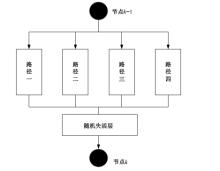
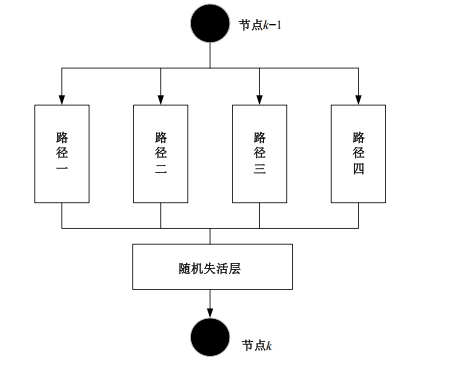
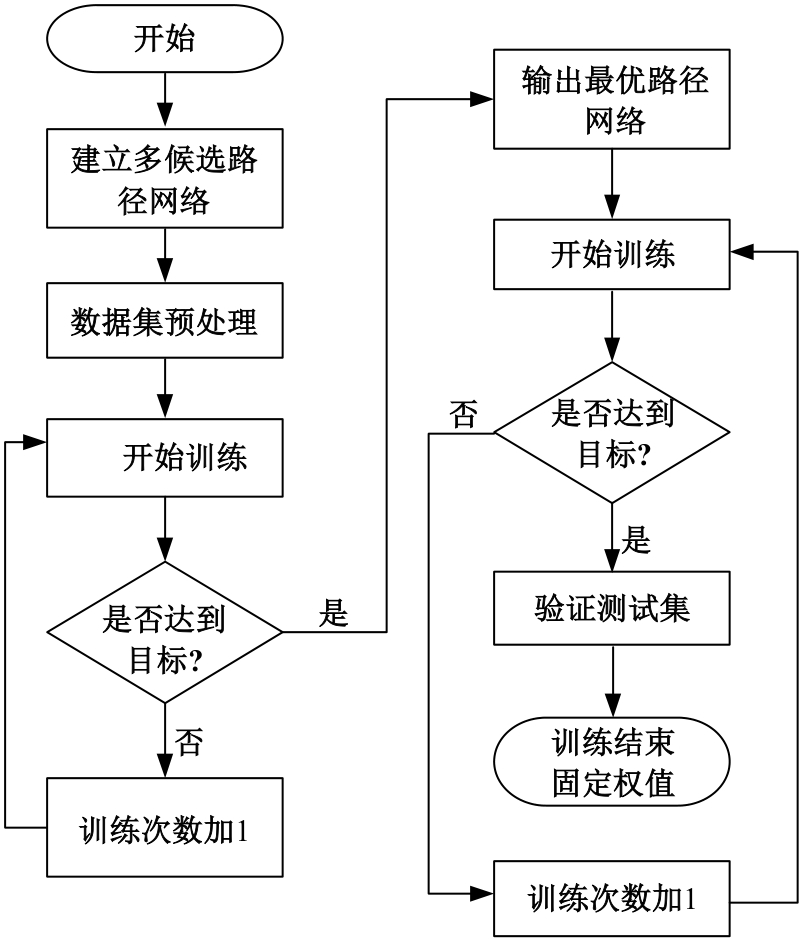
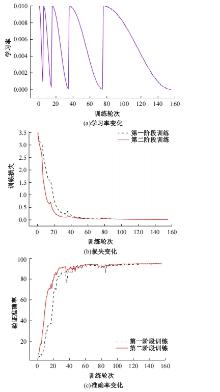
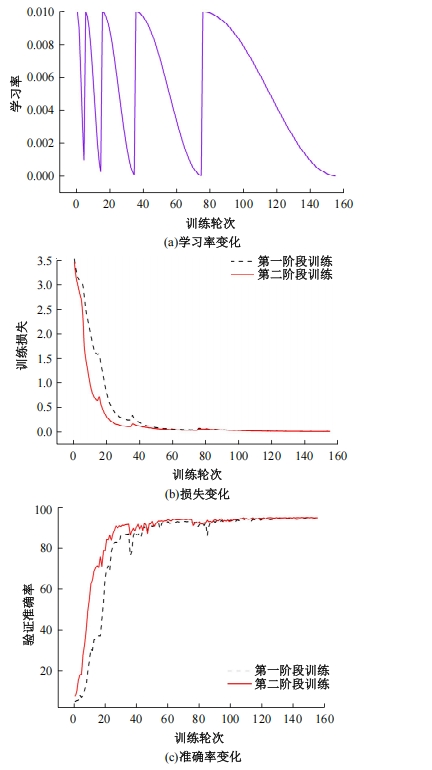
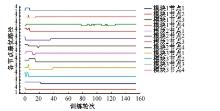
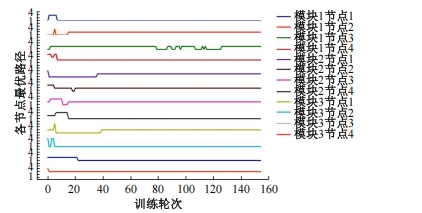
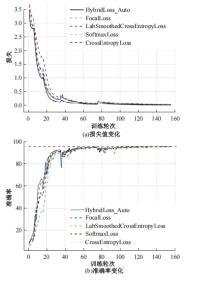
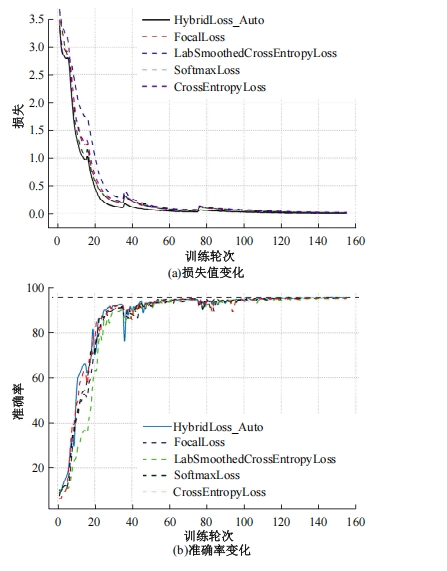
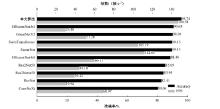
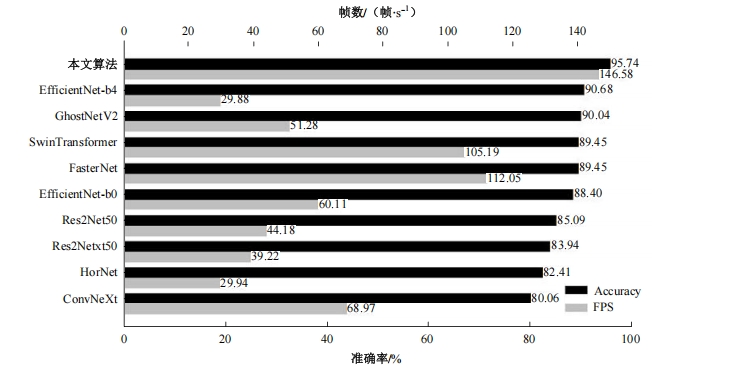
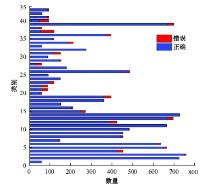
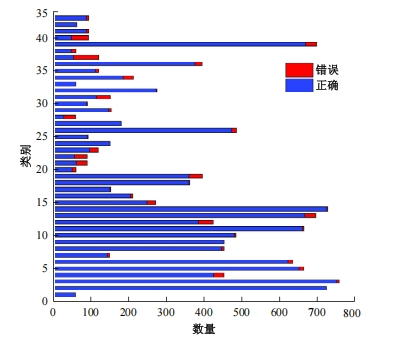
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1705-1713.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230812
Previous Articles Next Articles
Self-selected architecture network for traffic sign classification
Bin WEN1,2( ),Yi-fu DING1,Chao YANG1(
),Yi-fu DING1,Chao YANG1( ),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
- 1.College of Electrical Engineering and New Energy,China Three Gorges University,Yichang 443002,China
2.Hubei Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Power Transmission Line,Yichang 443002,China
3.School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 611731,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Babi D, Babi D, Fioli M, et al.Analysis of market-ready traffic sign recognition systems in cars: a test field study[J].Energies, 2021, 14: 14123697. |
| [2] | 冯润泽, 江昆, 于伟光, 等. 基于两阶段分类算法的中国交通标志牌识别 [J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(3): 434-441. |
| Feng Run-ze, Jiang Kun, Yu Wei-guang, et al. Chinese traffic sign recognition based on two-stage classification algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 434-441. | |
| [3] | Wang M, Liu R, Yang J, et al.Traffic sign three-dimensional reconstruction based on point clouds and panoramic images[J].Photogrammetric Record, 2022, 37(177): 87-110. |
| [4] | Shen L, You L, Peng B, et al.Group multi-scale attention pyramid network for traffic sign detection[J].Neuro Computing, 2021, 452(6): 1-14. |
| [5] | Liu Y, Peng J, Xue J H, et al. TSingNet: scale-aware and context-rich feature learning for traffic sign detection and recognition in the wild[J].Neurocomputing, 2021, 447(4): 10-22. |
| [6] | Vashisht M, Kumar B. Effective implementation of machine learning algorithms using 3D colour texture feature for traffic sign detection for smart cities[J]. Expert Systems, 2021, 39(5): e12781. |
| [7] | Wan H, Gao L, Su M, et al. A novel neural network model for traffic sign detection and recognition under extreme conditions[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 7: 9984787. |
| [8] | Yu L, Xia X, Zhou K. Traffic sign detection based on visual co-saliency in complex scenes [J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(2): 764-790. |
| [9] | Coţovanu D, Zet C, Foşalău C, et al. Detection of traffic signs based on support vector machine classification using HOG features[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical And Power Engineering, Iasi, Romania, 2018: 8559784. |
| [10] | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. |
| [11] | Simonyan K, Zisserman A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition [J/OL].(2015-04-10)[2023-07-30]. |
| [12] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 7780459. |
| [13] | Chollet F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 8099678. |
| [14] | Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J/OL].(2016-04-30)[2023-07-30]. |
| [15] | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 8237586. |
| [16] | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| [17] | Real E, Liang C, So D R, et al. AutoML-Zero: evolving machine learning algorithms from scratch[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 8007-8019. |
| [18] | Liu H, Simonyan K, Yang Y. DARTS: differentiable architecture search[J/OL].(2019-04-23)[2023-07-30]. |
| [19] | Gao S H, Cheng M M, Zhao K, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652-662. |
| [20] | Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C Y, et al. A convnet for the 2020s[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 9879745. |
| [21] | Pham H, Guan M Y, Zoph B, et al.Efficient neural architecture search via parameter sharing [J/OL].(2018-02-12)[2023-07-30]. |
| [22] | Tang Y, Han K, Guo J, et al. GhostNetV2: enhance cheap operation with long-range attention [J/OL].(2022-11-23)[2023-07-30]. |
| [23] | Rao Y, Zhao W, Tang Y, et al.HorNet: efficient high-order spatial interactions with recursive gated convolutions [J/OL].(2022-10-11)[2023-07-30]. |
| [24] | Chen J, Kao S H, He H, et al. Run, don't walk: chasing higher flops for faster neural networks [J/OL].(2023-05-21)[2023-07-30]. |
| [1] | Jian LI,Huan LIU,Yan-qiu LI,Hai-rui WANG,Lu GUAN,Chang-yi LIAO. Image recognition research on optimizing ResNet-18 model based on THGS algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1629-1637. |
| [2] | Ru-bo ZHANG,Shi-qi CHANG,Tian-yi ZHANG. Review on image information hiding methods based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1497-1515. |
| [3] | Zhen-jiang LI,Li WAN,Shi-rui ZHOU,Chu-qing TAO,Wei WEI. Dynamic estimation of operational risk of tunnel traffic flow based on spatial-temporal Transformer network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1336-1345. |
| [4] | Meng-xue ZHAO,Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Quan-le LIU. A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [5] | Yuan-ning LIU,Zi-nan ZANG,Hao ZHANG,Zhen LIU. Deep learning-based method for ribonucleic acid secondary structure prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [6] | Hui-zhi XU,Shi-sen JIANG,Xiu-qing WANG,Shuang CHEN. Vehicle target detection and ranging in vehicle image based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [7] | Lu Li,Jun-qi Song,Ming Zhu,He-qun Tan,Yu-fan Zhou,Chao-qi Sun,Cheng-yu Zhou. Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [8] | Lei ZHANG,Jing JIAO,Bo-xin LI,Yan-jie ZHOU. Large capacity semi structured data extraction algorithm combining machine learning and deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [9] | Bai-you QIAO,Tong WU,Lu YANG,You-wen JIANG. A text sentiment analysis method based on BiGRU and capsule network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [10] | Xin-gang GUO,Ying-chen HE,Chao CHENG. Noise-resistant multistep image super resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [11] | Li-ping ZHANG,Bin-yu LIU,Song LI,Zhong-xiao HAO. Trajectory k nearest neighbor query method based on sparse multi-head attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [12] | Ming-hui SUN,Hao XUE,Yu-bo JIN,Wei-dong QU,Gui-he QIN. Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [13] | Yu-kai LU,Shuai-ke YUAN,Shu-sheng XIONG,Shao-peng ZHU,Ning ZHANG. High precision detection system for automotive paint defects [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [14] | Xiong-fei LI,Zi-xuan SONG,Rui ZHU,Xiao-li ZHANG. Remote sensing change detection model based on multi⁃scale fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [15] | Guo-jun YANG,Ya-hui QI,Xiu-ming SHI. Review of bridge crack detection based on digital image technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
|