吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1489-1498.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210111
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于PSO-GPR的发动机性能与排放预测方法
秦静1,2( ),郑德1,2,裴毅强2,吕永3,苏庆鹏2,3,王膺博2
),郑德1,2,裴毅强2,吕永3,苏庆鹏2,3,王膺博2
- 1.天津大学 内燃机研究所,天津 300072
2.天津大学 内燃机燃烧学国家重点实验室 天津 300072
3.广州汽车集团股份有限公司 汽车工程研究院,广州 511434
Prediction method of engine performance and emission based on PSO-GPR
Jing QIN1,2( ),De ZHENG1,2,Yi-qiang PEI2,Yong LYU3,Qing-peng SU2,3,Ying-bo WANG2
),De ZHENG1,2,Yi-qiang PEI2,Yong LYU3,Qing-peng SU2,3,Ying-bo WANG2
- 1.Internal Combustion Engine Research Institute,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Engines,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
3.GAC Automotive Research & Development Center,Guangzhou 511434,China
摘要:
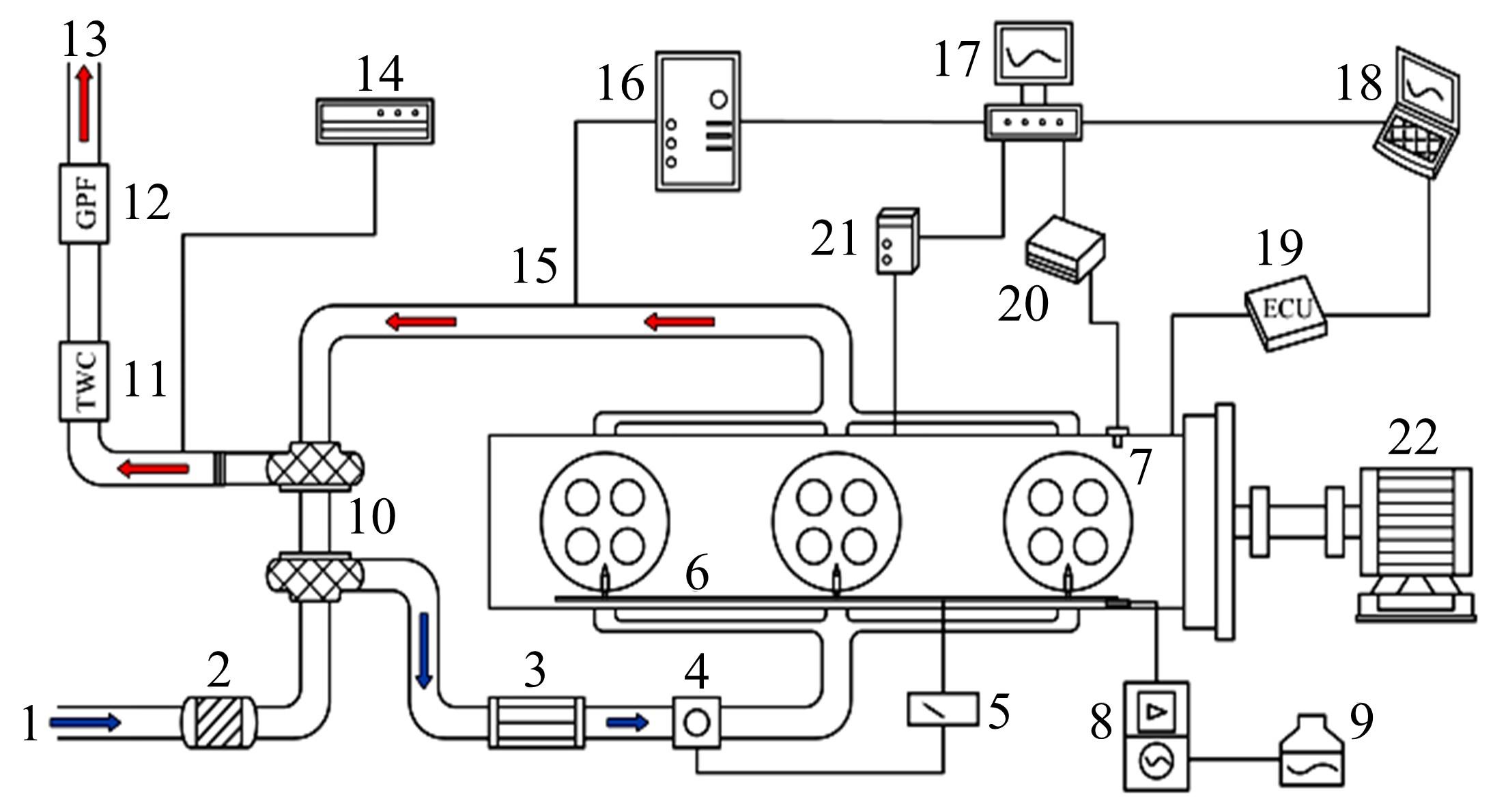
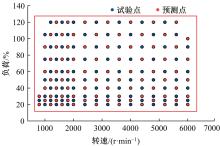
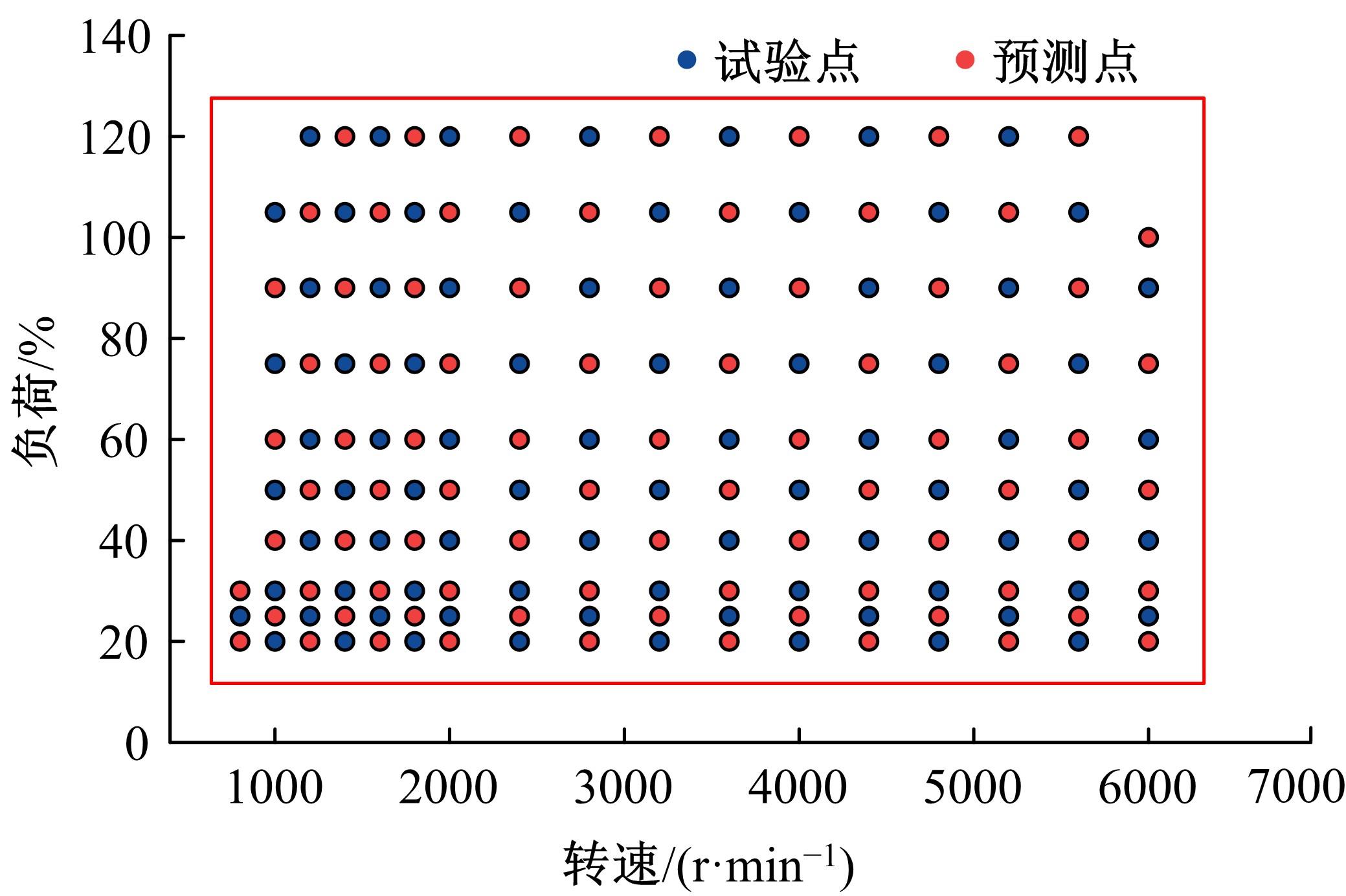
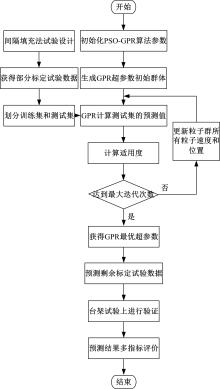
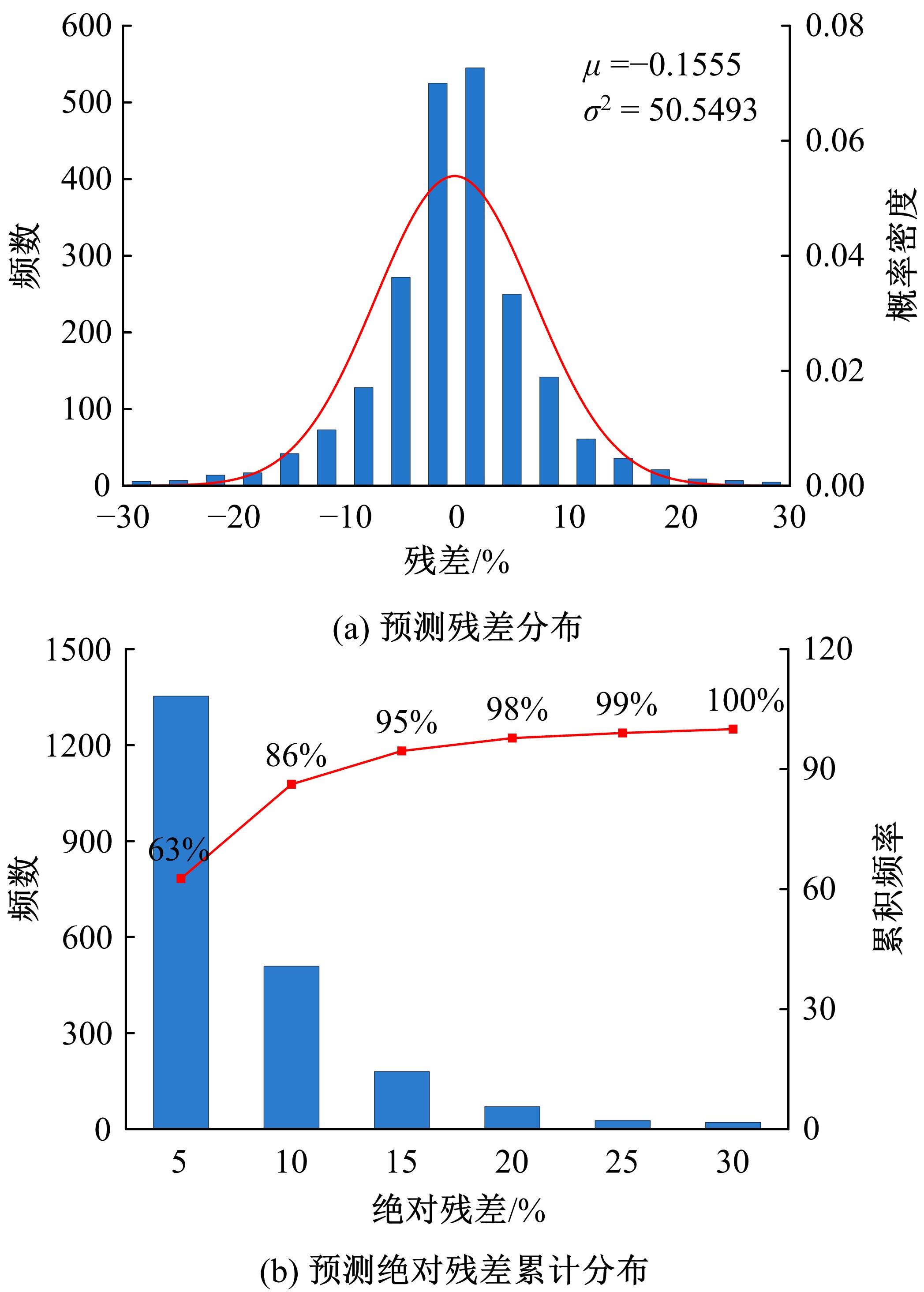
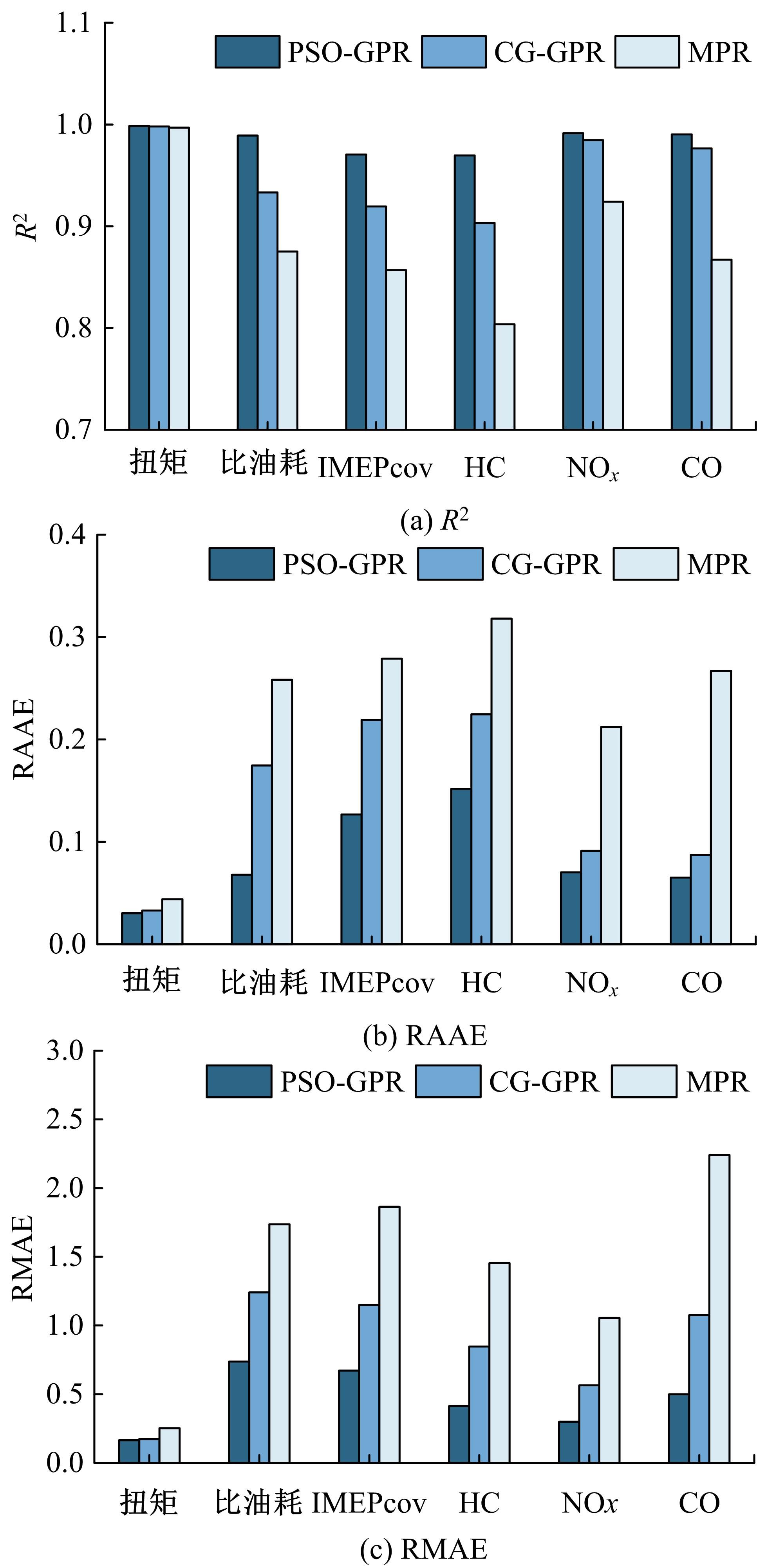
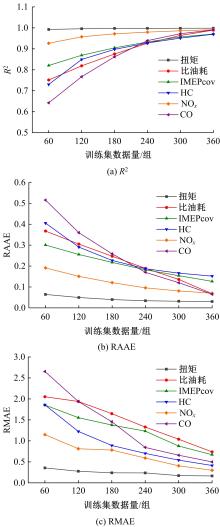
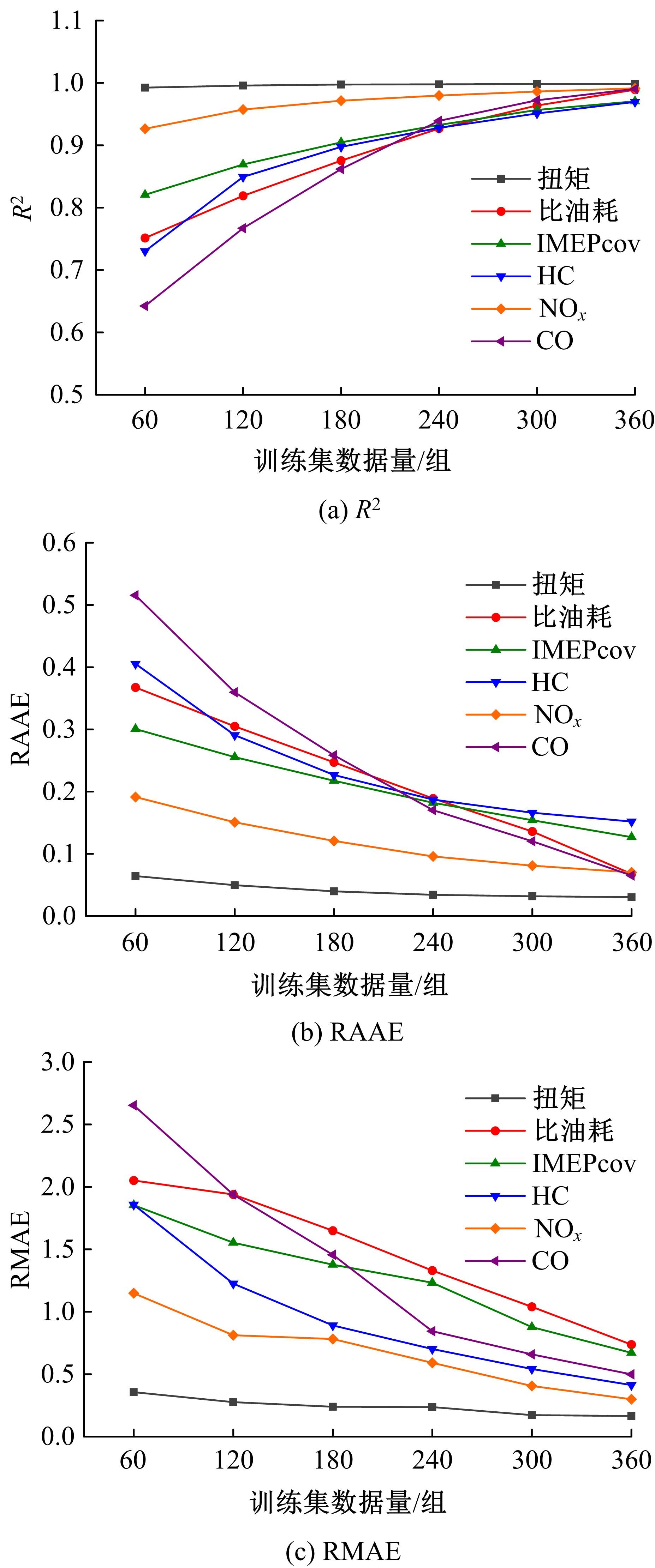
针对发动机标定试验成本大、开发周期长等问题,提出一种基于粒子群算法优化的高斯过程回归(PSO-GPR)模型,用于处理非线性、复杂的发动机性能和排放预测,以提高试验效率。基于一款汽油发动机的点火角标定试验,结合间隔填充试验设计,通过模型使用少量的试验数据预测扭矩、比油耗、IMEPcov及HC、NO x 和CO排放等发动机性能和排放参数,并引入R2、RAAE和RMAE对模型泛化能力进行评估。在此基础上研究了不同训练集数量对模型泛化能力的影响,并基于3种不同的机型对模型的普适性进行了验证。结果表明:PSO-GPR模型可以对发动机性能和排放参数进行预测,且精度优于传统的GPR模型和多元多项式回归(MPR)模型,同时该模型具有普适性,为减少发动机标定工作量提供了参考。
中图分类号:
- TK411
| 1 | 张文. 基于运行工况的发动机基本标定研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学机械与动力工程学院, 2019. |
| Zhang Wen. Research on basic engine calibration based on operating conditions[D]. Shanghai:School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019. | |
| 2 | 李志辉. 基于模型的电控发动机标定技术[J]. 内燃机与配件, 2020(21): 71-72. |
| Li Zhi-hui. Model-based electronic-controlled engine calibration technology [J]. Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2020(21): 71-72. | |
| 3 | 杜乐. 基于模型的直喷汽油机标定技术研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学机械科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Du Le. Research on model-based calibration of GDI engine[D]. Changchun: College of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering,Jilin University, 2013. | |
| 4 | Martínez M, Palacios H, Velázquez C. Modeling engine fuel consumption and NO x with RBF neural network and MOPSO algorithm[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2015, 16(6):1041-1049. |
| 5 | Francesco D N, Giovanni G, Alfredo G, et al. Volumetric efficiency estimation based on neural networks to reduce the experimental effort in engine base calibration[J]. Fuel, 2019, 244: 31-39. |
| 6 | Rask E, Sellnau M. Simulation-based engine calibration: tools, techniques, and applications[J]. SAE Transactions, 2004, 113:821-832. |
| 7 | Gao J, Shen T. Online calibration of spark advance for combustion phase control of gasoline SI engines[C]//Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Dali, China, 2016. |
| 8 | Carvalho R, Machado G B, Colaço M, et al. Estimating gasoline performance in internal combustion engines with simulation metamodels[J]. Fuel, 2017, 193: 230-240. |
| 9 | Zutta E, Acosta D, Andrés D, et al. Development of simulation metamodels to predict the performance and exhaust emission parameters of a spark ignition engine[J]. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM), 2020, 14(1):1-12. |
| 10 | 侯献军,高寒,席光维, 等. 基于BP神经网络的发动机最佳点火提前角MAP优化分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报:交通科学与工程版, 2018, 42(3): 353-356. |
| Hou Xian-jun, Gao Han, Xi Guang-wei, et al. Optimization analysis of engine ignition advance angle MAP based on BP neural network [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Traffic Science and Engineering Edition), 2018, 42(3): 353-356. | |
| 11 | 何志昆, 刘光斌, 赵曦晶, 等. 高斯过程回归方法综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2013(8): 1121-1129. |
| He Zhi-kun, Liu Guang-bin, Zhao Xi-jing, et al. A review of gaussian process regression methods[J]. Control and Decision, 2013, 28(8): 1121-1129. | |
| 12 | 王阳, 唐朝晖, 王紫勋, 等. 选用改进高斯过程回归模型的碳排放短期预测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2018, 54(23): 246-251, 258. |
| Wang Yang, Tang Chao-hui, Wang Zi-xun, et al. Short-term forecasting of carbon emission by using improved gaussian process regression[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(23): 246-251, 258. | |
| 13 | Keprate A, Chandima Ratnayake R M, Sankararaman S. Experimental validation of the adaptive gaussian process regression model used for prediction of stress intensity factor as an alternative to FEM[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 2018, 141(2):1-11. |
| 14 | 钟美, 赵兵涛, 黄朔. 基于高斯过程回归的燃煤烟气汞排放预测[J]. 动力工程学报, 2016, 36(12): 987-992. |
| Zhong Mei, Zhao Bing-tao, Huang Shuo. Prediction of Mercury emission from coal-fired flue gas based on Gaussian process regression[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Engineering, 2016, 36(12): 987-992. | |
| 15 | 黄南天, 齐斌, 刘座铭, 等. 采用面积灰关联决策的高斯过程回归概率短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42(23): 64-71. |
| Huang Nan-tian, Qi Bin, Liu Zuo-ming, et al. Gaussian process regression probability short-term load forecasting based on area grey relational decision[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(23): 64-71. | |
| 16 | 任利强, 张立民, 王海鹏, 等. 基于IPSO-GPR的短期负荷区间预测[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2019, 40(10): 3002-3008. |
| Ren Li-qiang, Zhang Li-min, Wang Hai-peng, et al. Short-term power load interval forecasting based on improved particle swarm optimization and Gaussian process regression[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2019, 40(10): 3002-3008. | |
| 17 | 杜常清, 曹锡良, 何彪, 等. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1556-1564. |
| Du Chang-qing, Cao Xi-liang, He Biao, et al. Parameters optimization of dual clutch transmission based on hybrid particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1556-1564. | |
| 18 | 张静, 刘向东. 混沌粒子群算法优化最小二乘支持向量机的混凝土强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| Zhang Jing, Liu Xiang-dong. Prediction of concrete strength based on least square support vector machine optimized by chaotic particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. | |
| 19 | 杨景明, 马明明, 车海军, 等. 多目标自适应混沌粒子群优化算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(12): 2168-2174. |
| Yang Jing-ming, Ma Ming-ming, Che Hai-jun, et al. Multi-objective adaptive chaotic particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(12): 2168-2174. | |
| 20 | 徐从东, 陈春. 一种自适应动态控制参数的粒子群优化算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2013, 39(10): 203-207. |
| Xu Cong-dong, Chen Chun. A particle swarm optimization algorithm of adaptive dynamic control parameter[J]. Computer Engineering, 2013, 39(10): 203-207. | |
| 21 | 李建平. 仿真元建模中的拟合方法及其应用研究[D]. 长沙:国防科学技术大学计算机学院, 2007. |
| Li Jian-ping. Study on fitting methods of simulation metamodelling and its application[D]. Changsha: College of Computer Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, 2007. | |
| 22 | Lee S, Chang J H. On Using Multivariate Polynomial Regression Model with Spectral Difference for Statistical Model-based Speech Enhancement[M]. London: Elsevier North-Holland, Inc., 2016. |
| 23 | 郭栋, 高松, 王晓原, 等. 轻型车微观排放模型的建立与比较分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 43(10): 4123-4128. |
| Guo Dong, Gao Song, Wang Xiao-yuan, et al. Comparative analysis of light-duty vehicle emission model[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(10): 4123-4128. |
| [1] | 金顺福,郄修尘,武海星,霍占强. 基于新型休眠模式的云虚拟机分簇调度策略及性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 237-246. |
| [2] | 王宏志,姜方达,周明月. 基于遗传粒子群优化算法的认知无线电系统功率分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [3] | 祖象欢,杨传雷,王贺春,王银燕. 船用柴油机废气再循环性能评估及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 805-815. |
| [4] | 杨帅, 冯志炜, 赵治国, 周毅. 不同米勒循环方式对柴油机工作过程影响的一维模拟分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1444-1454. |
| [5] | 刘颖, 张凯, 于向军. 基于代理模型的中空轴式大型静压轴承多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1130-1137. |
| [6] | 黄璇, 郭立红, 李姜, 于洋. 改进粒子群优化BP神经网络的目标威胁估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 996-1002. |
| [7] | 张家旭, 李静. 基于混合优化方法的UniTire轮胎模型参数辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 15-20. |
| [8] | 卢英, 王慧琴, 秦立科. 高大空间建筑火灾精确定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2067-2073. |
| [9] | 邵鹏, 吴志健, 周炫余. 基于反向学习的粒子群算法对线性相位低通FIR滤波器的优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 907-912. |
| [10] | 孔英秀, 赵丁选, 杨彬, 李天宇, 韩京元. 基于PSO-DE和LMI的鲁棒静态输出反馈控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | 李天宇, 赵丁选, 康怀亮, 张志文, 张正飞, 徐春博. 并联式混合动力装载机的参数匹配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 916-921. |
| [12] | 郝亮, 徐涛, 崔健, 吉野辰萌. 参数化诱导槽设计的吸能盒结构抗撞性多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 39-44. |
| [13] | 张立敏, 申桂香, 张英芝, 王晓峰, 郑珊, 孟书. 小样本数控刀架的可靠性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 96-99. |
| [14] | 胡茂凯, 陈西宏, 张群. 基于匹配滤波的正交频分复用信号盲识别[J]. , 2012, (06): 1581-1586. |
| [15] | 徐涛, 郝亮, 徐天爽, 左文杰, 郭桂凯, 程鹏. 轿车侧碰中车门抗撞性的快速优化 [J]. , 2012, (03): 677-682. |
|
||