Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 239-246.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240618
Previous Articles Next Articles
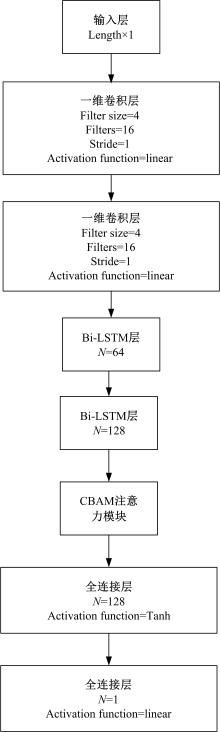
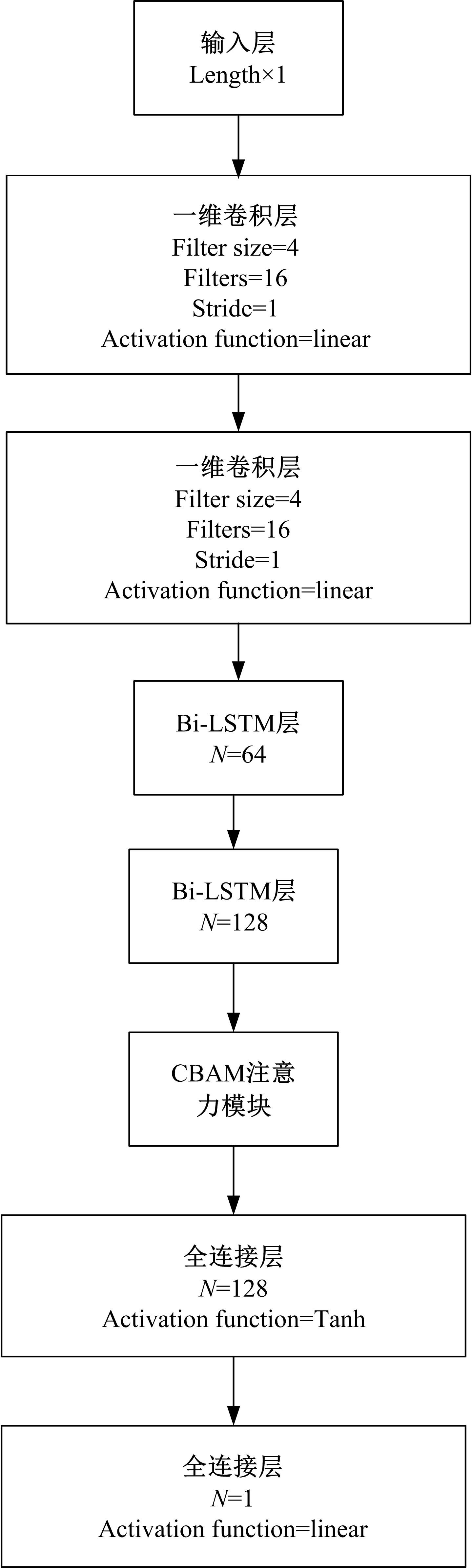
Non-intrusive load decomposition of unbalanced data based on attention mechanism
Qiu-zhan ZHOU1( ),Xin-meng LI1,Hao-qing-zi SHEN2,Hui-nan WU1(
),Xin-meng LI1,Hao-qing-zi SHEN2,Hui-nan WU1( ),Yuan-yuan LI1,Jing RONG1,Chun-hua HU3,Ping-ping LIU4
),Yuan-yuan LI1,Jing RONG1,Chun-hua HU3,Ping-ping LIU4
- 1.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Jinhua Power Supply Company Metering Center,State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Company,Jinhua 321000,China
3.Yantai Dongfang Wisdom Electric Co. ,Ltd. ,Yantai 264003,China
4.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP274
| [1] | Hart G W. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(12):1870-1891. |
| [2] | Chawla N V, Bowyer K W, Hall L O, et al. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16(1):321-357. |
| [3] | Han H, Wang W Y, Mao B H. Borderline-SMOTE: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning[C]∥International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Hefei,China, 2005: 878-887. |
| [4] | Guo Y, Xiong X, Fu Q, et al. Research on non-intrusive load disaggregation method based on multi-model combination[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2021, 200: No.107472. |
| [5] | Gales M, Young S. The application of hidden Markov models in speech recognition[J]. Foundations and Trends in Signal Processing, 2008, 1(3): 195-304. |
| [6] | Upadhyay A, Sharma S K, Upadhyay S. Face identification and verification using hidden Markov model with maximum score approach[J]. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 2017, 10(47): 671-677. |
| [7] | Kim H, Marwah M, Arlitt M, et al. Unsupervised disaggregation of low frequency power measurements[C]∥Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data, Mining, Mesa,USA, 2011: 747-758. |
| [8] | Pattem S. Unsupervised disaggregation for non-intrusive load monitoring[C]∥The 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications(ICMLA), Boca Raton,USA, 2012: 515-520. |
| [9] | Zoha A, Gluhak A, Nati M, et al. Low-power appliance monitoring using factorial hidden Markov models[C]∥IEEE 8th International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing,Melbourne,Australia, 2013: 527-532. |
| [10] | Wang X N, Wang J H, Shi D, et al. A factorial hidden Markov model for energy disaggregation based on human behavior analysis[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, USA,2018: 1-5. |
| [11] | Kolter J Z, Jaakkola T. Approximate inference in additive factorial HMMs with application to energy disaggregation[C]∥Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, La Palma,Spain, 2012: 1472-1482. |
| [12] | Kelly J, Knottenbelt W. Neural NILM: deep neural networks applied to energy disaggregation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Built Enviroments, New York,USA, 2015: 55-64. |
| [13] | Zhang C, Zhong M, Wang Z, et al. Sequence-to-point learning with neural networks for non-intrusive load monitoring[C]∥The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 2604-2611. |
| [14] | Wu Q, Wang F. Concatenate convolutional neural networks for non-intrusive load monitoring across complex background[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(8): 1572-1576. |
| [15] | Gomes E, Pereira L. PB-NILM: pinball guided deep non-intrusive load monitoring[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 48386-48398. |
| [16] | De Aguiar E L, Da Silva Nolasco L, Lazzaretti A E, et al. St-nilm: a wavelet scattering-based architecture for feature extraction and multilabel classification in nilm signals[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(7): 10540-10550. |
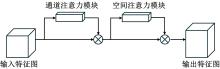
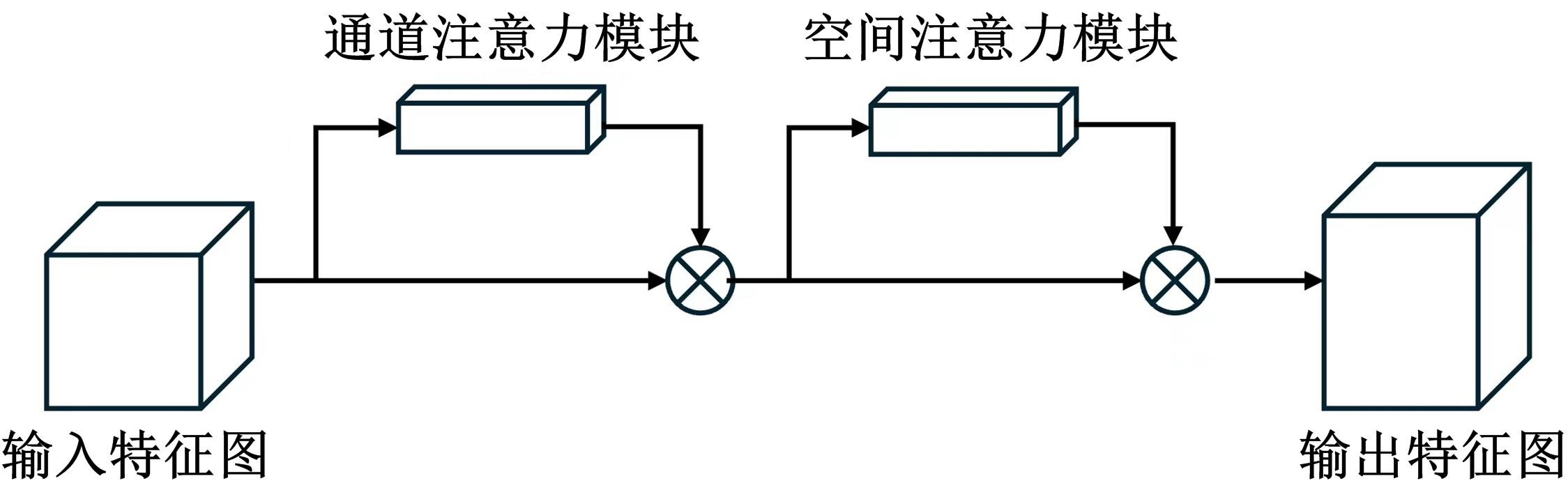
| [17] | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV),Munich,Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| [18] | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G,et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥IEEE/CVF Confernece on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Salt Lake City, USA,2018:7132-7141. |
| [19] | Simonsen J, Jensen O S. Contact quality in participation: a "sensethic" perspective[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th Participatory Design Conference: Short Papers, Interactive Exhibitions, Workshops,Aarhus,Denmark, 2016: 45-48. |
| [20] | Kelly J, Knottenbelt W. The UK-DALE dataset, domestic appliance-level electricity demand and whole-house demand from five UK homes[J]. Scientific Data, 2015, 2(1): 1-14. |
| [21] | Nalmpantis C, Vrakas D. Machine learning approaches for non-intrusive load monitoring: from qualitative to quantitative comparation[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52(1): 217-243. |
| [1] | Zhi-gang FENG,Meng-yuan REN,Bing DONG,Ming-yue YU. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on multi-band feature map and improved SqueezeNet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2026, 56(1): 96-108. |
| [2] | Zhen HUO,Li-sheng JIN,Qiang HUA, HEYang. Edge feature⁃guided semantic segmentation method for intelligent vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 3032-3041. |
| [3] | Qing-lin AI,Yuan-xiao LIU,Jia-hao YANG. Small target swmantic segmentation method based MFF-STDC network in complex outdoor environments [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2681-2692. |
| [4] | Yan PIAO,Ji-yuan KANG. RAUGAN:infrared image colorization method based on cycle generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2722-2731. |
| [5] | Shan-na ZHUANG,Jun-shuai WANG,Jing BAI,Jing-jin DU,Zheng-you WANG. Video-based person re-identification based on three-dimensional convolution and self-attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2409-2417. |
| [6] | Zhi-gang FENG,Shou-qi WANG,Ming-yue YU. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on variational mode extraction and lightweight network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1883-1891. |
| [7] | Ya-li XUE,Tong-an YU,Shan CUI,Li-zun ZHOU. Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [8] | Hua CAI,Yu-yao WANG,Qiang FU,Zhi-yong MA,Wei-gang WANG,Chen-jie ZHANG. Semantic segmentation network based on attention mechanism and feature fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1384-1395. |
| [9] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [10] | Yi-yong PAN,Xiang-yu XU. Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [11] | Yang LI,Xian-guo LI,Chang-yun MIAO,Sheng XU. Low⁃light image enhancement algorithm based on dual branch channel prior and Retinex [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1028-1036. |
| [12] | Xiang WANG,Guo-zhen TAN,Yan-fei PENG,Hao REN,Jian-ping LI. Autonomous driving decision⁃making model based on language reasoning and cognitive memory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 3918-3927. |
| [13] | Yun-hong LI,Mei WANG,Xue-ping SU,Li-min LI,Fu-xing ZHANG,Te-ji HAO. Road extraction from remote sensing images combining attention and context fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 4034-4044. |
| [14] | Duo PENG,Ming-shuo LIU,Kun XIE. Observation station parameter error joint multi-feature fusion attention mechanism TDOA/FDOA multi-aircraft passive localization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3751-3761. |
| [15] | Xiao-ran GUO,Tie-jun WANG,Yue YAN. Entity relationship extraction method based on local attention and local remote supervision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
|
||