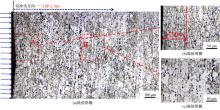
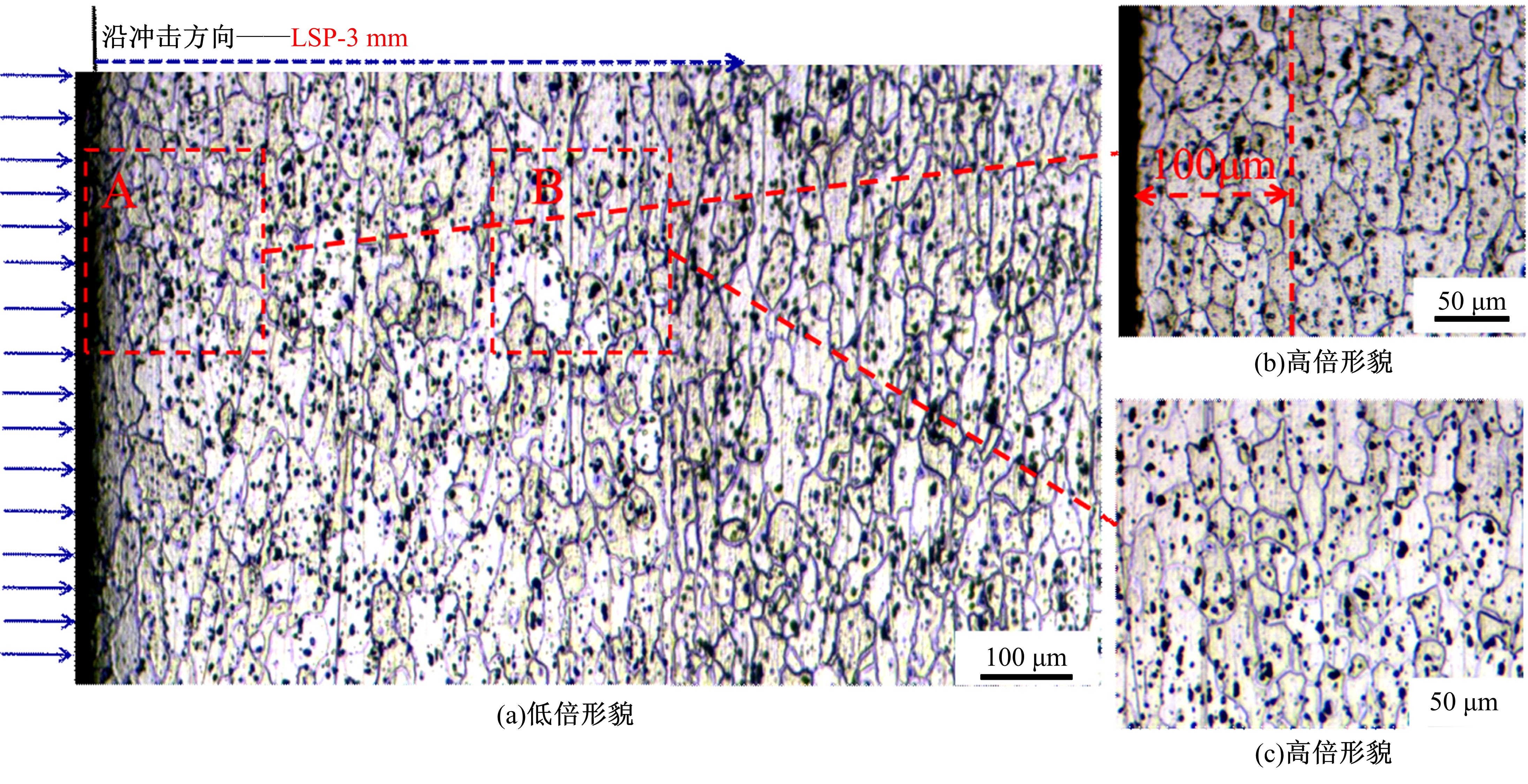
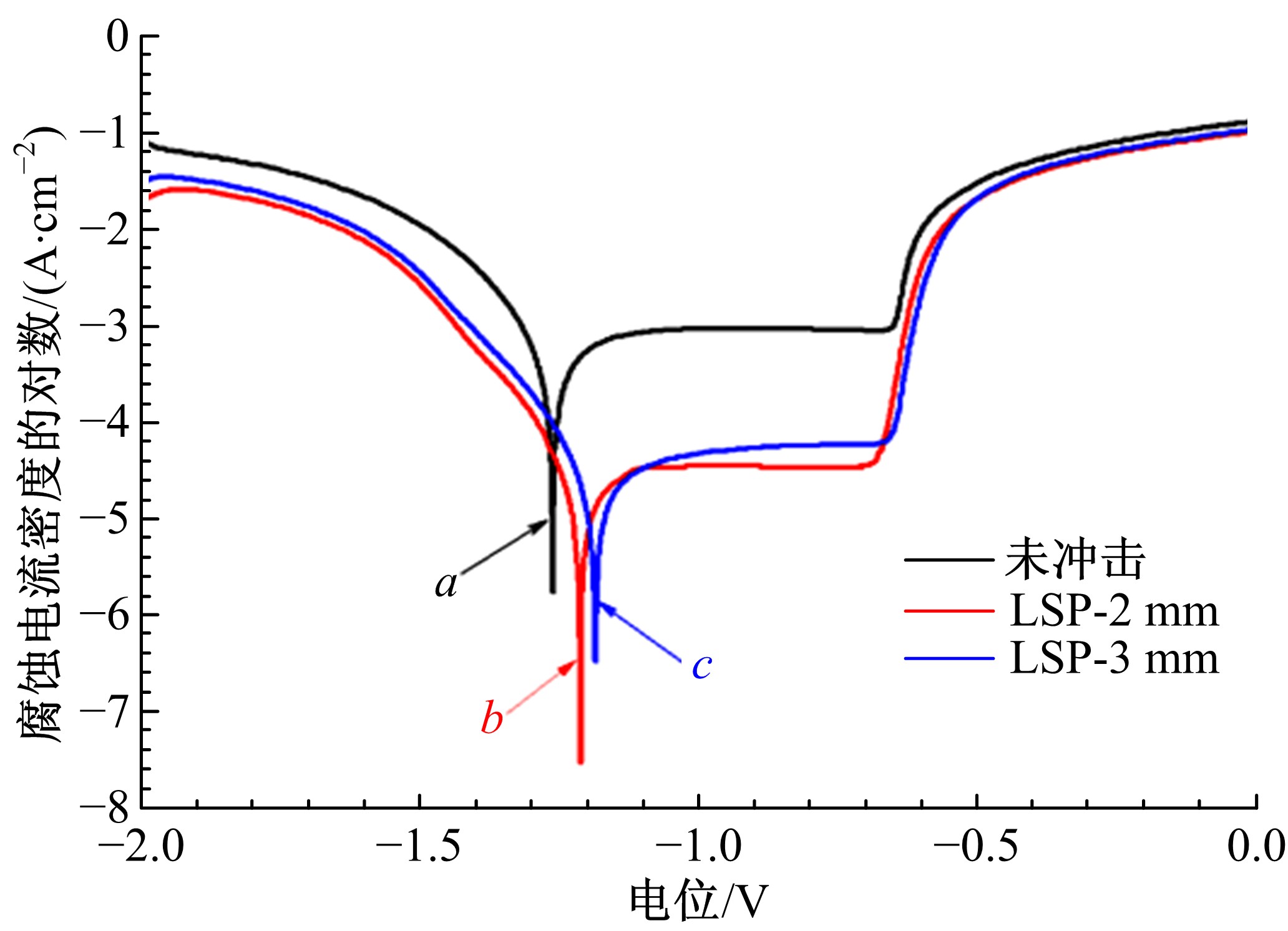
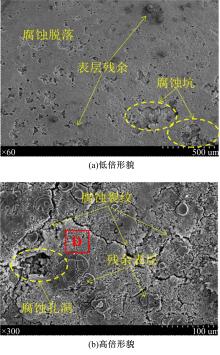
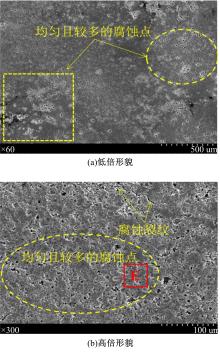
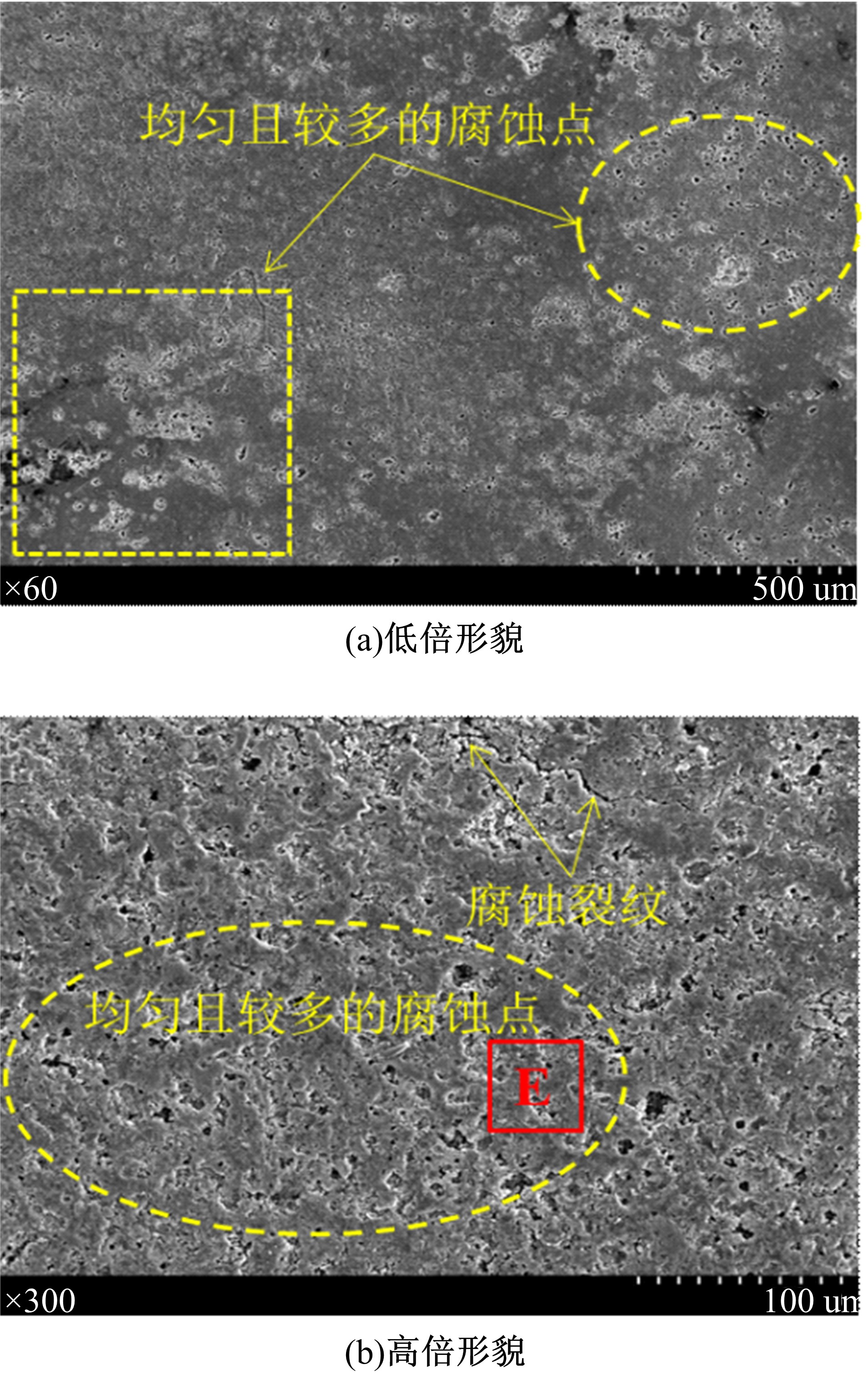
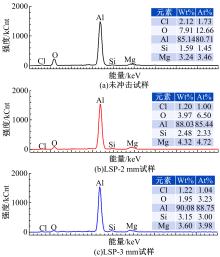
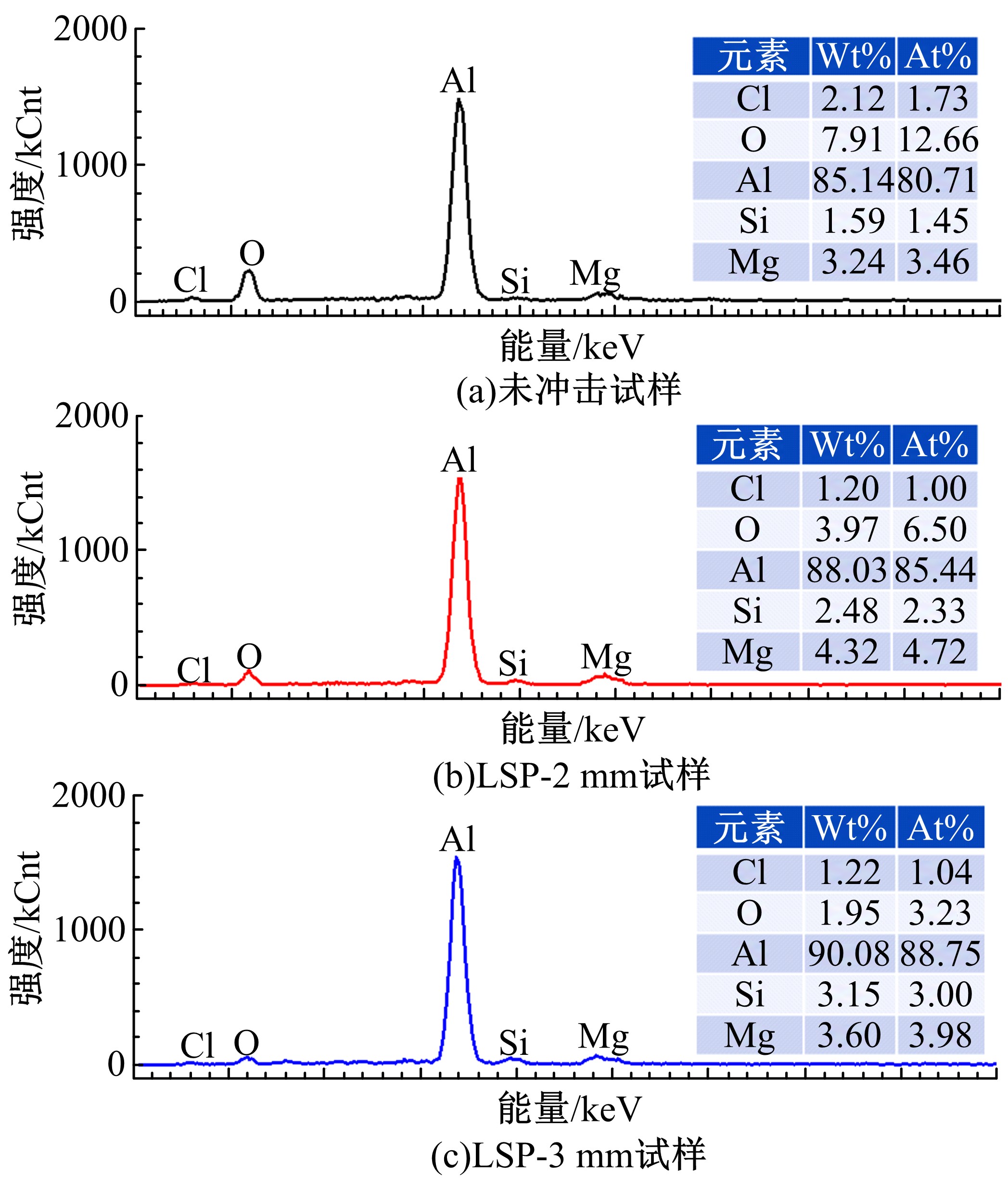
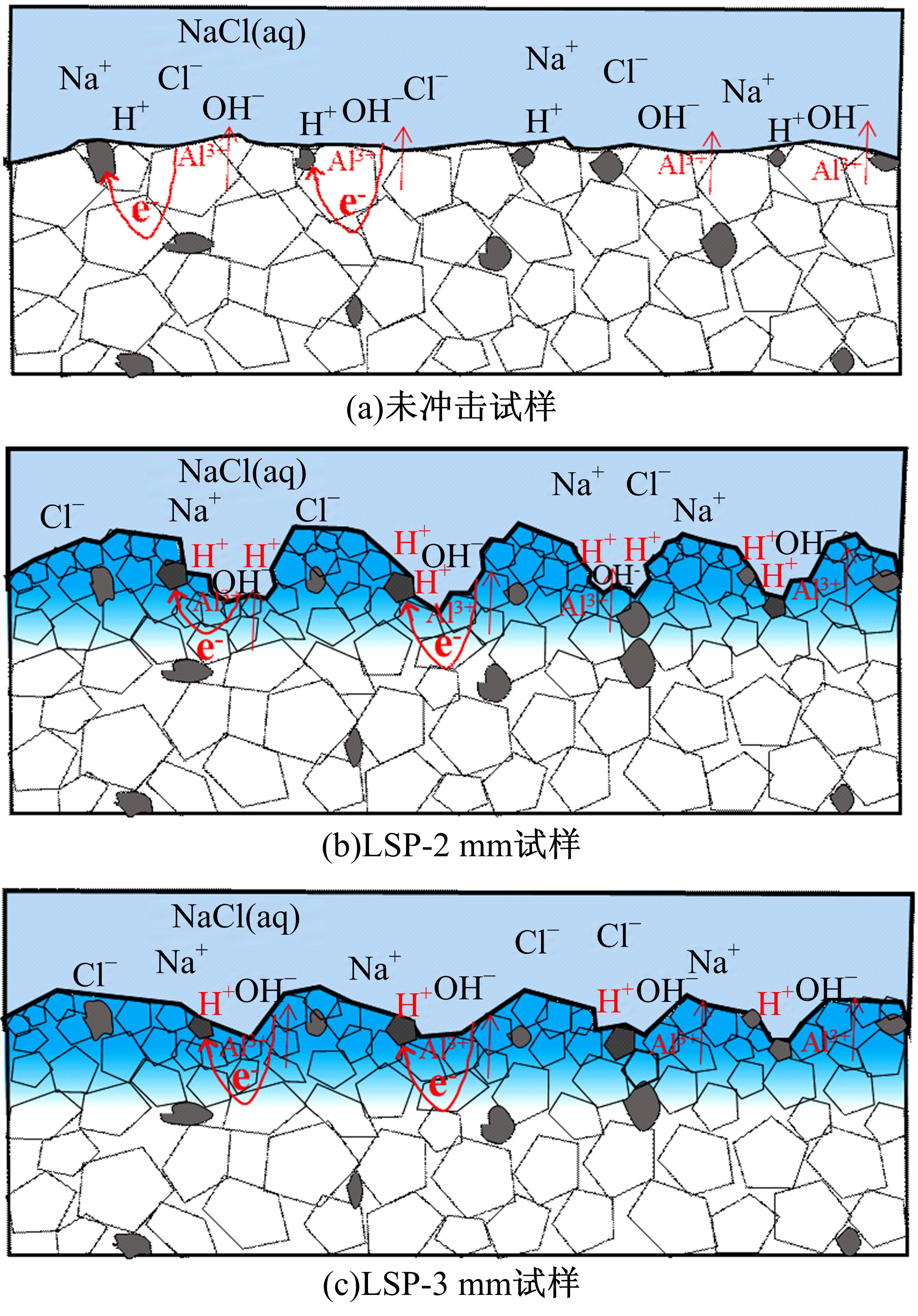
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 501-510.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200037
Effect of spot diameteron corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening
Kai-yu LUO1,2( ),Jun-cheng CHEN1,Chang-yu WANG1,Jin-zhong LU1
),Jun-cheng CHEN1,Chang-yu WANG1,Jin-zhong LU1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.College of Engineering Technology,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
CLC Number:
- TN249
| 1 | Salimianrizi A, Foroozmehr E, Badrossamay M, et al. Effect of laser shock peening on surface properties and residual stress of Al6061-T6[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 77: 112-117. |
| 2 | 缪宏, 左敦稳, 王珉, 等.喷丸强化对NAK80钢表面完整性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1290-1294. |
| Miao Hong, Zuo Dun-wen, Wang Min, et al. Effect of shot peening on surface integrity of NAK80 steel[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1290-1294. | |
| 3 | Sun Q Q, Han Q Y, Xu R, et al. Localized corrosion behaviour of AA7150 after ultrasonic shot peening:Corrosion depth vs. impact energy[J]. Corrosion Science,2018, 130: 218-230. |
| 4 | 汪志太, 林鑫, 曹永青, 等.外部冷却条件对激光熔凝Ni-Sn合金反常共晶形成的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(12): 91-96. |
| Wang Zhi-tai, Lin Xin, Cao Yong-qing, et al. External cooling condition effects on formation of anomalous eutectic in Ni-Sn alloy by laser remelting[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2014, 41(12): 91-96. | |
| 5 | 罗开玉, 邢月华, 柴卿锋, 等. 激光冲击强化对2Cr13不锈钢腐蚀疲劳性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3): 850-858. |
| Luo Kai⁃yu, Xing Yue⁃hua, Chai Qing⁃feng, et al. Effect of laser shock peening on corrosion fatigue behaviour of 2Cr13 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 850-858. | |
| 6 | 吴边, 王声波, 郭大浩, 等. 激光冲击铝合金改性处理研究[J]. 光学学报, 2005, 25(10): 1352-1356. |
| Wu Bian, Wang Sheng-bo, Guo Da-hao, et al. Research of material modification induced by laser s hock processing on aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2005, 25(10):1352-1356. | |
| 7 | 周建忠, 刘会霞, 冯爱新, 等. 激光冲击波技术用材料加工的研究进展[J]. 应用激光, 2005, 25(1): 27-31, 44. |
| Zhou Jian-zhong, Liu Hui-xia, Feng Ai-xin, et al. Advances on the application of laser induced shock wave in metal processing[J]. Applied Laser, 2005, 25(1): 27-31, 44. | |
| 8 | 张青来, 王荣, 张冰昕, 等. 激光冲击强化对AZ31镁合金力学性能和组织结构的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(3): 39-45. |
| Zhang Qing-lai, Wang Rong, Zhang Bing-xin, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on mechanical properties and microstructures of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2015, 42(3): 39-45. | |
| 9 | 汪诚, 赖志林, 何卫锋, 等. 激光冲击次数对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢高周疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(1): 46-51. |
| Wang Cheng, Lai Zhi-lin, He Wei-feng, et al. Effect of multi-impact on high cycle fatigue properties of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel subject to laser shock processing[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2014, 41(1): 46-51. | |
| 10 | 王江涛, 张永康, 陈菊芳, 等. 激光冲击对7075铝合金等离子弧焊接头电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(12): 106-115. |
| Wang Jiang-tao, Zhang Yong-kang, Chen Ju-fang, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy plasma arc weldments[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2015, 42(12): 106-115. | |
| 11 | 邢清蒲, 张凌峰, 李少哲, 等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2013, 25(5): 402-405. |
| Xing Qing-pu, Zhang Ling-feng, Li Shao-zhe, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 2A02 Aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2013, 25(5): 402-405. | |
| 12 | 宁成义, 黄亿辉, 张广义, 等. 激光冲击强化6061铝合金耐磨性能及电化学性能的实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(6): 254-259. |
| Ning Cheng-yi, Huang Yi-hui, Zhang Guang-yi, et al. Experimental study of wear resistance and eletrochemical corrosion properties of 6061 aluminum alloy treated by laser shock peening[J].China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House, 2018, 55(6): 254-259. | |
| 13 | Trdan U, Grum J. Evaluation of corrosion resistance of AA6082-T651 aluminium alloy after laser shock peening by means of cyclic polarisation and EIS methods[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 59: 324-333. |
| 14 | Luo K Y, Wang C Y, Sun G F, et al. Investigation and microstructural analyses of massive LSP impacts with coverage area on crack initiation location and tensile properties of AM50 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science Engineering A, 2016, 650: 110-118. |
| 15 | Luo K Y, Wang C Y, Cui C Y, et al. Effects of coverage layer on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Mg-Al-Mn alloy subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 782: 1058-1075. |
| 16 | Zhao X Y, Chen X, Wang X. Effect of aging processes on corrosion behavior and stress corrosion sensitivity of pre-stretched 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Material and Corrosion, 2018, 69(7): 850-857. |
| 17 | Torbati-Sarraf H, Stannard T J, Plante E C L, et al. Direct observations of microstructure-resolved corrosion initiation in AA7075-T651 at the nanoscale using vertical scanning interferometry (VSI)[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 161: 110166. |
| 18 | Yang Y, Zhou W F, Tong Z P, et al. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of 5083 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2019, 28(10): 1-11. |
| 19 | Lee H S, Kim D S, Jung J S, et al. Influence of peening on the corrosion properties of AISI 304 stainless steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(12): 2826-2830. |
| [1] | Ji-cai LIANG,Yan-fei LIAO,Fei TENG,Ce LIANG,Yi LI. Rectangular section profile thinning rate of three-dimensional multi-point stretch bending process [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 163-171. |
| [2] | Chun-guo LIU,Xiao-tong YU,Tao YUE,Dong-lai LI,Ming-zhe ZHANG. Springback prediction for double-curvature stiffened panel during milling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 188-199. |
| [3] | Wen-biao GONG,Rui ZHU,Xin-zhe QIE,Heng CUI,Ming-yue GONG. Microstructure and properties of 6082 aluminum alloyultra⁃thick plate preparated by friction stir weld [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 512-519. |
| [4] | Xiao-yu HU,Guo-xiang LI,Shu-zhan BAI,Ke SUN,Si-yuan LI. Modified boiling heat transfer model considering roughness and material of heating surface [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1945-1950. |
| [5] | Yi-lun LIU,Qing WANG,Chi LIU,Song-bai LI,Jun HE,Xian-qiong ZHAO. Effect of creep and artificial aging on fatigue crack growth performance of 2524 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1636-1643. |
| [6] | Wu⁃jiao XU,Cheng⁃shang LIU,Xin⁃yao LU. Simulation and prediction of surface roughness of 6061 aluminum alloy workpiece after shot peening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
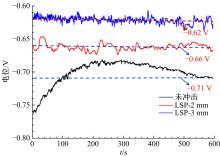
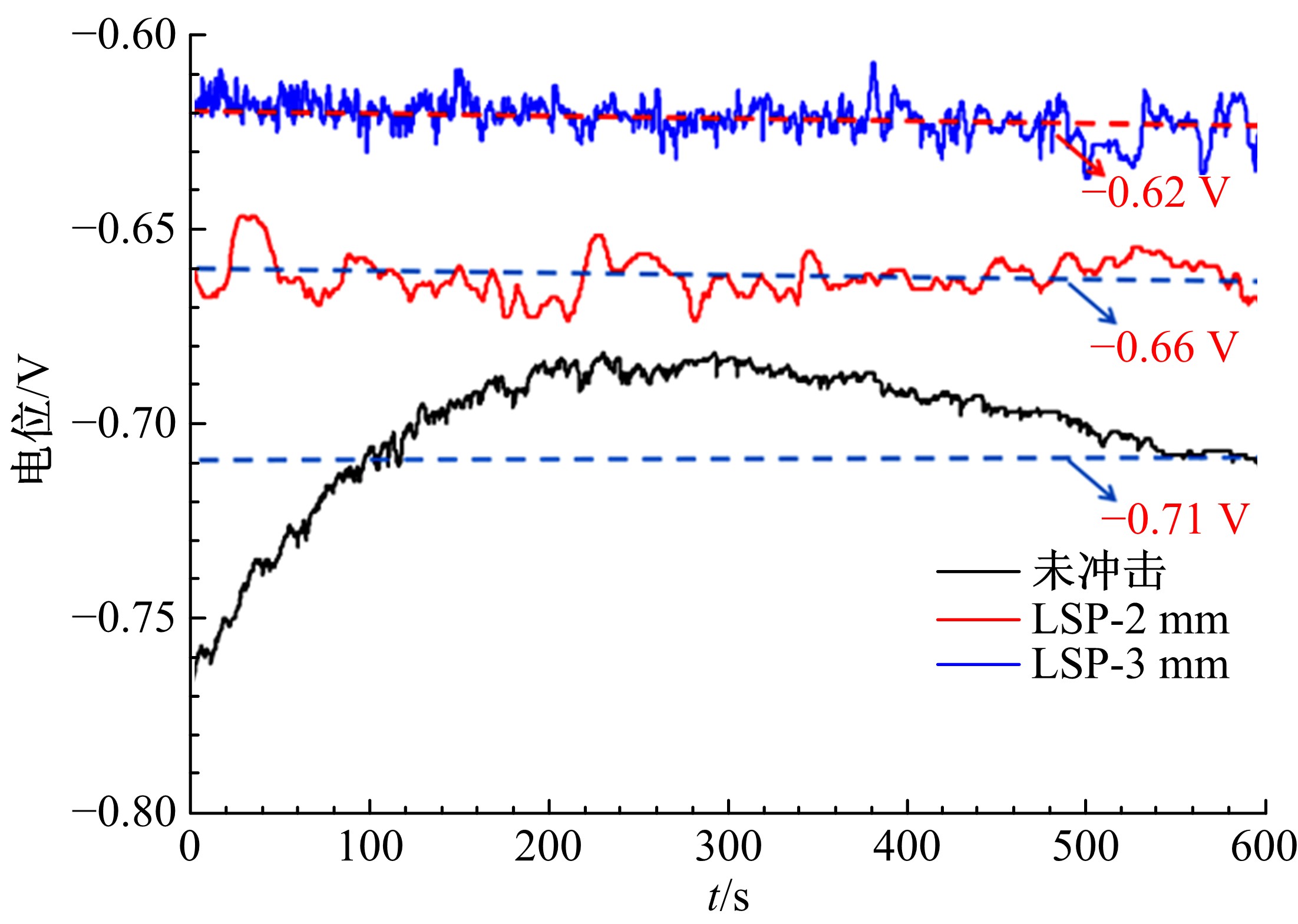
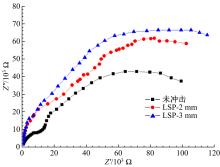
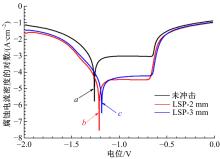
| [7] | Jin⁃zhong LU,Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO. Effect of coverage layer on corrosion resistance of 6061⁃T6 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 842-849. |
| [8] | Yu⁃peng LI,Da⁃qian SUN,Wen⁃biao GONG. Temperature fields in bobbin⁃tool friction stir welding for 6082⁃T6 aluminum alloy sheet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [9] | Kai⁃yu LUO,Yue⁃hua XING,Qing⁃feng CHAI,Shi⁃kai WU,Ye⁃fang YIN,Jin⁃zhong LU. Effects of laser shock peening on corrosion fatigue behaviour of 2Cr13 stainless steel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 850-858. |
| [10] | ZHAO Shuang,SHEN Ji-hong,ZHANG Liu,ZHAO Han,CHEN Ke-fan. Evaluation of surface roughness of micro electrical discharge machining based-on fast Gauss algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [11] | HU Zhi-qing, YAN Ting-xu, LI Hong-jie, LYU Zhen-hua, LIAO Wei, LIU Geng. Effect of cryogenic treatment on punch-shearing performance of aluminum alloy sheet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1524-1530. |
| [12] | LIU Zi-wu, LI Jian-feng. Erosion damage and evaluation of remanufacturing cladding layer for impeller metals FV520B [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 835-844. |
| [13] | HU Zhi-qing, ZHENG Hui-hui, XU Ya-nan, ZHANG Chun-ling, DANG Ting-ting. Effect of Al surface with micro/macro grooves on Al/CFRP adhesive-bonded joints [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 229-235. |
| [14] | FU Wen-zhi, LIU Xiao-dong, WANG Hong-bo, YAN De-jun, LIU Xiao-li, LI Ming-zhe, DONG Yu-qi, ZENG Zhen-hua, LIU Gui-bin. Multi-point forming process of 1561 aluminum alloy surfaces [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1822-1828. |
| [15] | CHEN Chao, ZHAO Sheng-dun, CUI Min-chao, HAN Xiao-lan, FAN Shu-qin, ISHIDA Tohru. Experimental study on reshaping method for joining AL5052 aluminum alloy sheets [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1512-1518. |
|
||