吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 631-640.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220565
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
内部废气耦合点火对甲醇燃烧和排放的影响
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林师范大学 计算机学院,长春 130022
Effect of internal exhaust gas coupling ignition on methanol combustion and emission
Xiao-na LI1( ),Fang-xi XIE1(
),Fang-xi XIE1( ),Jing-hua ZHAO1,2,Yu LIU1,Yao SUN1
),Jing-hua ZHAO1,2,Yu LIU1,Yao SUN1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Computer,Jilin Normal University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
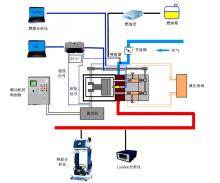
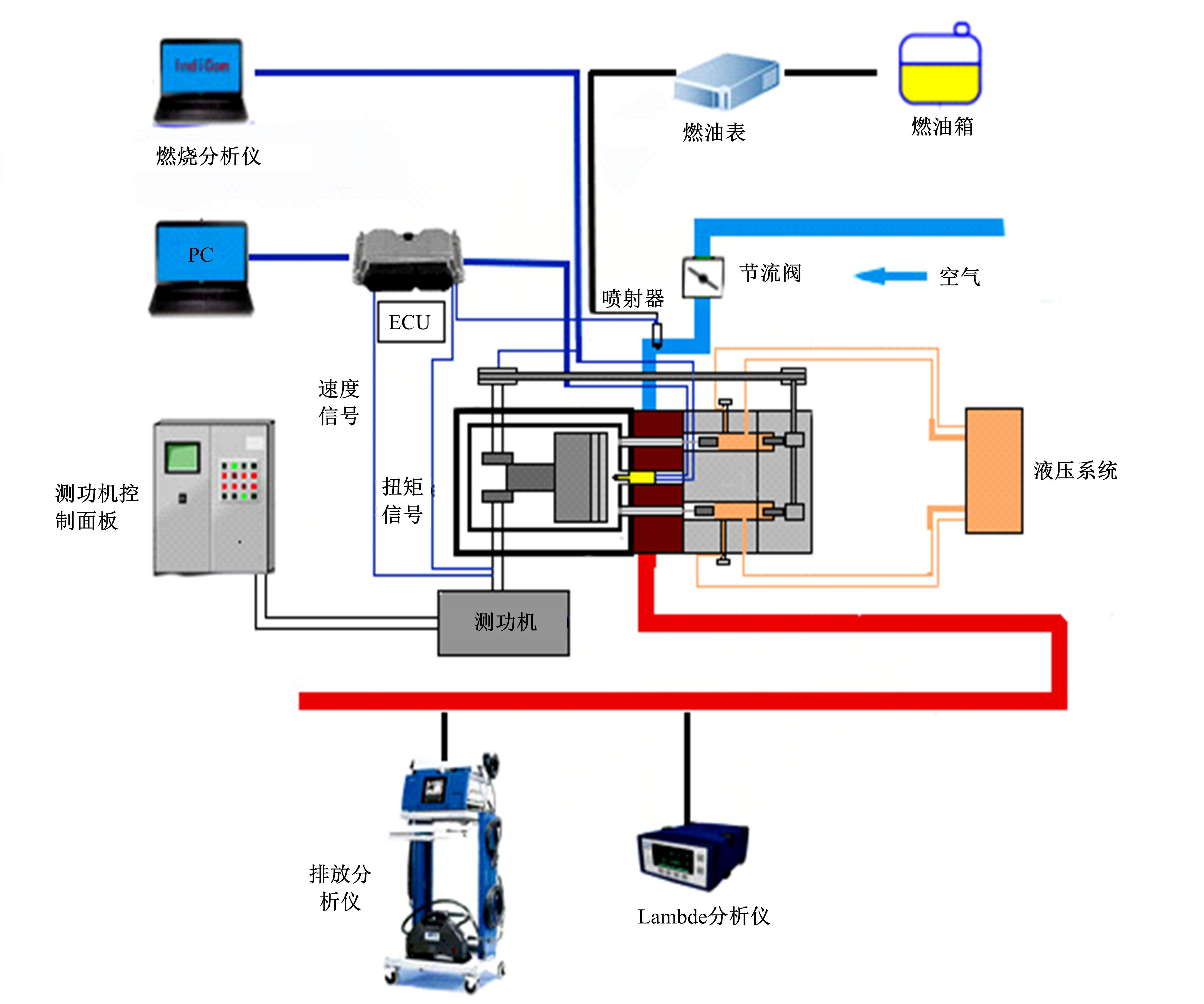
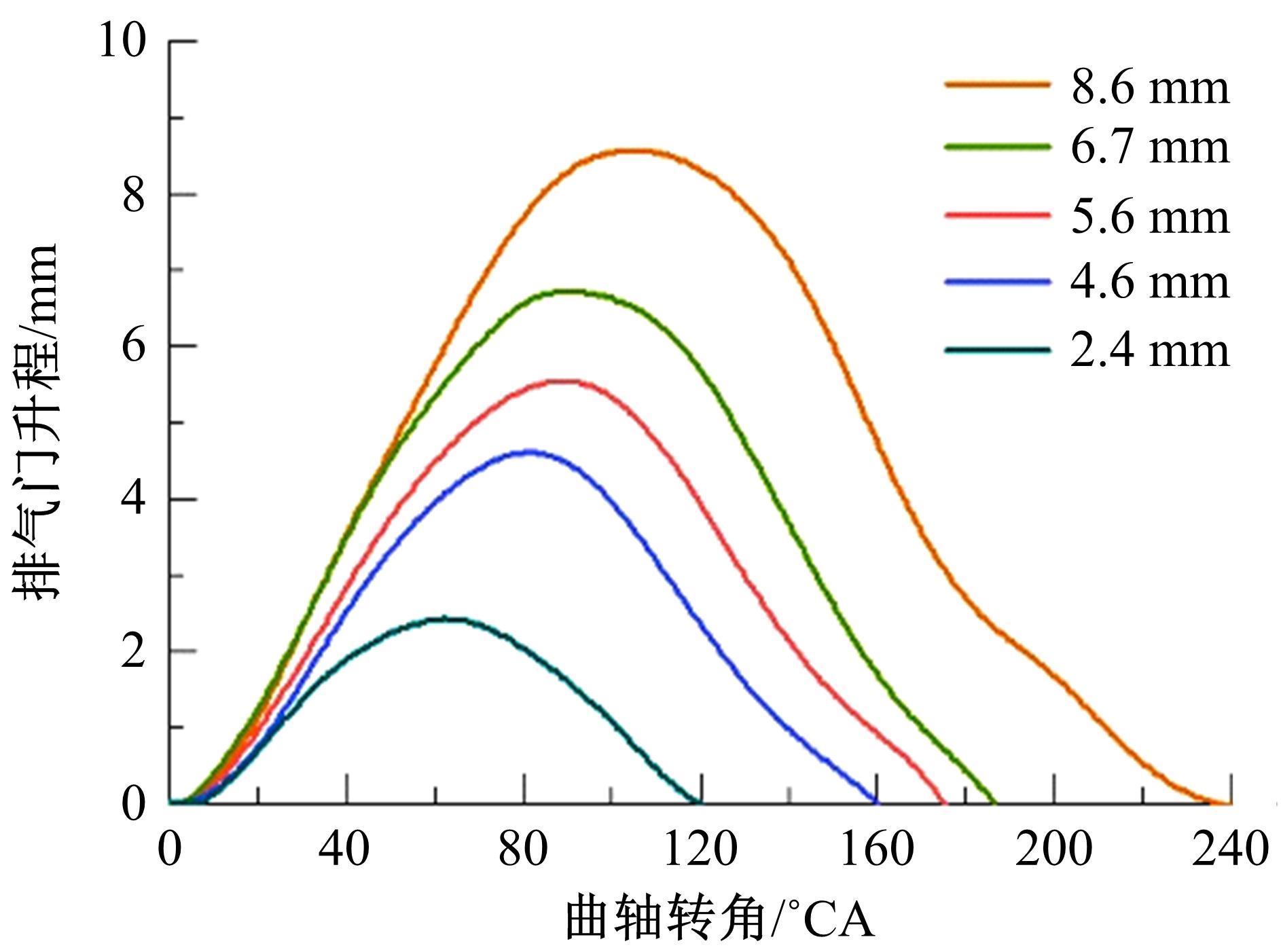
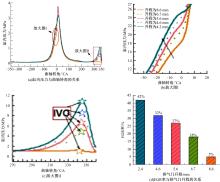
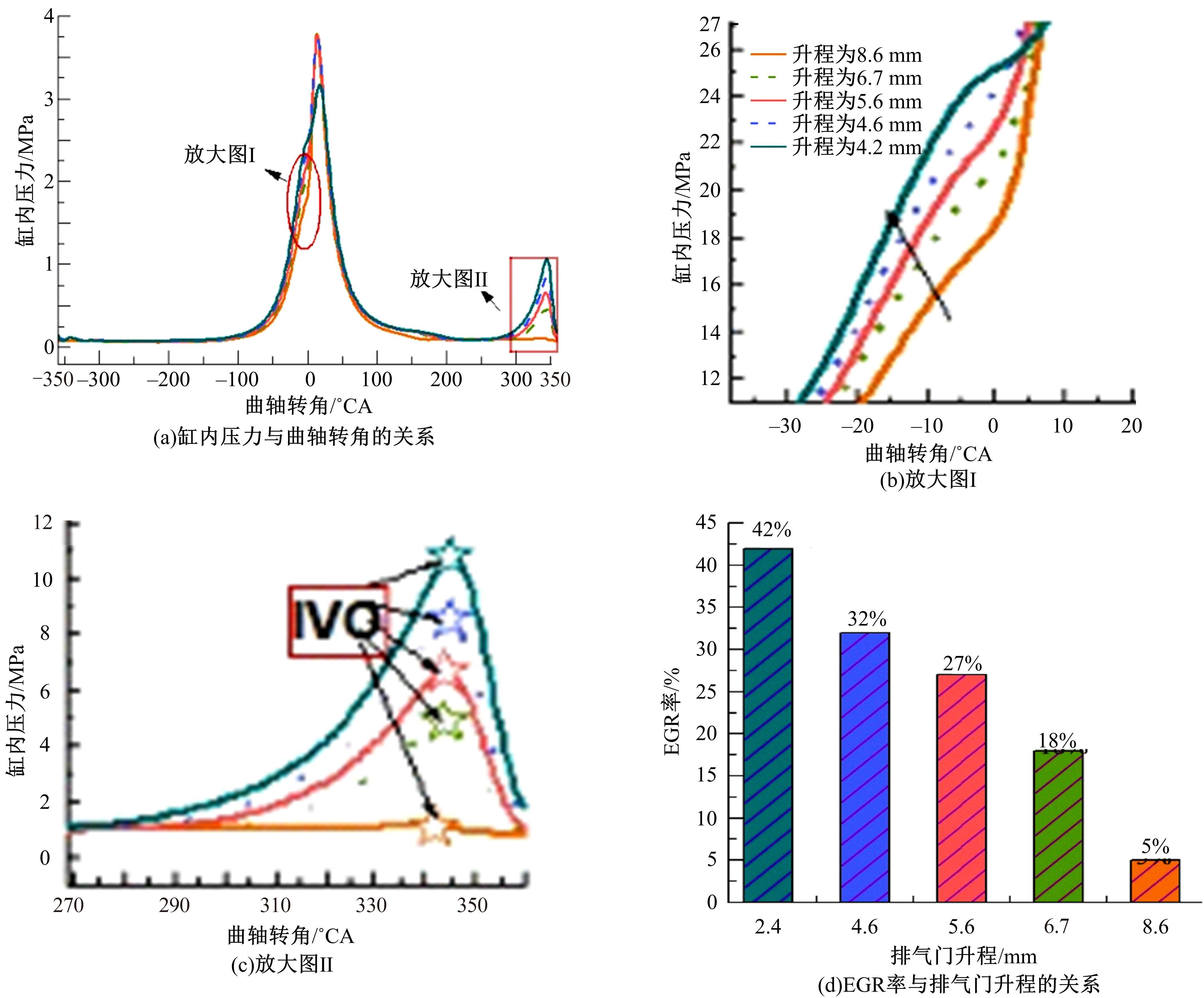
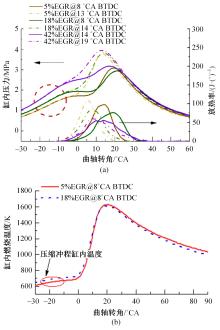
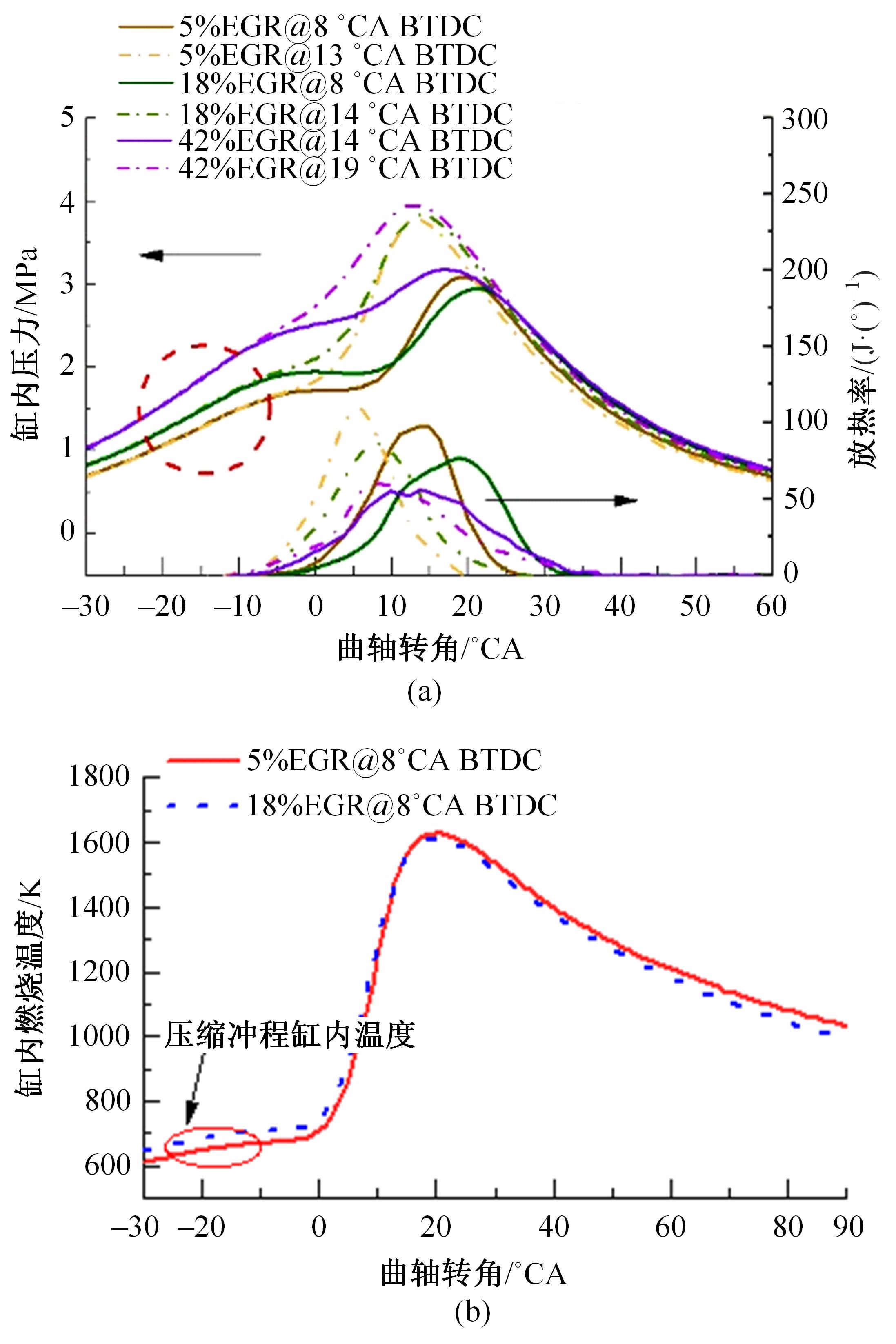
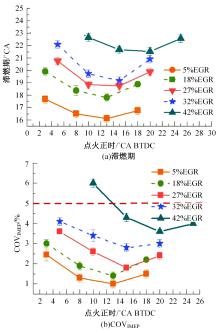
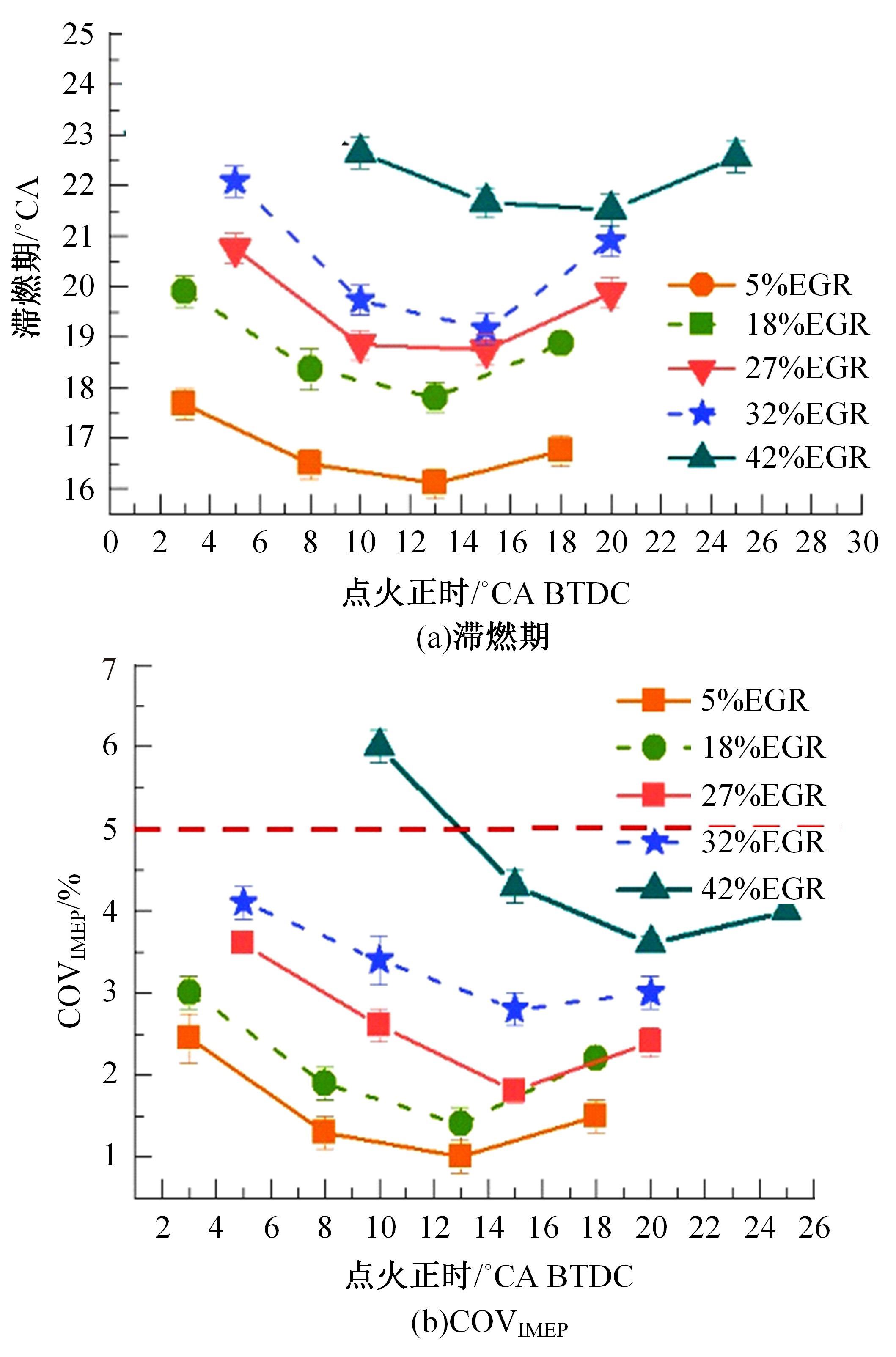
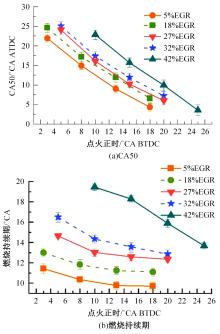
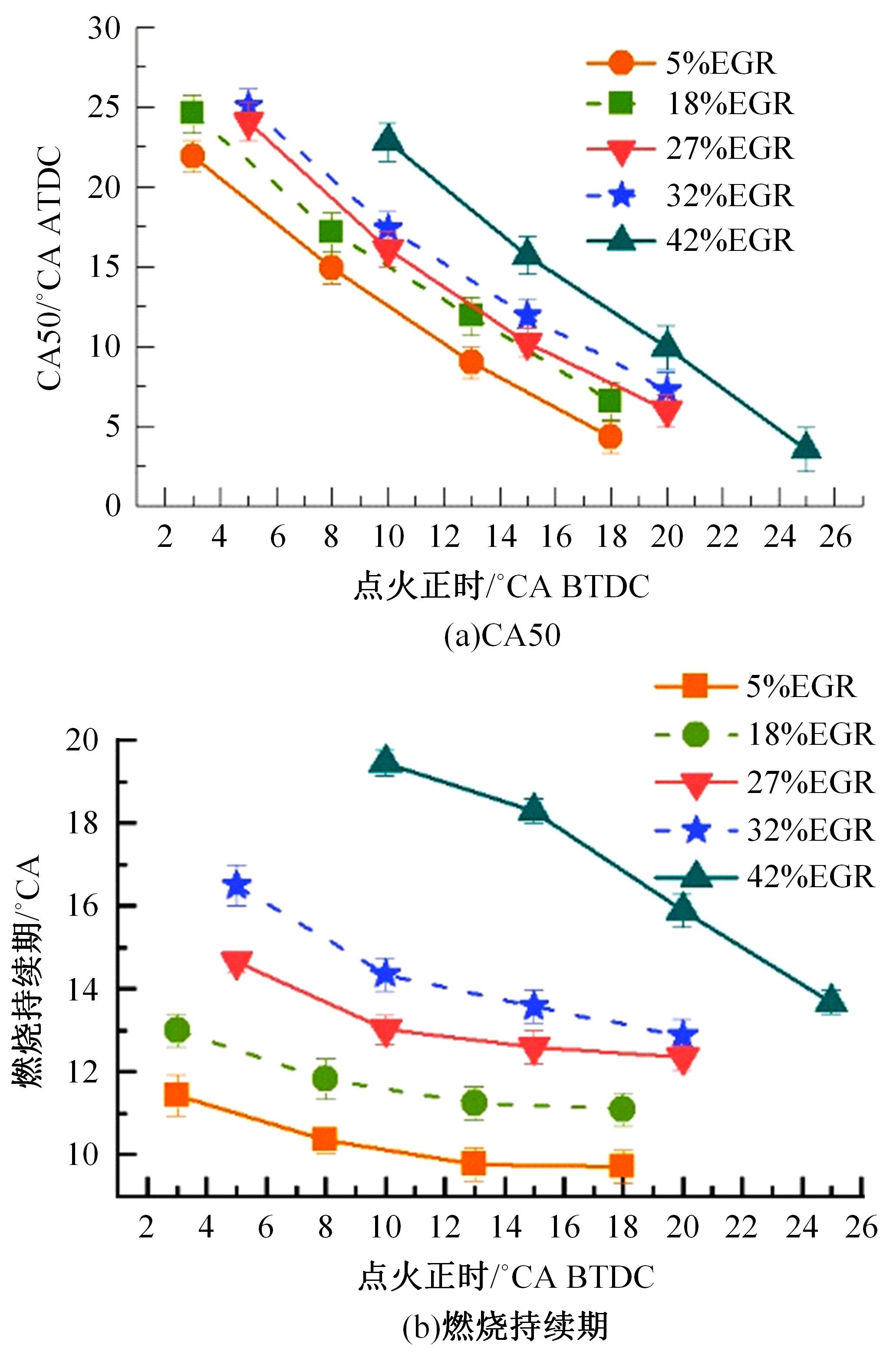
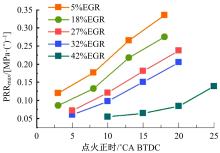
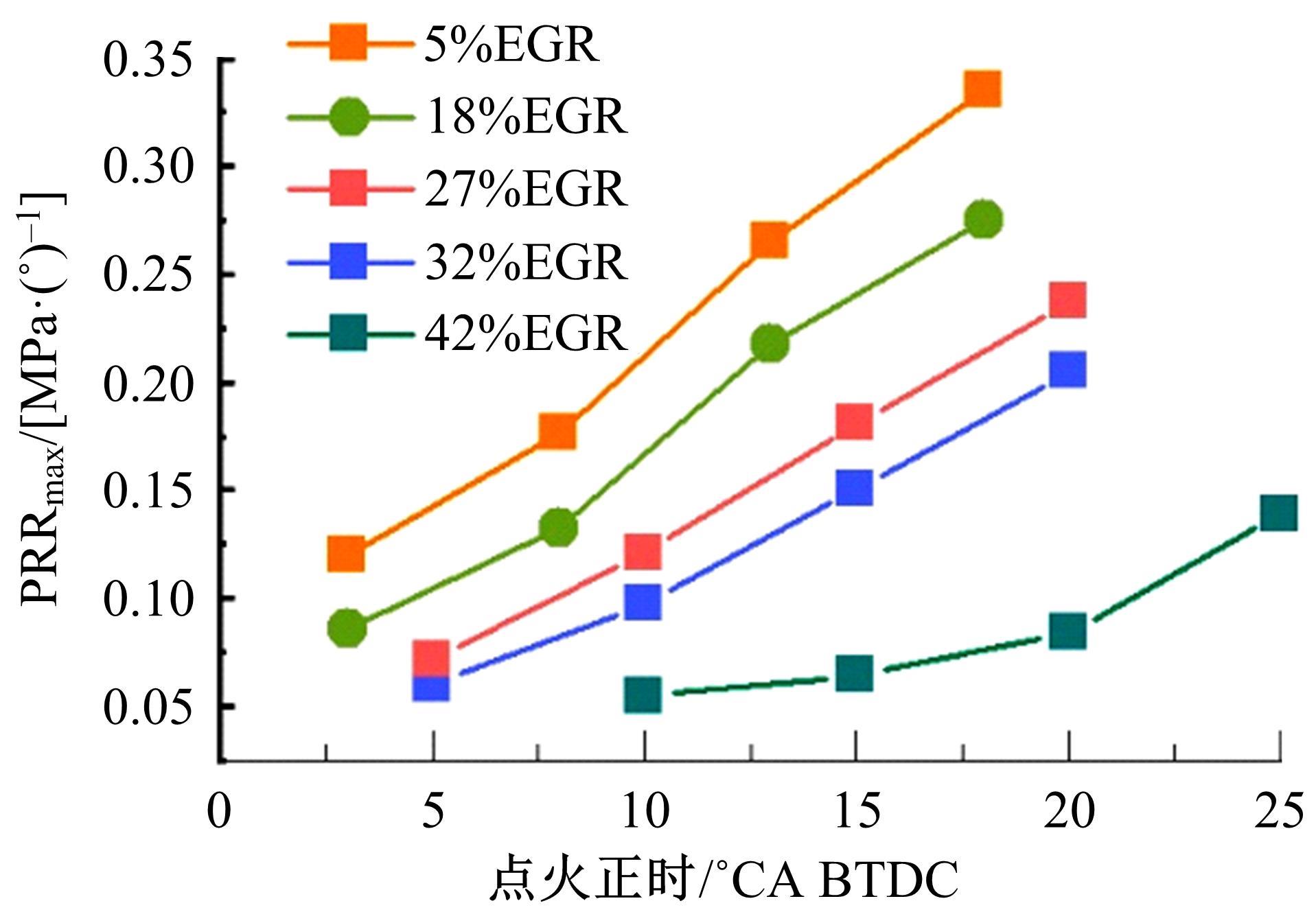
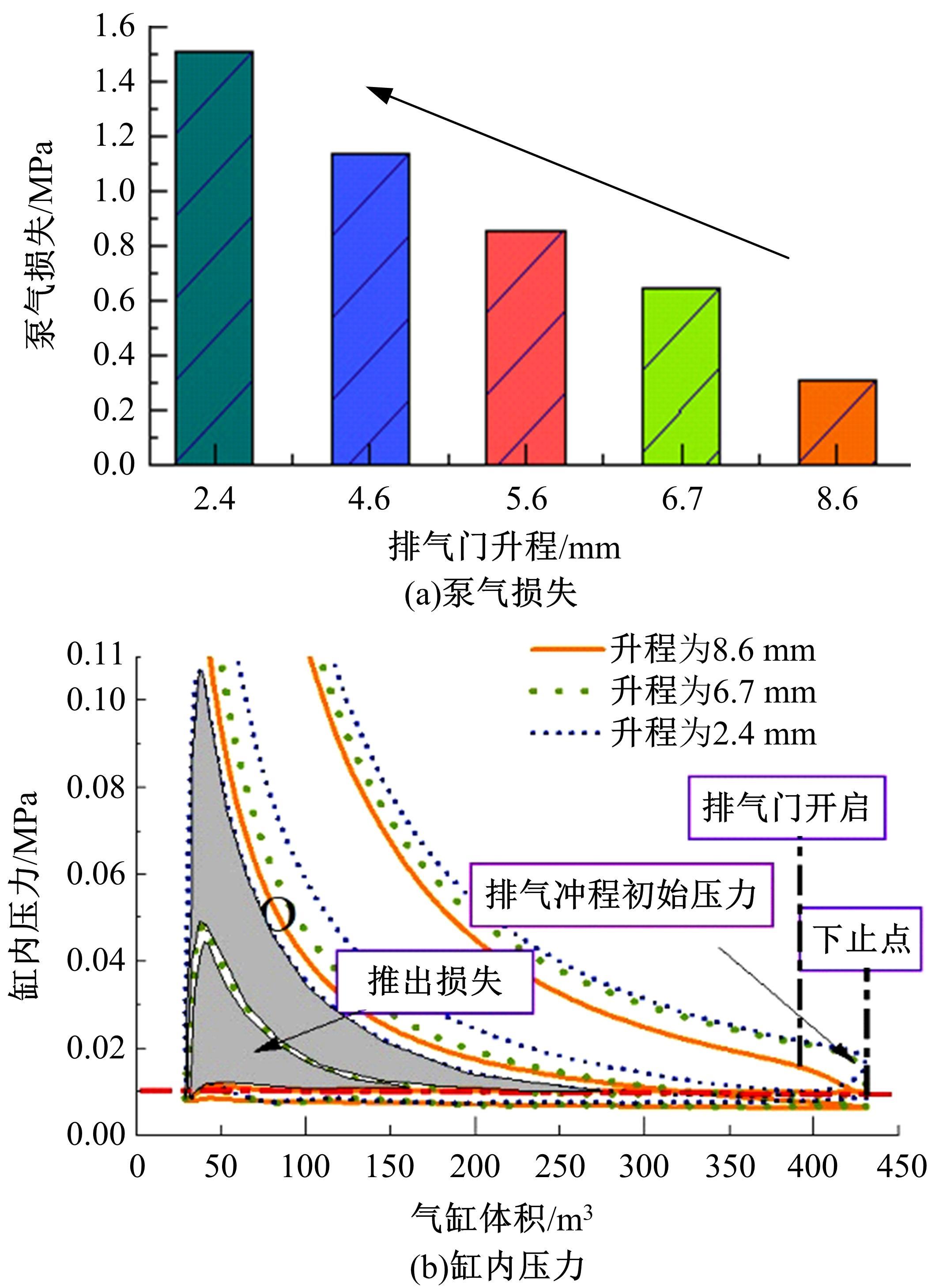
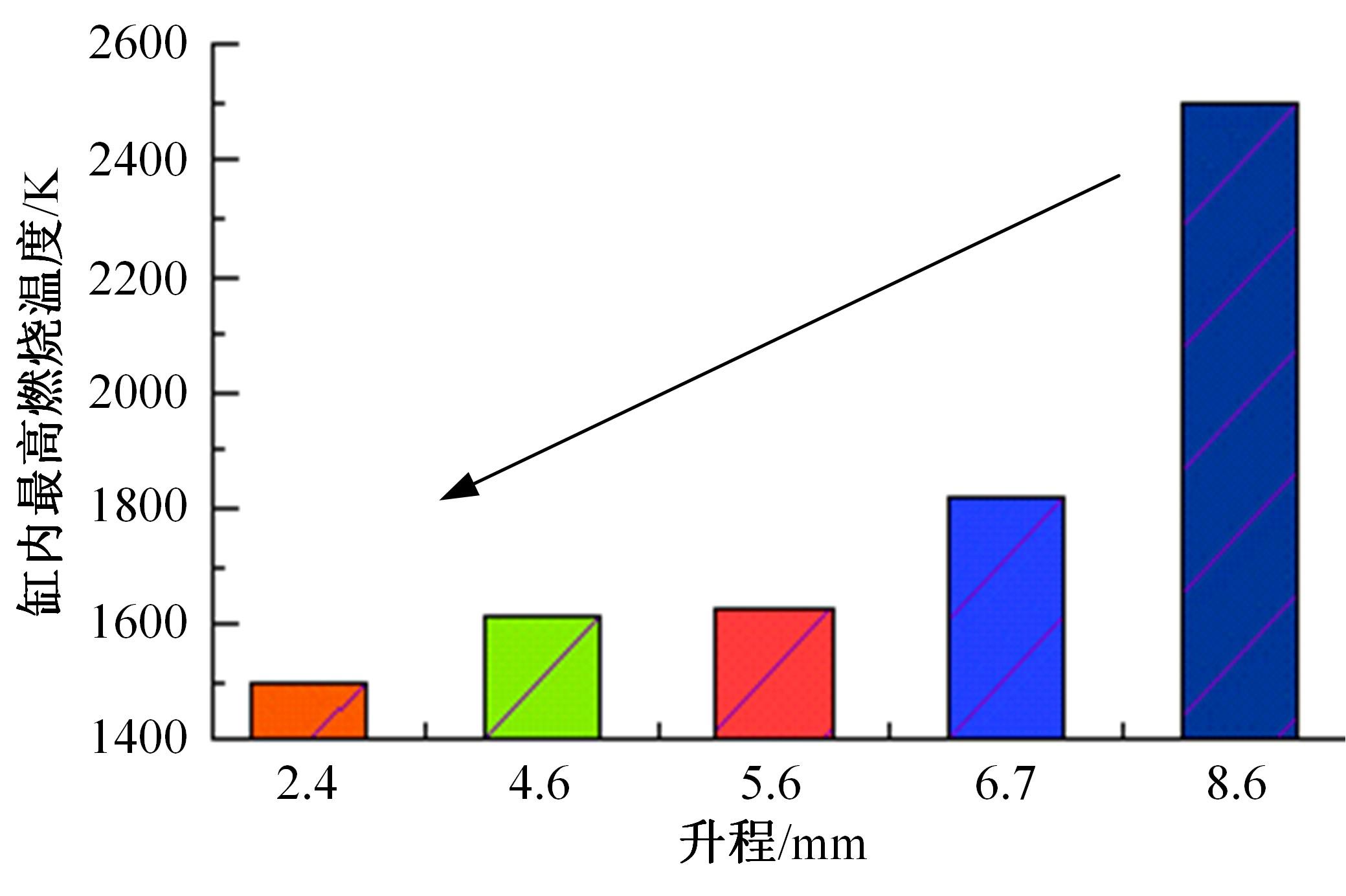
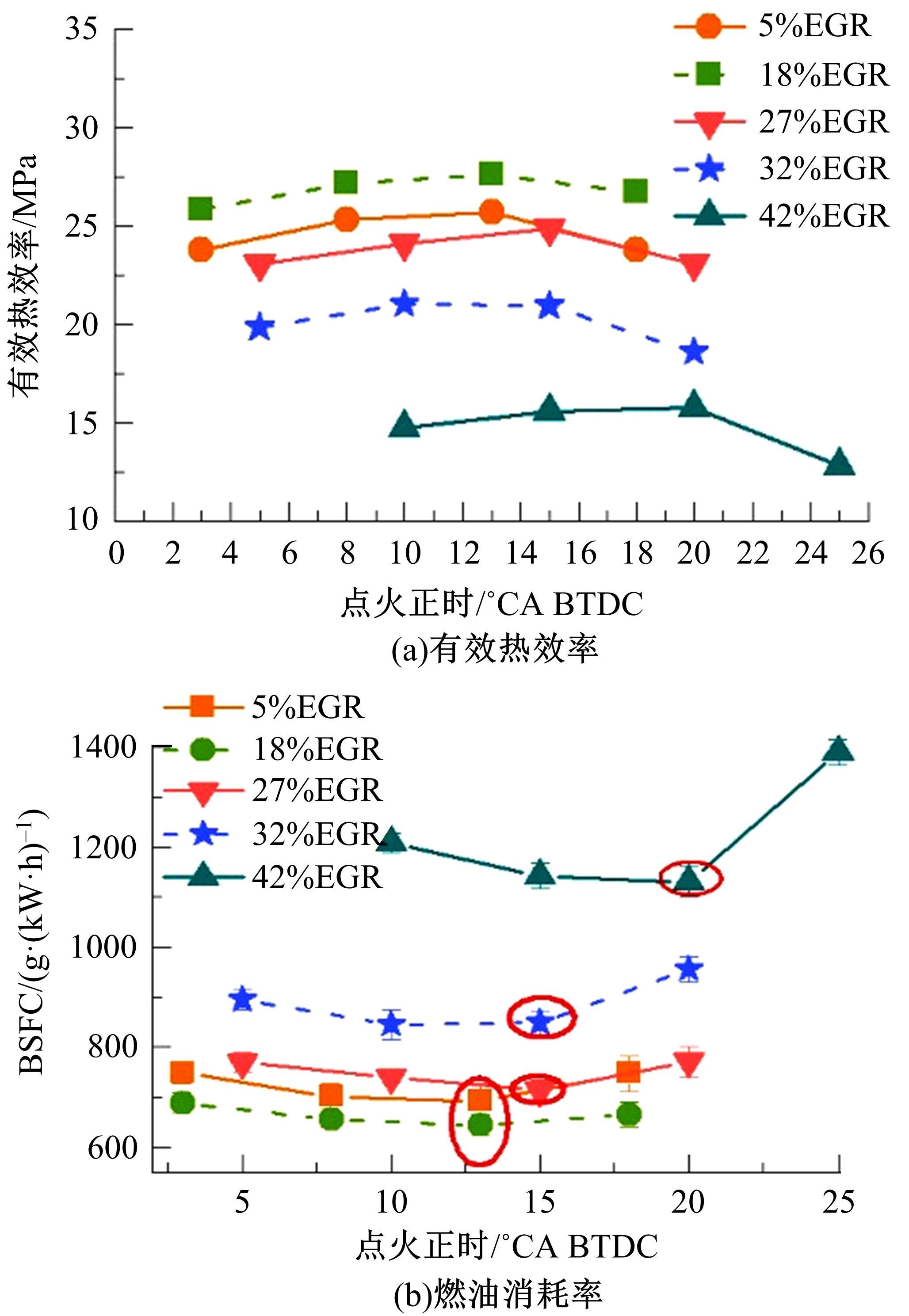
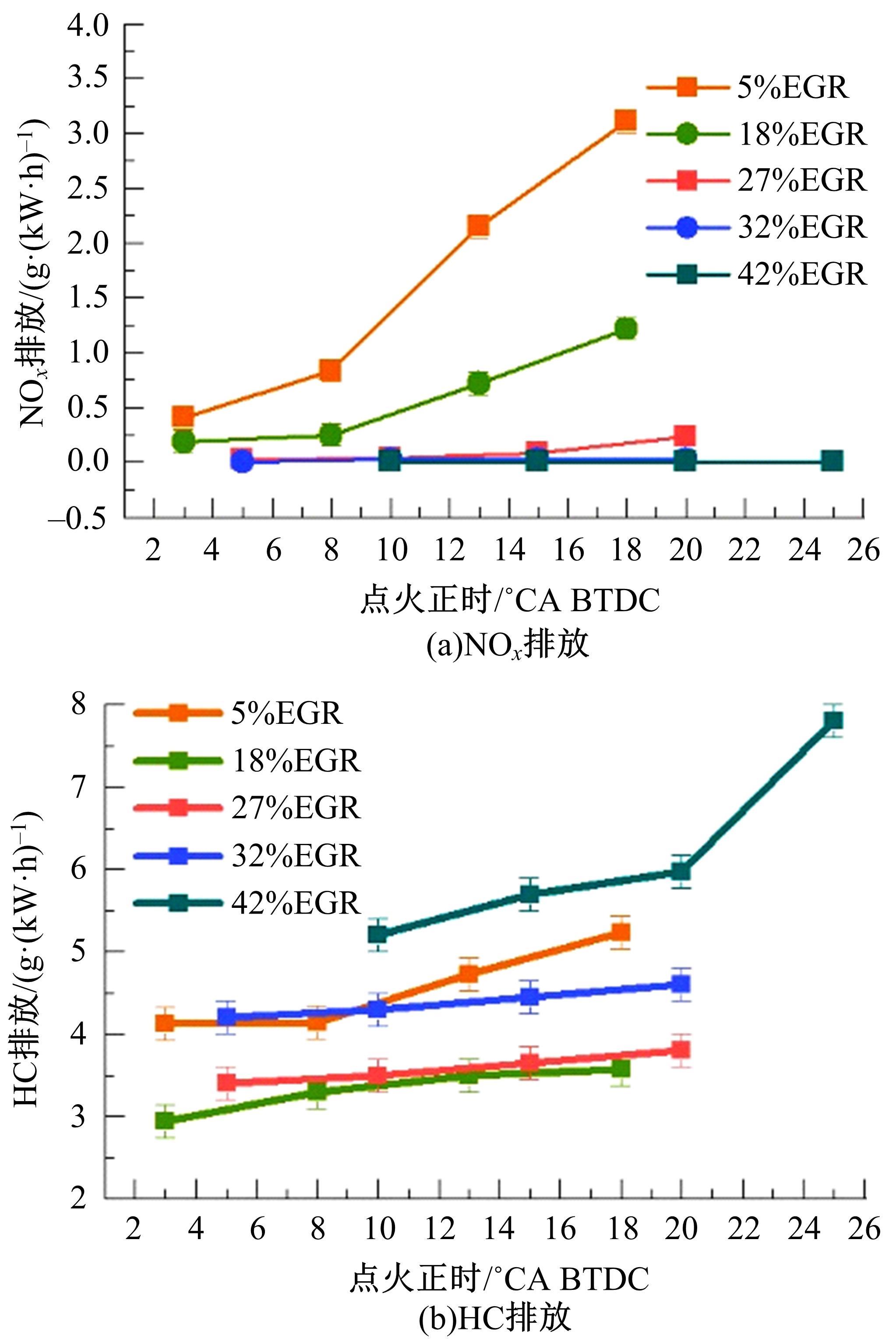
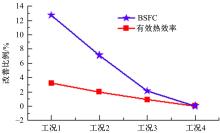
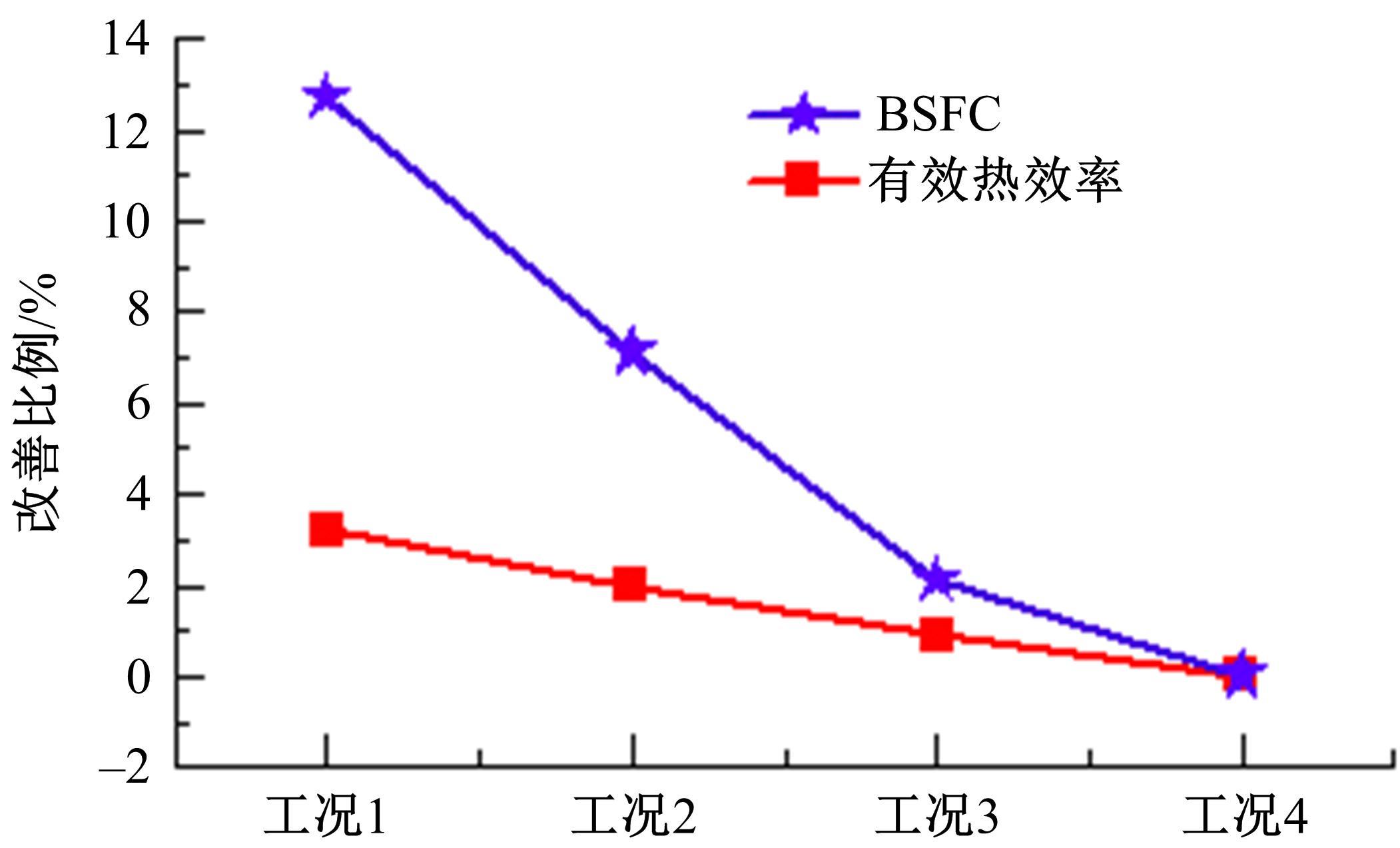
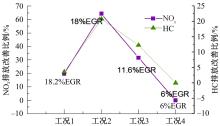
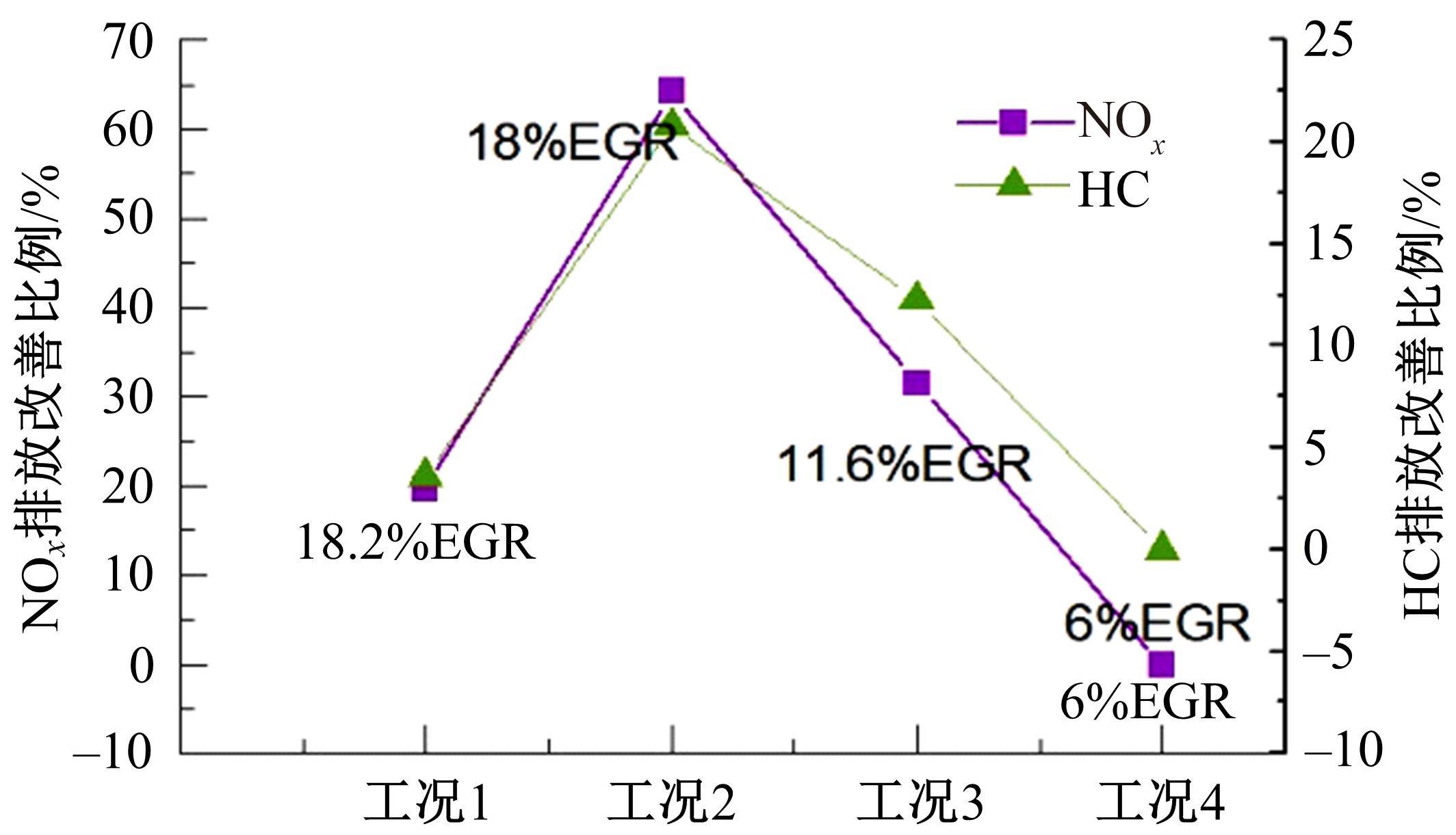
基于自主开发的液压可变气门机构,研究了内部废气再循环(EGR)耦合点火策略对甲醇发动机节能减排的改善潜力。结果表明,随着排气门升程的降低,内部EGR率增大。内部EGR增大导致缸内压力和缸内燃烧温度峰值下降,燃烧重心推迟,燃烧持续期延长,燃烧循环变动增加。适当地调整点火正时,甲醇发动机在42%内部EGR下仍能使燃烧重心分布在合理的范围内并平稳运行。另外,内部EGR结合点火正时在不同负荷下对油耗和排放的改善效果不同,在20%负荷下有效热效率和燃油消耗率改善效果最佳,分别提高了3.2%和12.7%;在40%负荷下对NO x 和HC排放改善效果最佳,分别降低了64.25%和20.8%。
中图分类号:
- TK421
| 1 | Li X, Zhen X, Wang Y, et al. The knock study of high com-pression ratio SI engine fueled with methanol in combination with different EGR rates[J]. Fuel, 2019, 257: No. 116098. |
| 2 | Zhou Y, Hong W, Yang Y, et al. Experimental investigation of diluents components on performance and emissions of a high compression ratio methanol SI engine[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(17): No. 3366. |
| 3 | Fu J, Liu J, Deng B, et al. An approach for exhaust gas energy recovery of internal combustion engine: Steam-assisted turbocharging[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 85: 234-244. |
| 4 | 黄明. EGR汽油发动机部分负荷下性能优化研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学机械与运载工程学院, 2011. |
| Huang Ming. Research on performance optimization of EGR gasoline engine under partial load[D]. Changsha: School of Mechanical and Transportation Engineering, Hunan University, 2011. | |
| 5 | 赵弘志, 曹林. CA6102电控汽油机废气再循环性能研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2005, 27(2): 264-268. |
| Zhao Hong-zhi, Cao Lin. A study on EGR performance of CA6102 electronically-controlled gasoline engine[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2005, 27(2): 264-268. | |
| 6 | 晁岳栋, 陆海峰, 李理光, 等. 基于理论循环的汽油机EGR技术节油机理[J]. 内燃机学报, 2017, 35(3): 208-214. |
| Zhao Yue-dong, Lu Hai-feng, Li Li-guang, et al. Mechanism of fuel consumption reduction on gasoline engines based on thermodynamics engine cycle[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2017, 35(3): 208-214. | |
| 7 | Zhen X, Wang Y, Liu D. Bio-butanol as a new generation of clean alternative fuel for SI (spark ignition) and CI (compression ignition) engines[J]. Renew Energy, 2020, 147: 2494-2521. |
| 8 | 潘明章. EGR对燃用不同燃料小型强化SI发动机性能及爆震的影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学动力机械及工程学院, 2014. |
| Pan Ming-zhang. Investigation on the effect of EGR on perfor-mance and knocking characteristics of down-sizing SI engine fueled with differenent fuels[D]. Tianjin:School of Power Machinery and Engineering, Tianjin University, 2014. | |
| 9 | Xie F, Hong W, Su Y, et al. Effect of external hot EGR dilution on combustion, performance and particulate emissions of a GDI engine[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 142: 69-81. |
| 10 | Gong C, Li Z, Yi L, et al. Experimental investigation of equivalence ratio effects on combustion and emissions characteristics of an H2/methanol dual-injection engine under different spark timings[J]. Fuel, 2020, 262: No. 11646. |
| 11 | Hu E J, Huang Z H, Liu B, et al. Experimental study on combustion characteristics of a spark-ignition engine fuelled with natural gas-hydrogen blends combining with EGR[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(2): No. 1035e1044. |
| 12 | Huang B, Hu E J, Huang Z H, et al. Cycle-by-cycle variations in a spark ignition engine fueled with natural gas-hydrogen blends combined with EGR[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(19): 8405-8414. |
| 13 | Moon G, Lee Y, Choi K, et al. Emission characteristics of diesel, gas to liquid, and biodiesel-blended fuels in a diesel engine for passenger cars[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89: 3840-3846. |
| 14 | 周遊, 洪伟, 解方喜, 等. 气门控制策略对无节气门发动机性能的影响[J/OL]. [2024-02-17]. |
| 15 | 汪洋, 王静, 史春涛, 等. 甲醇发动机排放特性的研究[J]. 内燃机学报, 2007, 25(1): 73-76. |
| Wang Yang, Wang Jing, Shi Chun-tao, et al. Research on emission characteristics of methanol engine[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2007, 25(1): 73-76. |
| [1] | 周遊,洪伟,解方喜,刘宇,宫洵,李小平. 气门控制策略对无节气门发动机性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 55-65. |
| [2] | 周遊,洪伟,解方喜,苏岩,刘宇,李小平,段加全. EGR协同点火对火花辅助压燃汽油机性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 31-40. |
| [3] | 秦静,郑德,裴毅强,吕永,苏庆鹏,王膺博. 基于PSO-GPR的发动机性能与排放预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1489-1498. |
| [4] | 宋昌庆,陈文淼,李君,曲大为,崔昊. 不同当量比下单双点火对天然气燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1929-1935. |
| [5] | 祖象欢,杨传雷,王贺春,王银燕. 船用柴油机废气再循环性能评估及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 805-815. |
| [6] | 杨帅, 冯志炜, 赵治国, 周毅. 不同米勒循环方式对柴油机工作过程影响的一维模拟分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1444-1454. |
| [7] | 江涛, 林学东, 李德刚, 顾静静. 压缩天然气缸内直喷发动机喷射方式对混合气形成及燃烧特性影响的模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 735-743. |
| [8] | 郭亮, 杨文昭, 王云开, 孙万臣, 程鹏, 李国良. 废气再循环对丁醇/柴油混合燃料发动机的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1767-1774. |
| [9] | 唐志刚, 张力, 尚会超, 吕晓惠, 陈曦, 郑仁蔚. 电热塞点火微型内燃机燃烧特性及残余废气对其的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 811-818. |
| [10] | 李小平, 洪伟, 解方喜, 李翔宇, 杨文海, 代志尧. 应用推迟点火、废气再循环及过稀混合气降低稀燃甲醇发动机NOx排放[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1478-1483. |
| [11] | 于秀敏, 商震, 张岳韬, 杜耀东. 废气再循环对直喷汽油机燃烧及排放影响的仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1109-1117. |
| [12] | 袁晨恒,冯慧华,王梦秋,左正兴. 自由活塞汽油直线发电机燃烧过程特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 127-132. |
| [13] | 包堂堂, 胡宗杰, 胡俊超, 阮逸平, 邓俊, 吴志军. 基于超声雾化的柴油/汽油混合燃料液滴群燃烧特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 903-908. |
| [14] | 赵靖华, 洪伟, 冯枫, 解方喜. 基于EGR策略的重型柴油机瞬态空燃比优化控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 151-155. |
| [15] | 高继东, 秦孔建, 梁荣亮, 李孟良. 实际道路工况和法规工况下中型柴油机排放特性的对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 33-38. |
|
||