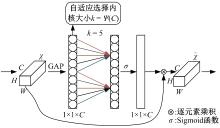
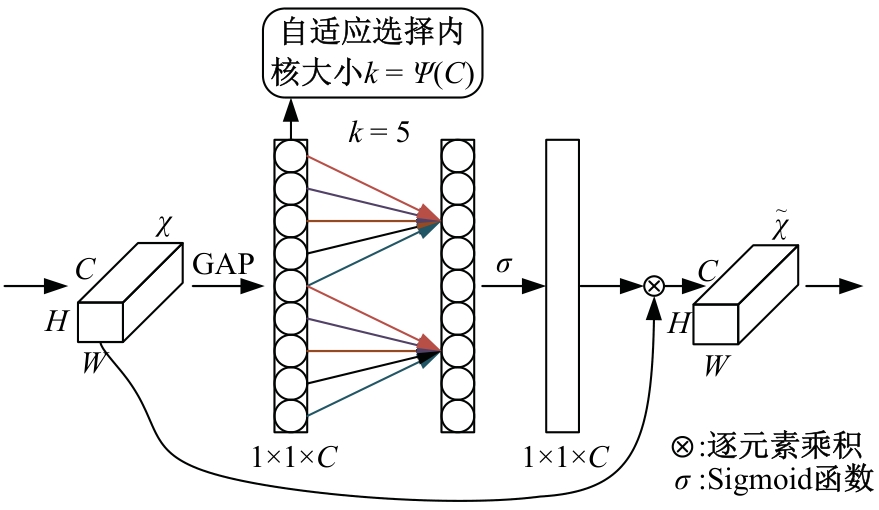
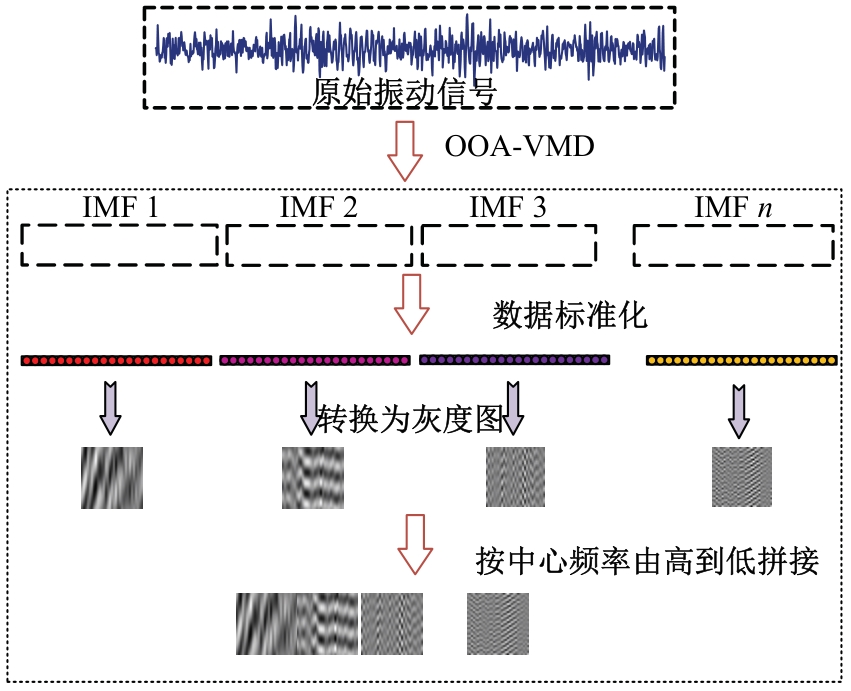
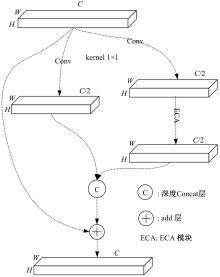
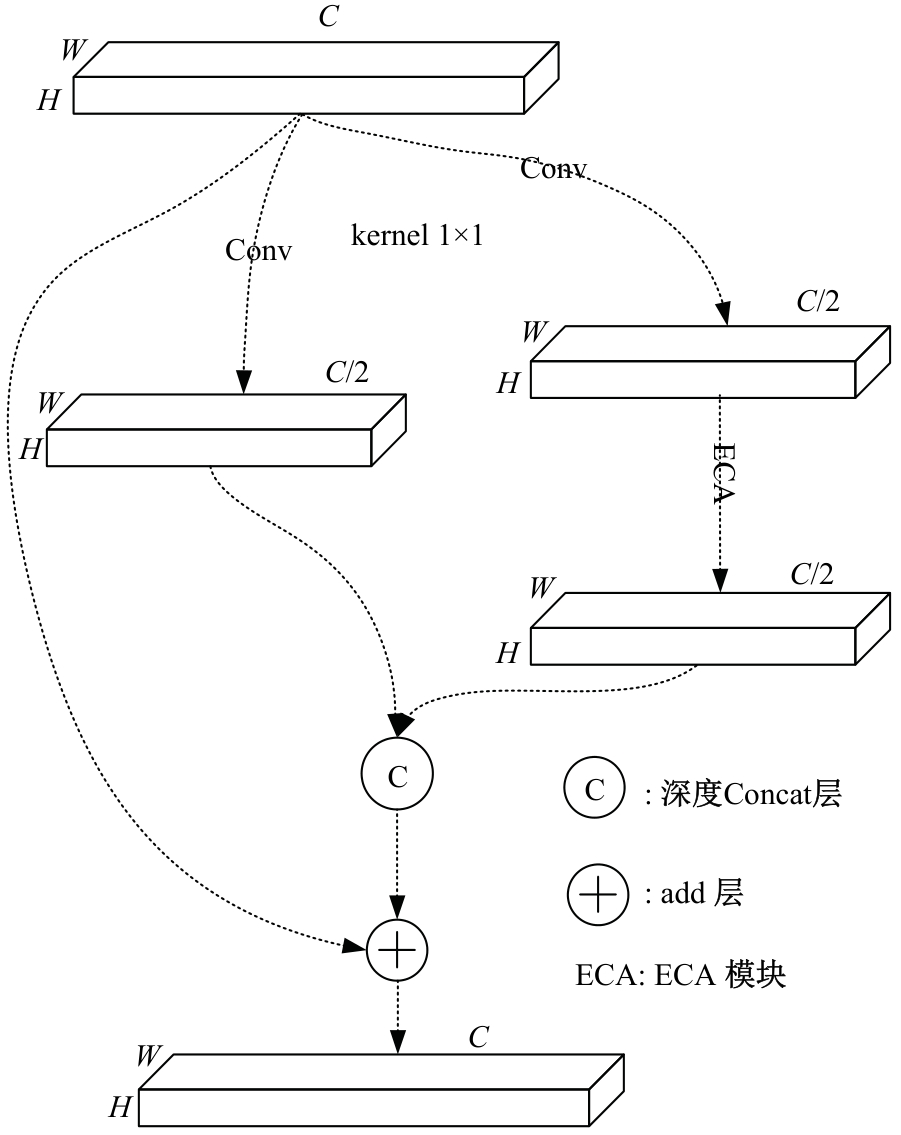
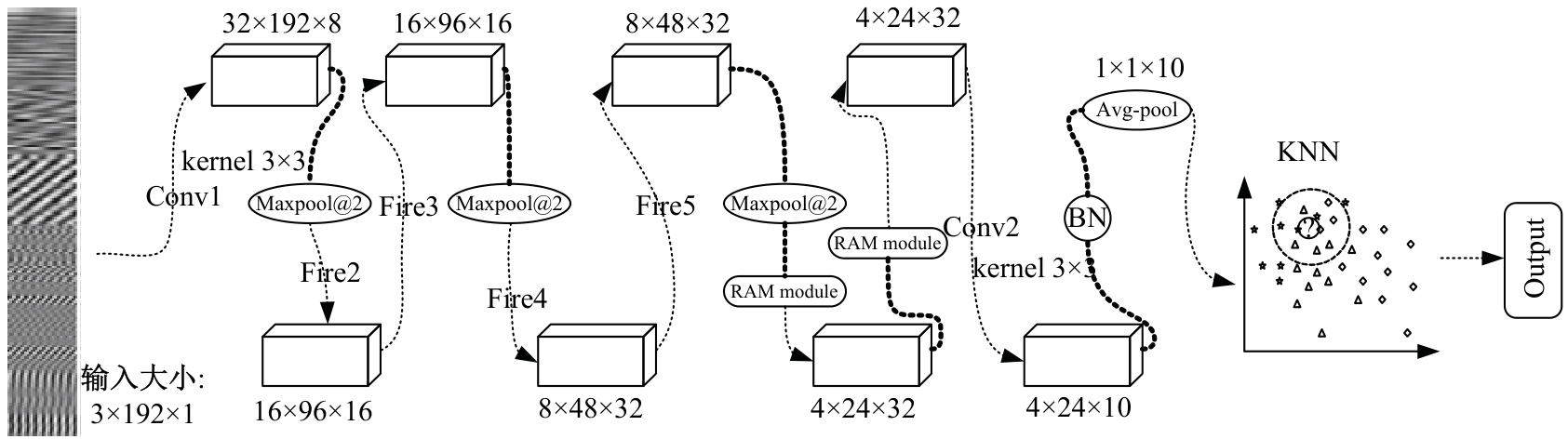
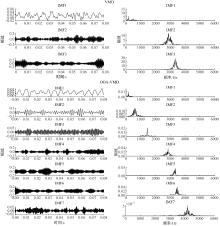
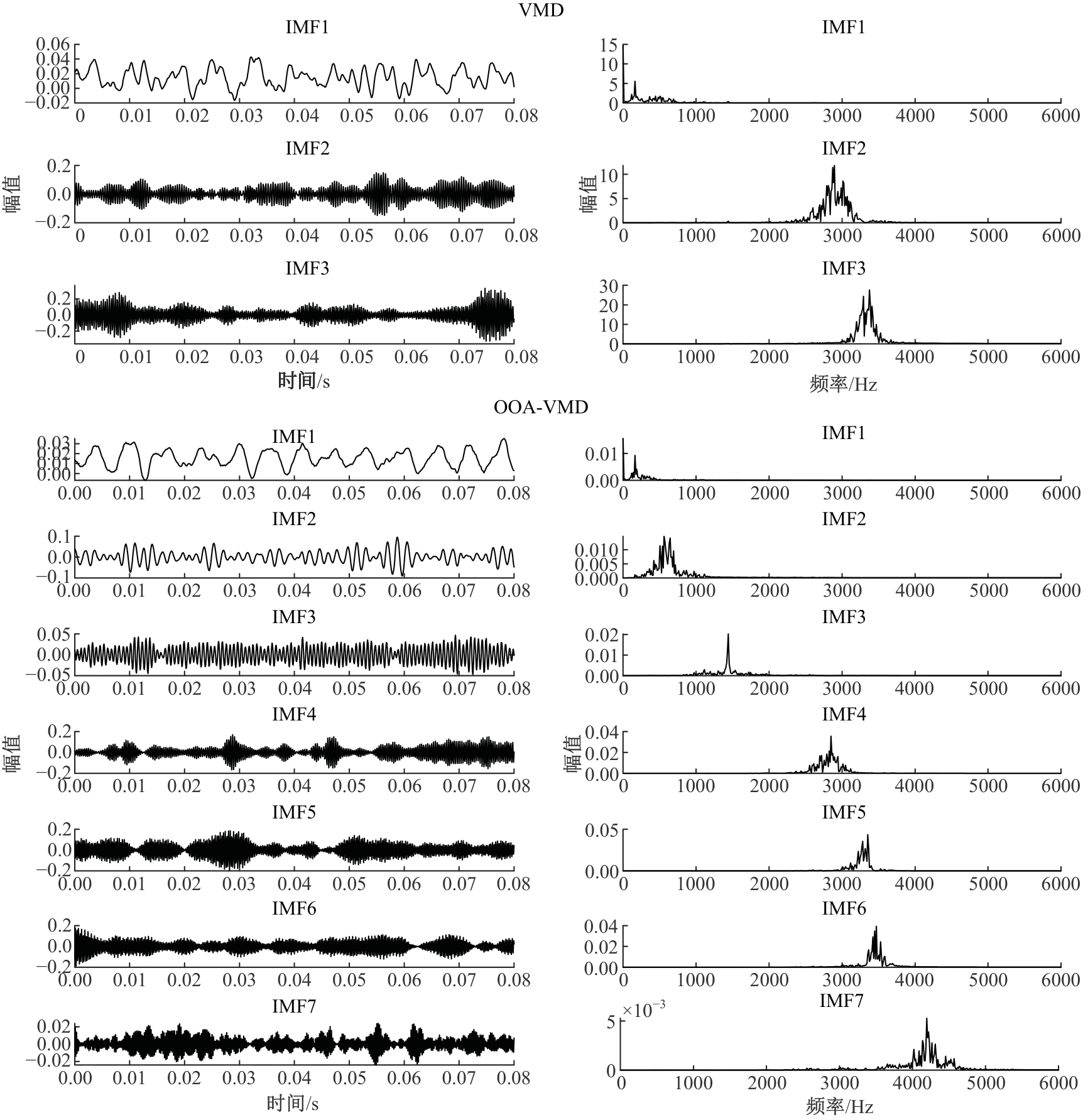
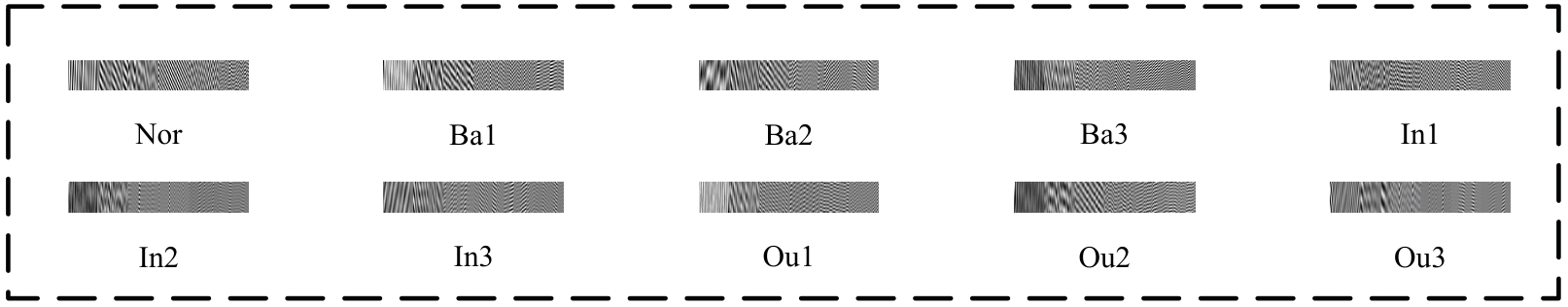
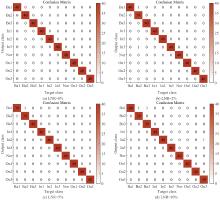
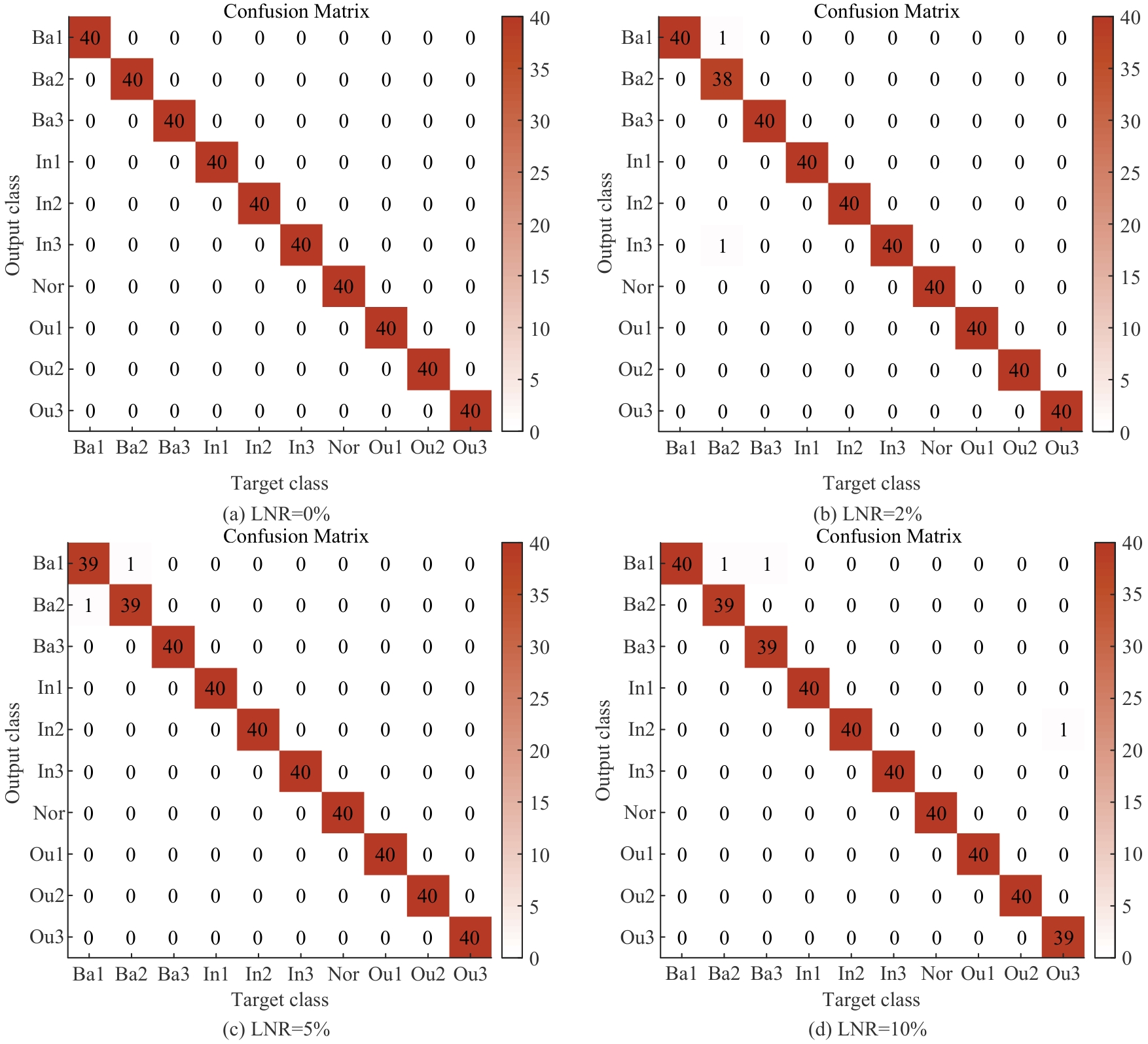
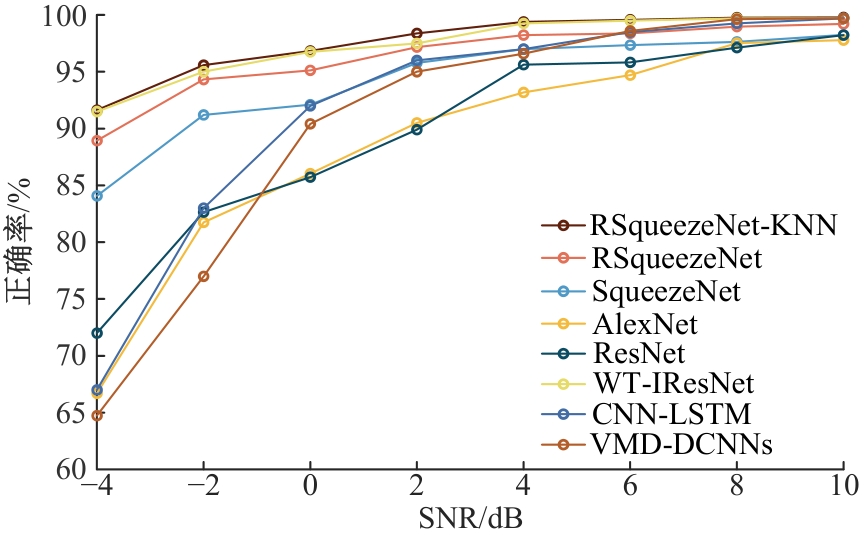
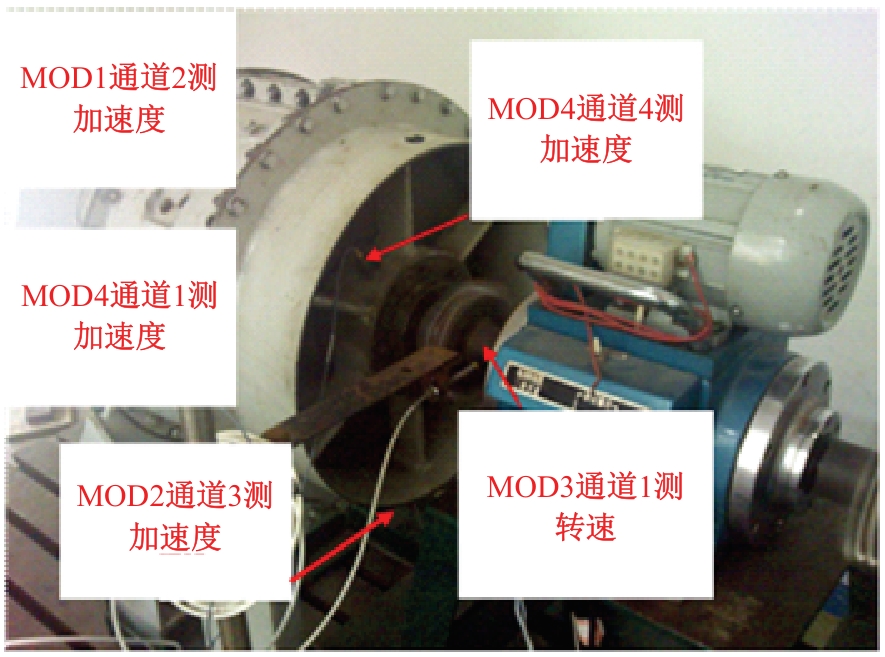
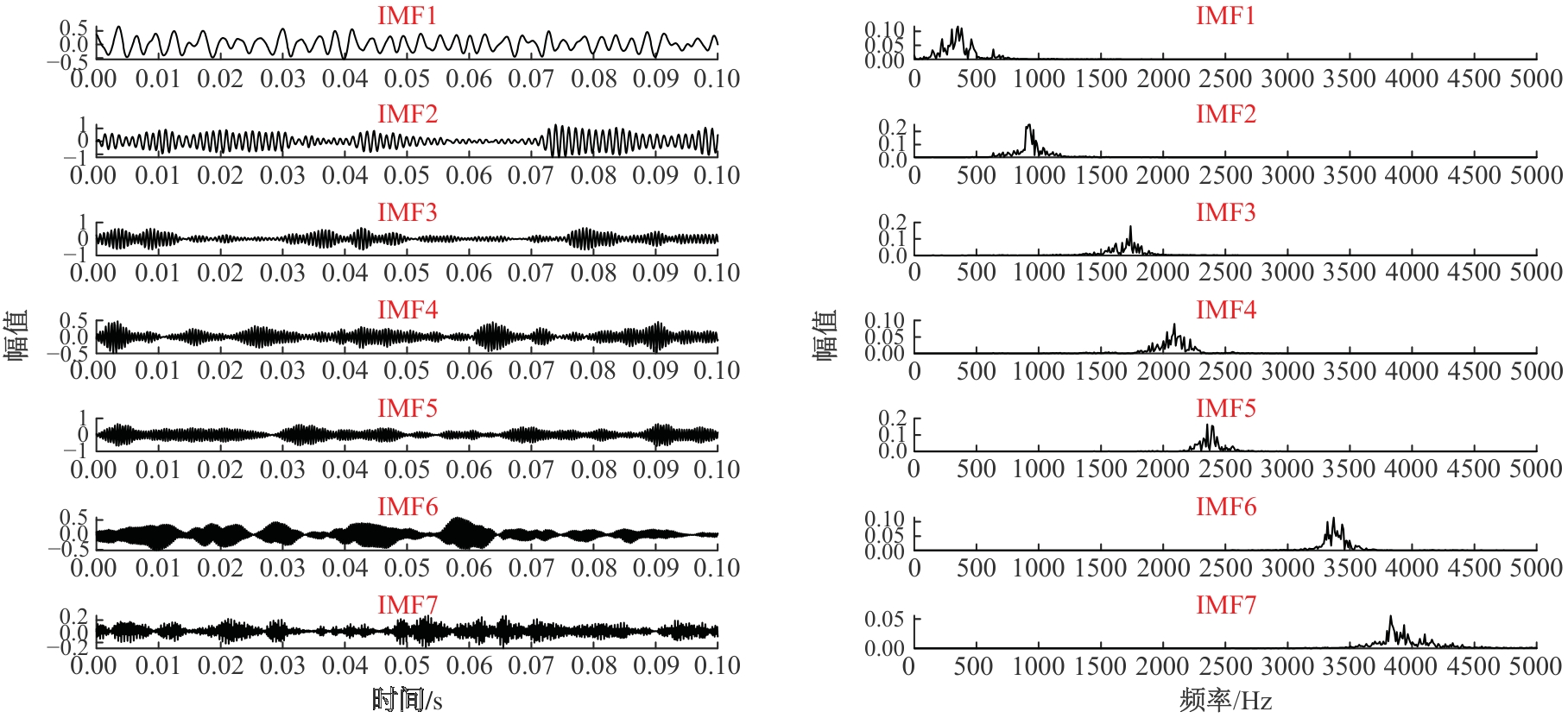
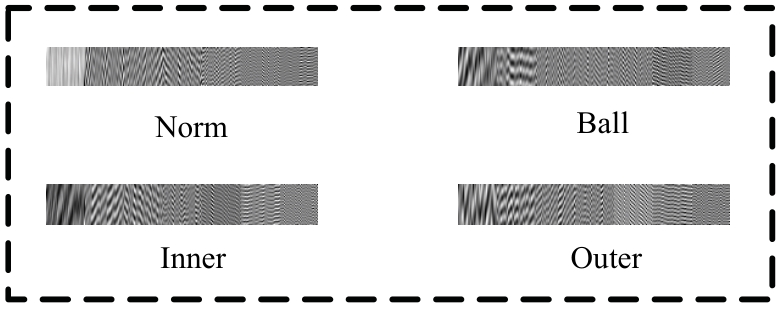
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 96-108.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240710
Previous Articles Next Articles
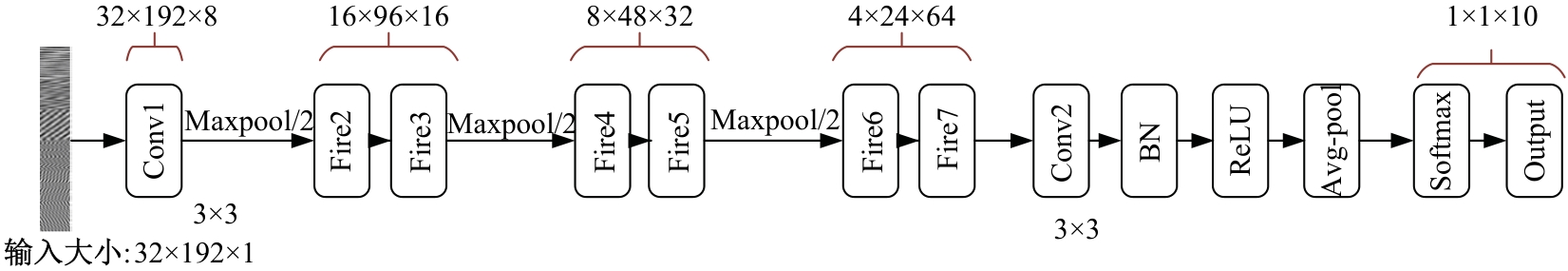
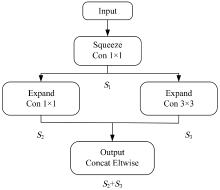
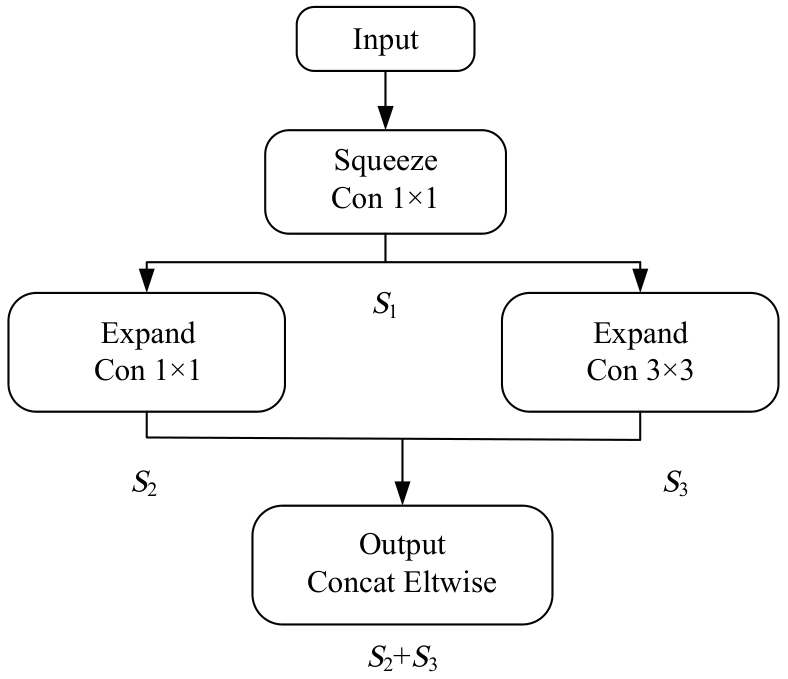
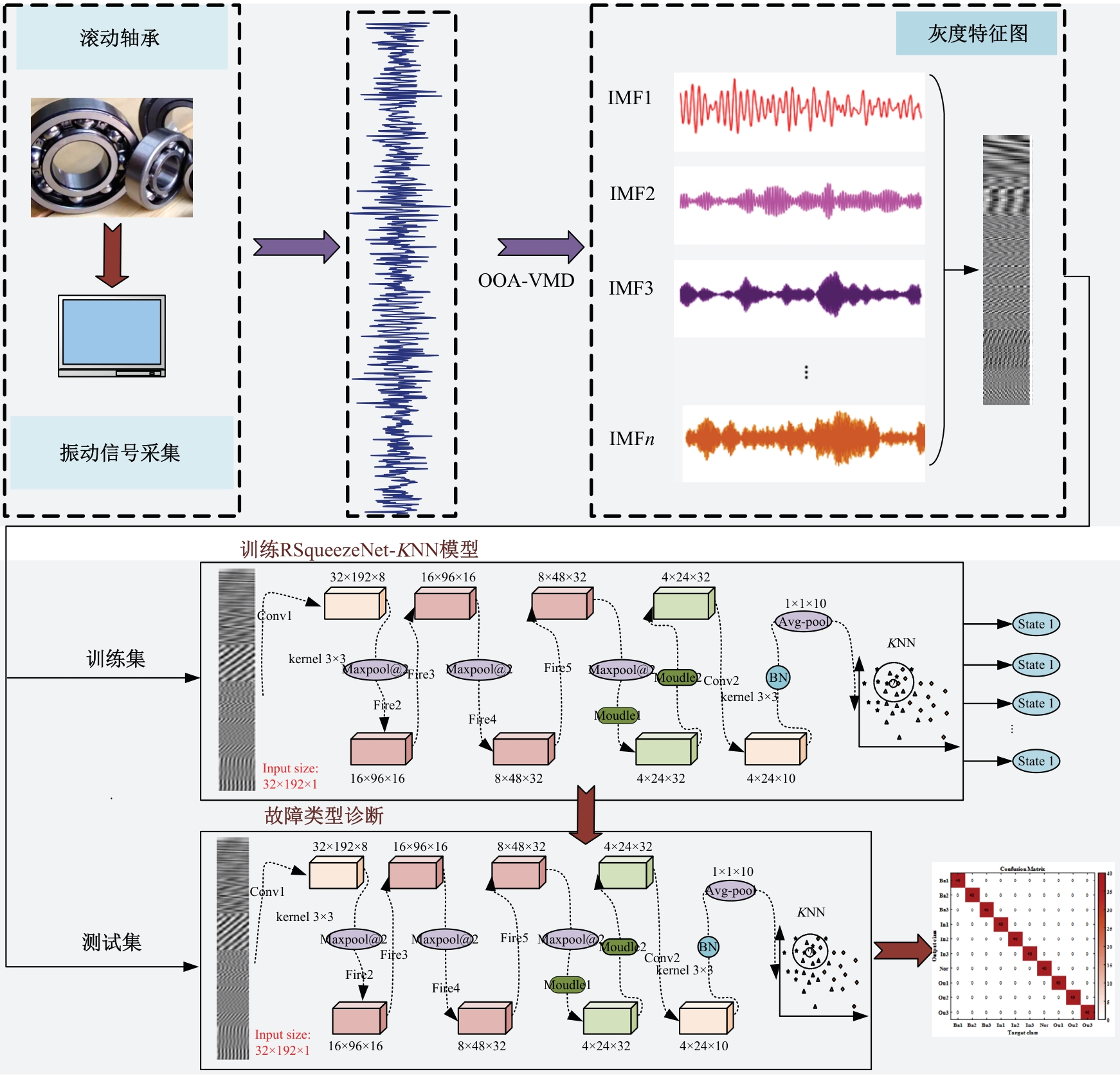
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on multi-band feature map and improved SqueezeNet
Zhi-gang FENG1( ),Meng-yuan REN1,Bing DONG2,Ming-yue YU1
),Meng-yuan REN1,Bing DONG2,Ming-yue YU1
- 1.School of Automation,Shenyang Aerospace University,Shenyang 110136,China
2.Aircraft Industry(Group) Co. ,Ltd. ,Shenyang 110000,China
CLC Number:
- TH17
| [1] | Bai R, Xu Q, Meng Z, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on multi-channel convolution neural network and multi-scale clipping fusion data augmentation[J]. Measurement, 2021, 184: No.109885. |
| [2] | 栾孝驰, 佟鑫宇, 沙云东, 等. 基于振动与声发射敏感参数识别的主轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 推进技术, 2024, 45(12): 269-281. |
| Luan Xiao-chi, Tong Xin-yu, Sha Yun-dong, et al. Main bearing fault diagnosis method based on vibration and acoustic emission snsitive parameter recognition[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2024, 45(12):269-281. | |
| [3] | 谷玉海, 朱腾腾, 饶文军, 等.基于EMD二值化图像和CNN的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2021, 41(1): 105-113, 203. |
| Gu Yu-hai, Zhu Teng-teng, Rao Wen-jun, et al. Fault diagnosis for rolling bearing based on EMD binarization image and CNN[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis,2021,41(1):105-113, 203. | |
| [4] | Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 62(3): 531-544. |
| [5] | 赵德宏, 李永利. 基于GA-VMD分解与支持向量机的刀具故障诊断研究[J].沈阳建筑大学学报: 自然科学版, 2024, 40(2): 361-371. |
| Zhao De-hong, Li Yong-li. Research on tool fault diagnosis based on GA-VMD decomposition and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University(Natural Science), 2024, 40(2): 361-371. | |
| [6] | 余萍, 赵康, 曹洁. 基于优化A-BiLSTM的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. |
| Yu Ping, Zhao Kang, Cao Jie. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on optimized A-BiLSTM[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. | |
| [7] | 杨战社, 孔晨再, 荣相, 等. 基于EEMD能量熵与ANN的矿用异步电机故障诊断[J]. 微电机, 2021, 54(8): 23-27, 61. |
| Yang Zhan-she, Kong Chen-zai, Rong Xiang, et al. Fault diagnosis of mine asynchronous motor based on EEMD energy entropy and ANN[J]. Micromotors,2021, 54(8): 23-27, 61. | |
| [8] | Pandya D H, Upadhyay S H, Harsha S P. Fault diagnosis of rolling element bearing with intrinsic mode function of acoustic emission data using APF-KNN[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2013, 40(10): 4137-4145. |
| [9] | Che C, Wang H, Xiong M, et al. Few-shot fault diagnosis of rolling bearing under variable working conditions based on ensemble meta-learning[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 131: No. 103777. |
| [10] | Gu J, Peng Y, Lu H, et al. A novel fault diagnosis method of rotating machinery via VMD, CWT and improved CNN[J]. Measurement, 2022, 200:No. 111635. |
| [11] | Wang Z, Zhao W, Du W, et al. Data-driven fault diagnosis method based on the conversion of erosion operation signals into images and convolutional neural network[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 149: 591-601. |
| [12] | Iandola F N, Han S, Moskewicz M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and<0.5 MB model size[J/OL].[2024-06-12]. . |
| [13] | Ren L, Jiang L, Li C. Label confidence-based noise correction for crowdsourcing[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 117: No.105624. |
| [14] | Dehghani M, Trojovský P. Osprey optimization algorithm: a new bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems[J]. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 8:No. 1126450. |
| [15] | Lin G, Lin A. Modified multiscale sample entropy and cross-sample entropy based on horizontal visibility graph[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2022, 165:No. 112802. |
| [16] | Han G, Zhang M, Wu W, et al. Improved U-Net based insulator image segmentation method based on attention mechanism[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7: 210-217. |
| [17] | Smith W A, Randall R B. Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the Case Western Reserve University data: a benchmark study[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 64/65: 100-131. |
| [18] | Wu Q L, Lin H X. Short-term wind speed forecasting based on hybrid variational mode decomposition and least squares support vector machine optimized by bat algorithm model[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(3): No.652. |
| [19] | Diao X, Jiang J, Shen G, et al. An improved variational mode decomposition method based on particle swarm optimization for leak detection of liquid pipelines[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 143: No.106787. |
| [20] | Nadirgil O. Carbon price prediction using multiple hybrid machine learning models optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 342: No.118061. |
| [21] | Wang H, Wu F, Zhang L. Application of variational mode decomposition optimized with improved whale optimization algorithm in bearing failure diagnosis[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2021, 60(5): 4689-4699. |
| [22] | Liang P, Wang W, Yuan X, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on wavelet transform and improved ResNet under noisy labels and environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 115: No.105269. |
| [23] | Hao S, Ge F X, Li Y, et al. Multisensor bearing fault diagnosis based on one-dimensional convolutional long short-term memory networks[J]. Measurement, 2020, 159: No.107802. |
| [24] | Xu Z, Li C, Yang Y. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing of wind turbines based on the variational mode decomposition and deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 95: No.106515. |
| [25] | Feng Z, Wang S, Yu M. A fault diagnosis for rolling bearing based on multilevel denoising method and improved deep residual network[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 140: No.104106. |
| [1] | Qiu-zhan ZHOU,Xin-meng LI,Hao-qing-zi SHEN,Hui-nan WU,Yuan-yuan LI,Jing RONG,Chun-hua HU,Ping-ping LIU. Non-intrusive load decomposition of unbalanced data based on attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2026, 56(1): 239-246. |
| [2] | Zhen HUO,Li-sheng JIN,Qiang HUA, HEYang. Edge feature⁃guided semantic segmentation method for intelligent vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 3032-3041. |
| [3] | Qing-lin AI,Yuan-xiao LIU,Jia-hao YANG. Small target swmantic segmentation method based MFF-STDC network in complex outdoor environments [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2681-2692. |
| [4] | Yan PIAO,Ji-yuan KANG. RAUGAN:infrared image colorization method based on cycle generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2722-2731. |
| [5] | Shan-na ZHUANG,Jun-shuai WANG,Jing BAI,Jing-jin DU,Zheng-you WANG. Video-based person re-identification based on three-dimensional convolution and self-attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2409-2417. |
| [6] | Zhi-gang FENG,Shou-qi WANG,Ming-yue YU. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on variational mode extraction and lightweight network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1883-1891. |
| [7] | Ya-li XUE,Tong-an YU,Shan CUI,Li-zun ZHOU. Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [8] | Hua CAI,Yu-yao WANG,Qiang FU,Zhi-yong MA,Wei-gang WANG,Chen-jie ZHANG. Semantic segmentation network based on attention mechanism and feature fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1384-1395. |
| [9] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [10] | Yang LI,Xian-guo LI,Chang-yun MIAO,Sheng XU. Low⁃light image enhancement algorithm based on dual branch channel prior and Retinex [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1028-1036. |
| [11] | Xiang WANG,Guo-zhen TAN,Yan-fei PENG,Hao REN,Jian-ping LI. Autonomous driving decision⁃making model based on language reasoning and cognitive memory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 3918-3927. |
| [12] | Yun-hong LI,Mei WANG,Xue-ping SU,Li-min LI,Fu-xing ZHANG,Te-ji HAO. Road extraction from remote sensing images combining attention and context fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 4034-4044. |
| [13] | Duo PENG,Ming-shuo LIU,Kun XIE. Observation station parameter error joint multi-feature fusion attention mechanism TDOA/FDOA multi-aircraft passive localization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3751-3761. |
| [14] | Xiao-ran GUO,Tie-jun WANG,Yue YAN. Entity relationship extraction method based on local attention and local remote supervision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [15] | Lu Li,Jun-qi Song,Ming Zhu,He-qun Tan,Yu-fan Zhou,Chao-qi Sun,Cheng-yu Zhou. Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
|
||