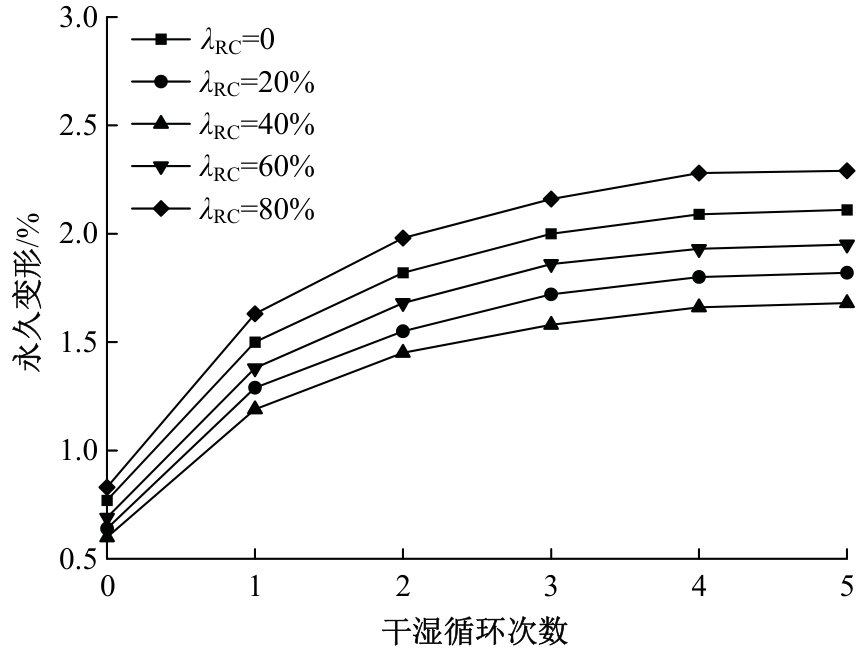
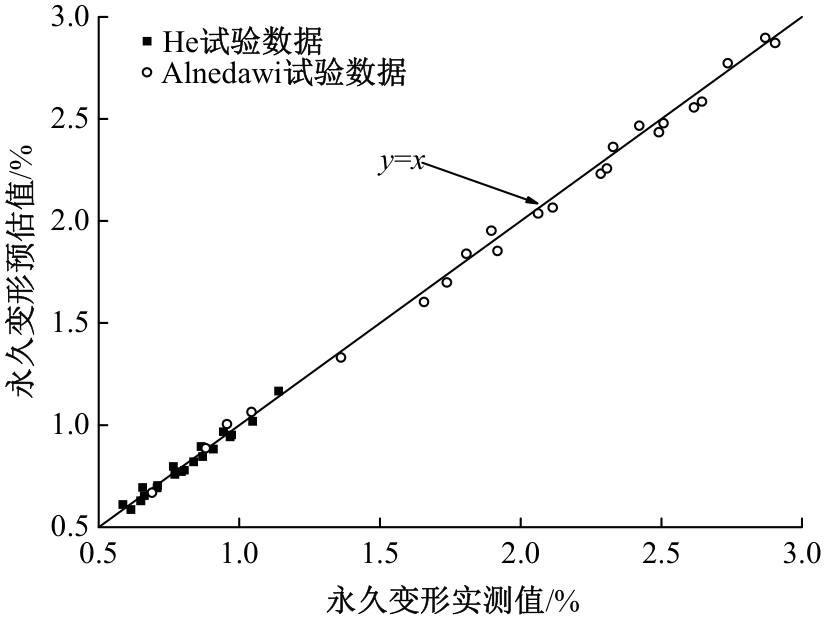
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3632-3640.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240195
Strength and deformation characteristics of gangue-red clay subgrade in hot and humid areas in south China
Bing-xu WEI1( ),Jing ZENG1,Chu-fang CHEN2
),Jing ZENG1,Chu-fang CHEN2
- 1.School of Transportation Engineering,Changsha University of Science & Technology,Changsha 410114,China
2.Guangxi Road Construction Engineering Group Co. ,Ltd,Nanning 530029,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| [1] | 石晓莉, 杜根杰, 杜建磊, 等. 大宗工业固体废物综合利用产业存在的问题及建议[J]. 现代矿业, 2022, 38(6): 227-229. |
| Shi Xiao-li, Du Gen-jie, Du Jian-lei, et al. Problems and suggestions on comprehensive utilization of bulk industrial solid waste[J].Modern Mining,2022,38(6):227-229. | |
| [2] | 张军辉, 丁乐, 张安顺. 建筑垃圾再生料在路基工程中的应用综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 135-154. |
| Zhang Jun-hui, Ding Le, Zhang An-shun. Application of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste in subgrade engineering:a review[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2021,34(10): 135-154. | |
| [3] | Azam A M, Cameron D A, Rahman M M. Model for prediction of resilient modulus incorporating matric suction for recycled unbound granular materials[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2013, 50(11): 1143-1158. |
| [4] | Delongui, Lucas, Matuella, et al. Construction and demolition waste parameters for rational pavement design[J].Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 168(20): 105-112. |
| [5] | 邱继生, 侯博雯, 关虓, 等. 煤矸石理化性质对混凝土抗压强度的影响[J]. 非金属矿,2019,42(2):29-32. |
| Qiu Ji-sheng, Hou Bo-wen, Guan Xiao, et al. Effect of physical and chemical properties of coal gangue under different stratas on compressive strength of concrete[J]. Non-Metallic Mines,2019,42(2):29-32. | |
| [6] | 贺建清, 靳明, 阳军生. 掺土煤矸石的路用工程力学特性及其填筑技术研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(5): 87-93. |
| He Jian-qing, Jin Ming, Yang Jun-sheng.A study on the road engineering mechanical properties of coal gangue mixed with clay and the filling techniques[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008,41(5) : 87-93. | |
| [7] | 朱小钢. 干湿循环作用下煤矸石路基材料应用性能研究[J]. 西部交通科技, 2023(4): 36-38, 78. |
| Zhu Xiao-gang. Research on the application performance of coal gangue roadbed materials under the action of dry and wet cycling[J].Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2023(4): 36-38, 78. | |
| [8] | 王学广, 李震, 康楠, 等. 改良土换填法与石灰桩法加固膨胀土边坡比较[J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(5):129-134. |
| Wang Xue-guang, Li Zhen, Kang Nan, et al. Numerical analysis of expansive soil slope reinforced by improved soil replacement method and lime pile method[J]. Yellow River,2019,41(5):129-134. | |
| [9] | 曲英杰, 毛伟兵, 孙玉霞, 等. 引黄泥沙对黏质盐土饱和导水率的影响[J]. 人民黄河, 2021, 43(5): 158-162. |
| Qu Ying-jie, Mao Wei-bing, Sun Yu-xia, et al. Effects of sand-mixingon saturated water permeability of clay saline soil[J]. Yellow River, 2021,43(5):158-162. | |
| [10] | 沈卓恒, 阮世强. 软土地层路基工后沉降预测及控制研究[J]. 交通科学与工程, 2020, 36(4): 17-21. |
| Shen Zhuo-heng, Ruan Shi-qiang.Study on prediction and control of post-construction settlement of subgrade in the soft soil layer[J]. Journal of Transport Science and Engineering,2020,36(4):17-21. | |
| [11] | Lin P, Tang L, Ni P. Field evaluation of subgrade soils under dynamic loads using orthogonal earth pressure transducers[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 121: 12-24. |
| [12] | Seed H B, Mcneill R L. Soil deformations in normal compression and repeated loading tests[J]. Highway Research Board Bulletin, 1956, 141: 44-53. |
| [13] | Hargis L L. A study of strain characteristics in a limestone gravel subjected to repetitive loading[D].Texas: Texas A&M University, 1963. |
| [14] | Wolff H, Visser A T. Incorporating elasto-plasticity in granular layer pavement design[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers Transport, 1994, 105(4): 259-272. |
| [15] | Monismith C L, Ogawa N, Freeme C. Permanent deformation characteristics of subgrade soils due to repeated loading[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1975, 537: 1-17. |
| [16] | Zhang Y, Kong L W, Guo A G, et al. Cumulative plastic strain of saturated soft clay under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(6): 1542-1548. |
| [17] | Puppala A J, Saride S, Chomtid S. Experimental and modeling studies of permanent strains of subgrade soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(10): 1379-1389. |
| [18] | Gabr A R, Cameron D A. Permanent strain modeling of recycled concrete aggregate for unbound pavement construction[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2012, 25(10): 1394-1402. |
| [19] | Azam A, Cameron D, Rahman M. Permanent strain of unsaturated unbound granular materials from construction and demolition waste[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27(3): 04014125. |
| [20] | Xu F, Zhai B, Leng W M, et al. Probabilistic method for evaluating the permanent strain of unbound granular materials under cyclic traffic loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 251(7): 118975. |
| [21] | Arulrajah A, Mohammadinia A, Maghool F, et al. Tire derived aggregates as a supplementary material with recycled demolition concrete for pavement applications[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 230: 129-136. |
| [22] | Zhang S, Tang C, Hu P, et al. Reversible and irreversible strain behavior of frozen aeolian soil under dynamic loading [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(3): 245-253. |
| [23] | He Z M, Xiang D, Liu Y X, et al. Deformation behavior of coarse-grained soil as an embankment filler under cyclic loading[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020(3): 1-13. |
| [24] | Alnedawi A, Nepal K P, Alameri R. New shakedown criterion and permanent deformation properties of unbound granular materials[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2019, 27(2): 108-119. |
| [1] | Bo LI,Yuan LIANG,Yun-dong MA,Lu YU. Intelligent monitoring and early warning for freeze⁃thaw instability of high⁃speed railway tunnel portal slopes in cold regions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2985-2997. |
| [2] | Ling XU,Xiao-bing WANG,Jie YUAN,Hua-ping REN,Yi-feng HAN,Xi-yong XU. Controlled low strength materials based on silty sand and its properties in narrow backfill zone [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2657-2668. |
| [3] | Yao-gang TIAN,Jing JIANG,Cheng ZHAO,Xiao-min YANG,Jun ZHANG,Kan JIA. Temperature resistance mechanism of high-early-strength cement mortar modified with waterborne epoxy resin [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2203-2211. |
| [4] | Kang YAO,Qiao DONG,Xue-qin CHEN,Bin SHI,Shi-ao YAN,Xiang WANG. Mixed⁃mode mesoscale fracture behavior of concrete based on a phase field regularized cohesive zone model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2286-2297. |
| [5] | Zhi-you LONG,Zhao-long WAN,Shi DONG,Chao YANG,Xiao-yang LIU. Displacement prediction of highway slope based on variational mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2320-2332. |
| [6] | Wan-feng WEI,Hong-gang ZHANG,Yang-peng ZHANG,Fan YANG,Bo-ming TANG,Ling-yun KONG. Research progress on modification mechanism, preparation and performance of waste rubber powder modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1834-1853. |
| [7] | Zhen YANG,Rui-ping ZHENG,Zhe GONG. Highway infrastructure performance and traffic state prediction on road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1973-1983. |
| [8] | An-shun ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Feng GAO. Shear properties and stress-strain relationships characterization of Changsha compacted clay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1604-1616. |
| [9] | Li-ming WANG,Zi-kun SONG,Hui ZHOU,Wen WEI,Hao YUAN. Rheological response and response mechanism of petroleum asphalt treated with ultrasound [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1346-1355. |
| [10] | Jun-peng XU,Chuan-feng ZHENG,Yan-tao DU,Yu-hang WANG,Zheng LU,Wen-jun FAN. Damage effects of water⁃heat⁃force coupling in permeable asphalt mixture in cold region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 877-887. |
| [11] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [12] | Yan-hai YANG,Bai-chuan LI,Ye YANG,Chong-hua WANG,Liang YUE. Aggregate ellipsoidal surface base reconstruction with virtual splitting tests [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 653-663. |
| [13] | Teng-fei NIAN,Zhao HAN,Zhi-qiang WEI,Guo-wei WANG,Jin-guo GE,Ping LI. Mesoscopic numerical modeling method of asphalt mix considering aggregate morphology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 639-652. |
| [14] | Zheng-feng ZHOU,Hu-cheng TANG,Xin-wang OU. Simulation analysis on SCB test of asphalt concrete using cohesive zone model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 3955-3963. |
| [15] | Liu YANG,Hong-hui LI,Wen-fang LI. Distance between upstream transition zones of freeway work zone considering automatic cars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3604-3613. |
|
||