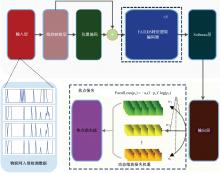
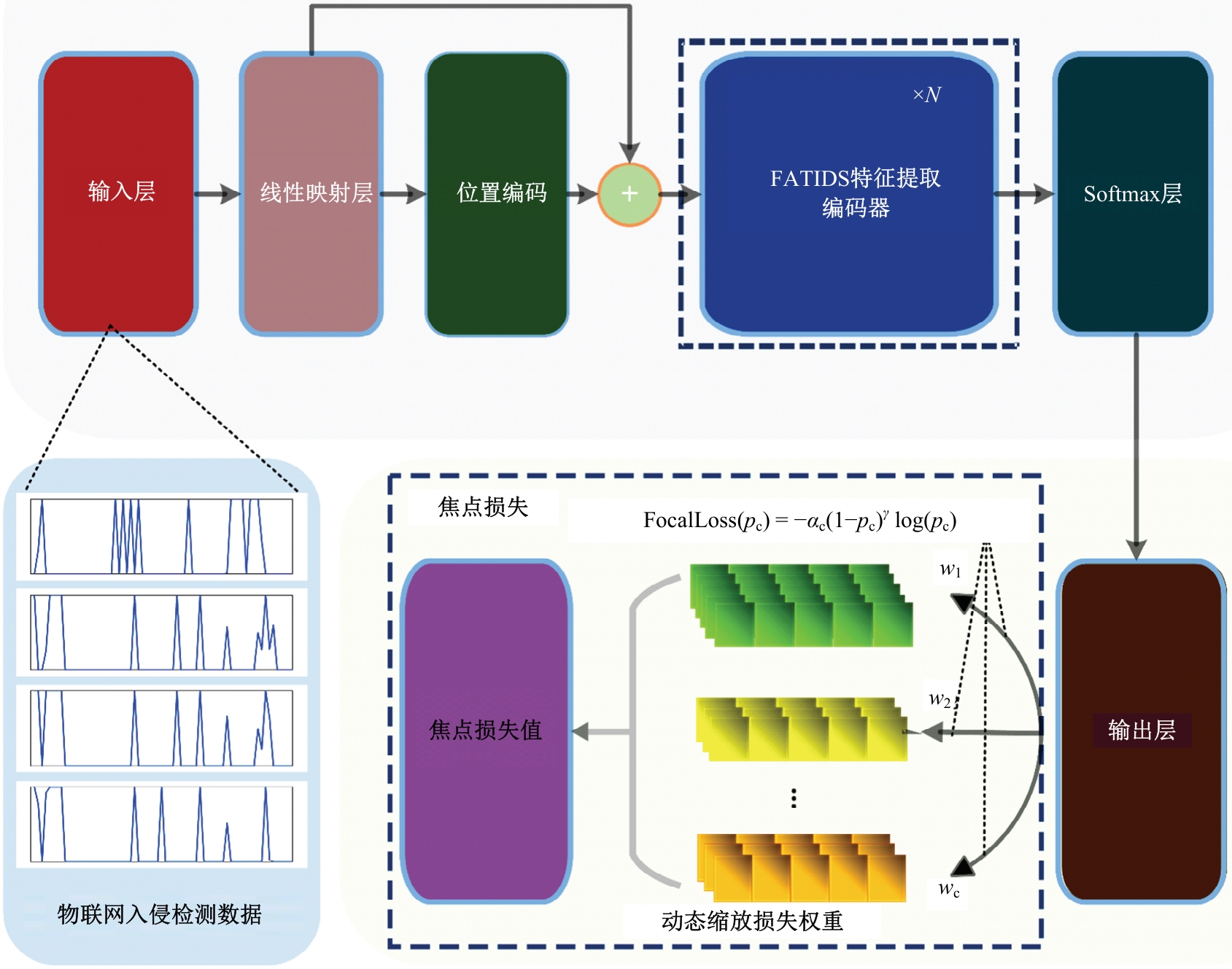
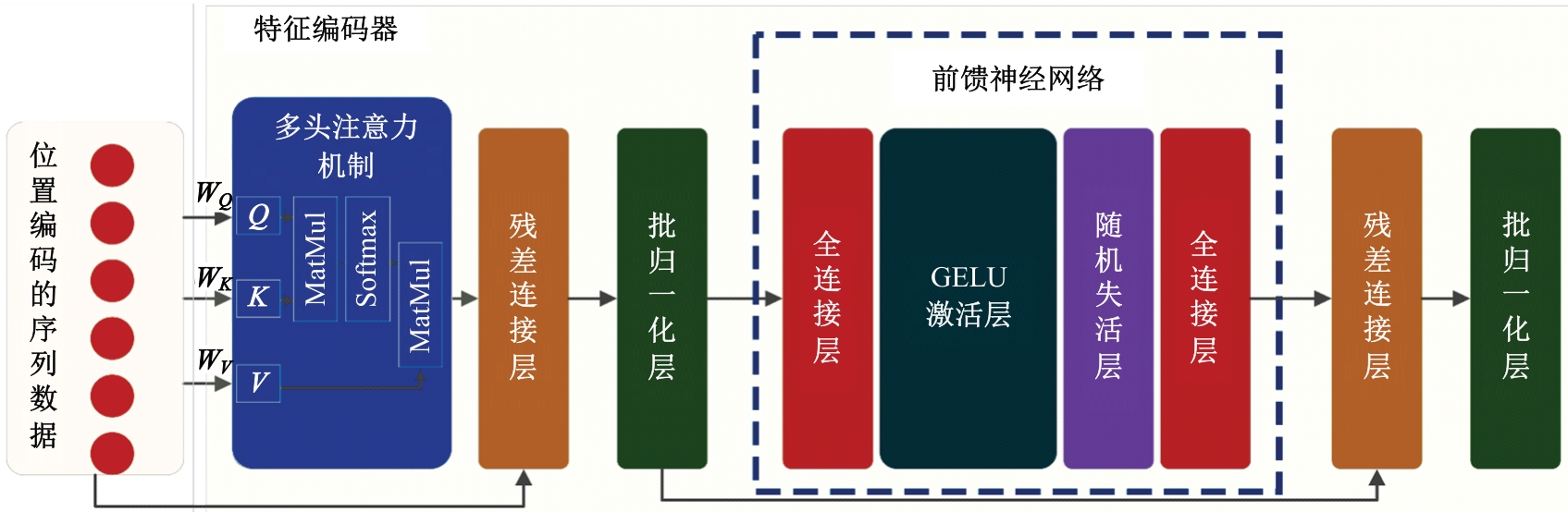
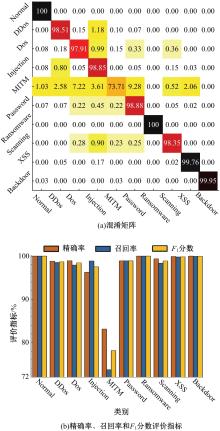
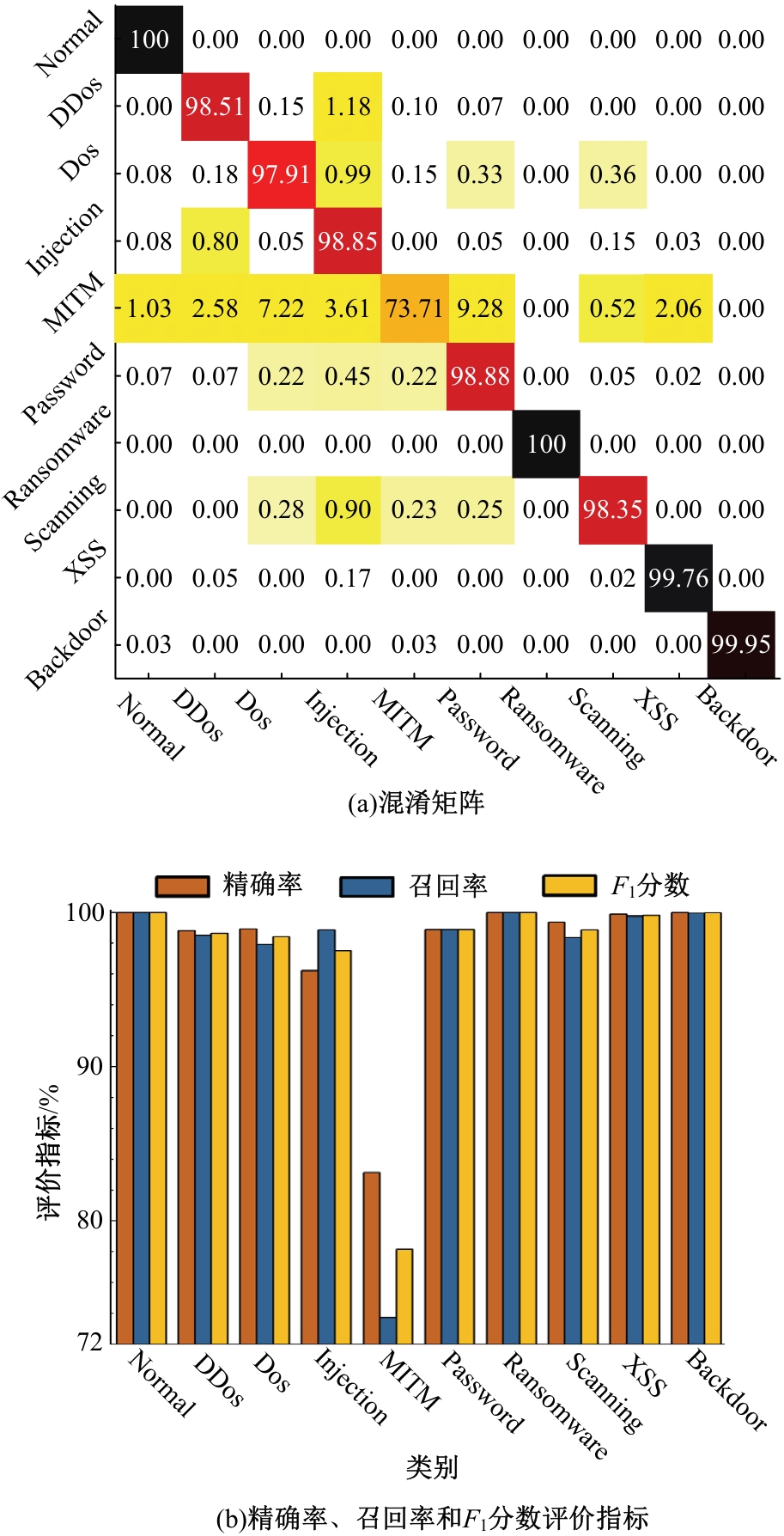
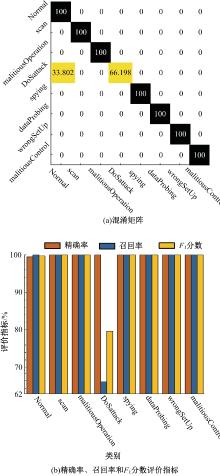
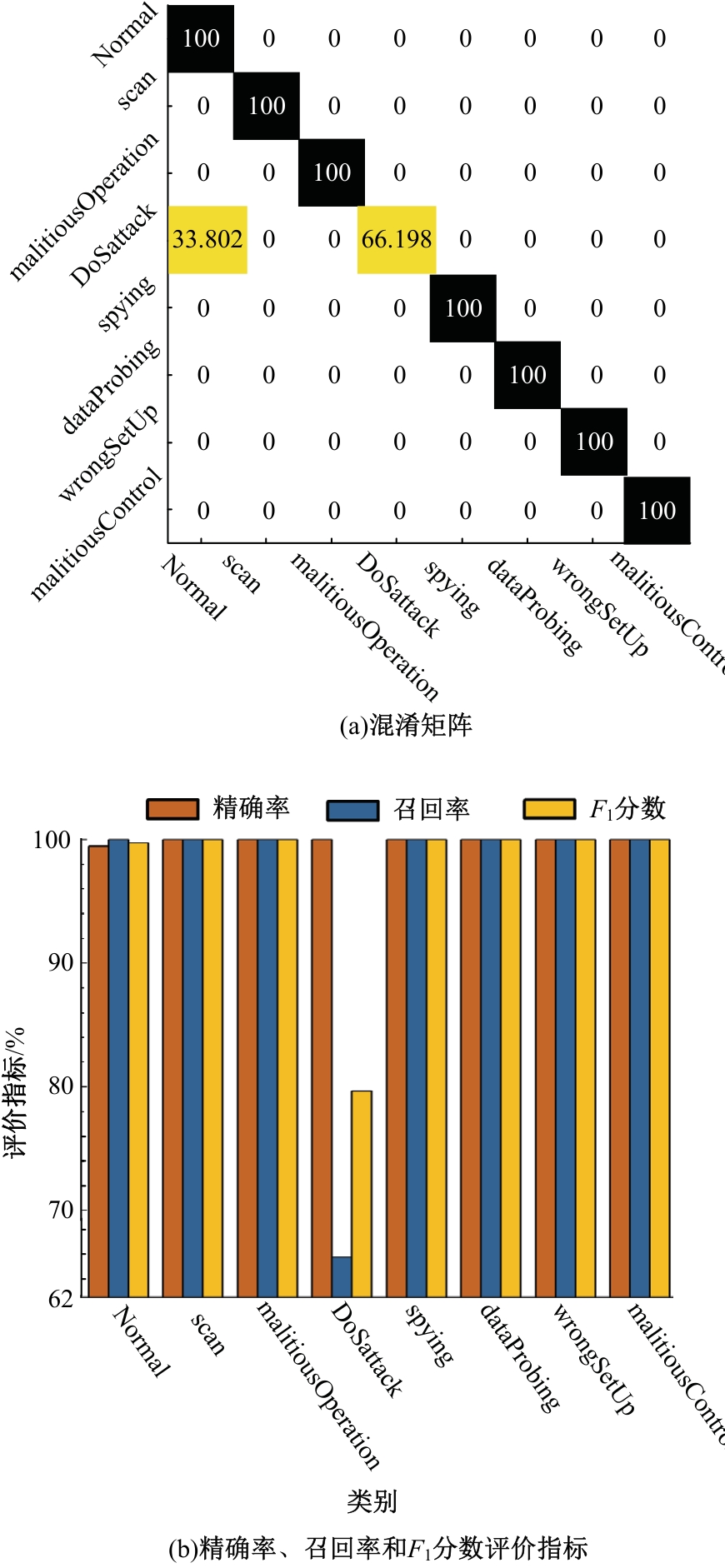
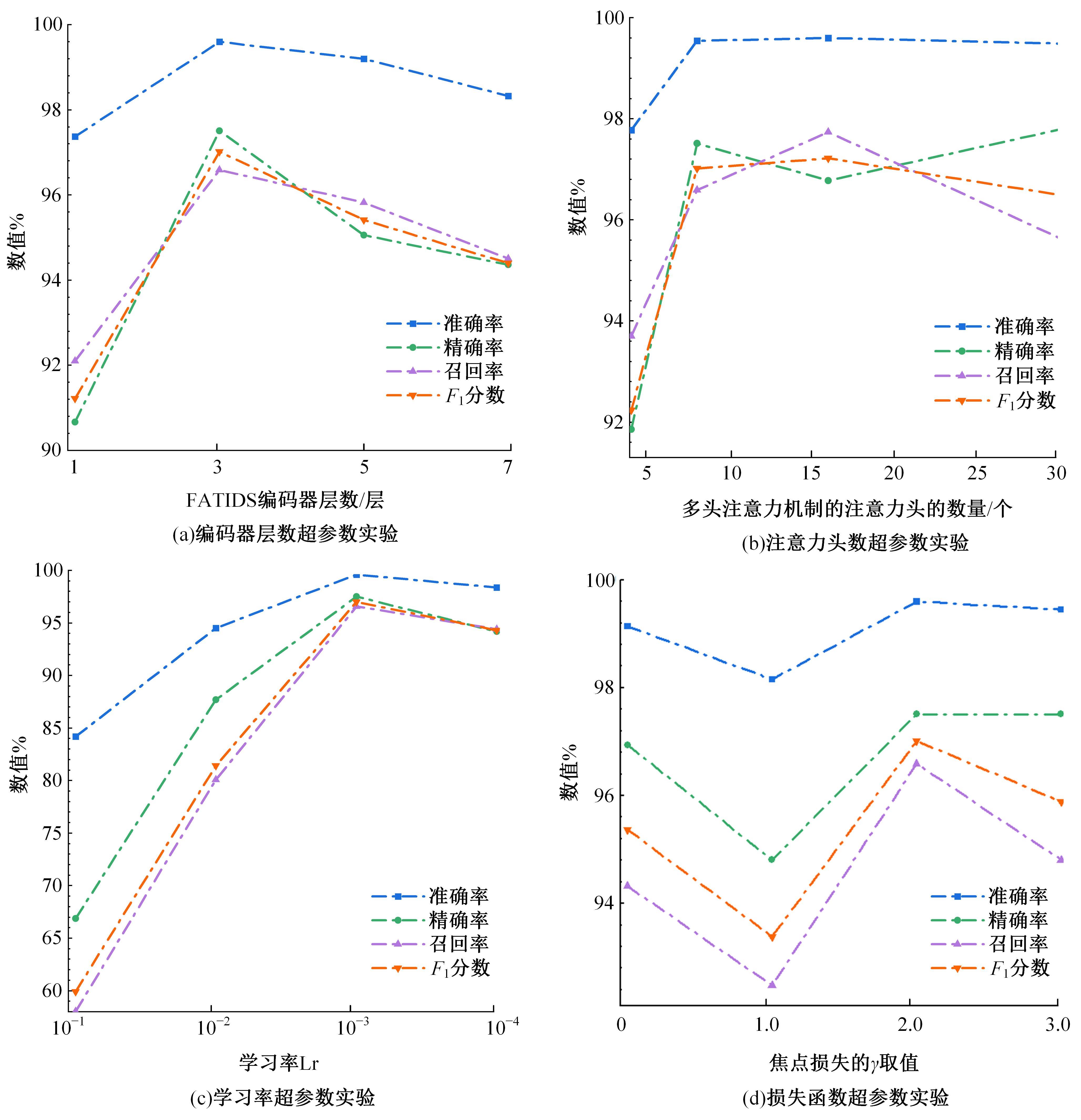
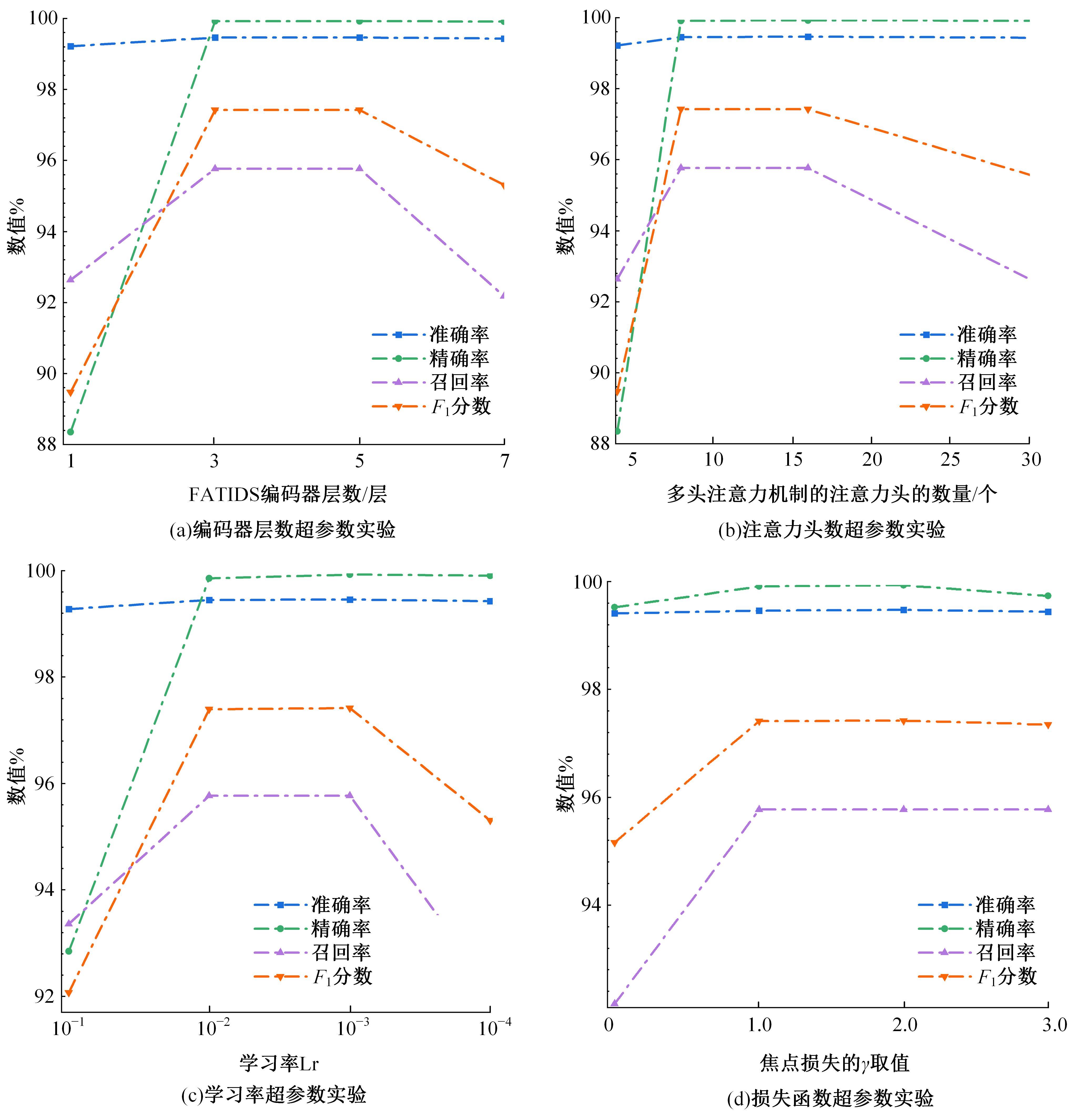
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 3986-3999.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240403
FATIDS: an IoT intrusion detection method for class⁃imbalanced samples
Peng WANG( ),Ya-fei SONG,Xiao-dan WANG(
),Ya-fei SONG,Xiao-dan WANG( ),Yan-li LU,Qian XIANG
),Yan-li LU,Qian XIANG
- Air and Missile Defense College,Air Force Engineering University,Xi'an 710051,China
CLC Number:
- TP183
| [1] | Heidari A, Jabraeil J M A. Internet of Things intrusion detection systems: a comprehensive review and future directions[J]. Cluster Computing, 2022, 1: 1-28. |
| [2] | Kaur B, Dadkhah S, Shoeleh F, et al. Internet of Things (IoT) security dataset evolution: challenges and future directions[J]. Internet of Things, 2023, 22: No.100780. |
| [3] | Khraisat A, Alazab A. A critical review of intrusion detection systems in the Internet of Things: techniques, deployment strategy, validation strategy, attacks, public datasets and challenges[J]. Cybersecurity, 2021, 4(1): No.18. |
| [4] | Alani M M, Awad A I. An intelligent two-layer intrusion detection system for the Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(1): 683-692. |
| [5] | Pajouh H H, Javidan R, Khayami R, et al. A Two-layer dimension reduction and two-tier classification model for anomaly-based intrusion detection in IoT backbone networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2019, 7(2): 314-323. |
| [6] | Saba T, Sadad T, RehmaN A, et al. Intrusion detection system through advance machine learning for the Internet of Things networks[J]. IT Professional, 2021, 23(2): 58-64. |
| [7] | Albulayhi K, Abu Al-haija Q, Alsuhibany S A, et al. IoT intrusion detection using machine learning with a novel high performing feature selection method [J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(10): No.5015. |
| [8] | Islam N, Farhin F, Sultana I, et al. Towards machine learning based intrusion detection in IoT networks[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2021, 69(2): 1801-1821. |
| [9] | Saba T, Rehman A, Sadad T, et al. Anomaly-based intrusion detection system for IoT networks through deep learning model[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 99: No.107810. |
| [10] | Abd Elaziz M, Al-qaness M A A, Dahou A, et al. Intrusion detection approach for cloud and IoT environments using deep learning and capuchin search algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2023, 176: No.103402. |
| [11] | Almiani M, Abughazleh A, Al-rahayfeh A, et al. Deep recurrent neural network for IoT intrusion detection system[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2020, 101: No. 102031. |
| [12] | Jeyanthi D V, Indrani B. IoT-based intrusion detection system for healthcare using RNNBiLSTM deep learning strategy with custom features[J]. Soft Computing, 2023, 27(16): 11915-11930. |
| [13] | 李晓佳, 赵国生, 汪洋, 等. 面向CNN和RNN改进的物联网入侵检测模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2023, 59(14): 242-250. |
| Li Xiao-jia, Zhao Guo-sheng, Wang Yang, et al. Improved intrusion detection model of Internet of Things for CNN and RNN[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(14): 242-250. | |
| [14] | Altunay H C, Albayrak Z. A hybrid CNN+LSTM-based intrusion detection system for industrial IoT networks[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2023, 38: No. 101322. |
| [15] | Dina A S, Siddique A B, Manivannan D. A deep learning approach for intrusion detection in Internet of Things using focal loss function[J]. Internet of Things, 2023, 22: No. 100699. |
| [16] | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J/OL].[2024-04-02]. |
| [17] | Alsaedi A, Moustafa N, Tari Z, et al. TON_IoT telemetry dataset: a new generation dataset of IoT and IIoT for data-driven intrusion detection systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 165130-165150. |
| [18] | Khare S, Totaro M. Ensemble learning for detecting attacks and anomalies in IoT smart home[C]∥3rd International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security (ICDIS), South Padre Island, USA, 2020:56-63. |
| [19] | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS'17), HookRed, USA, 2017: 6000-6010. |
| [20] | Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]∥Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference,Lille, France,2015: 448-456. |
| [21] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[J/OL]. [2024-04-03]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| [22] | Aguiar G, Krawczyk B, Cano A. A survey on learning from imbalanced data streams: taxonomy, challenges, empirical study, and reproducible experimental framework[J]. Machine Learning, 2024,113: 4165-4243. |
| [23] | Wang Z G, Oates T. Imaging time-series to improve classification and imputation[J/OL]. [2024-04-04]. |
| [24] | Lo W W, Layeghy S, Sarhan M, et al. E-GraphSAGE: a graph neural network based intrusion detection system for IoT[C]∥NOMS 2022-2022 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Budapest, Hungary, 2022: 1-9. |
| [25] | Čeponis D, Goranin N. Investigation of dual-flow deep learning models LSTM-FCN and GRU-FCN efficiency against single-flow CNN models for the host-based intrusion and malware detection task on univariate times series data[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(7): No.2373. |
| [26] | Fauvel K, Lin T, Masson V, et al. XCM: an explainable convolutional neural network for multivariate time series classification[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(23): No. 3137. |
| [27] | Zerveas G, Jayaraman S, Patel D, et al. A transformer-based framework for multivariate time series representation learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual Event, Singapore, 2021:2114-2124. |
| [28] | Hasan M, Islam M, Islam I, et al. Attack and anomaly detection in IoT sensors in IoT sites using machine learning approaches[J].Internet of Thing, 2019,7: No. 100059. |
| [29] | Benaddi H, Jouhari M, Ibrahimi K, et al. Anomaly detection in industrial IoT using distributional reinforcement learning and generative adversarial networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(21): No. 8085. |
| [30] | Huma Z E, Latif S, Ahmad J, et al. A hybrid deep random neural network for cyberattack detection in the Industrial Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 55595-55605. |
| [31] | Bai S J, Kolter J Z, Koltun V. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling[J/OL].[2024-04-06]. |
| [1] | Jiang-bo YU,Jian-cheng WENG,Peng-fei LIN,Yu-xing SUN,Jiao-long CHAI. Passenger flow prediction model of external transportation hub based on hybrid Transformer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2251-2259. |
| [2] | Guang-wen LIU,Xin-yue XIE,Qiang FU,Hua CAI,Wei-gang WANG,Zhi-yong MA. Spatiotemporal Transformer with template attention for target tracking [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1037-1049. |
| [3] | Lei JIANG,Zi-qi WANG,Zhen-yu CUI,Zhi-yong CHANG,Xiao-hu SHI. Visual Transformer based on a recurrent structure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2049-2056. |
| [4] | Li-ming LIANG,Long-song ZHOU,Jiang YIN,Xiao-qi SHENG. Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [5] | De-xing WANG,Kai GAO,Hong-chun YUAN,Yu-rui YANG,Yue WANG,Ling-dong KONG. Underwater image enhancement based on color correction and TransFormer detail sharpening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 785-796. |
| [6] | Jian LI,Qi XIONG,Ya-ting HU,Kong-yu LIU. Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden Markov model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [7] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Wheel odometry error prediction model based on transformer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [8] | Xiao-ran GUO,Ping LUO,Wei-lan WANG. Chinese named entity recognition based on Transformer encoder [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| [9] | WU Wei, DI Chong-feng, HU Ji-bin, YUAN Shi-hua. Adaptive reverse driving system based on hydraulic transformer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1906-1911. |
| [10] | WU Wei, DI Chong-feng, HU Ji-bin, YUAN Shi-hua. Static stiffness of hydraulic transformer controlled system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1130-1135. |
| [11] | YU He, QIN Gui-he, SUN Ming-hui, YAN Xin, WANG Xuan-zhe. Cyber security and anomaly detection method for in-vehicle CAN [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1246-1253. |
| [12] | MA De-yin, LIANG Yan-chun, GUAN Ren-chu, ZHAO Xiao-she, SHI Xiao-hu. Evaluation of transformer aging based on fuzzy theory and bidirectional associative memory neural networks [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1331-1337. |
| [13] | ZHAI Yuan, SUN Yue, SU Yu-gang, WANG Zhi-hui, TANG Chun-sen. Soft-switching push-pull converter of ICPT [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 1029-1034. |
| [14] | LIU Cheng-qiang, JIANG Ji-hai. Flow characteristic of inclined plate and axial plunger type hydraulic transformer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 85-90. |
| [15] | CHEN Yan-li, LIU Shun-an, SHANG Tao. Pulsating characteristic of optimal structure of hydraulic hybrid vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1326-1330. |
|
||