Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3309-3317.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240916
Previous Articles Next Articles
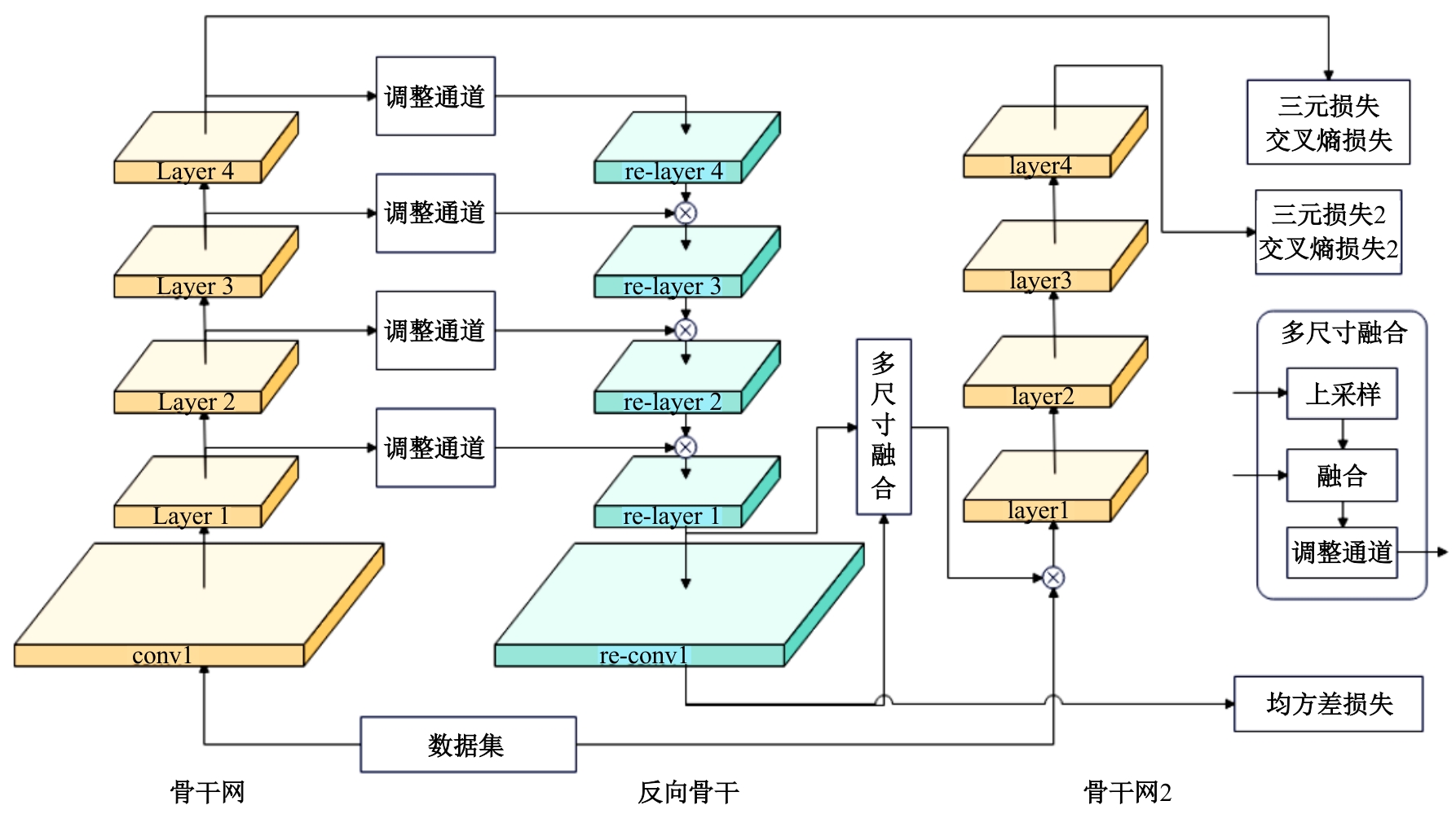
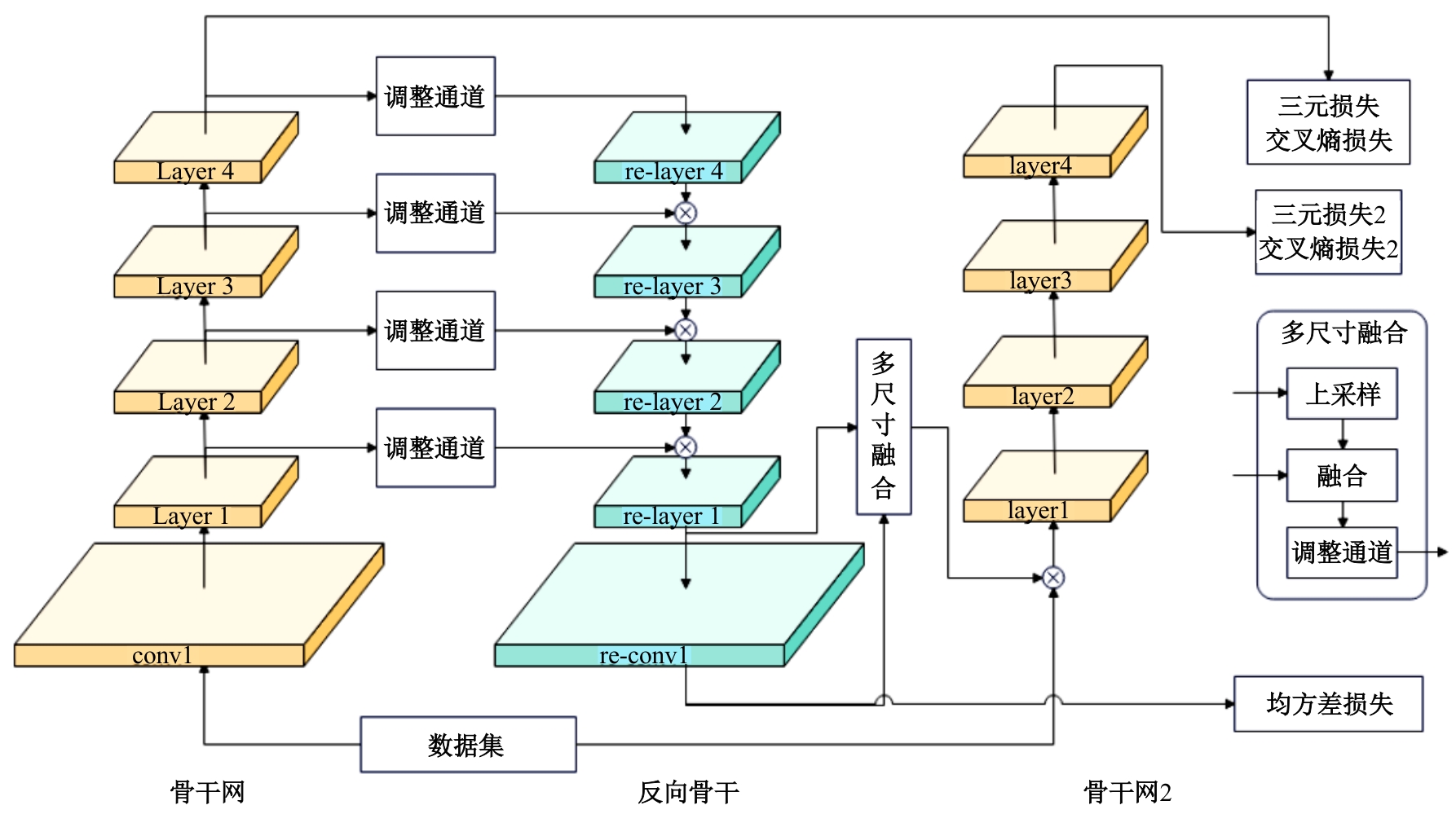
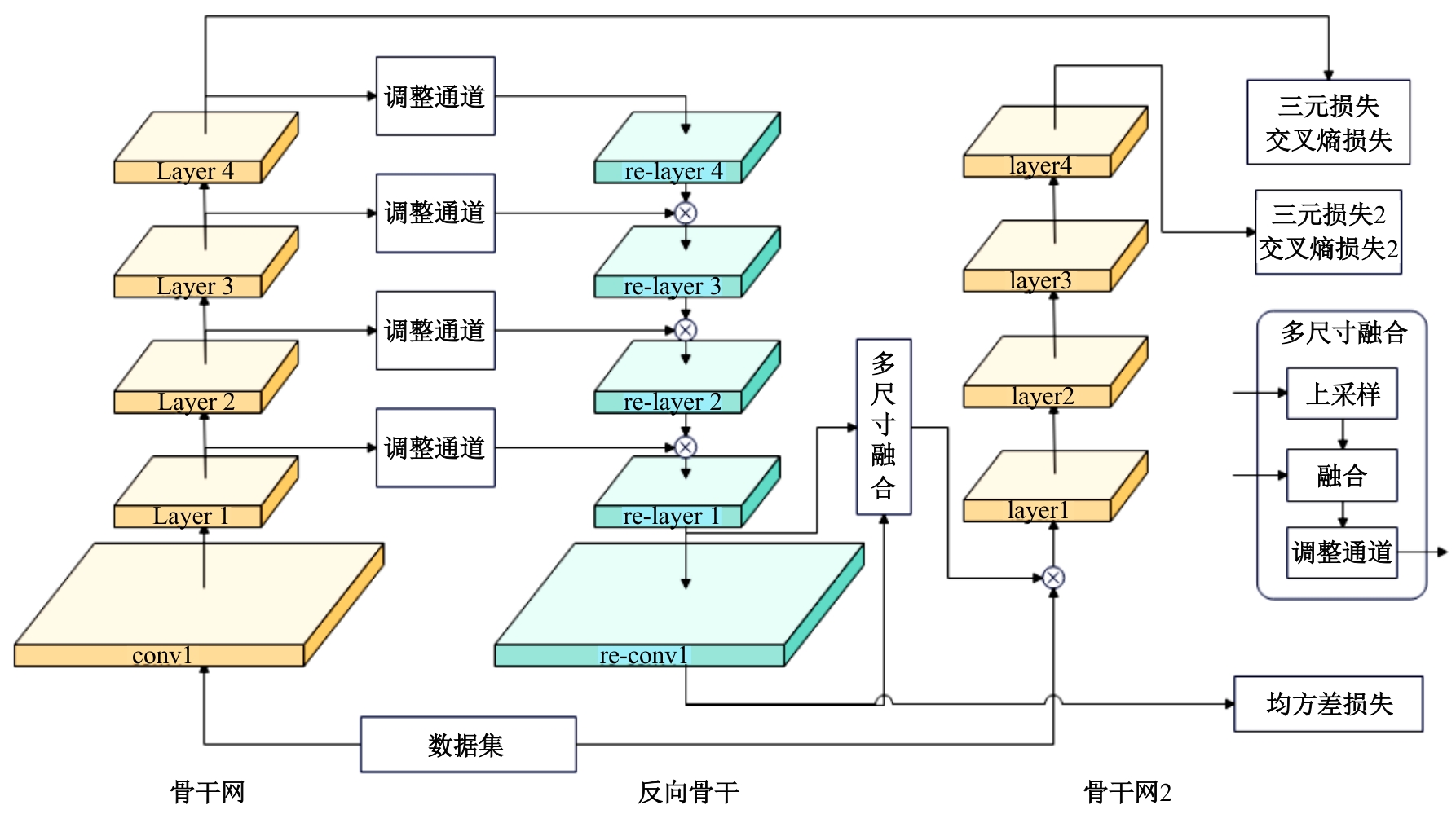
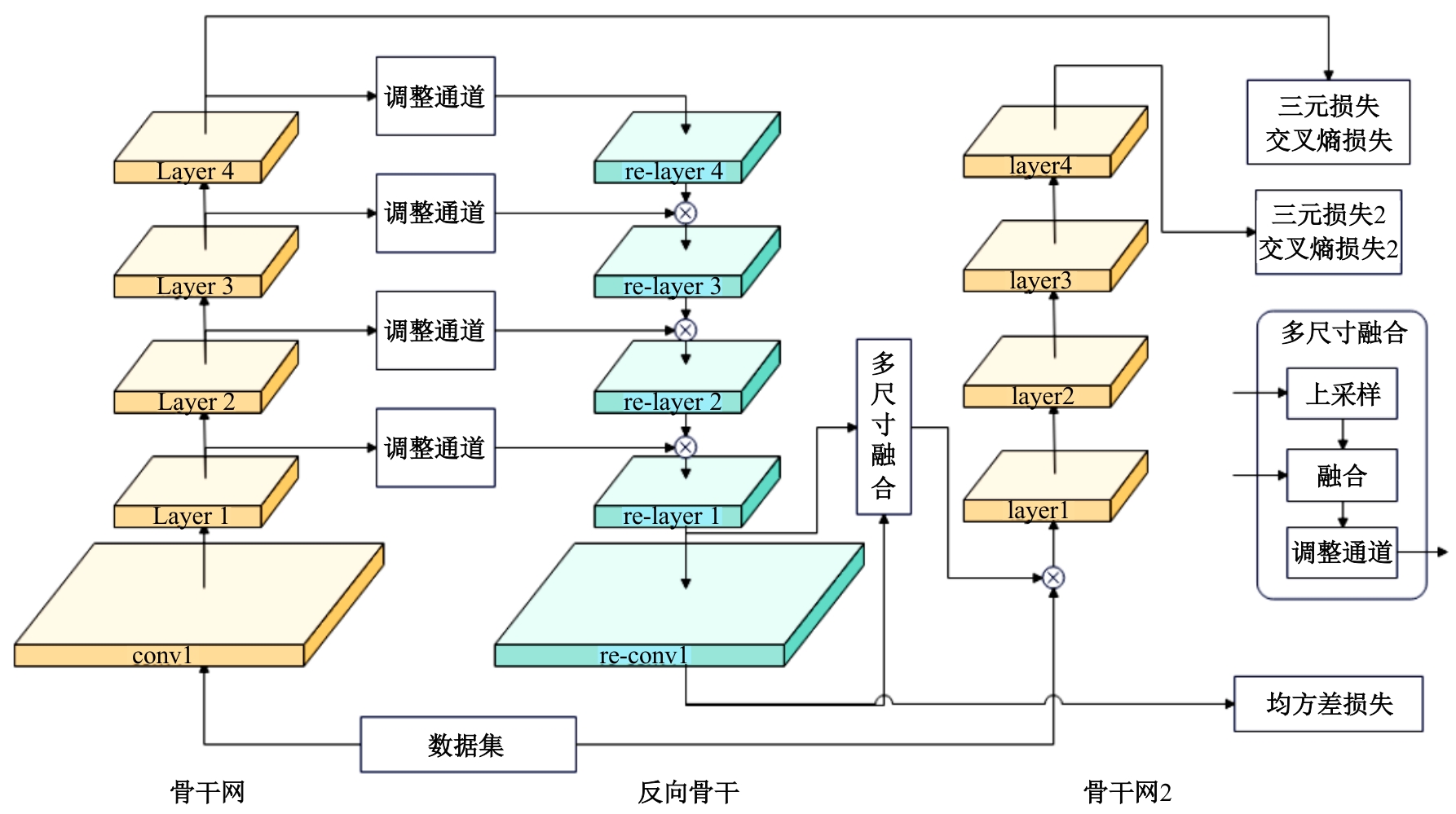
Reverse backbone net for unsupervised person re-identification
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Chiat P T, Sharmili R, Kim H Y. AANet: attribute attention network for person re-identifications[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7127-7136. |
| 2 | Lin Y T, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151-161. |
| 3 | Sun Y F, Zheng L, Yang Y, et al. Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]∥15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 501-518. |
| 4 | Miao J X, Wu Y, Yang Y. Identifying visible parts via pose estimation for occluded person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(9): 4624-4634. |
| 5 | Cai H L, Wang Z G, Cheng J X. Multi-scale body-part mask guided attention for person re-identification[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1555-1564. |
| 6 | Qiao S Y, Chen L C, Alan Y. Detectors: detecting objects with recursive feature pyramid and switchable atrous convolution[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10208-10219. |
| 7 | Hou S Q, Yin K N, Liang J, et al. Gradient-supervised person re-identification based on dense feature pyramid network[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2022, 8(6I): 5329-5342. |
| 8 | Zhang Z Z, Lan G L, Zeng W J, et al. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3183-3192. |
| 9 | Zhou K Y, Yang Y X, Cavallaro A, et al. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 3701-3711. |
| 10 | Divyansh G, Netra P, Thomas T, et al. Towards explainable person re-identification[C]∥IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Orlando, USA, 2021: 9660071. |
| 11 | Niki M, Gian L F, Christian M. Deep pyramidal pooling with attention for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7306-7316. |
| 12 | Yang F X, Zhong Z, Luo Z M, et al. Joint noise-tolerant learning and meta camera shift adaptation for unsupervised person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 4853-4862. |
| 13 | Antti T, Harri V. Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results[C]∥31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1195-1204. |
| 14 | Ge Y X, Chen D P, Li H S. Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification[C]∥8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 200101526. |
| 15 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 16 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5686-5696. |
| 17 | Martin E, Hans P K, Jorg S, et al. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise[C]∥2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, USA, 1996: 226-231. |
| 18 | Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, et al. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 1116-1124. |
| 19 | Ergys R, Francesco S, Roger Z, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]∥14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 17-35. |
| 20 | Wei L H, Zhang S L, Gao W, et al. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification[C]∥31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 79-88. |
| 21 | Park H J, Ham B. Relation network for person re-identification[C]∥34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 11839-11847. |
| 22 | He L X, Liao X Y, Liu W, et al. Fastreid: a pytorch toolbox for general instance re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2020, 10: 9662-9667. |
| 23 | Tan H C, Liu X P, Bian Y H, et al. Incomplete descriptor mining with elastic loss for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(1): 160-171. |
| 24 | Li Y L, He J F, Zhang T Z, et al. Diverse part discovery: occluded person re-identification with part-aware transformer[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2897-2906. |
| 25 | Li H J, Wu G J, Zheng W S. Combined depth space based architecture search for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 6725-6734. |
| 26 | Zheng K C, Liu W, He L X, et al. Group-aware label transfer for domain adaptive person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 5306-5315. |
| 27 | Wang D K, Zhang S L. Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(12): 2924-2939. |
| 28 | Zou Y, Yang X D, Yu Z D, et al. Joint disentangling and adaptation for cross-domain person re-identification[C]∥16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 87-104. |
| 29 | Jin X, Lan C L, Zeng W J, et al. Global distance-distributions separation for unsupervised person re-identification[C]∥16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 735-751. |
| 30 | Zhong Z, Zheng L, Luo Z M, et al. Learning to adapt invariance in memory for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2723-2738. |
| 31 | Chen G Y, Gu T P, Lu J W, et al. Person re-identification via attention pyramid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7663-7676. |
| [1] | Yi CAO,Yu XIA,Qing-yuan GAO,Pei-tao YE,Fan YE. Skeleton-based action recognition based on hyper-connected graph convolutional network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 731-740. |
| [2] | Pei-guang JING,Yu-dou TIAN,Shao-chu WANG,Yun LI,Yu-ting SU. Traffic flow prediction algorithm based on dynamic diffusion graph convolution [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [3] | Fu-heng QU,Yue-tao PAN,Yong YANG,Ya-ting HU,Jian-fei SONG,Cheng-yu WEI. An efficient global K-means clustering algorithm based on weighted space partitioning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [4] | Shuai-shuai SUN,Chun-xiao FENG,Liang ZHANG. Path planning for multimodal quadruped robots based on discrete sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [5] | Zhi-gang JIN,Ren-jun SU,Xiao-fang ZHAO. Psychological assessment method based on heterogeneous graph network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [6] | Jing-peng GAO,Guo-xuan WANG,Lu GAO. LSTM⁃MADDPG multi⁃agent cooperative decision algorithm based on asynchronous collaborative update [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [7] | Liu LIU,Kun DING,Shan-shan LIU,Ming LIU. Event detection method as machine reading comprehension [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [8] | Jian LI,Qi XIONG,Ya-ting HU,Kong-yu LIU. Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden Markov model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [9] | Peng YU,Yan PIAO. New method for extracting person re-identification attributes based on multi-scale features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [10] | Chun-hui LIU,Si-chang WANG,Ce ZHENG,Xiu-lian CHEN,Chun-lei HAO. Obstacle avoidance planning algorithm for indoor navigation robot based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [11] | Tian BAI,Ming-wei XU,Si-ming LIU,Ji-an ZHANG,Zhe WANG. Dispute focus identification of pleading text based on deep neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [12] | Sheng-sheng WANG,Lin-yan JIANG,Yong-bo YANG. Transfer learning of medical image segmentation based on optimal transport feature selection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [13] | Hao-yu TIAN,Xin MA,Yi-bin LI. Skeleton-based abnormal gait recognition: a survey [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [14] | Yong LIU,Lei XU,Chu-han ZHANG. Deep reinforcement learning model for text games [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [15] | Chun-ping HOU,Qing-yuan YANG,Mei-yan HUANG,Zhi-peng WANG. Cross⁃modality person re⁃identification based on semantic coupling and identity⁃consistence constraint [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2954-2963. |
|
||