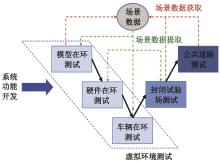
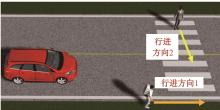
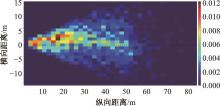
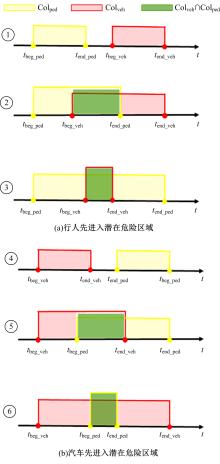
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2511-2519.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221425
Construction of virtual test scenario for intelligent vehicle and pedestrian interaction
Hong-yan GUO1,2( ),Jia-ming ZHANG1,2,Jun LIU1,3(
),Jia-ming ZHANG1,2,Jun LIU1,3( ),Yun-feng HU1,2
),Yun-feng HU1,2
- 1.National Key Laboratory of Automotive Chassis Integration and Bionics,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TP13
| 1 | Ridel D, Rehder E, Lauer M, et al. A literature review on the prediction of pedestrian behavior in urban scenarios[C]∥Proceeding of 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC), Maui, USA, 2018: 3105-3112. |
| 2 | Yuan Q, Hu M, Li Y. Scenario design and driving simulation experiment of vehicle-to-pedestrain accidents based on real accident data[J]. J Automotive Safety and Energy, 2012,3(1): 19-25. |
| 3 | Daniel J, Kara K. Preparing a nation for autonomous vehicles: opportunities, barriers and policy recommendations[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2015(77): 167-181. |
| 4 | J3016.Taxonomy and definitions for terms related to driving automation systems for on-road motor vehicles [S]. |
| 5 | Rasouli A, Tsotsos J. Autonomous vehicles that interact with pedestrians: a survey of theory and practice[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(3): 900-918. |
| 6 | Ray L, Joshué P, Martin D. A complete framework for developing and testing automated driving controllers[J]. IFAC-Papers On Line, 2017,50(1): 258-263. |
| 7 | 刘颖,贺锦鹏,朱西产,等.自动紧急制动系统行人测试场景的研究[J].汽车技术,2014(3):35-39. |
| Liu Ying, He Jin Peng, Zhu Xi-chan, et al. Research on test scenarios for AEB pedestrian system[J]. Automobile Technology, 2014(3): 35-39. | |
| 8 | 马峻岩,田叶凡,赵祥模,等.基于自然驾驶数据挖掘的二阶车辆与行人交互测试场景[J].中国公路学报, 2022,35(3):139-152. |
| Ma Jun-yan, Tian Ye-fan, Zhao Xiang-mo, et al. Two-stages test scenarios for interaction of vehicles and pedestrians based on naturalistic driving data mining[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022,35(3):139-152. | |
| 9 | V9.0.4. Vulnerable road user (VRU) protection [S]. |
| 10 | Swanson E, Yanagisawa M, Naim W, et al. Crash avoidance needs and countermeasure profiles for safety applications based on light-vehicle-to-pedestrian communications[R]. Washington DC: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, 2016. |
| 11 | Lenard J, Welsh R, Danton R. Time-to-collision analysis of pedestrian and pedal-cycle accidents for the development of autonomous emergency braking systems[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention,2018,115: 128-136. |
| 12 | 谭正平, 车瑶栎, 肖凌云, 等.面向自动驾驶的典型汽车与行人事故冲突场景研究[J].安全与环境学报,2021,21(4): 1573-1582. |
| Tan Zheng-ping, Che Yao-yue, Xiao Ling-yun, et al. Trace analysis for the typical precrash scenario between car vehicle and pedestrian caused by the automatic driving[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(4): 1573-1582. | |
| 13 | Huang X, Zhao D, Peng H. Empirical study of DSRC performance based on safety pilot model deployment data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017,18(10): 2619-2628. |
| 14 | 中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司. 中国新车评价规程(C-NCAP)2018年版管理规则[EB/OL]. [2022-11-02]. |
| 15 | 郭晓东. 轿车前方行人识别及碰撞预警系统研究[D].沈阳:东北大学机械工程与自动化学院,2012. |
| Guo Xiao-dong. Study on pedestrian recognition ahead of vehicle and collision warning system[D]. Shenyang:School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation,Northeastern University, 2012. | |
| 16 | 李霖,朱西产,陈海林.驾驶员制动和转向避撞极限[J].同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 44(11): 1743-1748. |
| Li Lin, Zhu Xi-chan, Chen Hai-lin. Drivers´ collision avoidance limit by braking and steering[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2016,44(11): 1743-1748. | |
| 17 | 蒋拯民,党少博,李慧云,等.自动驾驶汽车场景测试研究进展综述[J].汽车技术, 2022(8):10-22. |
| Jiang Zheng-min, Dang Shao-bo, Li Hui-yun, et al. A survey on the research progress of scenario-based testing for autonomous vehicles[J]. Automobile Technology, 2022(8): 10-22. |
| [1] | Bin XIAN,Yin-xin WANG,Ling WANG. Distributed robust tracking control for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles: theory and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2093-2103. |
| [2] | Xian-yi XIE,Ming-jun ZHANG,Li-sheng JIN,Bin ZHOU,Tao HU,Yu-fei BAI. Artificial bee colony trajectory planning algorithm for intelligent vehicles considering comfortable [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1570-1581. |
| [3] | Xian-yi XIE,Yu-han WANG,Li-sheng JIN,Xin ZHAO,Bai-cang GUO,Ya-ping LIAO,Bin ZHOU,Ke-qiang LI. Intelligent vehicle trajectory tracking control based on adjusting step size of control horizon [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 620-630. |
| [4] | Zhen-hai GAO,Rong-gui CAI,Tian-jun SUN,Tong YU,Hao-yuan ZHAO,Hao BAN. Data⁃filtering method for driving behavior based on vehicle shared autonomy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 589-599. |
| [5] | Li-xin YAN,Jin-pei FENG,Jun-hua GUO,Yi-ke GONG. Analysis of characteristics of the takeover behavior of co⁃driving intelligent vehicles under different dangerous scenarios [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [6] | Shou-tao LI,Jia-lin LI,Qing-yu MENG,Hong-yan GUO. Loop-closure detection algorithm based on point cloud histogram and vehicle positioning method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2395-2403. |
| [7] | Dan MA,Yu-long PEI,Tao LIU,Rui LIU. Decision making model and technical corrective measures of pedestrian's bad crossing behavior in urban road section [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 111-123. |
| [8] | Chong ZHANG,Yun-feng HU,Xun GONG,Yao SUN. Design of model⁃free adaptive sliding mode controller for cathode flow of fuel cell [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2085-2095. |
| [9] | Yun-feng HU,Tong YU,Hui-ce YANG,Yao SUN. Optimal control method of fuel cell start⁃up in low temperature environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2034-2043. |
| [10] | Wei ZHANG,Shu-pei ZHANG,Chong-en LUO,Sheng ZHANG,Guo-lin WANG. Collision avoidance trajectory planning for intelligent vehicles in emergency conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [11] | Xue-yun CHEN,Xue-yu BEI,Qu YAO,Xin JIN. Pedestrian segmentation and detection in multi-scene based on G-UNet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [12] | Xian-yan KUANG,Zi-ru CHEN. Dynamic game comity behavior at pedestrians′ crossing on unsignal-controlled roads based on cellular automata [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 837-846. |
| [13] | Yan-ling ZHANG,Can WANG,Xu ZHANG,Ang-yang WANG,Yun-sheng LI. Human⁃induced vibration analysis and pedestrian comfort evaluation for suspension footbridge with different hunger systems [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2644-2652. |
| [14] | Yuan-hong LIU,Pan-pan GUO,Yan-sheng ZHANG,Xin LI. Feature extraction of sparse graph preserving projection based on Riemannian manifold [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2268-2279. |
| [15] | De-feng HE,Jie LUO,Xiao-xiang SHU. Delay-feedback predictive cruise control of autonomous and connected vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 349-357. |
|
||