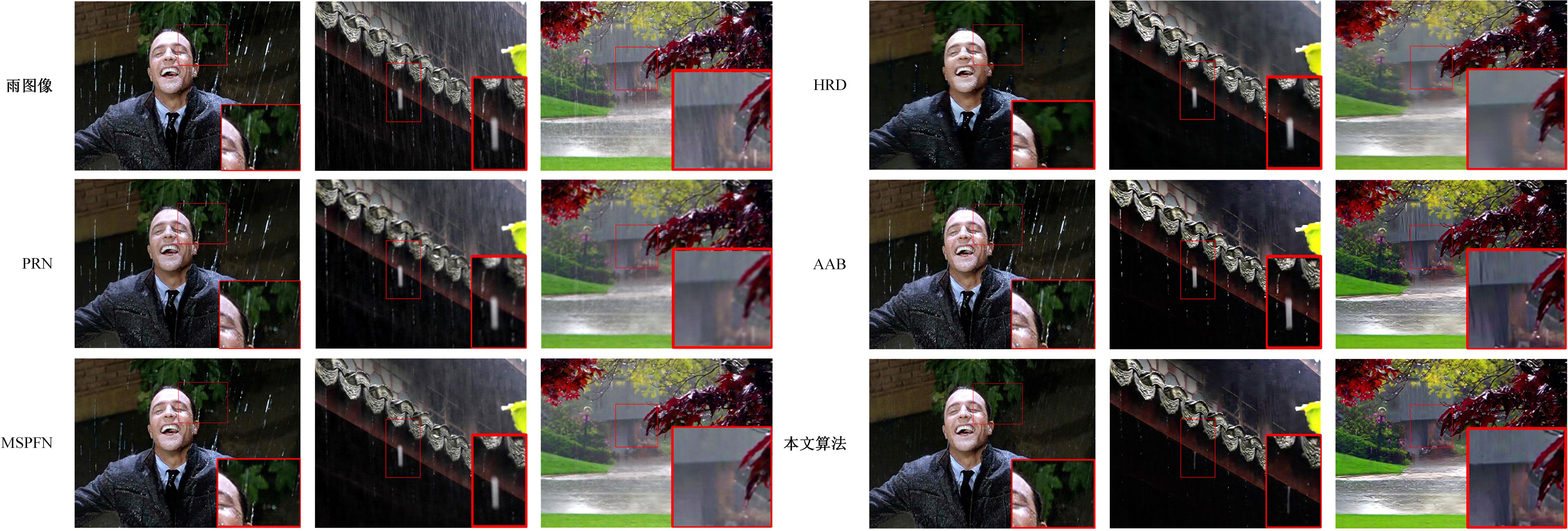
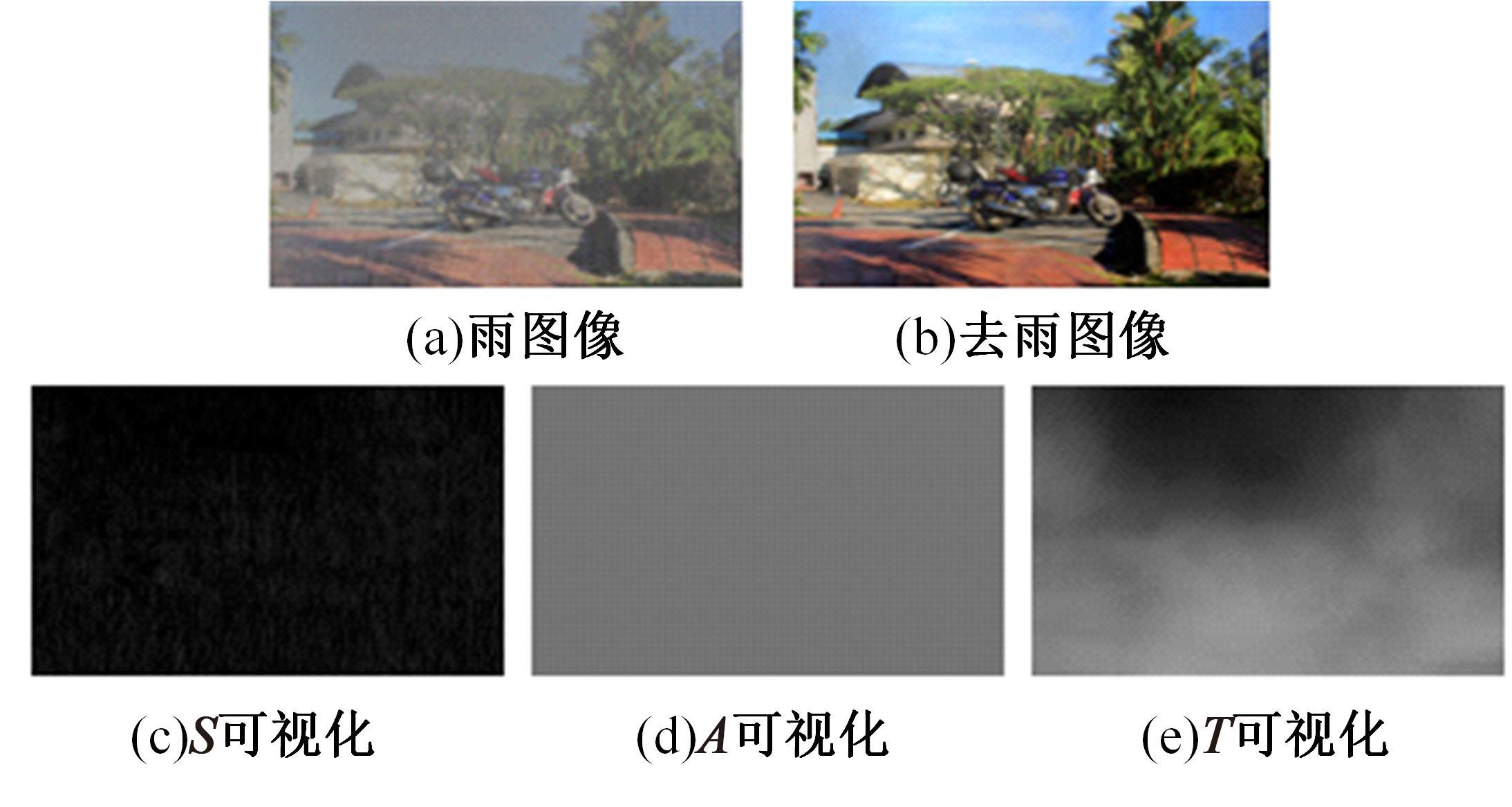
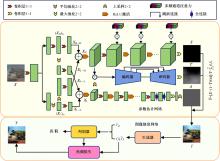
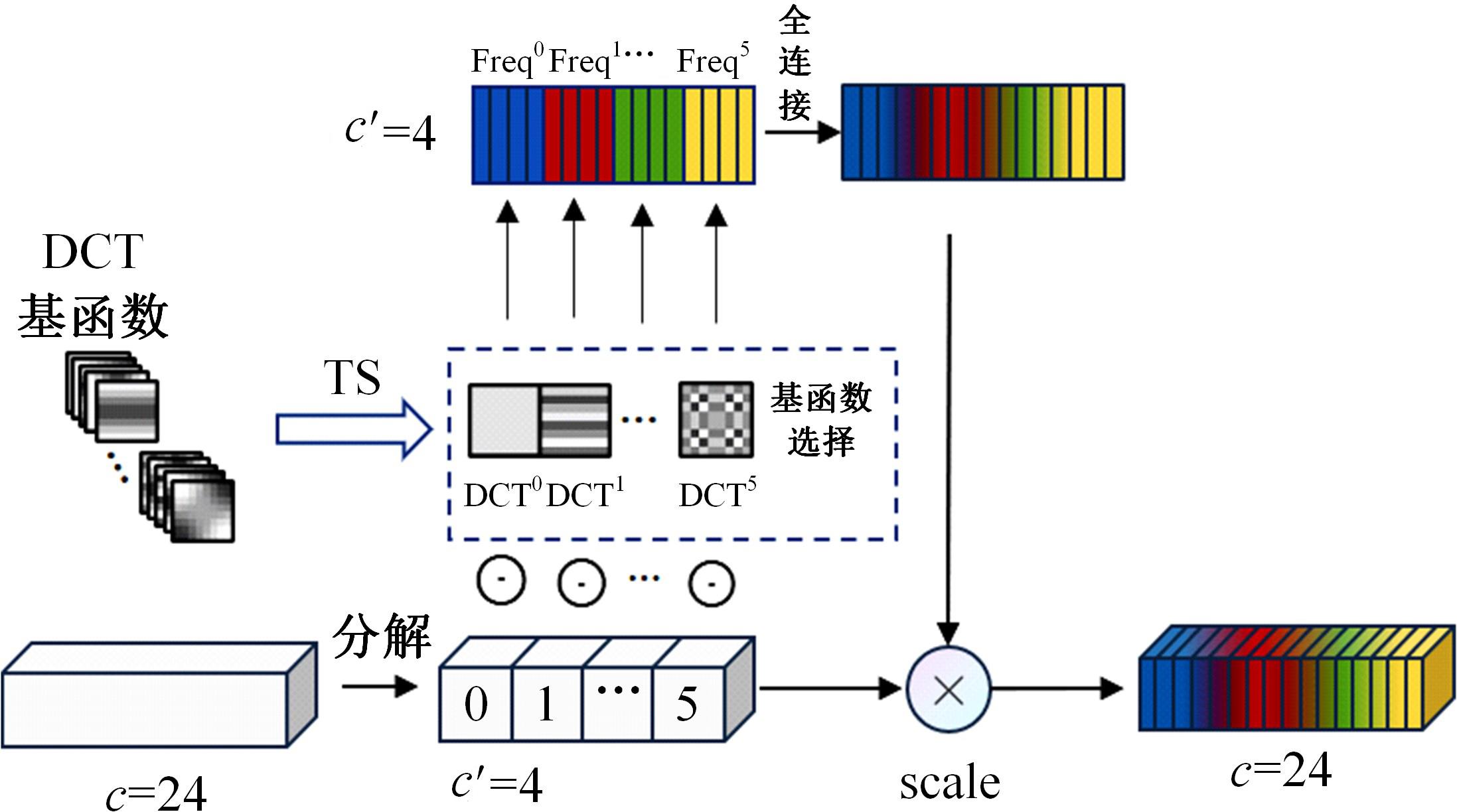
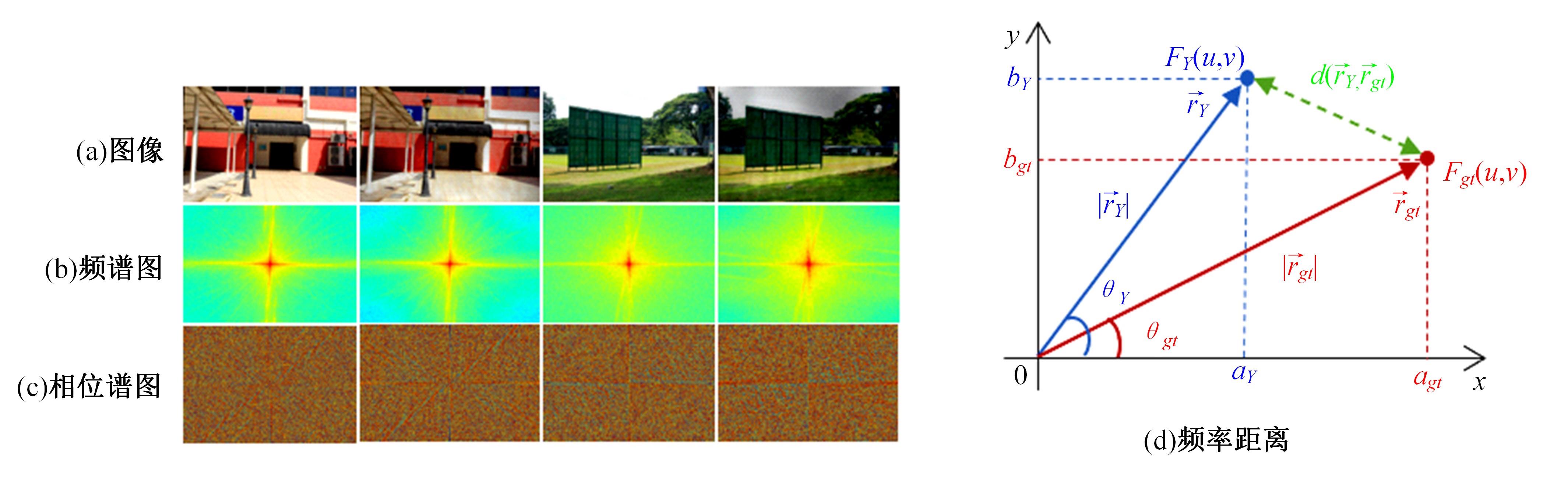
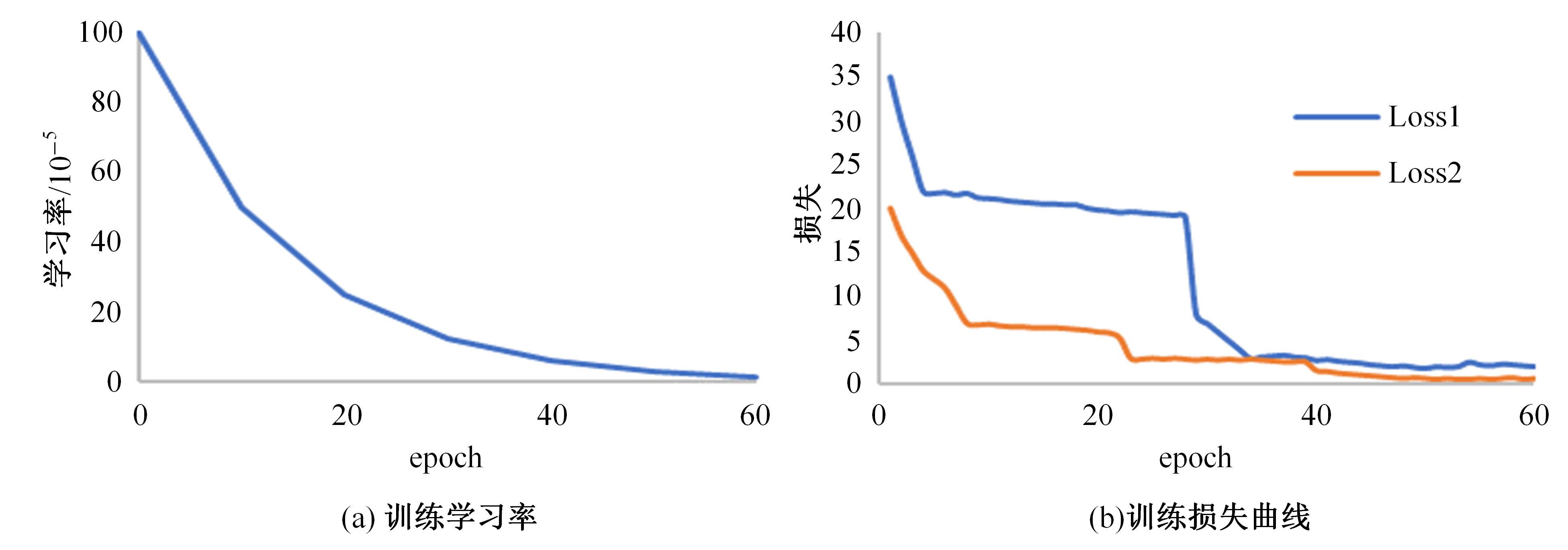
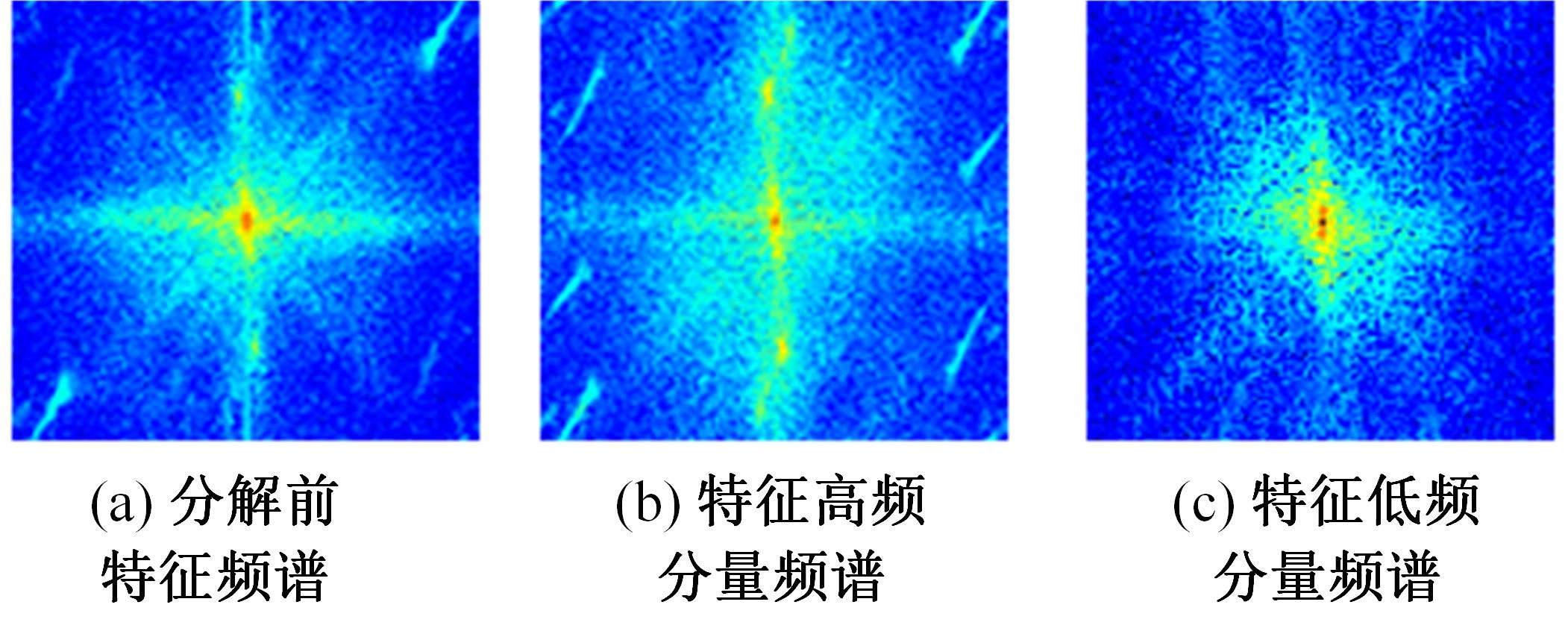
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2952-2962.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221571
Image de-rain based on deep frequency feature attention mechanism
Qing YANG1,2( ),Ming YU3(
),Ming YU3( ),Gang YAN3
),Gang YAN3
- 1.College of Electronic Information Engineering,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
2.Shijiazhuang Campus of Army Engineering University,Shijiazhuang 050003,China
3.School of Artificial Intelligence,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
CLC Number:
- TN911.73
| 1 | Garg K, Nayar S K. When does a camera see rain?[C]//Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,New York, USA, 2005: 1067-1074. |
| 2 | Chen J, Tan C H, Hou J, et al. Robust video content alignment and compensation for clear vision through the rain[J/OL]. [2020-04-26]., 2018 |
| 3 | Fu X, Huang J, Ding X, et al. Clearing the skies: a deep network architecture for single-image rain removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2944-2956. |
| 4 | Fu X, Huang J, Zeng D, et al. Removing rain from single images via a deep detail network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3855-3863. |
| 5 | Ren D, Zuo W, Hu Q, et al. Progressive image deraining networks: a better and simpler baseline[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3937-3946. |
| 6 | Jiang K, Wang Z, Yi P, et al. Multi-scale progressive fusion network for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8346-8355. |
| 7 | Chen C, Li H. Robust representation learning with feedback for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2021: 7742-7751. |
| 8 | Rai S N, Saluja R, Arora C, et al. FLUID: Few-shot self-supervised image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Hawaii,USA, 2022: 3077-3086. |
| 9 | Yang H, Zhou D, Cao J, et al. DPNet: detail-preserving image deraining via learning frequency domain knowledge[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022: No.103740. |
| 10 | Yang W, Tan R T, Feng J, et al. Deep joint rain detection and removal from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1357-1366. |
| 11 | Li R, Cheong L F, Tan R T. Heavy rain image restoration: integrating physics model and conditional adversarial learning[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1633-1642. |
| 12 | Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, et al. Multi-stage progressive image restoration[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2021: 14821-14831. |
| 13 | Liang J, Cao J, Sun G, et al. Swinir: image restoration using swin transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 1833-1844. |
| 14 | Chen W T, Huang Z K, Tsai C C, et al. Learning multiple adverse weather removal via two-stage knowledge learning and multi-contrastive regularization: toward a unified model[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 17653-17662. |
| 15 | Tancik M, Srinivasan P, Mildenhall B, et al. Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 7537-7547. |
| 16 | Chen Y, Fan H, Xu B, et al. Drop an octave: reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 3435-3444. |
| 17 | Li X, Wu J, Lin Z, et al. Recurrent squeeze-and-excitation context aggregation net for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 254-269. |
| 18 | Qin Z, Zhang P, Wu F, et al. Fcanet: frequency channel attention networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 783-792. |
| 19 | Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1125-1134. |
| 20 | Jiang L, Dai B, Wu W, et al. Focal frequency loss for image reconstruction and synthesis[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 13919-13929. |
| 21 | Li S, Ren W, Wang F, et al. A comprehensive benchmark analysis of single image deraining: current challenges and future perspectives[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1301-1322. |
| 22 | Saad M A, Bovik A C, Charrier C. Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(8): 3339-3352. |
| 23 | Liu L, Liu B, Huang H, et al. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2014, 29(8): 856-863. |
| [1] | Dong-yuan GE,Wen-jiang XIANG,Jian LI,En-chen LIU,Xi-fan YAO. Automatic positioning method of electric vehicle charging based on machine vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3465-3471. |
| [2] | Chun-yan ZENG,Kang YAN,Zhi-feng WANG,Zheng-hui WANG. Multi-scale generative adversarial network for image compressed sensing and reconstruction algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2923-2931. |
| [3] | Chun-ping HOU,Chun-yue ZHAO,Zhi-peng WANG,Hai-rui TIAN. Video anomaly detection algorithm based on effective anomaly sample construction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1823-1829. |
| [4] | Hou⁃jie LI,Fa⁃sheng WANG,Jian⁃jun HE,Yu ZHOU,Wei LI,Yu⁃xuan DOU. Pseudo sample regularization Faster R⁃CNN for traffic sign detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1251-1260. |
| [5] | Fu LIU, Mei-jing QUAN, Ke WANG, Yun LIU, Bing KANG, Zhi-wu HAN, Tao HOU. Indoor positioning method based on location fingerprinting of imitating mechanism of scorpion vibration source [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2076-2082. |
| [6] | DING Ning, CHANG Yu-chun, ZHAO Jian-bo, WANG Chao, YANG Xiao-tian. High-speed CMOS image sensor data acquisition system based on USB 3.0 [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1298-1304. |
| [7] | LIU Dong-liang, WANG Qiu-shuang. Instantaneous velocity extraction method on NGSLM data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 330-335. |
| [8] | WU Wei, WANG Shi-gang, ZHAO Yan, WEI Jian, ZHONG Cheng. Hexagonal elemental image array generation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 290-294. |
| [9] | WANG Fang-shi, WANG Jian, LI Bing, WANG Bo. Deep attribute learning based traffic sign detection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 319-329. |
| [10] | WU Wei, WANG Shi-gang, WANG Hong-zhi, ZHAO Yan, ZHONG Cheng, WEI Jian. Elemental image generation based on Maya [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1314-1320. |
| [11] | WANG Pin, HE Xuan, LYU Yang, LI Yong-ming, QIU Ming-guo, LIU Shu-jun. Automatic segmentation of articular cartilages using multi-feature SVM and elastic region growing [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1688-1696. |
| [12] | LU Yan-fei, ZHANG Tao, ZHENG Jian, LI Ming, ZHANG Cheng. No-reference blurring image quality assessment based on local standard deviation and saliency map [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1337-1343. |
| [13] | ZHENG Xin, PENG Zhen-ming, XING Yan. Novel method of evaluating image segmentation algorithms based on activity degree [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 311-317. |
| [14] | LI Yi-bing, YANG Peng, YE Fang, LIU Dan-dan. Texture image segmentation using hierarchical MRF model based on the interactive potential function and mean-field parameter estimation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2075-2079. |
| [15] | ZHAO Dan-feng, WANG Bo, YANG Da-wei. Content-aware image resizing based on random permutation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1324-1328. |
|
||