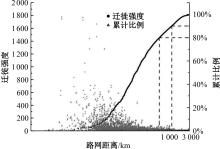
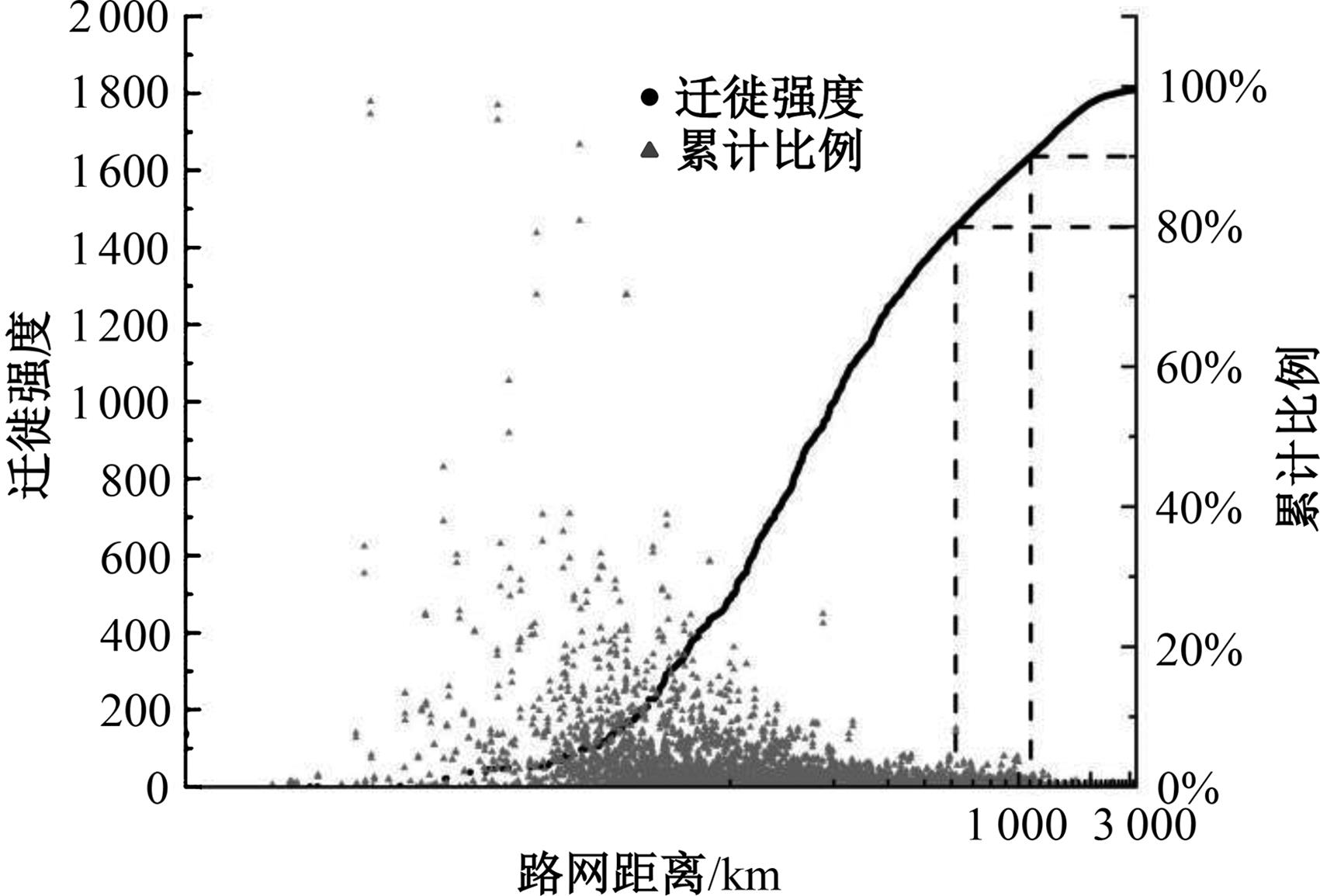
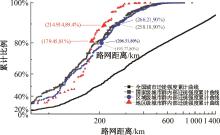
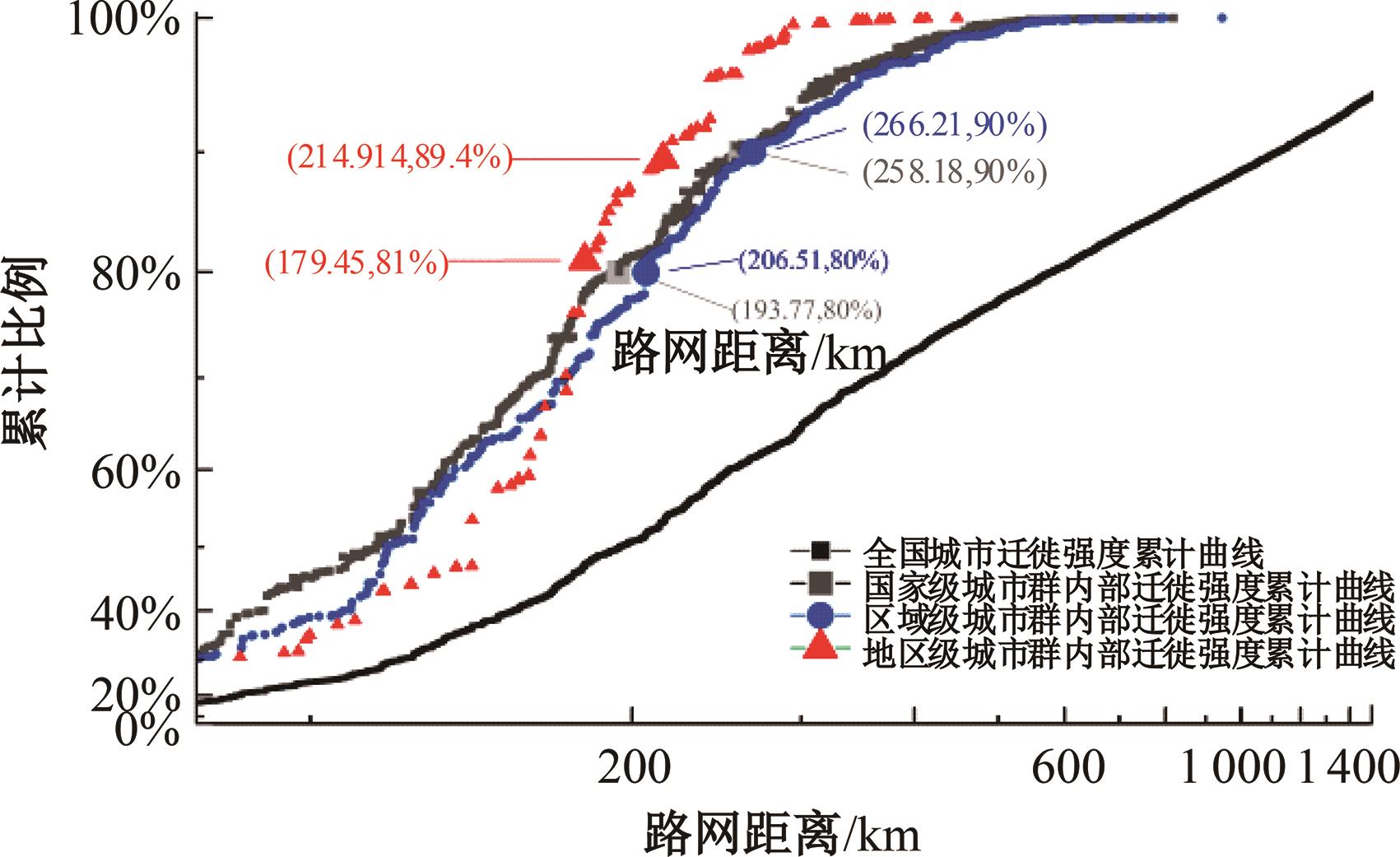
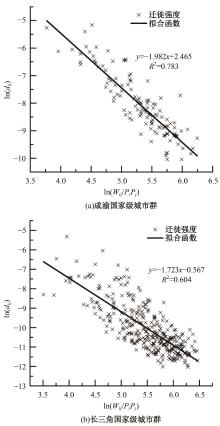
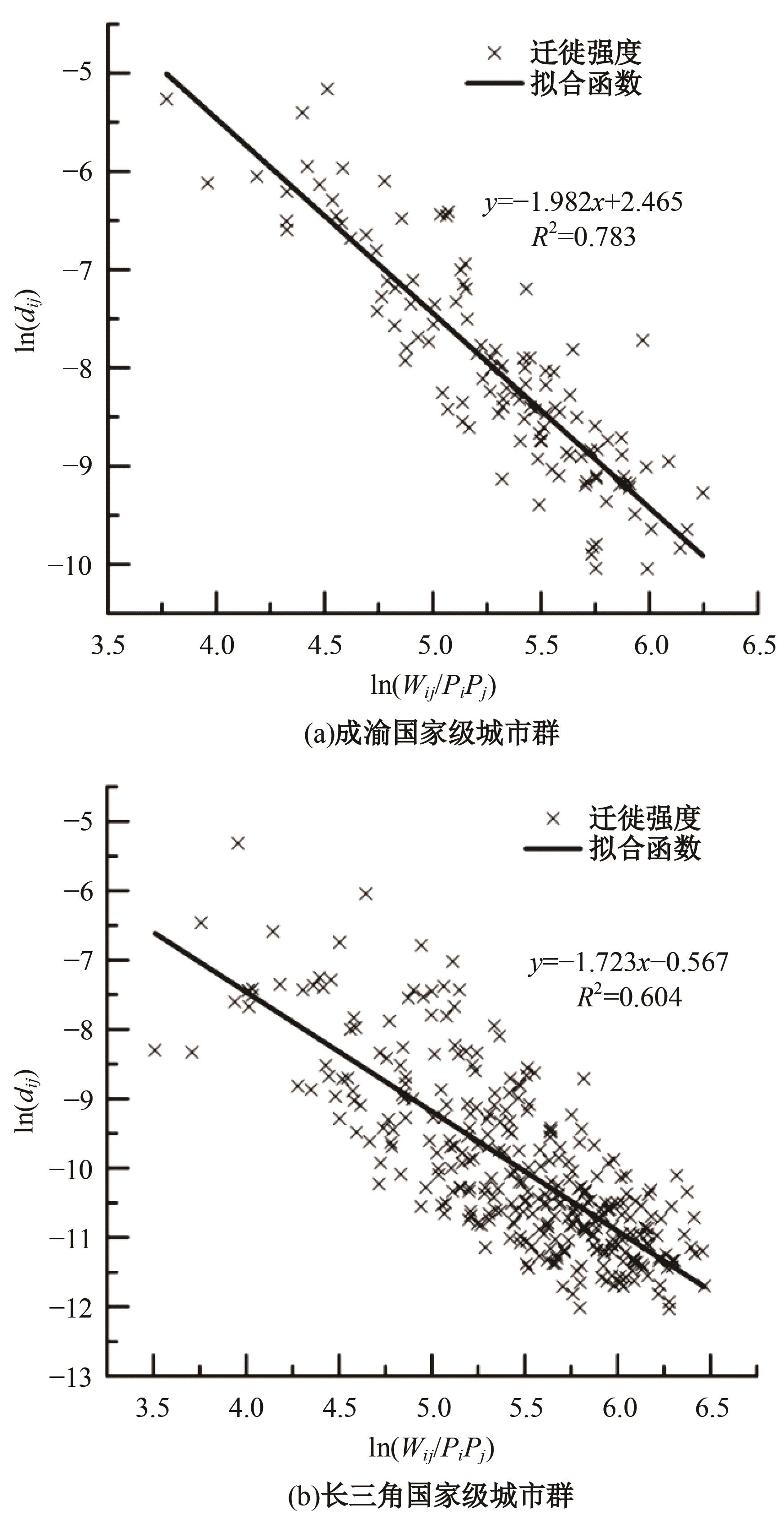
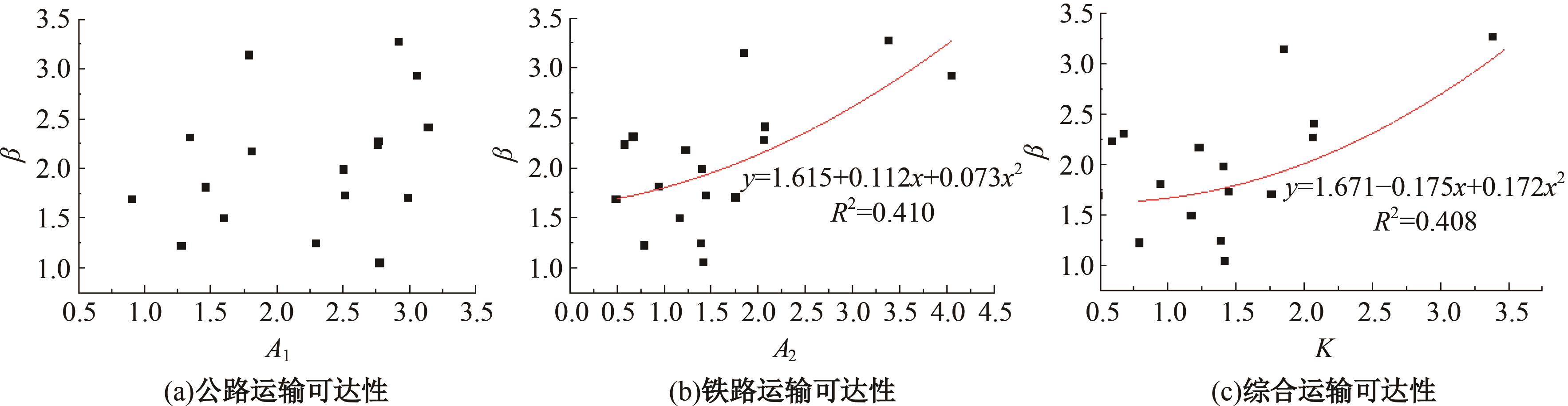
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3199-3208.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230017
Distance-decay effects of travel intensity within city clusters
Li-ying WEI1( ),Huan-huan PENG1,2
),Huan-huan PENG1,2
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.Transportation and Safety Research Institute,Zhejiang Scientific Research Institute of Transport,Hangzhou 310023,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | 冯慧芳,柏凤山,徐有基. 基于轨迹大数据的城市交通感知和路网关键节点识别[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(3): 42-47. |
| Feng Hui-fang, Bai Feng-shan, Xu You-ji. Urban traffic perception and critical node identification of road network based on trajectory big data[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(3): 42-47. | |
| 2 | 贾洪飞, 郭明雪, 罗清玉, 等. GPS数据下的城市路网关键路段识别[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Guo Ming-xue, Luo Qing-yu, et al. Identifying critical links of urban road netwoks based on GPS data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. | |
| 3 | Ding F, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, et al. Large-scale full-coverage traffic speed estimation under extreme traffic conditions using a big data and deep learning approach: case study in China[J]. Transportation Engineering Part A Systems, 2019, 145(5): 05019001. |
| 4 | 李自圆, 孙昊, 李林波. 基于手机信令数据的长三角全域城际出行网络分析[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 62(7): 1203-1211. |
| Li Zi-yuan, Sun Hao, Li Lin-bo. Analysis of intercity travel in the yangtze river delta based on mobile signaling data[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(7): 1203-1211. | |
| 5 | Shang Y, Li X G, Jia B, et al. Freeway traffic state estimation method based on multisource data[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part A Systems, 2022, 148(4): 4022005. |
| 6 | Soriguera F, Rosas D, Robuste F. Travel time measurement in closed toll highways[J]. Transportation Research Part B Methodological, 2010, 44(10): 1242-1267. |
| 7 | Lu X J, Ma C X. The impact of inter-city traffic restriction on COVID-19 transmission from spatial econometric perspective[J]. Promet-traffic & Transportation, 2021, 33(5): 705-716. |
| 8 | 王录仓, 刘海洋, 刘清. 基于腾讯迁徙大数据的中国城市网络研究[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(4): 853-869. |
| Wang Lu-cang, Liu Hai-yang, Liu Qing. China's city network based on Tencent's migration big data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(4): 853-869. | |
| 9 | Xu X L, Wang S H, Dong J H, et al. An analysis of the domestic resumption of social production and life under the COVID-19 epidemic[J]. Plos One, 2020, 15(7): 0236387. |
| 10 | 项昀, 徐铖铖, 于维杰, 等. 基于人口迁徙大数据的城市对外交通客运方式优势出行距离研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(1): 241-246. |
| Xiang Yun, Xu Cheng-cheng, Yu Wei-jie, et al. Dominant trip distance of urban external passenger transport mode based on big data of migration[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(1): 241-246. | |
| 11 | 王聪, 严洁. 百度迁徙规模指数构造方法反演[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2021, 50(4): 616-626. |
| Wang Cong, Yan Jie. An inversion of the constitution of the Baidu migration scale index[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021, 50(4): 616-626. | |
| 12 | 项昀, 王炜, 郑敦勇, 等. 区域综合网络货运交通方式的优势运距研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2016, 16(6): 33-39. |
| Xiang Yun, Wang Wei, Zheng Dun-yong, et al. Dominant transportation distance for multi transportation modes in regional integrated freight network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2016, 16(6): 33-39. | |
| 13 | 方创琳. 中国城市群地图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. |
| 14 | 陈卓, 金凤君, 杨宇, 等. 高速公路流的距离衰减模式与空间分异特征——基于福建省高速公路收费站数据的实证研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. |
| Chen Zhuo, Jin Feng-jun, Yang Yu, et al. Distance-decay pattern and spatial differentiation of expressway flow: an empirical study using data of expressway toll station in Fujian Province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. | |
| 15 | 刘瑜, 龚俐, 童庆禧. 空间交互作用中的距离影响及定量分析[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 50(3): 526-534. |
| Liu Yu, Gong Li, Tong Qing-xi. Quantifying the distance effect in spatial interactions[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2014, 50(3): 526-534. | |
| 16 | Hansen W G. How accessibility shapes land use[J]. Journal of the American Institute of Planners, 1959, 25(2): 73-76. |
| 17 | 徐明非, 欧晓培, 王元庆. 城市群公路可达性与衔接提升研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(11): 245-254. |
| Xu Ming-fei, Xiao-pei Ou, Wang Yuan-qing. Study on highway accessibility of urban agglomerations and its connection improvement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(11): 245-254. | |
| 18 | 戢晓峰, 郝京京, 陈方. 综合运输可达性与物流经济的空间分异及耦合[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(5): 24-31. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Hao Jing-jing, Chen Fang. Spatial differentiation and coupling between integrated transport accessibility and logistics economy[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(5): 24-31. |
| [1] | Tian-yang GAO,Da-wei HU,Rui-sen JIANG,Xue WU,Hui-tian LIU. Optimization study of zonal-based flexible feeder bus routes based on modular vehicle system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [2] | Shu-hong MA,Jun-jie ZHANG,Xi-fang CHEN,Guo-mei LIAO. Identifying urban functional structures using time-series taxi data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 603-613. |
| [3] | Yu-ran LI,Fei WANG,Cai-hua ZHU,Fei HAN,Yan LI. Chain-effect utility of factors influencing residents' commuting mode choice in polluted weather [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 577-590. |
| [4] | Hui-zhi XU,Shi-sen JIANG,Xiu-qing WANG,Shuang CHEN. Vehicle target detection and ranging in vehicle image based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [5] | Chang-jiang ZHENG,Tong-tong TAO,Zhi-chao CHEN. Cascading failure model based on adjustable redistribution of traffic flow [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [6] | Xiao-yue WEN,Guo-min QIAN,Hua-hua KONG,Yue-jie MIU,Dian-hai WANG. TrafficPro: a framework to predict link speeds on signalized urban traffic network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [7] | Yun-juan YAN,Wei-xiong ZHA,Jun-gang SHI,Li-ping YAN. Double layer optimization model of charging pile based on random charging demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [8] | Da-yi QU,Hao-min LIU,Zi-yi YANG,Shou-chen DAI. Dynamic allocation mechanism and model of traffic flow in bottleneck section based on vehicle infrastructure cooperation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [9] | Gui-zhen CHEN,Hui-ting CHENG,Cai-hua ZHU,Yu-ran LI,Yan LI. A risk evaluation method for urban intersections considering drivers' physiological information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [10] | Xiao-hua ZHAO,Chang LIU,Hang QI,Ju-shang OU,Ying YAO,Miao GUO,Hai-yi YANG. Influencing factors and heterogeneity analysis of highway traffic accidents [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [11] | Xiu-jian YANG,Xiao-han JIA,Sheng-bin ZHANG. Characteristics of mixed traffic flow taking account effect of dynamics of vehicular platoon [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [12] | Bo-song FAN,Chun-fu SHAO. Urban rail transit emergency risk level identification method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [13] | Chang-jiang ZHENG,Huan HU,Mu-qing DU. Design of multimodal express delivery network structure considering hub failure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [14] | Dian-hai WANG,You-wei HU,Zheng-yi CAI,Jia-qi ZENG,Wen-bin YAO. Dynamic road resistance model of intermittent flow on urban roads based on BPR function [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [15] | Yan-bo LI,Bai-song LIU,Bo-bin YAO,Jun-shuo CHEN,Kai-fa QU,Qi-sheng WU,Jie-ning CAO. Location of electrical changing station of expressway considering stochastic characteristics of road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
|
||