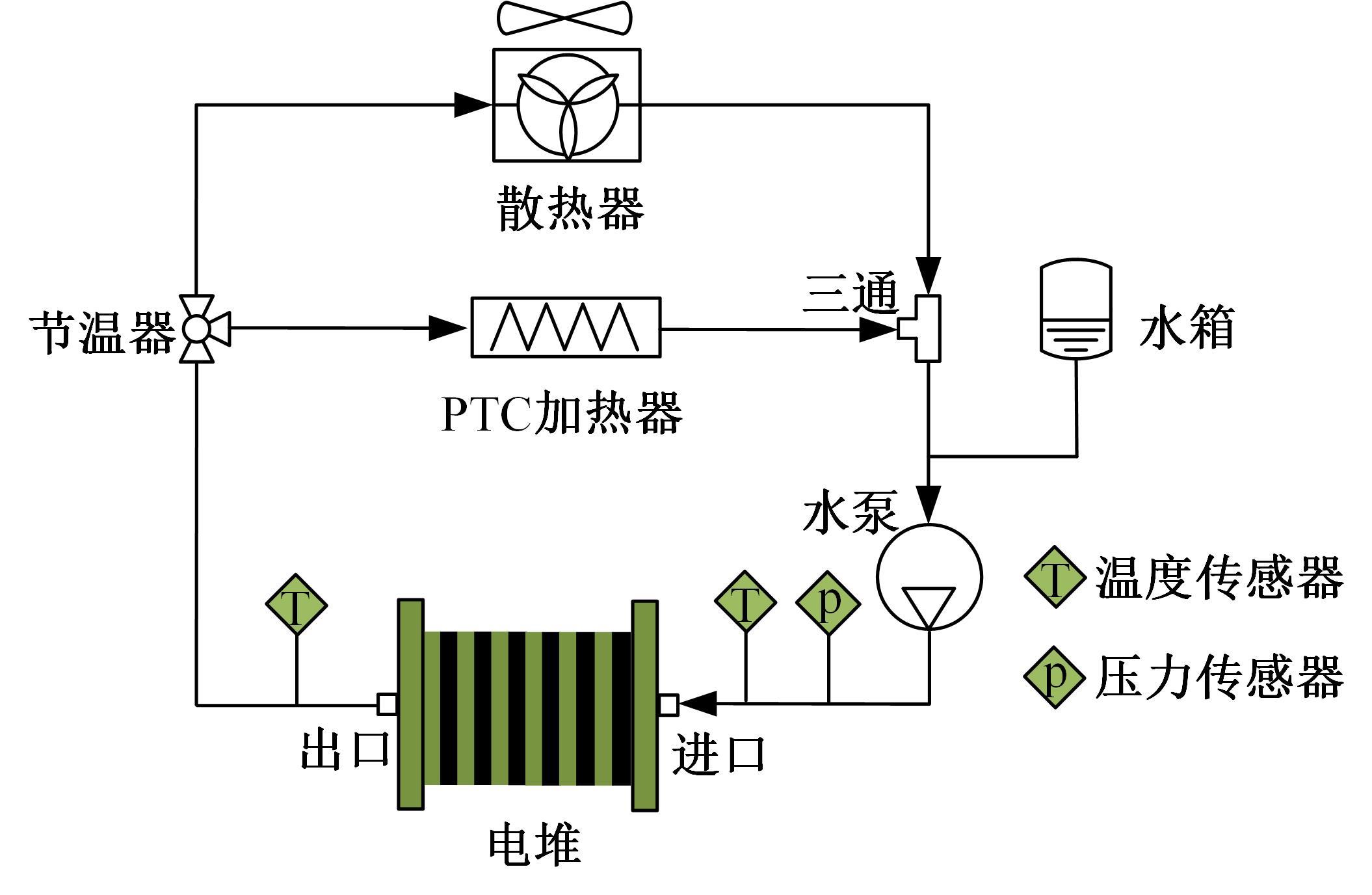
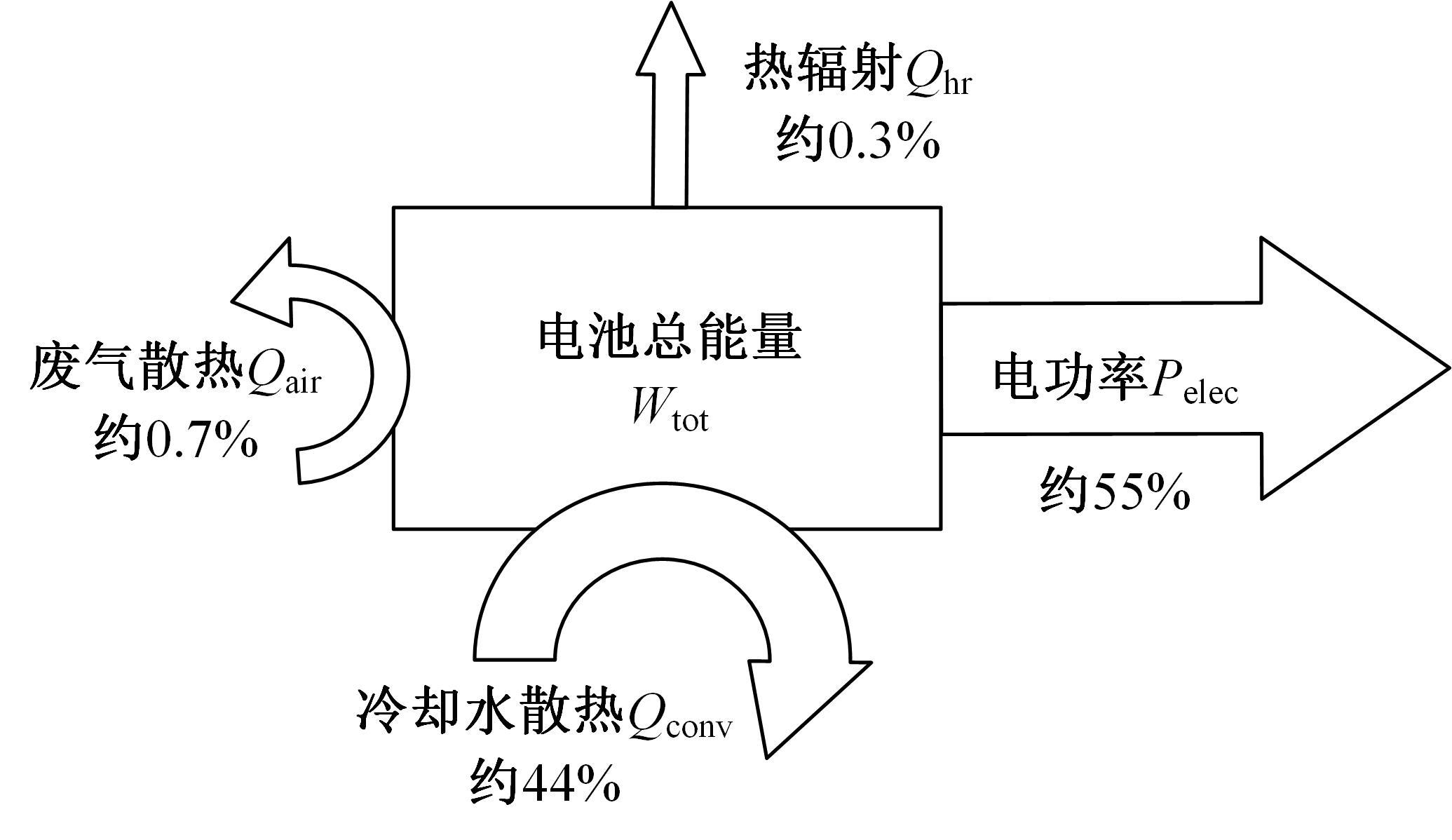
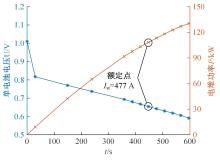
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2014-2024.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220259
Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control
Yao-wang PEI1( ),Feng-xiang CHEN1(
),Feng-xiang CHEN1( ),Zhe HU2,Shuang ZHAI2,Feng-lai PEI3,Wei-dong ZHANG4,Jie-ran JIAO1
),Zhe HU2,Shuang ZHAI2,Feng-lai PEI3,Wei-dong ZHANG4,Jie-ran JIAO1
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Shanghai Re-fire Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201800,China
3.Shanghai Motor Vehicle Inspection Certification & Tech Innovation Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201805,China
4.College of Information and Communication Engineering,Hainan University,Haikou 570228,China
CLC Number:
- U469.72
| 1 | Pandiyan S, Jayakumar K, Rajalakshmi N, et al. Thermal and electrical energy management in a PEMFC stack—an analytical approach[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(3/4): 469-473. |
| 2 | Rojas J D, Ocampo-Martínez C, Kunusch C. Thermal modelling approach and model predictive control of a water-cooled PEM fuel cell system[C]∥39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 2013: 3806-3811. |
| 3 | Han J, Yu S, Yi S. Advanced thermal management of automotive fuel cells using a model reference adaptive control algorithm[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(7): 4328-4341. |
| 4 | Chen F, Jiao J, Yu Y, et al. Active control of stack inlet and outlet coolant temperature for the PEM fuel cell system[C]∥2017 International Conference on Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology, Tianjin, China, 2017: No. V001T01A001. |
| 5 | Yu S, Jung D. A study of operation strategy of cooling module with dynamic fuel cell system model for transportation application[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(11): 2525-2532. |
| 6 | Saygili Y, Eroglu I, Kincal S. Model based temperature controller development for water cooled PEM fuel cell systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(1): 615-622. |
| 7 | Pukrushpan J T. Modeling and control of fuel cell systems and fuel processors[D]. Michigan: The University of Michigan, 2003. |
| 8 | 牛茁,张玉瑾,邓惠文,等. 基于OPC技术的水冷PEMFC热管理控制系统[J]. 太阳能学报,2019, 40(4): 942-949. |
| Niu Zhuo, Zhang Yu-jin, Deng Hui-wen, et al. Thermal management system of water-cooled PEMFC based on OPC technology[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2019, 40(4), 942-949. | |
| 9 | 郑文杰,杨径,朱林培,等. 车用燃料电池热管理性能仿真与试验研究[J]. 汽车工程,2021,43(3): 381-386. |
| Zheng Wen-jie, Yang Jing, Zhu Lin-pei, et al Simulation and experimental study on thermal management system of vehicle fuel cell[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(3): 381-386. | |
| 10 | 郭爱,陈维荣,刘志祥,等. 燃料电池机车热管理系统建模和动态分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(5): 953-960. |
| Guo Ai, Chen Wei-rong, Liu Zhi-xiang, et al. Modeling and dynamic analysis of thermal management system for fuel cell locomotive[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(5): 953-960. | |
| 11 | 赵洪波,刘杰,马彪,等. 水冷PEMFC热管理系统控制策略及仿真研究[J]. 化工学报,2020,71(5): 2139-2150. |
| Zhao Hong-bo, Liu Jie, Ma Biao, et al. Control strategy and simulation research of water-cooled PEMFC thermal management system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2139-2150. | |
| 12 | Cheng Si-liang, Fang Chuan, Xu Liang-fei, et al. Model-based temperature regulation of a PEM fuel cell system on a city bus[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(39): 13566-13575. |
| 13 | Huang L H, Chen J, Liu Z Y, et al. Adaptive thermal control for PEMFC systems with guaranteed performance[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(25): 11550-11558. |
| 14 | Liso V, Nielsen M P, Kaer S K, et al. Thermal modeling and temperature control of a PEM fuel cell system for forklift applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(16): 8410-8420. |
| 15 |
刘岩, 丁天威, 王宇鹏, 等. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220346 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220346 |
|
Liu Yan, Ding Tian-wei, Wang Yu-peng, Du Jing, Zhao hong-hui. Thermal management strategy of fuel cell engine based on adaptive control strategy[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220346 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220346 |
|
| 16 | Chen F X, Jiao J R, Hou Z J, et al. Robust polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell temperature tracking control based on cascade internal model control[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 479: No. 229008. |
| 17 | Han J, Park J, Yu S. Control strategy of cooling system for the optimization of parasitic power of automotive fuel cell system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(39): 13549-13557. |
| 18 | 沈维道,童钧耕. 工程热力学[M]. 4版. 北京:高等教育出版社出版,2007. |
| 19 | 谭羽飞. 工程热力学[M]. 6版. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2016. |
| 20 | 刘占孟,兰蔚. 流体力学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2017. |
| 21 | Rojas J D, Ocampo-Martinez C, Kunusch C. Thermal modelling approach and model predictive control of a water-cooled pem fuel cell system[C]∥39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 2013: No.14003725. |
| 22 | 郭爱. 基于过氧比的车载燃料电池系统控制技术[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学电气工程学院, 2015. |
| Guo Ai. Control of fuel cell system for vehicle based on oxygen excess ratio[D]. Chengdu: School of Electrical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015. |
| [1] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [2] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Jun-yu ZHANG,Feng-lai PEI,Ming-tao HOU,Qi-peng LI,Pei-qing LI,Yang-yang WANG,Wei-dong ZHANG. Modeling and selection scheme of proton exchange membrane fuel cell hydrogen supply system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1982-1995. |
| [3] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [4] | Kui-yang WANG,Ren HE. Recognition method of braking intention based on support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
| [5] | Qing GAO,Hao-dong WANG,Yu-bin LIU,Shi JIN,Yu CHEN. Experimental analysis on spray mode of power battery emergency cooling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1733-1740. |
| [6] | Jun-cheng WANG,Lin-feng LYU,Jian-min LI,Jie-yu REN. Optimal sliding mode ABS control for electro⁃hydraulic composite braking of distributed driven electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1751-1758. |
| [7] | Han-wu LIU,Yu-long LEI,Xiao-feng YIN,Yao FU,Xing-zhong LI. Multi⁃point control strategy optimization for auxiliary power unit of range⁃extended electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1741-1750. |
| [8] | Hong-bo YANG,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Nian-cheng GUO,Yan-yan ZHAO. Optimization of tooth surface modification based on a two-stage reduction gear system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1541-1551. |
| [9] | Guang-ming NIE,Bo XIE,Yan-tao TIAN. Design of cooperative adaptive cruise control algorithm based on Frenet framework [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1687-1695. |
| [10] | Shuai HAO,Chuan-tai CHENG,Jun-nian WANG,Jun-yuan ZHANG,You YU. Ergonomic optimization and test evaluation of sports SUV cockpit layout design [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1477-1488. |
| [11] | Jia-xu ZHANG,Chong GUO,Chen WANG,Jian ZHAO,Xin-zhi WANG. Performance evaluation of automatic parking system based on hardware in the loop simulation platform [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1552-1560. |
| [12] | Chen HUA,Run-xin NIU,Biao YU. Methods and applications of ground vehicle mobility evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [13] | Xiong LI,Feng-chong LAN,Ji-qing CHEN,Fang TONG. Comparison of injuries in front impact between Hybird III dummy model and CHUBM human biomechanical model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1264-1272. |
| [14] | Ying-chao ZHANG,Yun-hang LI,Zi-yu GUO,Guo-hua WANG,Zhe ZHANG,Chang SU. Optimization of the aerodynamic drag reduction of a cab behind engine vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 745-753. |
| [15] | Wen-ku SHI,Shu-guang ZHANG,You-kun ZHANG,Zhi-yong CHEN,Yi-fei JIANG,Bin-bin LIN. Parameter identification of magnetorheological damper model with modified seagull optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 764-772. |
|
||