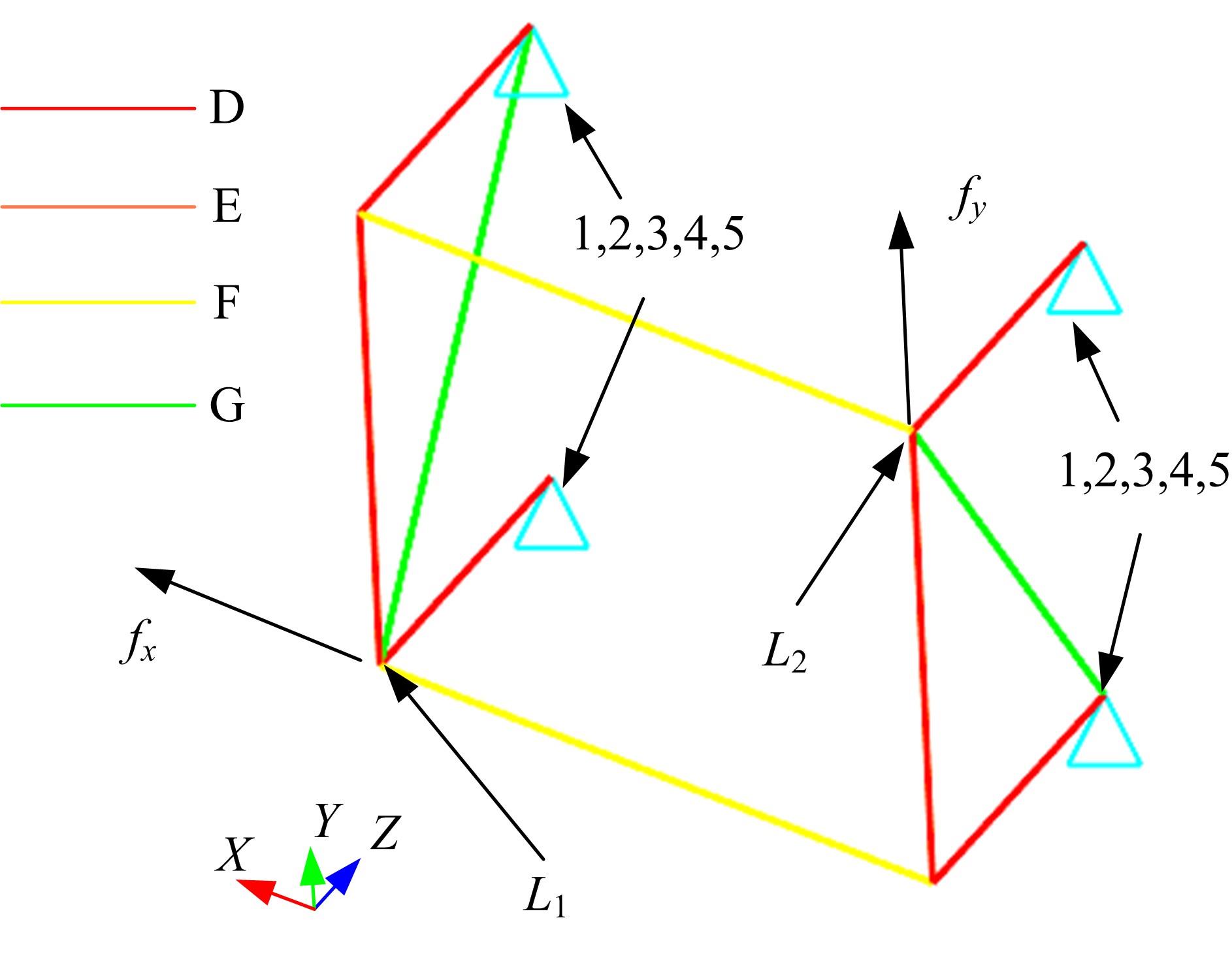
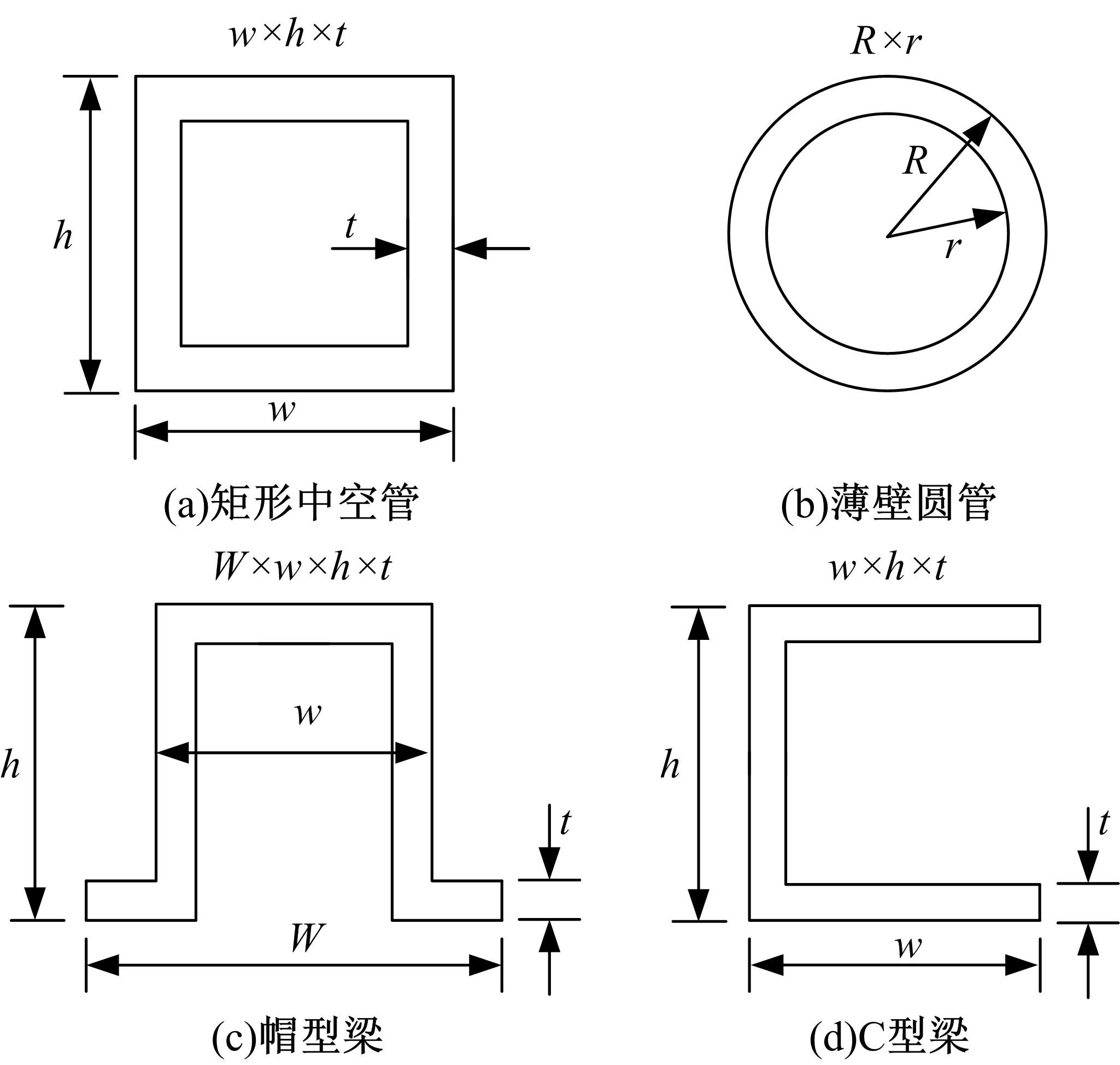
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1583-1592.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200506
Optimization of multi⁃material and beam cross⁃sectional shape and dimension of skeleton⁃type body
Chao MA1( ),Yun-kai GAO1(
),Yun-kai GAO1( ),Zhe LIU1,Yue-xing DUAN1,Lin-li TIAN2,3
),Zhe LIU1,Yue-xing DUAN1,Lin-li TIAN2,3
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Hubei Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Automotive Components,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
3.Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Automotive Components Technology,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
CLC Number:
- U463
| 1 | 侯文彬, 张红哲, 徐金亭,等. 基于概念设计的客车车身结构设计与优化系统[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 40(10): 58-63. |
| Hou Wen-bin, Zhang Hong-zhe, Xu Jin-ting, et al. System of design and optimization system for bus body structure based on concept design[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2013, 40(10): 58-63. | |
| 2 | Gui C, Bai J, Zuo W. Simplified crashworthiness method of automotive frame for conceptual design[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 131(10): 324-335. |
| 3 | 赵永宏, 李永成, 陈东, 等. 基于改进图分解法的多材料车身结构优化设计方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(4): 560-566. |
| Zhao Yong-hong, Li Yong-cheng, Chen Dong, et al. Optimization design method of multi-material car body structure based on modified graphic decomposition[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 560-566. | |
| 4 | 王震虎, 王万林, 张松波, 等. 基于车身概念模型的白车身主断面尺寸优化[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(8): 904-911. |
| Wang Zhen-hu, Wang Wan-lin, Zhang Song-bo, et al. Size optimization on main cross-sections of body-in-white based on conceptual model for car body[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(8): 904-911. | |
| 5 | 那景新, 高剑峰. 基于局部搜索和整体优化的客车杆件截面参数正向设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1564-1570. |
| Na Jing-xin, Gao Jian-feng. Top-down design method based on local search and global optimization for cross-sectional size of bus body[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1564-1570. | |
| 6 | 康元春, 李园, 高永正. 基于DOE方法的客车车身骨架尺寸优化[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 33(4): 160-163. |
| Kang Yuan-chun, Li Yuan, Gao Yong-zheng. Size optimization of bus body frame based on DOE[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Sciences), 2014, 33(4): 160-163. | |
| 7 | 柯俊, 陈志勇, 史文库, 等. 基于振动控制的客车地板模态分析及结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(3): 719-725. |
| Ke Jun, Cheng Zhi-yong, Shi Wen-ku, et al. Modal analysis and structure optimization of bus floor based on floor vibration control[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(3): 719-725. | |
| 8 | 苏瑞意, 桂良进, 王旭, 等. 燃料电池城市客车结构有限元分析与轻量化设计[J]. 汽车工程, 2008, 30(12): 1099-1102. |
| Su Rui-yi, Gui Liang-jin, Wang Xu, et al. Finite element analysis and light weight design of a fuel cell city bus structure[J].Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(12): 1099-1102. | |
| 9 | 郑若瑜, 肖守讷, 朱涛, 等. 25T客车车体结构轻量化研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2017(11): 157-160. |
| Zheng Ruo-yu, Xiao Shou-ne, Zhu Tao, et al. Contrastive research on lightweight schemes of 25T locomotive body[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2017(11): 157-160. | |
| 10 | 范子杰. 基于多目标遗传算法的大客车骨架结构协同拓扑优化方法研究[C]∥第十二届设计与制造前沿国际会议(ICFDM2016)论文集, 沈阳, 2016: 488. |
| 11 | Cheng M, Prayogo D, Wu Y, et al. A hybrid harmony search algorithm for discrete sizing optimization of truss structure[J]. Automation in Construction, 2016, 69(9): 21-33. |
| 12 | Qin H, Guo Y, Liu Z, et al. Shape optimization of automotive body frame using an improved genetic algorithm optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2018, 121(7): 235-249. |
| 13 | 侯文彬, 王增飞, 张伟, 等. 基于复杂工程约束的车身梁截面优化设计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(18): 127-133. |
| Hou Wen-bin, Wang Zeng-fei, Zhang Wei, et al. Optimization design for auto-body beam section based on complex engineering constraints[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(18): 127-133. | |
| 14 | Cui X, Zhang H, Wang S, et al. Design of lightweight multi-material automotive bodies using new material performance indices of thin-walled beams for the material selection with crashworthiness consideration[J].Materials and Design, 2011, 32(2): 815-821. |
| 15 | 兰凤崇, 陈元, 周云郊, 等. 轻质多材料动力电池包箱体选材与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1227-1234. |
| Lan Feng-chong, Chen Yuan, Zhou Yun-jiao, et al. Multi-material selection and optimization of lightweight battery pack enclosure[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1227-1234. | |
| 16 | Tejani G G, Savsani V J, Patel V K, et al. Size, shape, and topology optimization of planar and space trusses using mutation-based improved metaheuristics[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2018, 5(2): 198-214. |
| 17 | Hasancebi O, Azad S K. Adaptive dimensional search: a new metaheuristic algorithm for discrete truss sizing optimization[J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 154(7): 1-16. |
| 18 | Lieu Q X, Do D T T, Lee J. An adaptive hybrid evolutionary firefly algorithm for shape and size optimization of truss structures with frequency constraints[J]. Computers & Structures, 2018, 195(1): 99-112. |
| 19 | Kazemzadeh A S, Hasancebi O, Saka M P. Guided stochastic search technique for discrete sizing optimization of steel trusses: a design-driven heuristic approach[J]. Computers & Structures, 2014, 134(4): 62-74. |
| 20 | Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Bahreininejad A, et al. Water cycle, mine blast and improved mine blast algorithms for discrete sizing optimization of truss structures[J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 149(3): 1-16. |
| 21 | Silih S, Kravanja S, Premrov M. Shape and discrete sizing optimization of timber trusses by considering of joint flexibility[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2010, 41(2): 286-294. |
| 22 | Lei F, Lv X, Fang G J, et al. Multiobjective discrete optimization using the TOPSIS and entropy method for protection of pedestrian lower extremity[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020(152): 106349. |
| 23 | 田林雳. 骨架式车身结构及其力流分析方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学汽车学院, 2016. |
| Tian Lin-li. Research on framework of frame-type body and its load path analysis[D]. Shanghai: School of Automotive Studies, Tongji University, 2016. | |
| 24 | Deb K, Jain H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point based non-dominated sorting approach, part I: solving problems with box constraints[J]. Evolutionary Computation, IEEE Transactions on, 2014, 18(4): 577-601. |
| 25 | 高云凯, 马超, 刘哲, 等. 基于NSGA-III的白车身焊装生产平台的离散拓扑优化[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(12): 1324-1334. |
| Gao Yun-kai, Ma Chao, Liu Zhe, et al. Discrete topology optimization of body-in-white welding production platform based on NSGA-III[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University,2020, 54(12): 1324-1334. | |
| 26 | 高云凯, 段少东. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ算法的客车底架的离散拓扑优化[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(11): 92-97. |
| Gao Yun-kai, Duan Shao-dong. Discrete topology optimization of bus chassis frame based on NSGA-Ⅱ[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2017, 45(11): 92-97. |
| [1] | Yong LUO,Yong-heng WEI,Huan HUANG,Ren-jie XIAO,Lin REN,Huan-yu CUI. Starting control of P2.5 plug⁃in hybrid configuration dual⁃clutch based on driver's intention recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [2] | Jian YANG,Qi XIA,Hai-chao ZHOU,Guo-lin WANG. Noise reduction mechanism of truck radial tire based on modified carcass string contour design [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [3] | Jiang-qi LONG,Jin-tao XIANG,Ping YU,Jun-cheng WANG. Linear disturbance observer suitable for sliding mode control of nonlinear active suspension [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1230-1240. |
| [4] | Xin CHEN,Gui-shen YU,Biao ZHANG,Kai-xuan PAN,Li-fei YANG. Equivalent modeling of tensile-shear behavior for friction stir spot welding joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1190-1197. |
| [5] | Li-sheng JIN,Bai-cang GUO,Fang-rong WANG,Jian SHI. Dynamic multiple object detection algorithm for vehicle forward based on improved YOLOv3 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [6] | Feng-chong LAN,Ji-wen LI,Ji-qing CHEN. DG-SLAM algorithm for dynamic scene compound deep learning and parallel computing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [7] | Bo WANG,Yang-yang HE,Bing-bing NIE,Shu-cai XU,Jin-huan ZHANG. Abdominal injury of vehicle occupant in underbody blast events [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 792-798. |
| [8] | Wei-min ZHUANG,Peng-yue WANG,Rui-juan GAO,Dong-xuan XIE. Effect of hot forming on static mechanical properties of AA5754 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 847-854. |
| [9] | Qiang SONG,Dan-ting SUN,Wei ZHANG. Shift nonlinear modeling and control of automated mechanical transmission in pure electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 810-819. |
| [10] | Jia-xu ZHANG,Xin-zhi WANG,Jian ZHAO,Zheng-tang SHI. Path planning and discrete sliding mode tracking control for high⁃speed lane changing collision avoidance of vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [11] | Zhe-ming YUAN,Hong-jie YUAN,Yu-xuan YAN,Qian LI,Shuang-qing LIU,Si-qiao TAN. Automatic recognition and classification of field insects based on lightweight deep learning model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [12] | Ren HE,Xiao-cong ZHAO,Yi-bin YANG,Jian-qiang WANG. Man⁃machine shared driving model using risk⁃response mechanism of human driver [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 799-809. |
| [13] | Da-feng SONG,Li-li YANG,Xiao-hua ZENG,Xing-qi WANG,Wei-zhi LIANG,Nan-nan YANG. Battery life optimization of hybrid electric vehicle based on driving cycle construction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [14] | Guo-ying CHEN,Jun YAO,Peng WANG,Qi-kun XIA. Stability control strategy for rear in⁃wheel motor drive vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 397-405. |
| [15] | Wei-da WANG,Yan-jie WU,Jia-lei SHI,Liang LI. Electronic hydraulic brake power system control strategy based on driver intention recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 406-413. |
|
||