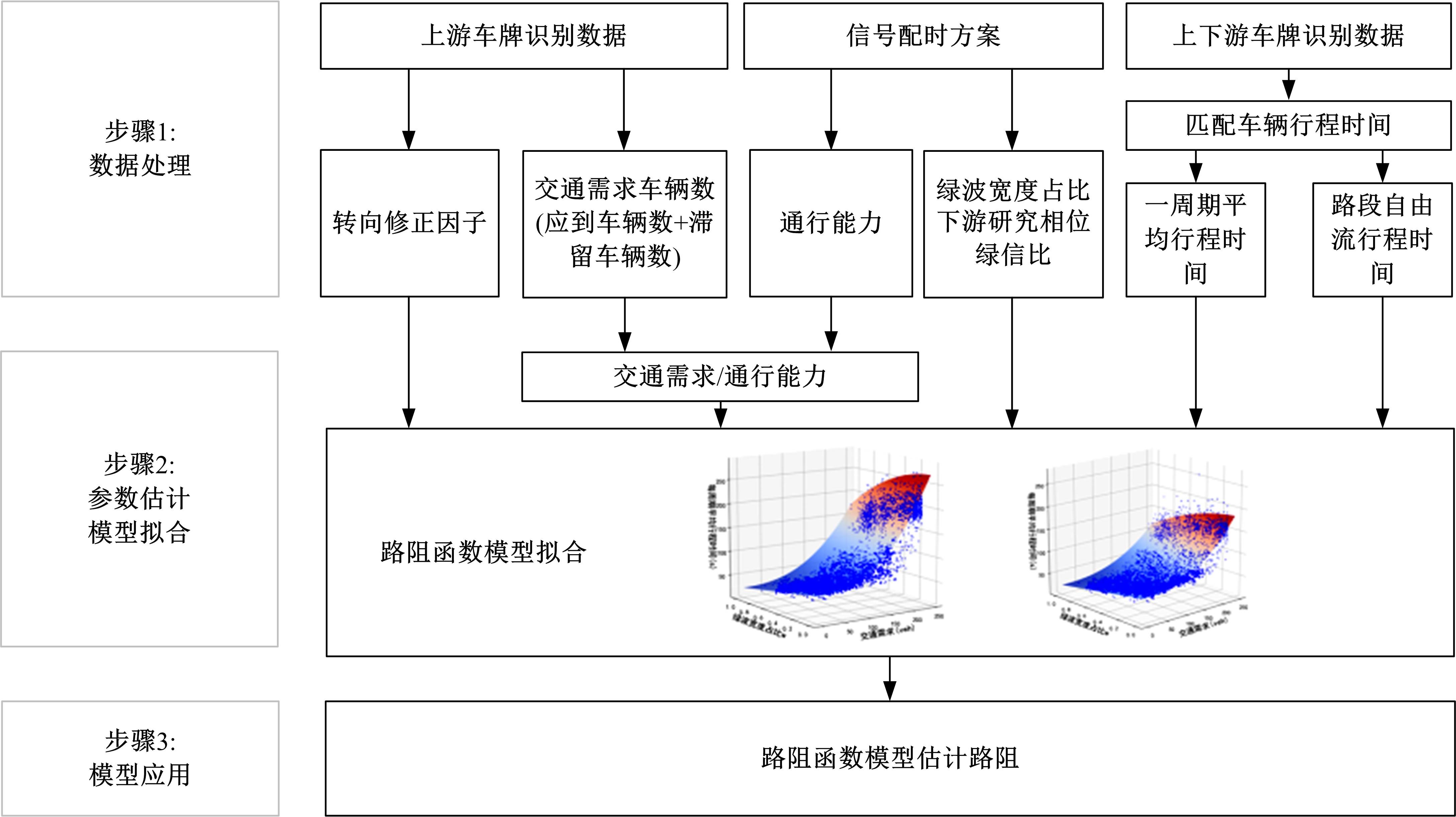
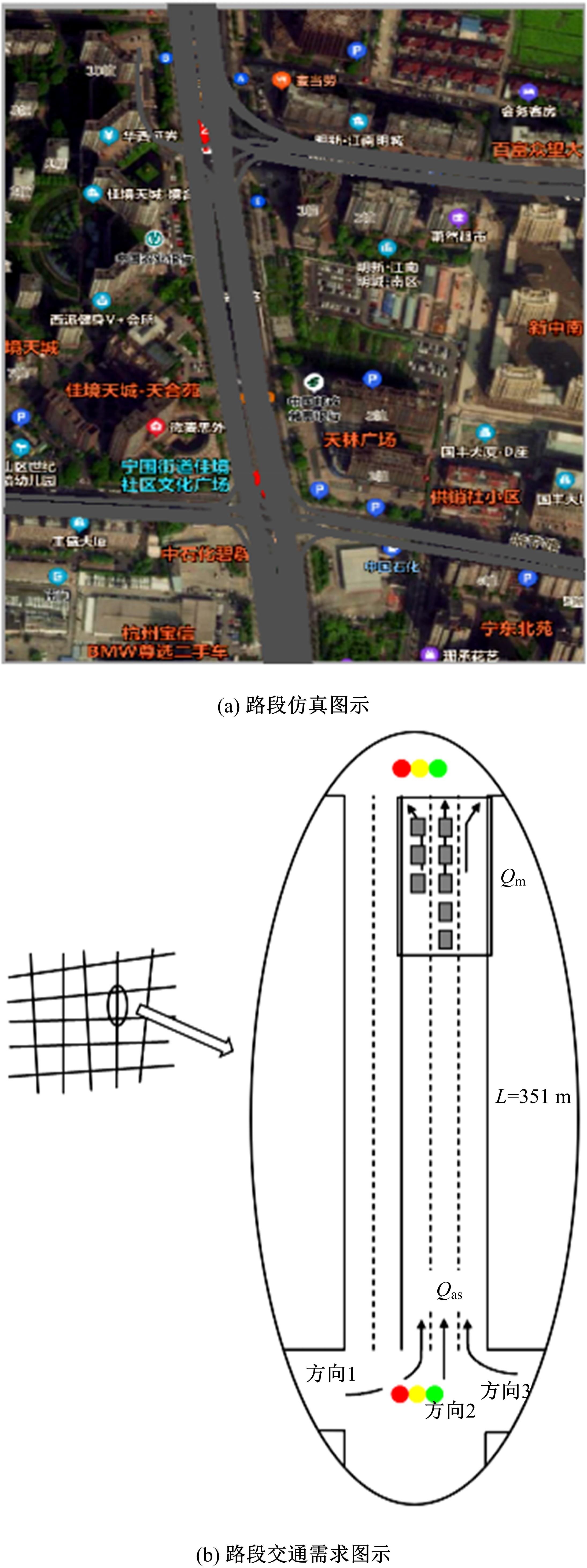
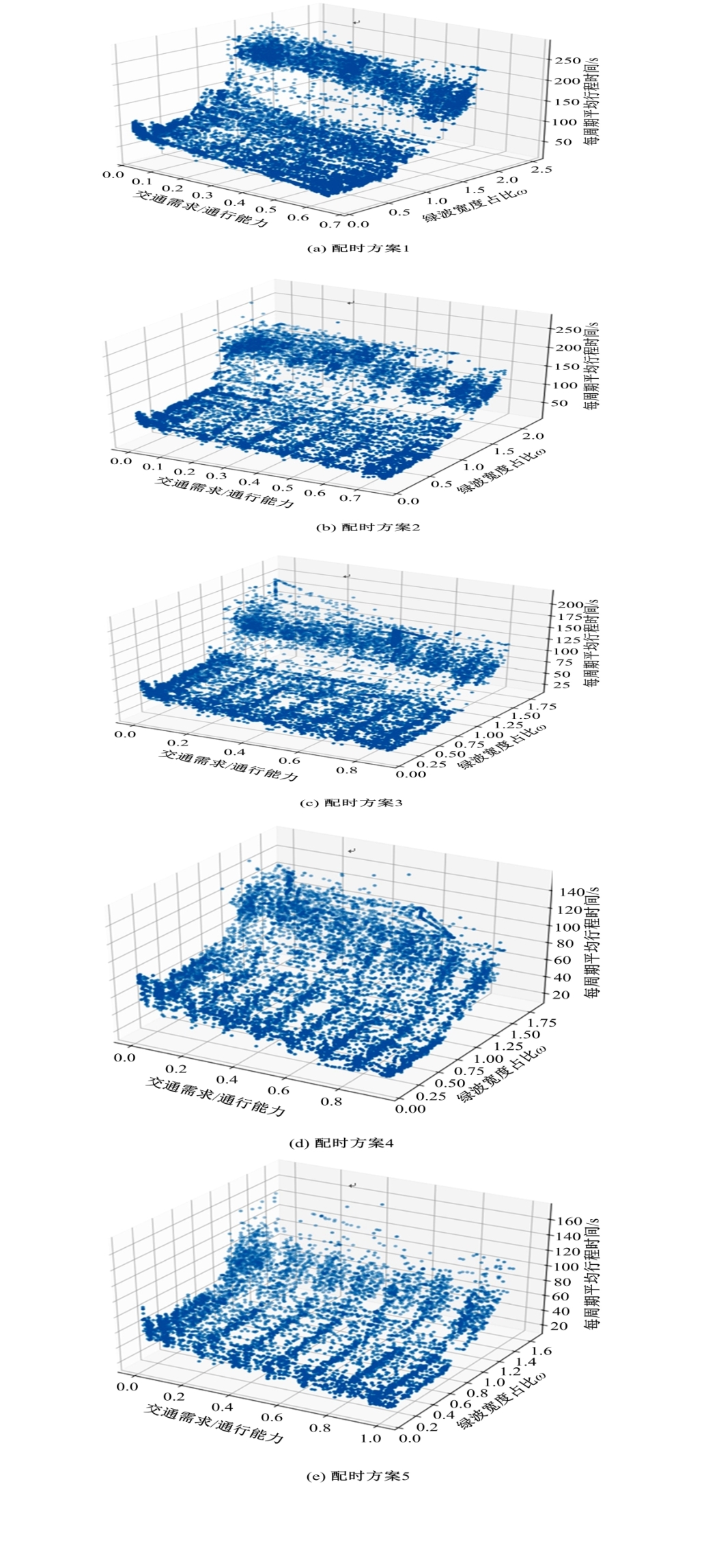
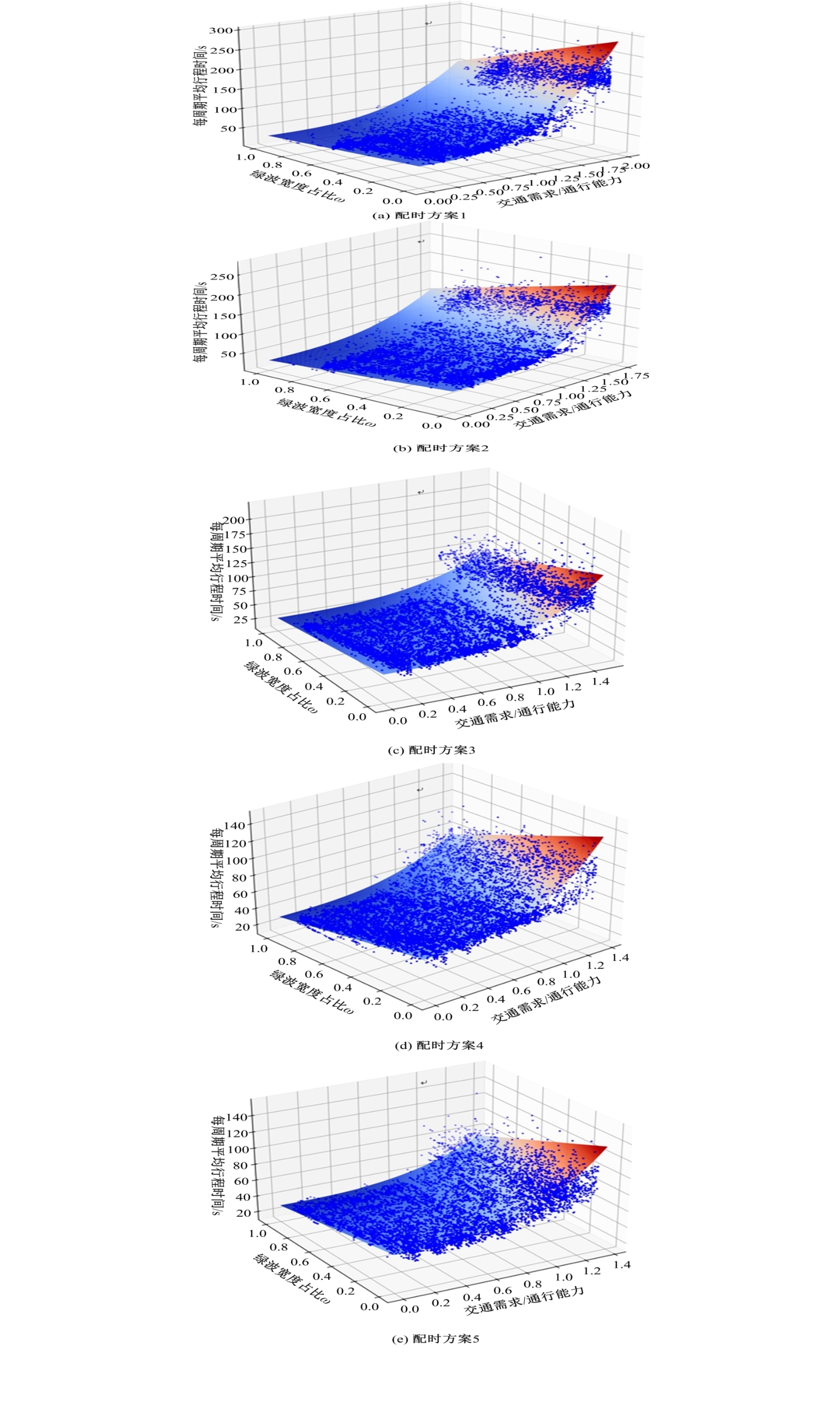
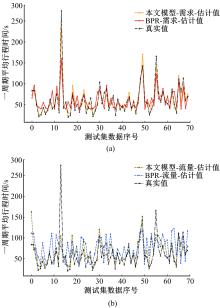
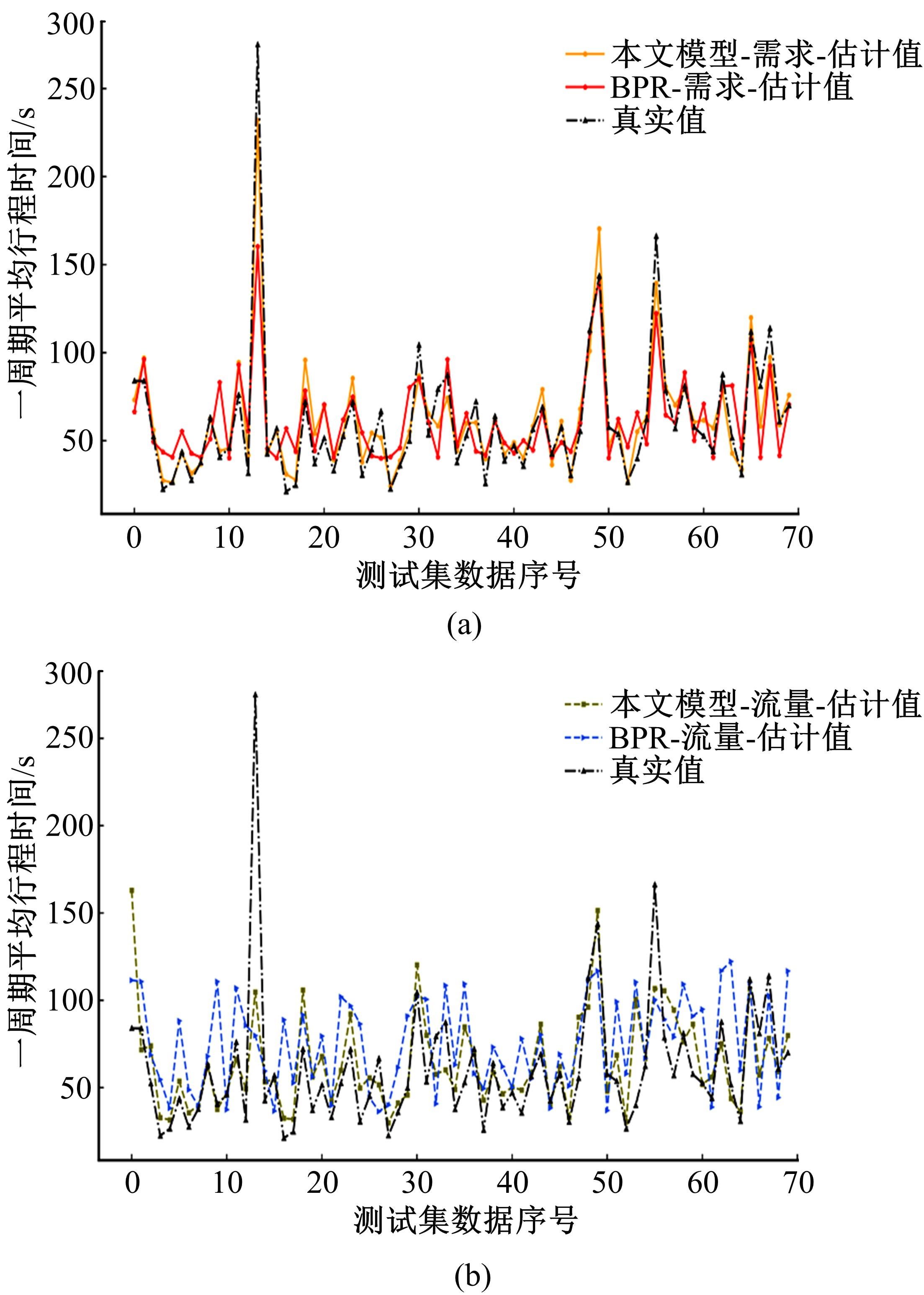
针对BPR函数在过饱和情况下难以应用、不符合城市间断流特性的局限性进行了改进,重新定义交通需求,提出考虑上下游信号配时影响的城市道路间断流动态路阻函数形式。基于VISSIM路段仿真数据,采用SMOTE过采样算法平衡仿真数据集,标定改进路阻函数。研究表明,在BPR函数中加入绿波宽度占比
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Bureau of Public Roads. Traffic Assignment Manual[M]. Washington D C: Urban Planning Division, US Department of Commerce, 1964. |
| 2 | Zhao F, Fu L, Zhong M, et al. Development and validation of improved impedance functions for roads with mixed traffic using taxi GPS trajectory data and simulation[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020(1):1-12. |
| 3 | Neuhold R, Fellendorf M. Volume delay functions based on stochastic capacity[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2014, 2421(1): 93-102. |
| 4 | Rafal K, Arkadiusz D. Estimating macroscopic volume delay functions with the traffic density derived from measured speeds and flows[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2017, 2017(3): 1-10. |
| 5 | So J J, Stevanovic A, Koonce P. Estimating performance of traffic signals based on link travel times: travel time-based signal performance measure[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2016, 50(5): 786-801. |
| 6 | Yuan G, Chen Y Y, Lu Y, et al. Research on the road resistant function model of urban express way[C]∥The 19th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals, Nanjing,China, 2019: 5257- 5268. |
| 7 | 潘义勇, 余婷, 马健霄. 基于路段与节点的城市道路阻抗函数改进[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 36(8):76-81. |
| Pan Yi-yong, Yu Ting, Ma Jian-xiao. Improvement of urban road impedance function based on section impedance and node impedance[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University: Natural Science, 2017, 36(8): 76-81. | |
| 8 | 温惠英, 卢德佑, 汤左淦. 考虑行程时间波动性的城市道路阻抗函数模型[J]. 公路工程, 2019, 44(3): 27-32. |
| Wen Hui-ying, Lu De-you, Tang Zuo-gan. Urban road impedance function model considering travel time volatility[J]. Highway Engineering, 2019, 44(3): 27-32. | |
| 9 | 刘宁, 赵胜川, 何南. 基于BPR函数的路阻函数研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报:交通科学与工程版, 2013, 37(3): 545-548. |
| Liu Ning, Zhao Sheng-chuan, He Nan. Research on resistance function based on BPR function[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Transportation Science & Engineering), 2013,37(3):545-548. | |
| 10 | 王飞, 徐维祥. 基于LSTM神经网络改进的路阻函数模型[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2021, 55(6): 1065-1071. |
| Wang Fei, Xu Wei-xiang. Improved model of road resistance function based on LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science Edition), 2021, 55(6): 1065-1071. | |
| 11 | 李彦瑾, 罗霞. 基于模糊神经网络的混合交通流路阻测算模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 53-59. |
| Li Yan-jin, Luo Xia. Road resistance measurement model of mixed traffic flow based on fuzzy neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University( Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 53-59. | |
| 12 | Huntsinger L F, Rouphail N M. Bottleneck and queuing analysis: calibrating volume-delay functions of travel demand models[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011, 2255(1): 117-124. |
| 13 | So J J, Stevanovic A, Ostojic M. Methodology to estimate volume-capacity ratios at traffic signals based on upstream-link travel times[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2017, 143(4):1-13. |
| 14 | 姜桂艳, 李继伟, 张春勤. 城市主干路路段行程时间估计的BPR修正模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2010, 45(1): 124-129. |
| Jiang Gui-yan, Li Ji-wei, Zhang Chun-qin. Modified BPR functions for travel time estimation of urban arterial road segment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(1): 124-129. | |
| 15 | Publications TRB. Highway capacity manual 2010[M]. Washington D C: National Research Council, 2011. |
| 16 | 王进, 白玉, 杨晓光. 关联信号交叉口排队长度计算模型[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 40(11): 1634-1640. |
| Wang Jin, Bai Yu, Yang Xiao-guang. Calculating model of queue length at correlated signalized intersections[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(11): 1634-1640. |
| [1] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [2] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [3] | 卢凯,徐广辉,叶志宏,林永杰. 考虑清空时间的双向队首绿波协调控制数解算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 421-429. |
| [4] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [5] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [6] | 朱凌,王秋成. 空间几何约束下新能源汽车驱动系统协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1509-1514. |
| [7] | 李昂,杨泓渊,雷小萌,宋凯文,千承辉. 基于等效连杆模型的六足机器人行进姿态闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1696-1708. |
| [8] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [9] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [10] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [11] | 贾彦峰,曲大义,林璐,姚荣涵,马晓龙. 基于运行轨迹的网联混合车流速度协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| [12] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [13] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
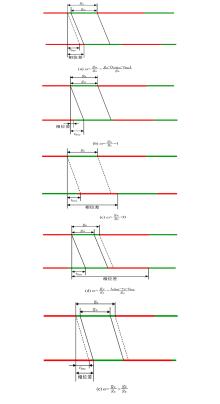
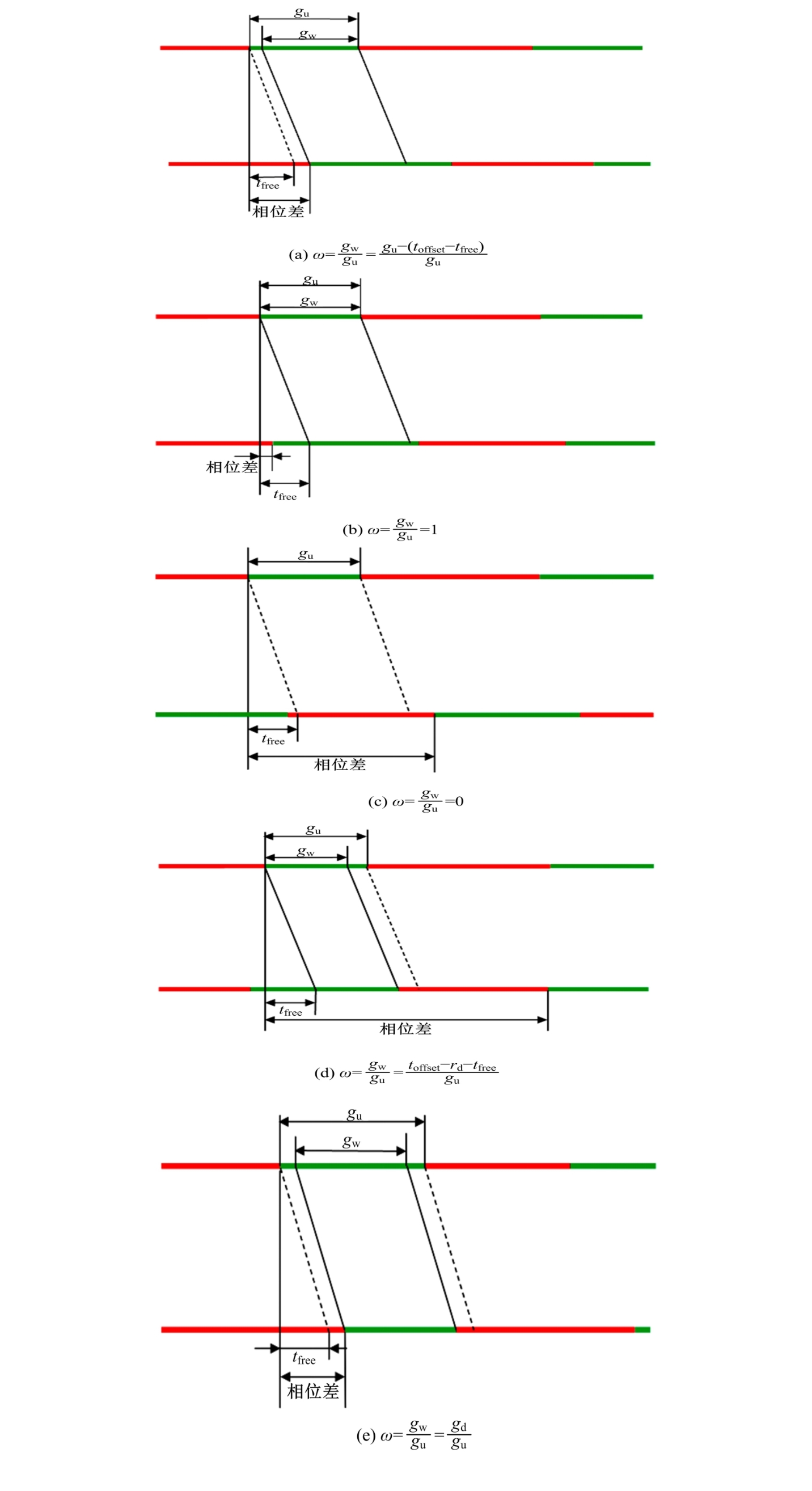
| [14] | 王殿海,沈辛夷,罗小芹,金盛. 车均延误最小情况下的相位差优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [15] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
|
||