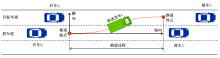
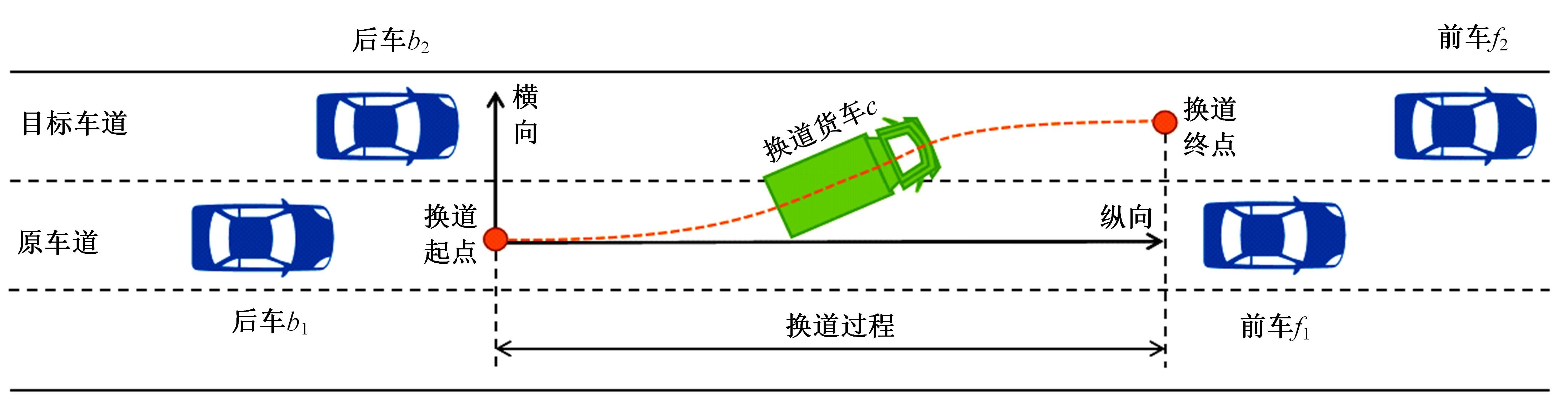
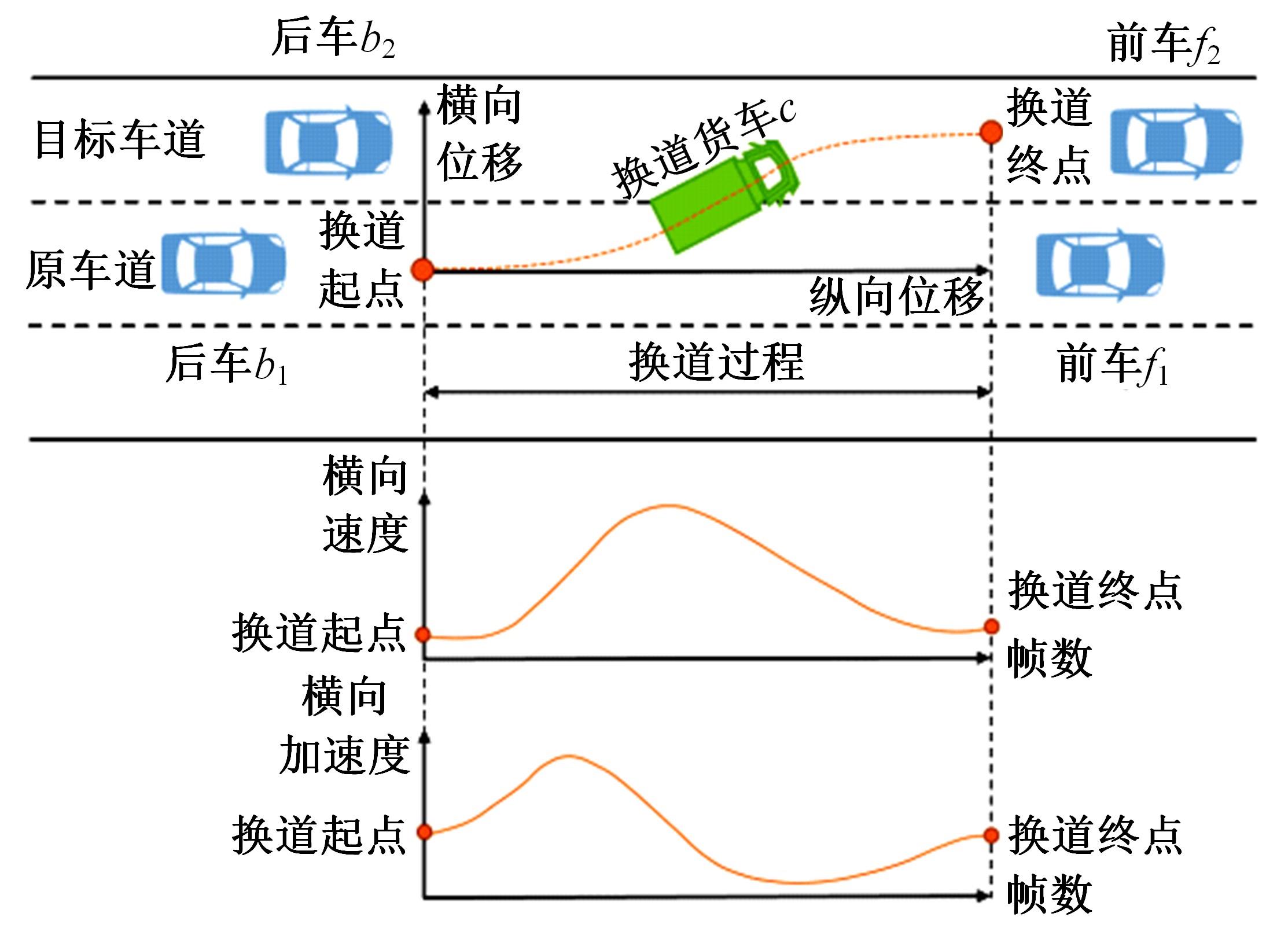
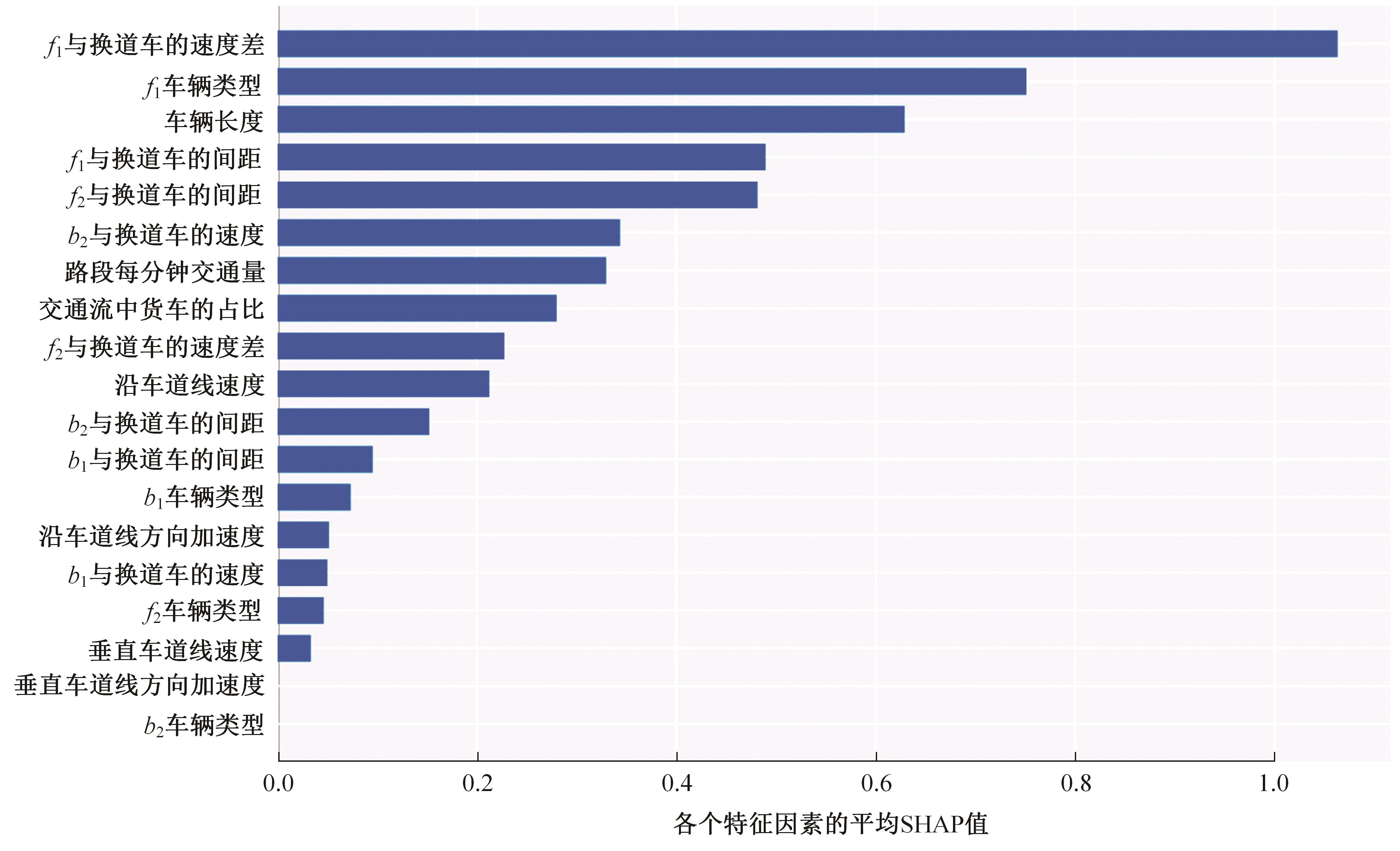
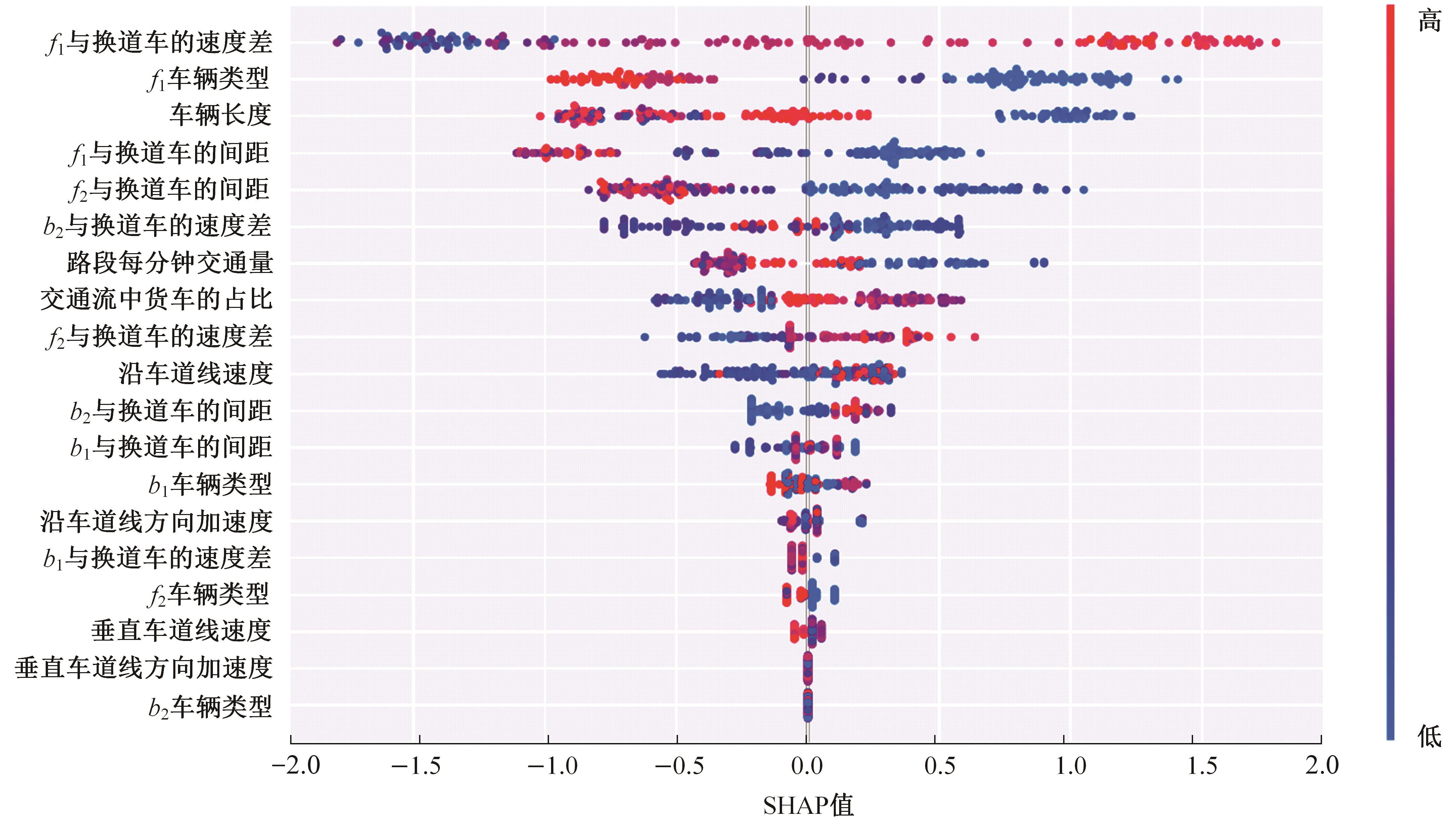
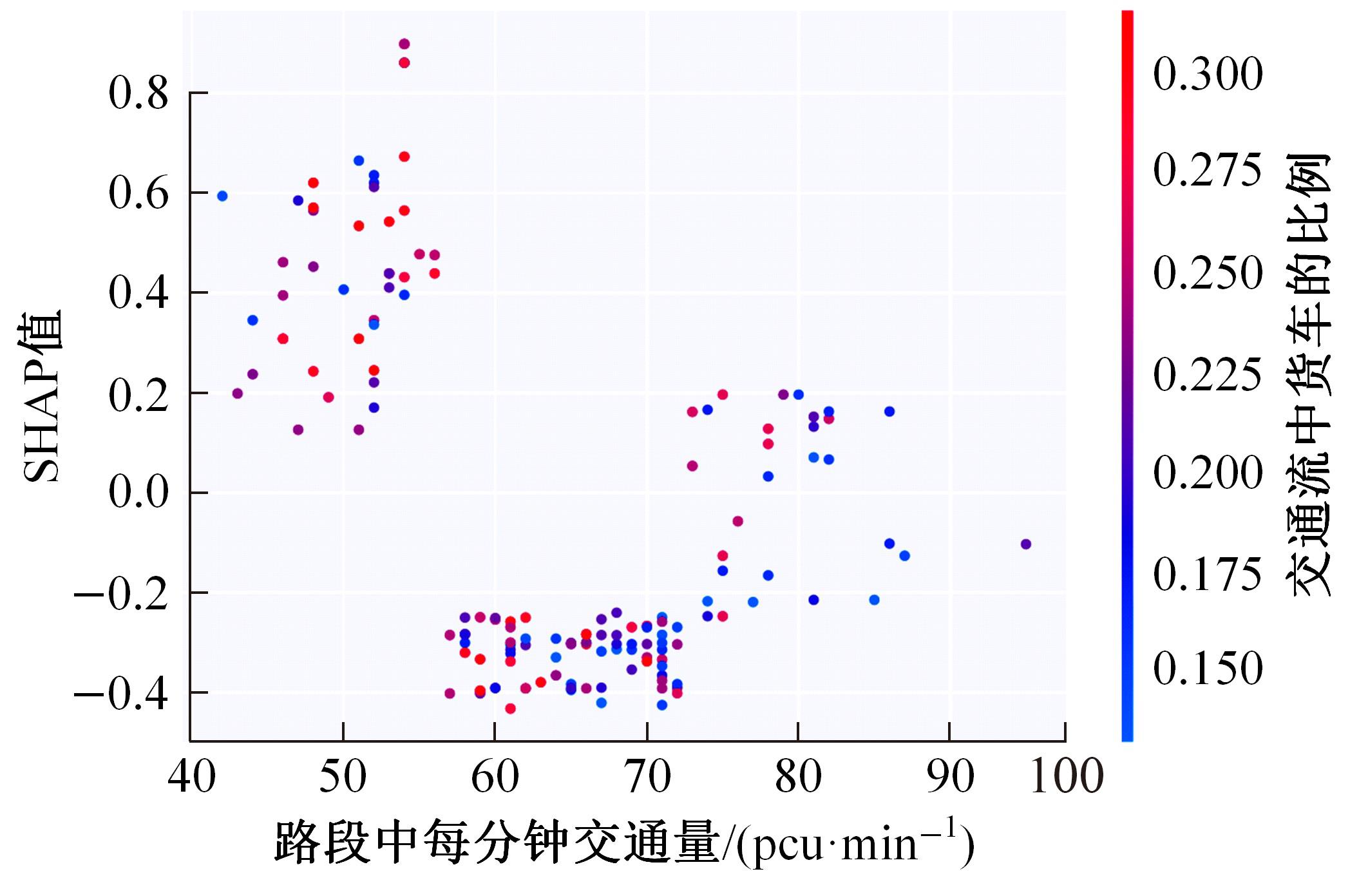
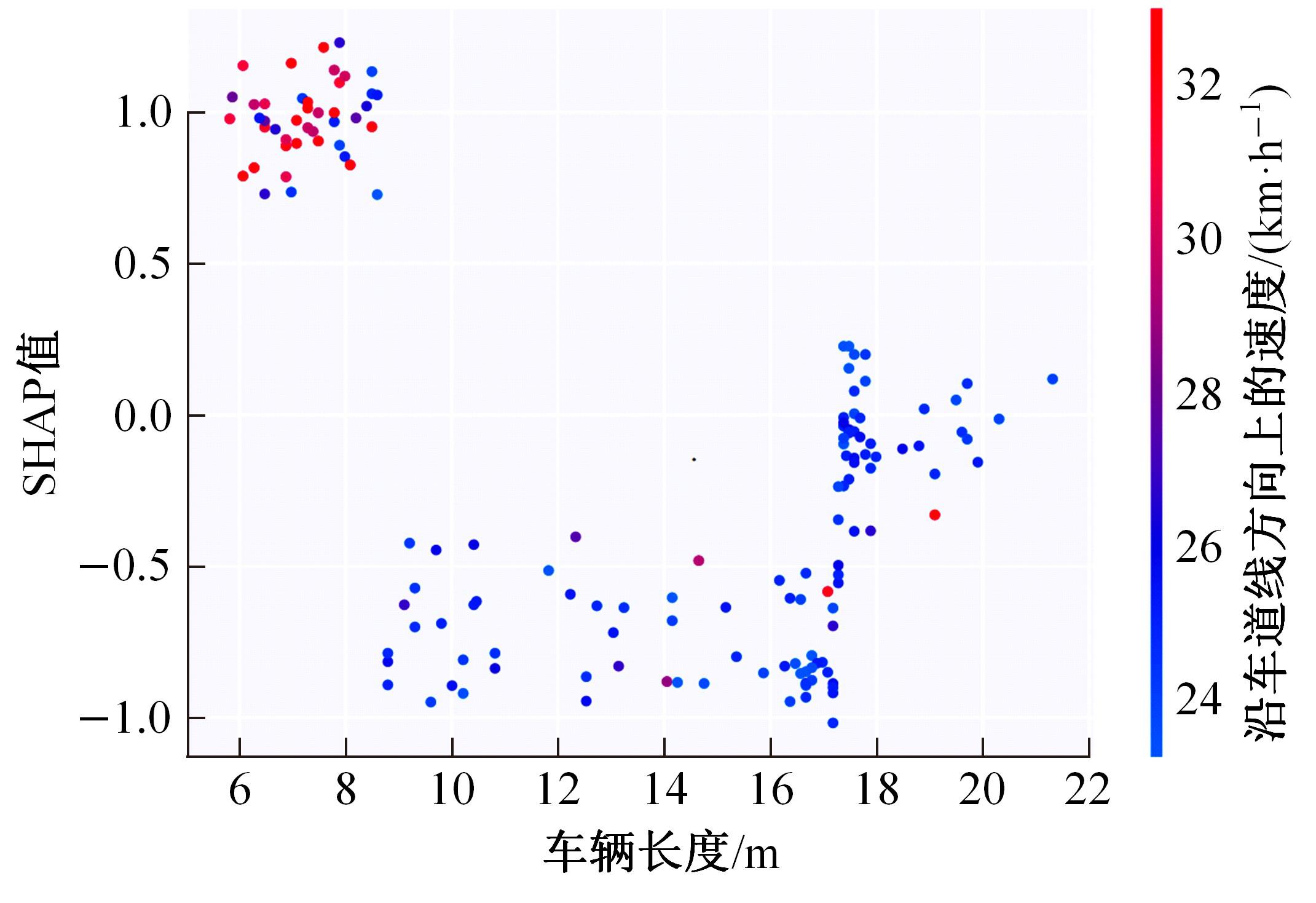
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2827-2836.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221569
Traffic conflict prediction and influencing factors analysis of truck lane change on expressway
Hui-ying WEN( ),Zi-qi HE,Qiu-ling LI,Sheng ZHAO(
),Zi-qi HE,Qiu-ling LI,Sheng ZHAO( )
)
- School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510641,China
CLC Number:
- U491.31
| 1 | 陈永恒, 王新慧, 曲昭伟, 等. 基于移动瓶颈交通波理论的上坡路段货车对客车干扰建模[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2014, 44(5): 1290-1295. |
| Chen Yong-heng, Wang Xin-hui, Qu Zhao-wei, et al. Modeling of buses interference with trucks based on kinematic wave theory of moving bottlenecks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(5): 1290-1295. | |
| 2 | Ahmed M M, Franke R, Ksaibati K, et al. Effects of truck traffic on crash injury severity on rural highways in Wyoming using Bayesian binary logit models[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 117: 106-113. |
| 3 | 胥川, 谢琨, 杨迪,等. 货车重量对事故严重程度的影响研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2019, 17(2): 10-15, 22. |
| Xu Chuan, Xie Kun, Yang Di, et al. Analysis the impact of truck weight levels on injury severity[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2019, 17(2): 10-15, 22. | |
| 4 | Uddin M, Huynh N. Injury severity analysis of truck-involved crashes under different weather conditions[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 141: No.105529. |
| 5 | 张驰, 胡涛, 侯宇迪,等. 基于制动毂温升的连续下坡货车事故风险评价模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 48(11): 19-29. |
| Zhang Chi, Hu Tao, Hou Yu-di, et al. Crash risk evaluation model based on brake heating for trucks under continuous downhill road conditions[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 19-29. | |
| 6 | Hyun K K, Jeong K, Tok A, et al. Assessing crash risk considering vehicle interactions with trucks using point detector data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 130: 75-83. |
| 7 | 戢晓峰, 耿昭师. 山区双车道公路货车碰撞预测的双变量冲突极值模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(2): 230-238. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Geng Zhao-shi. Bivariate traffic conflict extreme value model of truck collision prediction on two-lane mountain highway[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(2): 230-238. | |
| 8 | Doran J W, Linn D M. Proceedings of the first workshop on traffic conflicts[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 1979, 11(4): 317-318. |
| 9 | 朱顺应, 蒋若曦, 王红, 等. 机动车交通冲突技术研究综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(2): 15-33. |
| Zhu Shun-ying, Jiang Ruo-xi, Wang Hong, et al. Review of research on traffic conflict techniques[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(2): 15-33. | |
| 10 | Wu J, Wen H, Qi W. A new method of temporal and spatial risk estimation for lane change considering conventional recognition defects[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 148: No.105796. |
| 11 | Oh C, Park S, Ritchie S G. A method for identifying rear-end collision risks using inductive loop detectors[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2006, 38(2): 295-301. |
| 12 | Son H D, Kweon Y J, Park B B. Development of crash prediction models with individual vehicular data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2011, 19(6): 1353-1363. |
| 13 | Wu Y, Abdel-Aty M, Cai Q, et al. Developing an algorithm to assess the rear-end collision risk under fog conditions using real-time data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 87: 11-25. |
| 14 | Chen Q, Gu R, Huang H, et al. Using vehicular trajectory data to explore risky factors and unobserved heterogeneity during lane-changing[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 151: No.105871. |
| 15 | Park H, Oh C, Moon J, et al. Development of a lane change risk index using vehicle trajectory data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 110: 1-8. |
| 16 | ISO. 2008-17387. Intelligent transport systems-lane change decision aid systems (LC )-Performance requirements and test procedures[S]. |
| 17 | Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 785-794. |
| 18 | Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. |
| 19 | Friedman J H. Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine[J]. Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(5): 1189-1232. |
| 20 | Krajewski R, Bock J, Kloeker L, et al. The highD dataset: a drone dataset of naturalistic vehicle trajectories on German highways for validation of highly automated driving systems[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC),Maui, USA, 2018: 2118-2125. |
| 21 | , 公路路线设计规范 [S]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2017. |
| 22 | . 收费公路车辆通行费车型分类 [S]. |
| 23 | Lundberg S M, Erion G G, Lee S I. Consistent individualized feature attribution for tree ensembles[J/OL].[2020-05-18]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2018. |
| [1] | Rong-gui ZHOU,Pei GAO,Yu-xuan LI,Jian ZHOU. Abnormal driving behavior thresholds of highway minibuses based on trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2581-2587. |
| [2] | Yun PU,Yin XU,Hai-xu LIU,Yi-fan TAN. An improved car⁃following model for connected and automated vehicles considering impact of multiple vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1285-1292. |
| [3] | Qing-lu MA,Hao YAN,Zhen-yu NIE,Yang-mei LI. Cooperative control method for intelligent networked vehicles in ramp confluence area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1332-1346. |
| [4] | Qian CAO,Zhi-hui LI,Peng-fei TAO,Hai-tao LI,Yong-jian MA. Deployment of heterogeneous sensors for traffic accident detection and prevention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 969-978. |
| [5] | Xiao-chi MA,Jian LU. Real⁃time crash prediction of elevated expressway based on gene expression programming algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 719-726. |
| [6] | Xin ZHANG,Qi-zhou HU,Jun HE,Xiao-yu WU. Traffic condition diagnosis of confluence areas considering traffic infarction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 478-484. |
| [7] | Wei-hua ZHANG,Jia-ming LIU,Li-peng XIE,Heng DING. Lane⁃changing model of autonomous vehicle in weaving area of expressway in intelligent and connected mixed environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [8] | Yi-yong PAN,Jing-ting WU,Xuan-ye Miao. Temporal instability analysis of factors affecting injury severities of elderly drivers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. |
| [9] | Xiao-jing DU,Rong-han YAO. Evolutionary game mechanism of mandatory lane changing for exiting for intelligent connected bus [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 124-135. |
| [10] | Hai-long GAO,Yi-bo XU,Kun LIU,Chun-yang LI,Xiao-yu LU. High-speed highway road network short-term traffic flow parameters based on multi-source data fusion prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 155-161. |
| [11] | Hao YUE,Qi-yue ZHANG,Zi-yu YANG,Meng-jie REN,Xu ZHANG. Iterative weighted algorithms of static congestion traffic assignment considering spatial queuing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 136-145. |
| [12] | Jian ZHANG,Qing-yang LI,Dan LI,Xia JIANG,Yan-hong LEI,Ya-ping JI. Merging guidance of exclusive lanes for connected and autonomous vehicles based on deep reinforcement learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [13] | Zhuang-lin MA,Shan-shan CUI,Da-wei HU,Jin WANG. Travel mode choice of traditional car travelers after implementation of driving restriction policy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1981-1993. |
| [14] | Ya-li ZHANG,Rui FU,Wei YUAN,Ying-shi GUO. Classification and recognition model of entering and leaving stops' driving style considering energy consumption [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [15] | Chao-ying YIN,Ying LU,Chun-fu SHAO,Jian-xiao MA,De-jie XU. Impacts of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial autocorrelation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
|
||