吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1792-1799.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210248
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.浙江大学建筑设计研究院有限公司,杭州 310028
Fluctuation characteristics and prediction method of bus travel time between stations
Xian-min SONG1( ),Shu-tian YANG1,Ming-xin LIU2(
),Shu-tian YANG1,Ming-xin LIU2( ),Zhi-hui LI1
),Zhi-hui LI1
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.The Architectural Design & Research Institute of Zhejiang University Co. ,Ltd. ,Hangzhou 310028,China
摘要:
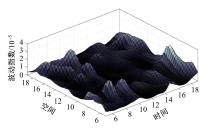
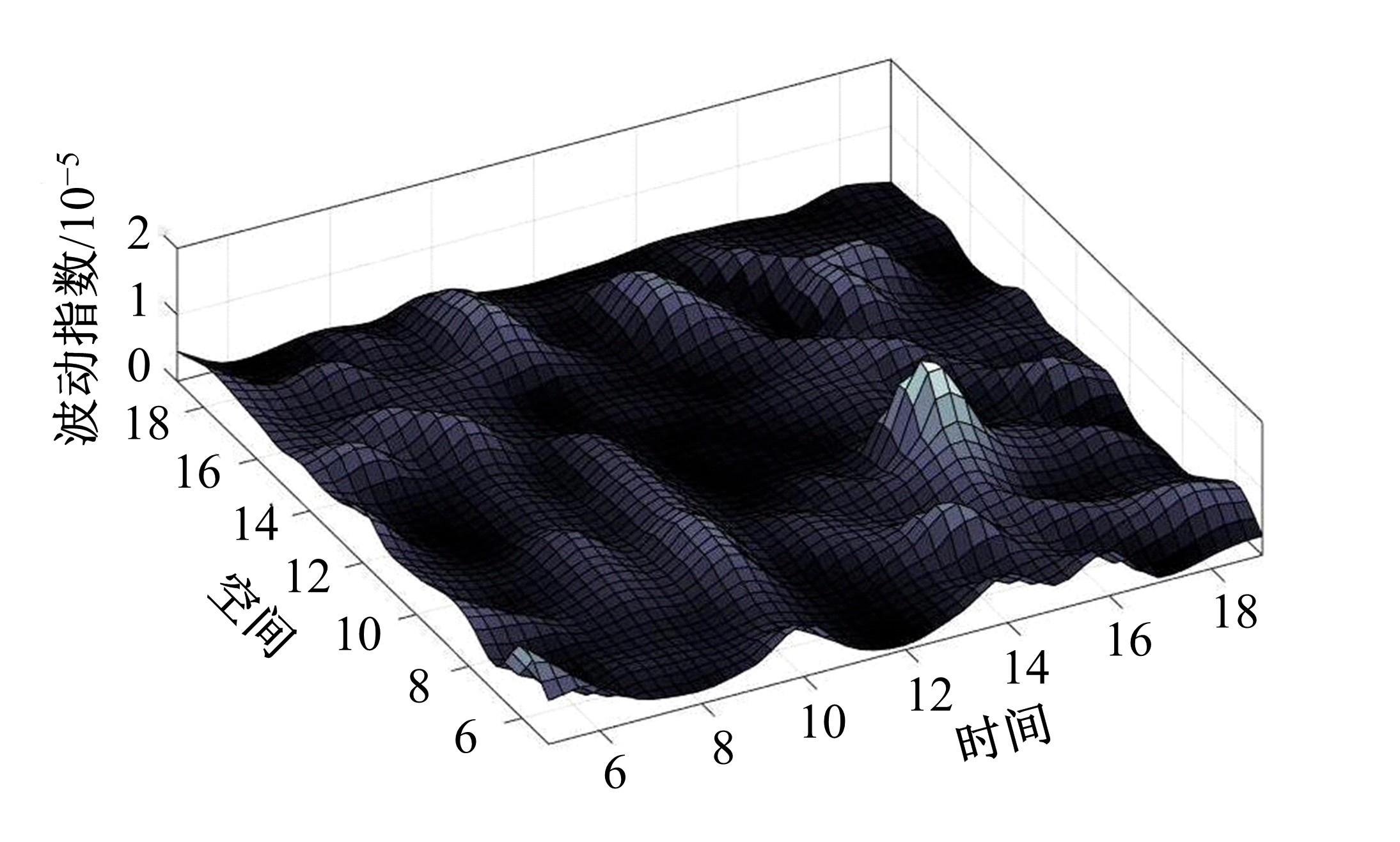
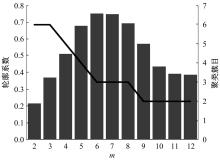
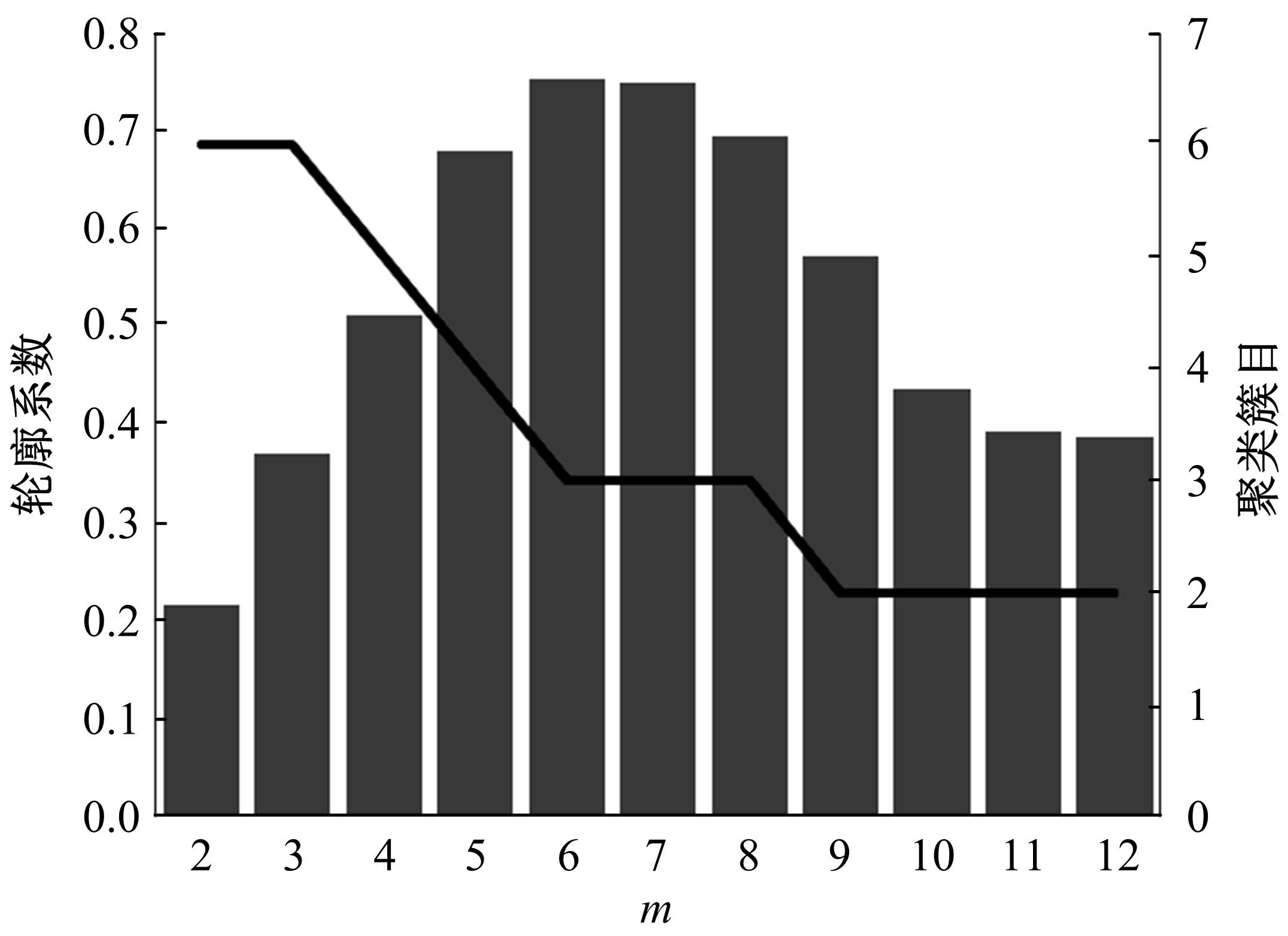
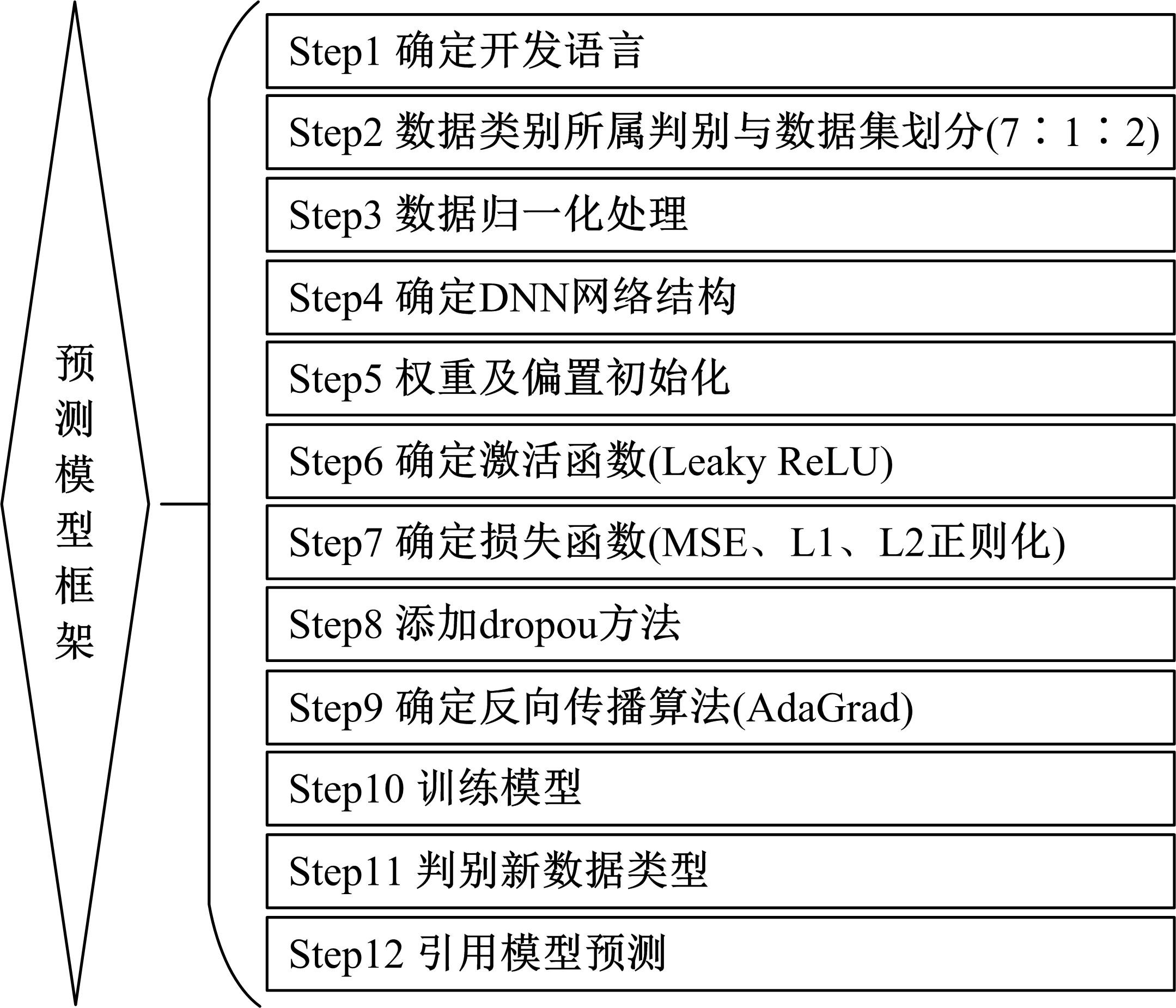
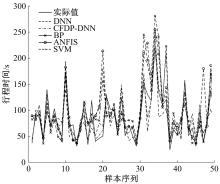
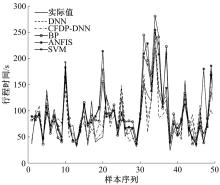
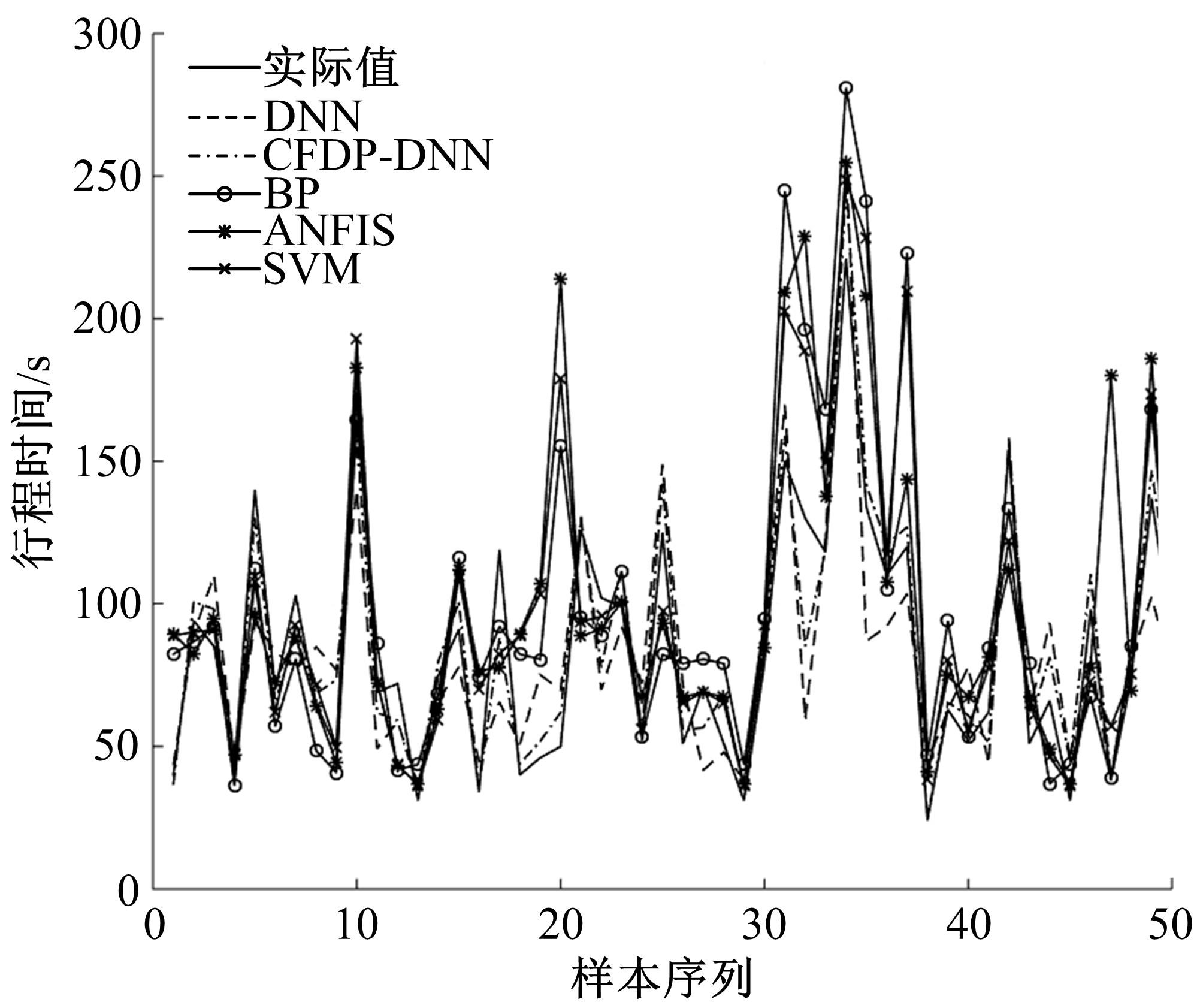
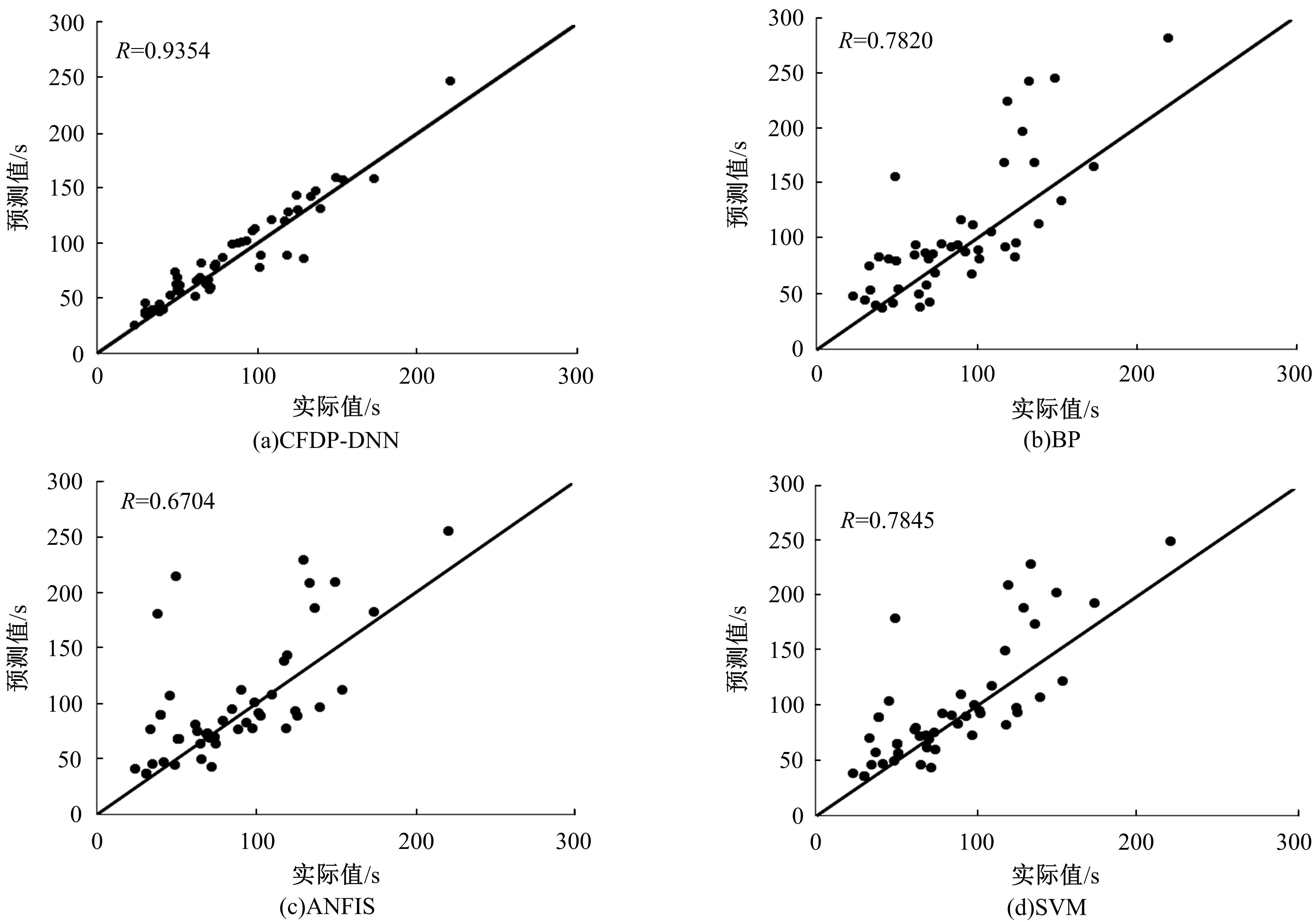
提出了基于公交车车头时距的行程时间波动性指标,并应用快速搜索与密度峰值聚类算法建立了公交运行环境划分方法,将其划分为低波动性、中波动性、高波动性。分析了站点间公交行程时间影响因素,设计了基于嵌入法的模型输入变量集选择方法,建立了考虑公交运行环境的深度神经网络预测方法(CFDP-DNN)。为验证该方法的有效性,将其分别与SVM、ANFIS、BP神经网络等方法进行对比,实验结果表明:CFDP-DNN的预测结果相关性为0.9354,MAPE误差为11%~22%,显示了基于公交车车头时距的交通运行环境的划分能有效提高行程时间的预测精度。本文预测方法能实现实时精确的站点间公交行程时间预测,为公交动态调度提供理论支持。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Shalaby A, Farhan A. Prediction model of bus arrival and departure times using AVL and APC data[J]. Journal of Public Transportation, 2004, 7(1): 41-61. |
| 2 | 童小龙, 卢冬生, 张腾, 等. 基于时间序列法的公交车站间行程时间预测模型研究——以苏州1路公交为例[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2017, 15(4): 114-119, 126. |
| Tong Xiao-long, Lu Dong-sheng, Zhang Teng, et al. Research on bus inter-site travel time prediction model: a case study based on suzhou No.1 bus route[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2017, 15(4): 114-119, 126. | |
| 3 | 苗旭, 王忠宇, 吴兵, 等. 考虑前序路段状态的公交到站时间双层BPNN预测模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(2): 127-133. |
| Miao Xu, Wang Zhong-yu, Wu Bing, et al. Bi-layer BPNN prediction model for bus arrival time considering preceding segment state[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(2): 127-133. | |
| 4 | Cong B, Peng Z R, Lu Q C, et al. Dynamic bus travel time prediction models on road with multiple bus routes[J]. Computational Intelligence & Neuroscience, 2015, 2015: 432389. |
| 5 | Farid Y Z, Christofa E, Paget-Seekins L. Estimation of short-term bus travel time by using low-resolution automated vehicle location data[J].Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2016, 2539(1): 113-118. |
| 6 | 梁士栋, 赵淑芝, 马明辉, 等. 路段直线式公交站点对公交车延误的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(6): 1807-1817. |
| Liang Shi-dong, Zhao Shu-zhi, Ma Ming-hui, et al. Impacts of linear bus stop on bus delays[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1807-1817. | |
| 7 | 邝先验, 罗会超, 钟蕊, 等. 基于天牛须小波神经网络的公交到站时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(1): 110-117. |
| Kuang Xian-yan, Luo Hui-chao, Zhong Rui, et al. Bus arrival time prediction based on wavelet neural network optimized by beetle antennae search[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 110-117. | |
| 8 | 杨世军, 裴玉龙, 潘恒彦, 等. 城市公交车辆驻站时间特征分析及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2031-2039. |
| Yang Shi-jun, Pei Yu-long, Pan Heng-yan, et al. Characteristics analysising and prediction of dwelling time of urban bus[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2031-2039. | |
| 9 | Sharmila R B, Velaga N, Choudhary P. Bus arrival time prediction and measure of uncertainties using survival models[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(8): 900-907. |
| 10 | Rodriguez A, Laio A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6191):1492-1496. |
| 11 | Hinton G E, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, et al. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors[J]. Computer Science, 2012, 3(4): 212-223. |
| 12 | Hadgu A T, Nigam A, Diaz-Aviles E. Large-scale learning with AdaGrad on spark[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Santa Clara, USA, 2015: 2828-2830. |
| [1] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [2] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [3] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [4] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [5] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [6] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [7] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [8] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [9] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [10] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [11] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [12] | 贾彦峰,曲大义,林璐,姚荣涵,马晓龙. 基于运行轨迹的网联混合车流速度协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| [13] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [14] | 陆文琦,周天,谷远利,芮一康,冉斌. 基于张量分解理论的车道级交通流数据修复算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1708-1715. |
| [15] | 卢凯,吴蔚,林观荣,田鑫,徐建闽. 基于KNN回归的客运枢纽聚集人数组合预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1241-1250. |
|
||