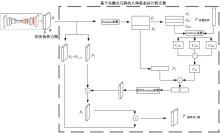
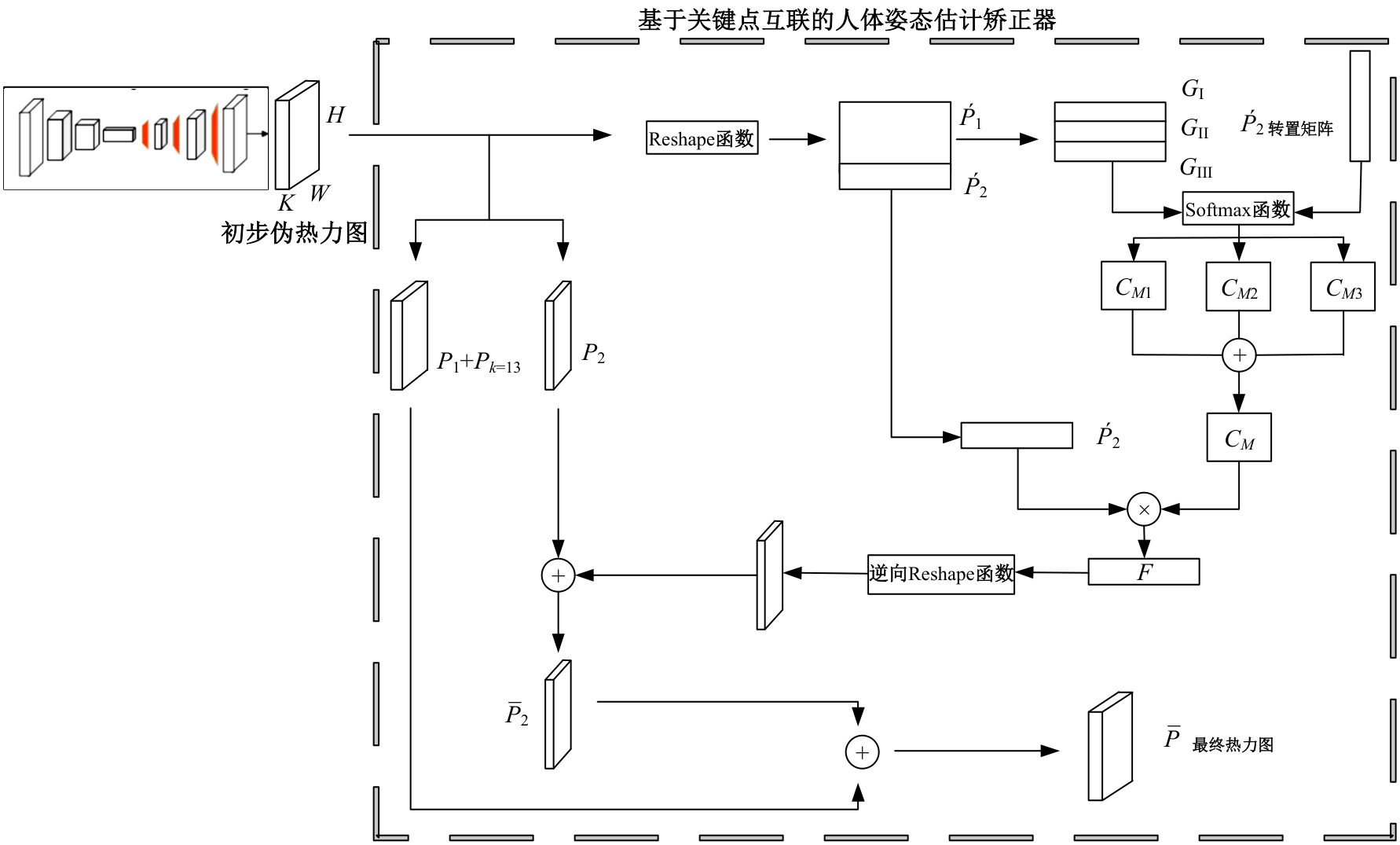
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 1061-1071.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230600
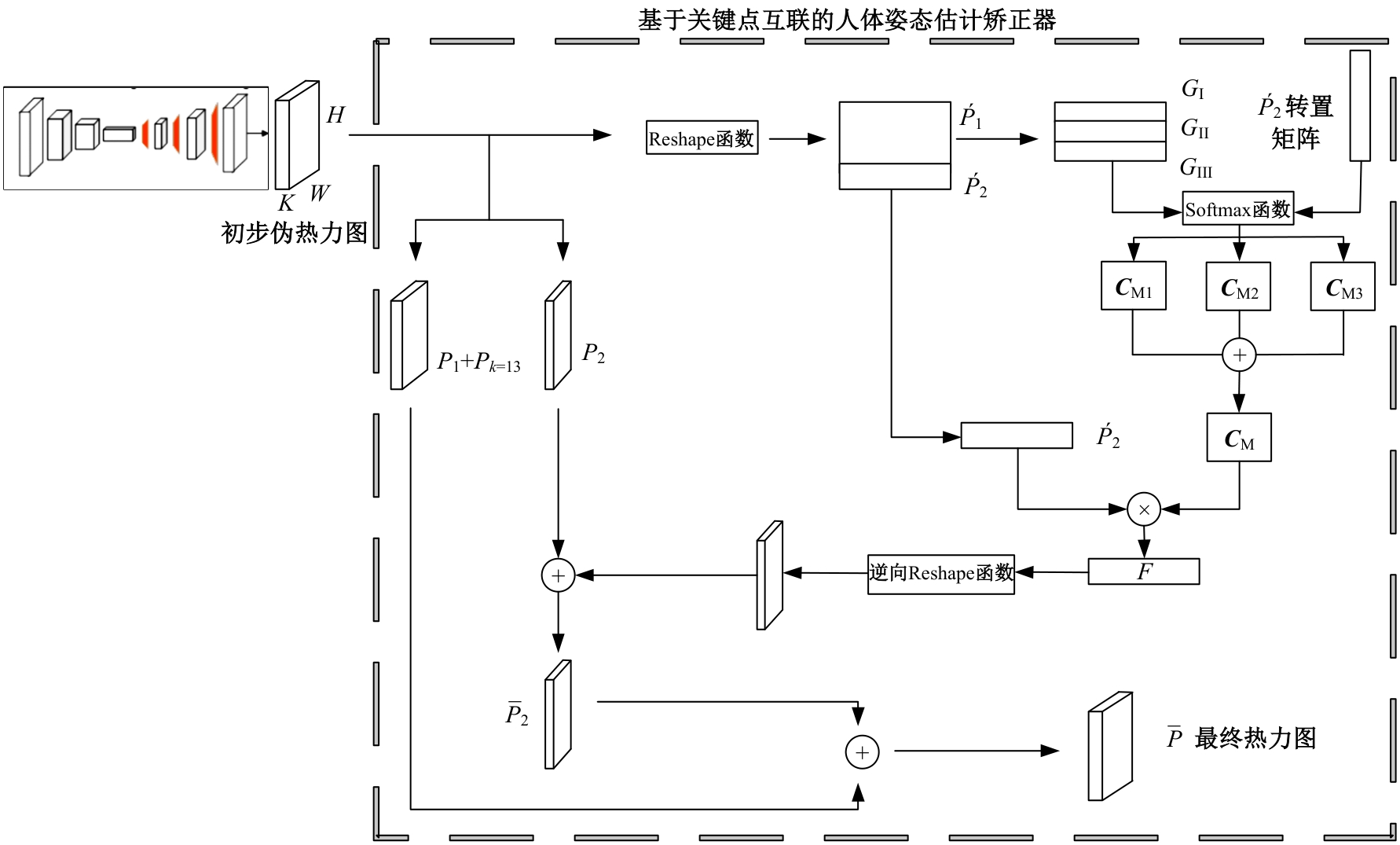
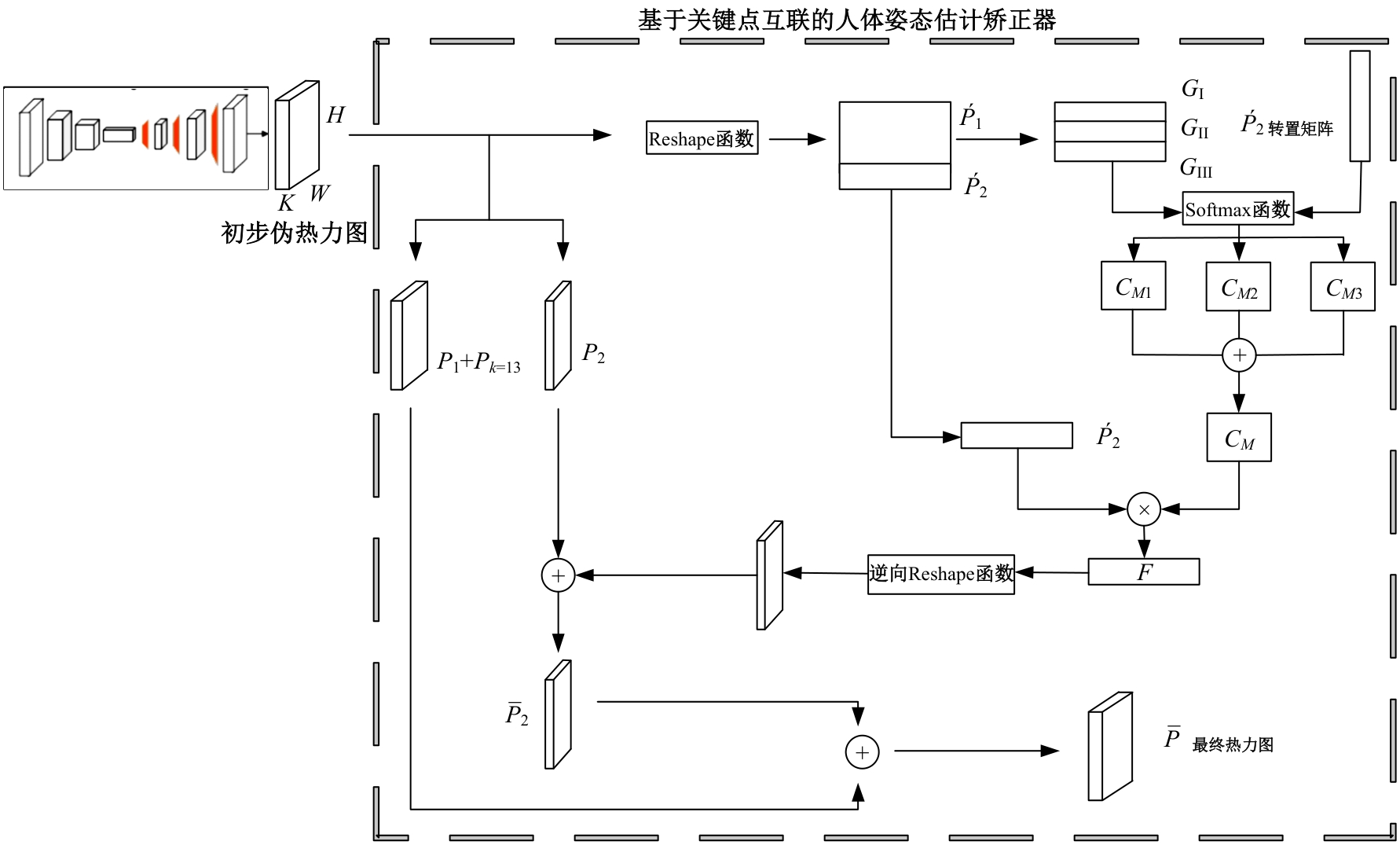
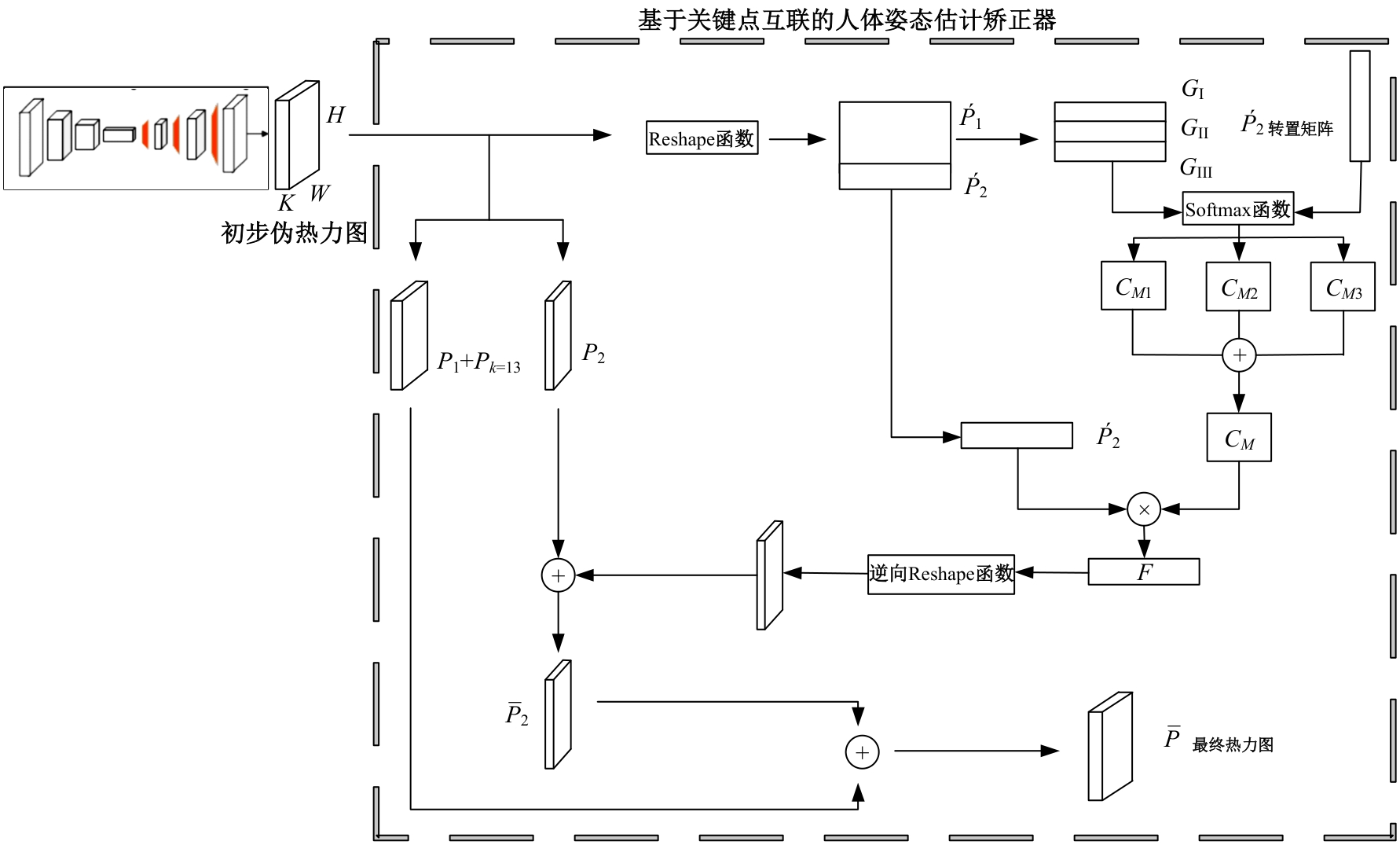
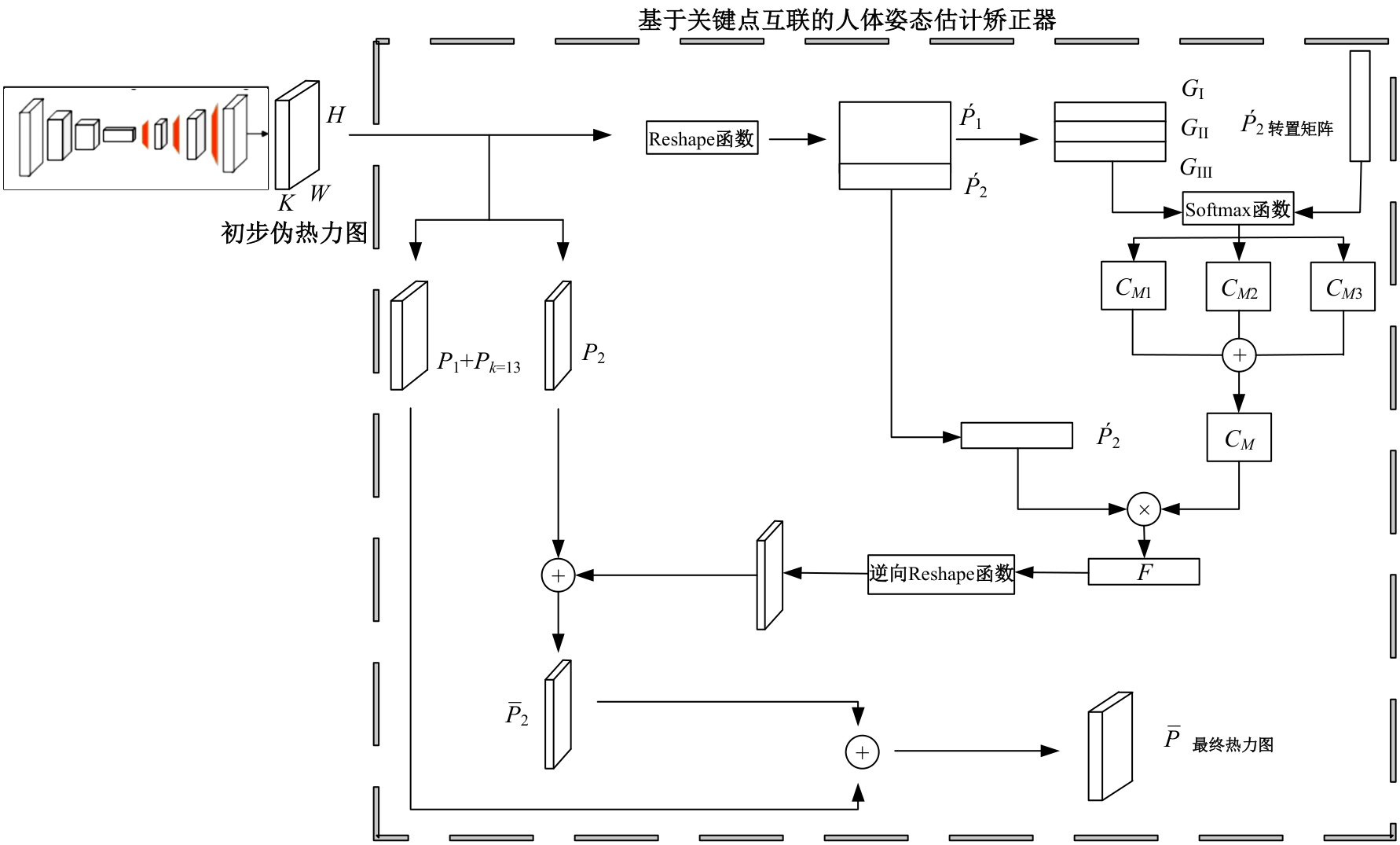
Human pose estimation corrector algorithm based on implicit key point interconnection
Hua CAI1( ),Rui-kun ZHU1,Qiang FU2,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3,Jun-xi SUN4
),Rui-kun ZHU1,Qiang FU2,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3,Jun-xi SUN4
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Opto-Electronic Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.No. 2 Department of Urology,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
4.College of Information Science and Technology,North Normal University,Changchun 130117,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Andriluka M, Iqbal U, Insafutdinov E, et al. PoseTrack:a benchmark for human pose estimation and tracking[C]∥IEEE / CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City,USA, 2018: 5167-5176. |
| 2 | Liu Q, Zhang Y, Bai S, et al. Explicit occlusion reasoning for multi-person 3D human pose estimation[C] ∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Switzerland, 2022: 497-517. |
| 3 | Wu H, Ma X, Li Y. Multi-level channel attention excitation network for human action recognition in videos[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2023, 114: No. 116940. |
| 4 | Nguyen P, Liu T, Prasad G, et al. Weakly supervised action localization by sparse temporal pooling network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 6752-6761. |
| 5 | Ren Z, Zhang Q, Gao X, et al. Multi-modality learning for human action recognition[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(11): 16185-16203. |
| 6 | Tang Y, Liu R. Skeleton embedding of multiple granularity attention network for human action recognition[C]∥International Conference on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 12878-12885. |
| 7 | Liang Z J, Wang X L, Huang R, et al. An expressive deep model for human action parsing from a single image[C]∥EEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Chengdu,China, 2014: 1-6. |
| 8 | Goh E S, Sunar M S, & Ismail A W. 3D object manipulation techniques in handheld mobile augmented reality interface: a review[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 40581-40601. |
| 9 | Yang X, Chen Y, Liu J, et al. Rapid prototyping of tangible augmented reality interfaces: towards exploratory learning for science education[J].Interactive Learning Environments, 2019, 27(4): 469-483. |
| 10 | Zhang D, Peng Y, Yang W, et al. Multi-viewpoint interaction with social robots: a case study of speech therapy for children with autism[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2018, 92(3/4): 359-3728. |
| 11 | Zhang R, Li J, Xiao T, et al. BodyPoseNet: body pose estimation driven by deep neural networks[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 99:No.116290. |
| 12 | Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4):834-848. |
| 13 | Zeng W, Gao Y, Zheng Y, et al. DenseReg: fully convolutional dense regression for accurate 3D human pose estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2830-2842. |
| 14 | Li J, Wang C, Zhu H, et al. Efficient crowded scenes pose estimation and a new benchmark[EB/OL].[2023-05-01]. |
| 15 | Moon G, Chang J Y, Lee K M. PoseFix: Model-agnostic general human pose refinement network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 7773-7781. |
| 16 | Zhou C, Chen S, Ding C, et al. Learning contextual and attentive information for brain tumor segmentation[C]∥Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, Granada, Spain, 2019: 497-507. |
| 17 | Ji X, Yang Q, Yang X, et al. Human pose estimation: multi-stage network based on HRNet[J]Journal of Physics, 2022, 2400(1): No.012034. |
| 18 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. |
| 19 | Papandreou G, Zhu T, Kanazawa N, et al. Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4903-4911. |
| 20 | Wei L, Zhang S, Dai J, et al. ST-GCN: spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City, USA, 2018: 7452-7461. |
| 21 | Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C,et al. U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: No.107404. |
| 22 | Zhou F, Zhu M, Bai J, et al. Deformable ConvNets v2: more deformable, better results[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City,USA, 2018: 9308-9316. |
| 23 | Carreira J, Agrawal P, Fragkiadaki K, et al. Associative embedding: end-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2274-2284. |
| 24 | Papandreou G, Zhu T, Chen L C, et al. PersonLab: person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany,2018: 282-299. |
| 25 | Kreiss S, Bertoni A, Alahi A. PifPaf: composite fields for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019:11977-11986. |
| 26 | Insafutdinov M, Pishchulin L, Andres B, et al. DeepCut: joint subset partition and labeling for multi person pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: No.533. |
| 27 | Newell A, Yang A, Deng J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, Holland, 2016 :483-499. |
| 28 | Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, et al. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City,USA, 2018: 7103-7112. |
| 29 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5693-5703. |
| 30 | Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y. Simple baseline for human pose estimation and tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 742-757. |
| 31 | Wei L, Zhang S, Yin W, et al. Convolutional pose machines[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Munich, Germany, 2016: 4724-4732. |
| 32 | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al.Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. |
| 33 | Lin G, Li Q, Li M, et al. A novel bottleneck-activated feedback neural network model for time series prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(4): 1621-1635. |
| 34 | Cao Z, Hidalgo Martinez G, Simon T, et al. OpenPose: realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 43(1): 172-186. |
| [1] | Guang-wen LIU,Xin-yue XIE,Qiang FU,Hua CAI,Wei-gang WANG,Zhi-yong MA. Spatiotemporal Transformer with template attention for target tracking [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1037-1049. |
| [2] | Sheng-jie ZHU,Xuan WANG,Fang XU,Jia-qi PENG,Yuan-chao WANG. Multi-scale normalized detection method for airborne wide-area remote sensing images [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [3] | Ming-hui SUN,Hao XUE,Yu-bo JIN,Wei-dong QU,Gui-he QIN. Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [4] | Dian-wei WANG,Chi ZHANG,Jie FANG,Zhi-jie XU. UAV target tracking algorithm based on high resolution siamese network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [5] | Yu WANG,Kai ZHAO. Postprocessing of human pose heatmap based on sub⁃pixel location [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [6] | Yun-long GAO,Ming REN,Chuan WU,Wen GAO. An improved anchor-free model based on attention mechanism for ship detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [7] | Lin MAO,Hong-yang SU,Da-wei YANG. Temporal salient attention siamese tracking network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3327-3337. |
| [8] | Wen-cai SUN,Xu-ge HU,Zhi-fa YANG,Fan-yu MENG,Wei SUN. Optimization of infrared-visible road target detection by fusing GPNet and image multiscale features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2799-2806. |
| [9] | Jing-hong LIU,An-ping DENG,Qi-qi CHEN,Jia-qi PENG,Yu-jia ZUO. Anchor⁃free target tracking algorithm based on multiple attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
| [10] | Kan WANG,Hang SU,Hao ZENG,Jian QIN. Deep target tracking using augmented apparent information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2676-2684. |
| [11] | Jie CAO,Xue QU,Xiao-xu LI. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [12] | Tao XU,Ke MA,Cai-hua LIU. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [13] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhao LI,Jing LIU,Huang-shui HU,Dan WANG,Xue-bai ZANG. Scene classification based on degree of naturalness and visual feature channels [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [14] | CHE Xiang-jiu, WANG Li, GUO Xiao-xin. Improved boundary detection based on multi-scale cues fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [15] | XU Yan-yan, CHEN Hui, LIU Jia-ju, YUAN Jin-zhao. Cell processor stereo matching parallel computation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 952-958. |
|
||