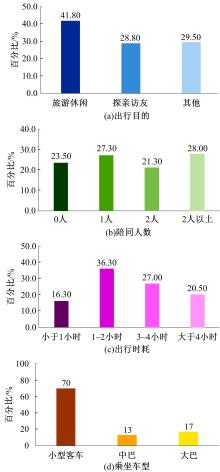
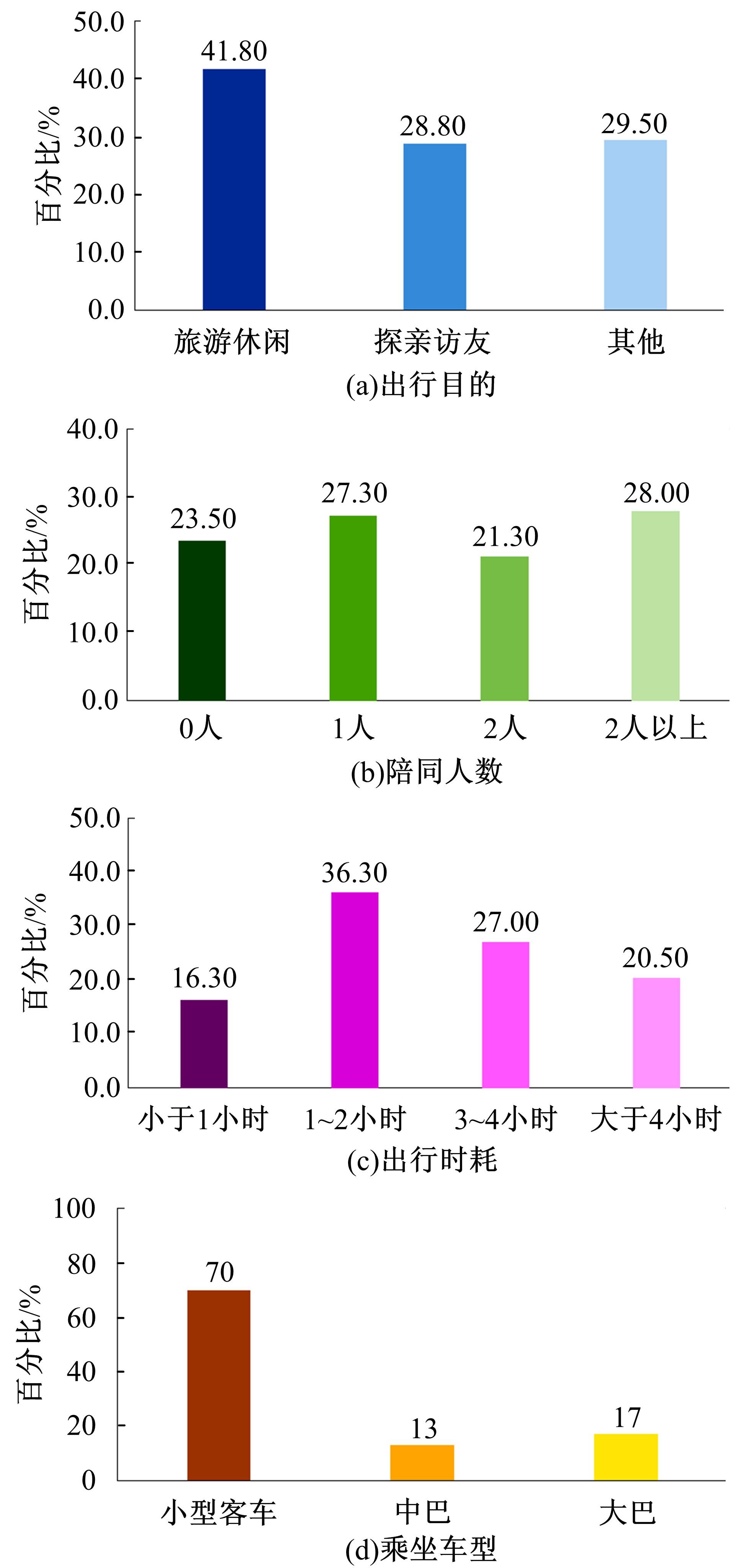
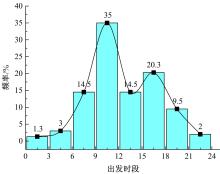
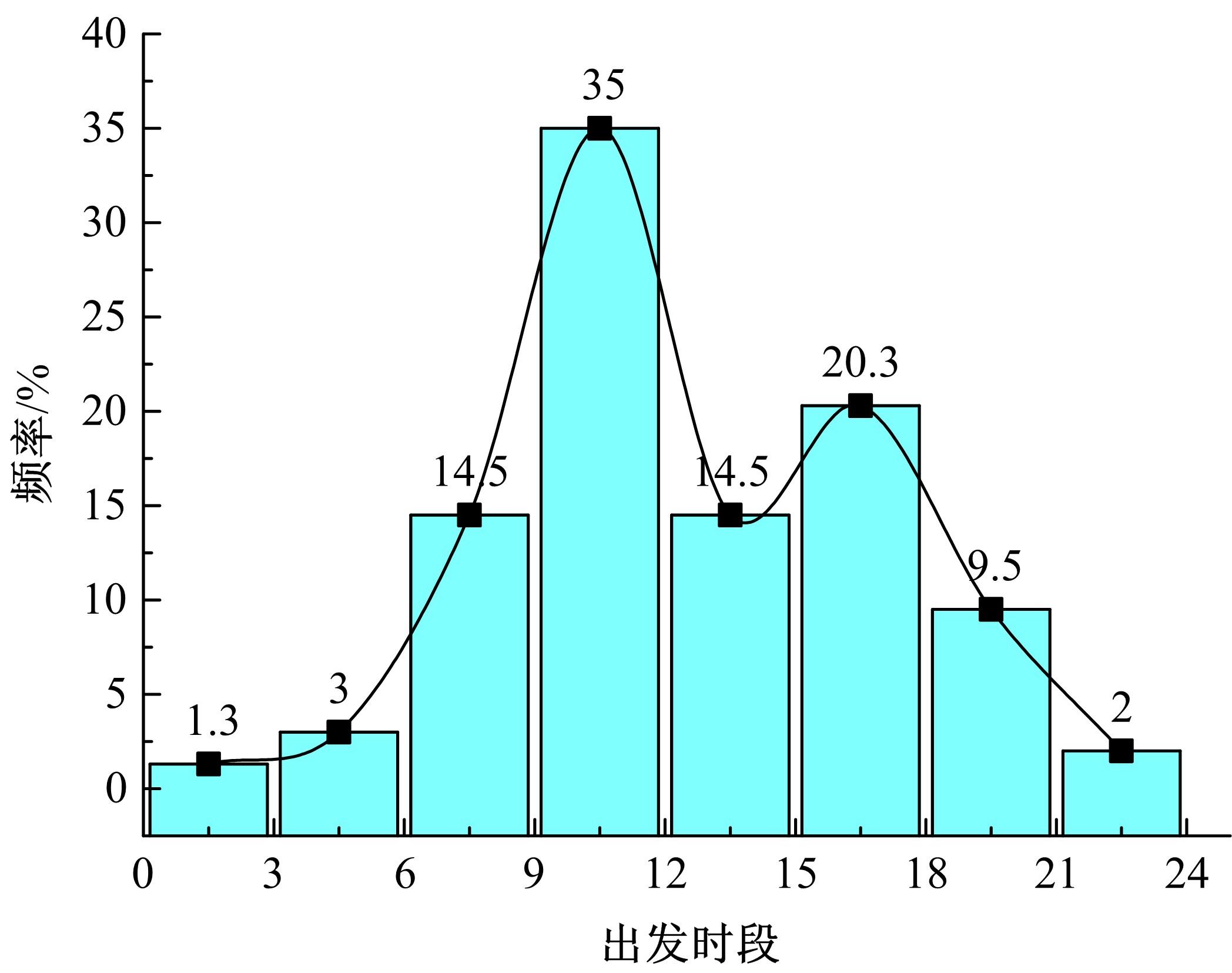
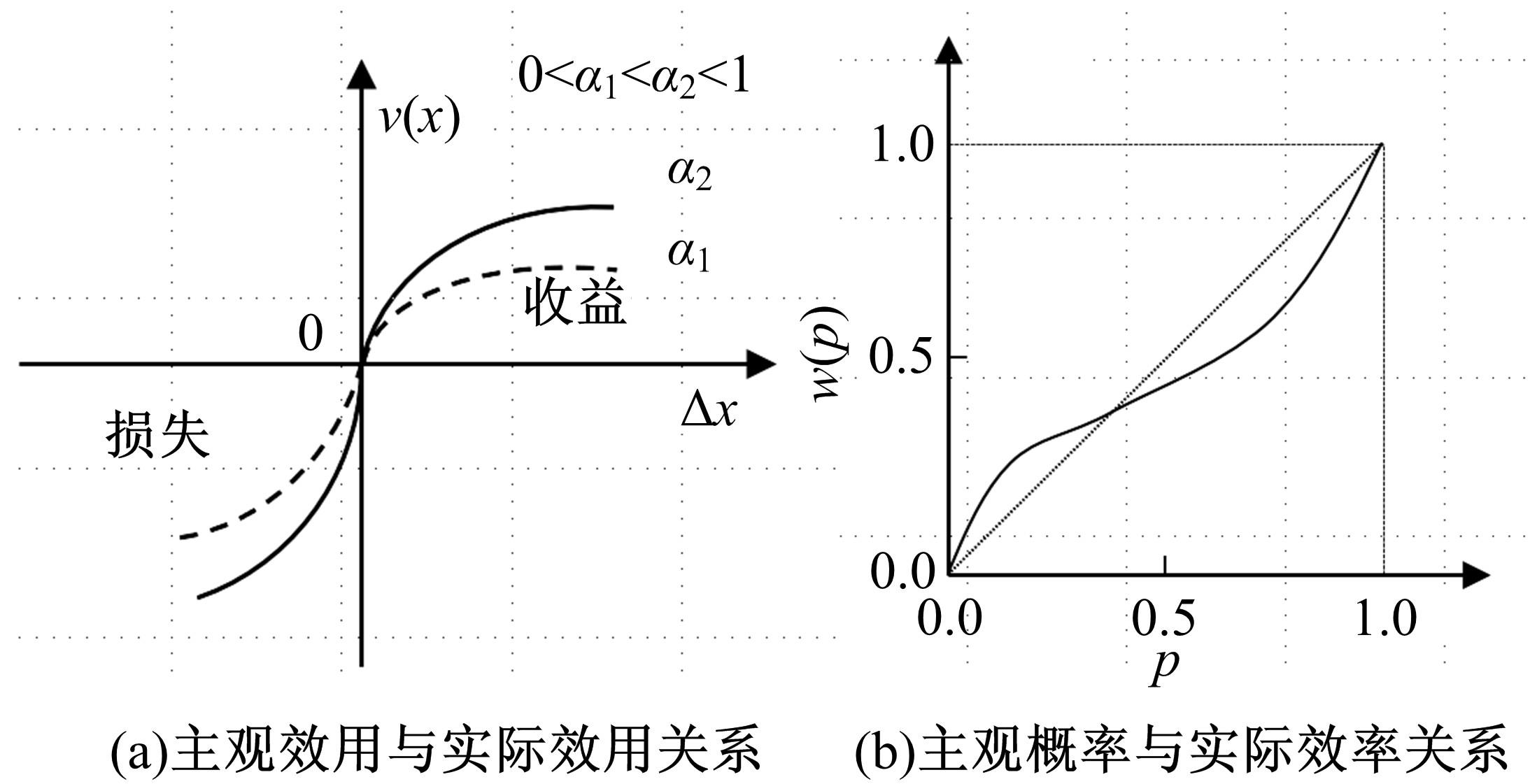
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1673-1683.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200409
Model of highway travel selection considering individual risk preference difference
Ying-ying MA1,2( ),Si-yuan LU2(
),Si-yuan LU2( ),Xiao-ming ZHANG2,Wen-shu WEI2
),Xiao-ming ZHANG2,Wen-shu WEI2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
2.Transportation Planning and Design Studio,Guangzhou Urban Planning & Design Survey Research Institute,Guangzhou 510060,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | 贾洪飞, 龚勃文, 宗芳. 交通方式选择的非集计模型及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2007, 37(6): 1288-1293. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Gong Bo-wen, Zong Fang. Disaggregation model of traffic mode selection and its application[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2007, 37(6): 1288-1293. | |
| 2 | Kumagai S J, Uchiyama H, Takashima S. Formation of bus network based on traffic mode selection model with disaggregate data[J]. Physics Letters A, 2011, 375(17): 1831-1838. |
| 3 | Ozbay K, Yanmaz-Tuzel O. Valuation of travel time and departure time choice in the presence of time-of-day pricing[J]. Transportation Research Part A Policy & Practice, 2008, 42(4): 577-590. |
| 4 | 张旭, 栾维新, 赵冰茹. 基于非集计模型的武广线高铁与民航竞争研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12(6): 17-21. |
| Zhang Xu, Luan Wei-xin, Zhao Bing-ru. Research on competition between Wuhan Guangzhou high speed railway and civil aviation based on disaggregation model[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2012, 12(6): 17-21. | |
| 5 | McFadden D, Train K. Mixed MNL models for discrete response[J]. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 2000, 15(5): 447-470. |
| 6 | 李华民, 黄海军. 基于一种新效用函数形式的分层Logit模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(): 63-65. |
| Li Hua-min, Huang Hai-jun. Layered logit model based on a new utility function form[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(Sup.2): 63-65. | |
| 7 | 唐洁, 隽志才, 高林杰. 城市居民出行空间和方式联合选择模型研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(5): 83-87. |
| Tang Jie, Zhi-cai Juan, Gao Lin-jie. Research on joint choice model of urban residents' travel space and mode[J]. Highway Transportation Technology, 2010, 27(5): 83-87. | |
| 8 | 诸葛承祥, 邵春福, 李霞, 等. 通勤者出行时间与出行方式选择行为研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12(2): 130-135. |
| Cheng-xiang Zhu-ge, Shao Chun-fu, Li Xia, et al. Study on commuter travel time and travel mode selection behavior[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2012, 12(2): 130-135. | |
| 9 | 陈林. 基于Logit模型的成渝通道交通选择行为研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2013. |
| Chen Lin. Study on traffic choice behavior of Chengdu Chongqing corridor based on logit model[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 10 | Kahneman D, Tversky A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[J]. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 263-292. |
| 11 | Kahneman A T. Advances in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty[J]. Journal of Risk & Uncertainty, 1992, 5(4): 297-323. |
| 12 | Avineri E J T S. The effect of reference point on stochastic network equilibrium[J]. Transportation Science, 2006, 40(4): 409-420. |
| 13 | 施海燕, 施放. 期望效用理论与前景理论之比较[J]. 统计与决策, 2007(11): 22-24. |
| Shi Hai-yan, Shi Fang. Comparison of expected utility theory and prospect theory[J]. Statistics and Decision Making, 2007(11): 22-24. | |
| 14 | 刘玉印, 刘伟铭, 吴建伟. 基于累积前景理论的出行者路径选择模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 38(7): 84-89. |
| Liu Yu-yin, Liu Wei-ming, Wu Jian-wei. Travel path selection model based on cumulative prospect theory[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(7): 84-89. | |
| 15 | Hu L, Dong J, Lin Z. Modeling charging behavior of battery electric vehicle drivers: a cumulative prospect theory based approach[J]. Transportation Research, 2019, 102: 474-489. |
| 16 | Guan Y, Annaswamy A M, Tseng H E. Cumulative prospect theory based dynamic pricing for shared mobility on demand services[C]∥2019 IEEE 58th Conference on Decision and Control(CDC), 2019: 04824. |
| 17 | Jhala K, Natarajan B, Pahwa A. Prospect theory-based active consumer behavior under variable electricity pricing[J]. Smart Grid, IEEE Transactions on, 2019, 10(3): 2809-2819. |
| 18 | 邢睿. 基于前景理论的城市居民交通出行方式选择研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学交通运输工程学院, 2014. |
| Xing Rui. Research on urban residents' travel mode selection based on prospect theory[D]. Changsha: School of Transportation Engineering, Changsha University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 19 | 马书红, 周烨超, 张艳. 基于NL-累计前景理论的出行方式选择预测模型研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2019, 19(4): 135-142. |
| Ma Shu-hong, Zhou Ye-chao, Zhang Yan. Study on travel mode selection prediction model based on NL cumulative prospect theory[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2019, 19(4): 135-142. | |
| 20 | 杨志勇. 基于前景理论的出发时刻和出行路径选择模型研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2007. |
| Yang Zhi-yong. Research on departure time and travel path selection model based on prospect theory[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007. | |
| 21 | 秦世环. 基于前景理论的出行方式与路径联合选择行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Qin Shi-huan. Research on joint choice behavior of travel mode and route based on prospect theory[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. |
| [1] | Yao-rong CHENG,Qian YANG,Guo-hua ZHENG. Tractor scheduling optimization of drop and pull transport in large⁃scale manufacturing enterprises considering carbon emission [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 893-899. |
| [2] | Fang WANG,Jia HU,Sheng JING,Wei CHENG,Xiao-ying HE,Xiao-guang LI. Modeling and analysis of road speed micro model in long straight line section of desert [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 575-582. |
| [3] | Zhi-jun TENG,Yu ZHANG,Hao-tian LI,Ming-yang SUN. Adaptive D⁃S evidence theory map matching algorithm of complex road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 524-530. |
| [4] | Yang LI,Lian-jun WANG. Applicability analysis of two dimensional modelingmethods for wide embankment composite foundation in high speed railway stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 621-630. |
| [5] | Fang WANG,Xiao-guang LI,Hui GUO,Jia HU. Optimization of straight segment index between highway curves of desert grassland based on driver’s visual interest region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 114-120. |
| [6] | LI Ye, WANG Wei, XING Lu, WANG Hao, DONG Chang-yin. Improving traffic efficiency of highway by integration of adaptive cruise control and variable speed limit control [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1420-1425. |
| [7] | XU Jin, CHEN Wei, ZHOU Jia, LUO Xiao, SHAO Yi-ming. Correlation between steering and driver's workload [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 438-445. |
| [8] | TANG Xiao-feng, GAO Feng, XU Guo-yan, DING Neng-gen, CAI Yao, LIU Jian-xing. Vehicle driving dynamics prediction based on highway intelligent space-vehicle framework theory [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1395-1401. |
| [9] | WANG Ying-jie,WANG Lei ,RONG Qi-guo,WU Yong-hui. Danger evaluation of debris flow along highway based on path analysis and extension method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 895-900. |
| [10] | ZHAN Wei, LYU Qing, SHANG Yue-quan. Analysis of gray-Markov forecasting for traffic accidents in highway tunnel group region [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 62-67. |
| [11] | WANG Guo-lin, FU Nai-ji, ZHANG Jian, PEI Zi-rong. Simulation of the radial tire curing process based on K-R kinetic model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(03): 659-664. |
| [12] | LIAO Jun-hong, SHAO Chun-fu, WU Hong-bo, SUN Yi-xuan, WANG Shu-ling. Calculation and assessment technique of highway 3D dynamic sight distance [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(03): 640-645. |
| [13] | XU Hong-guo, CHEN Xiu-feng, LIU San-bing. Prediction model of free-flow operation speed on mountain slope [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 189-192. |
| [14] | CHENG Yong-chun, GUO Qing-lin, TAN Guo-jin. Improved viscoelastic parameter identification for asphalt mixture [J]. , 2012, (03): 629-633. |
| [15] | LI Xia,GAO Li,LIU Yu-guo. Simultaneous residential location and travel mode choice es-timation around rail transit station based on cross-nested logit model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1614-1617. |
|
||