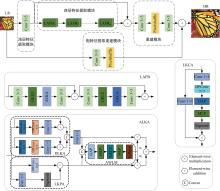
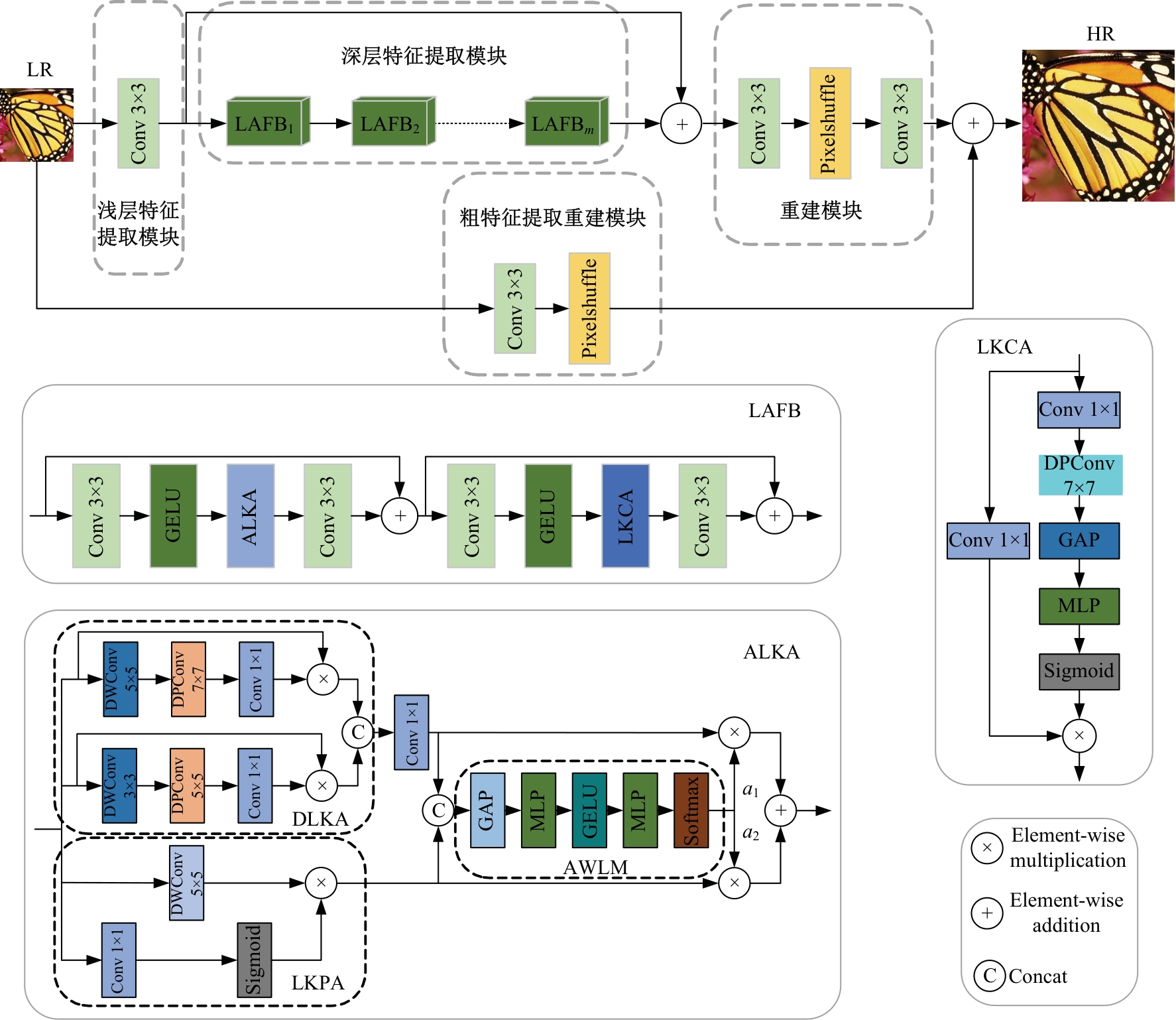
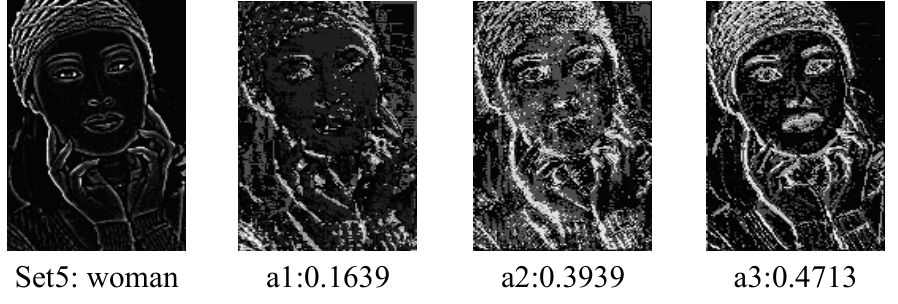
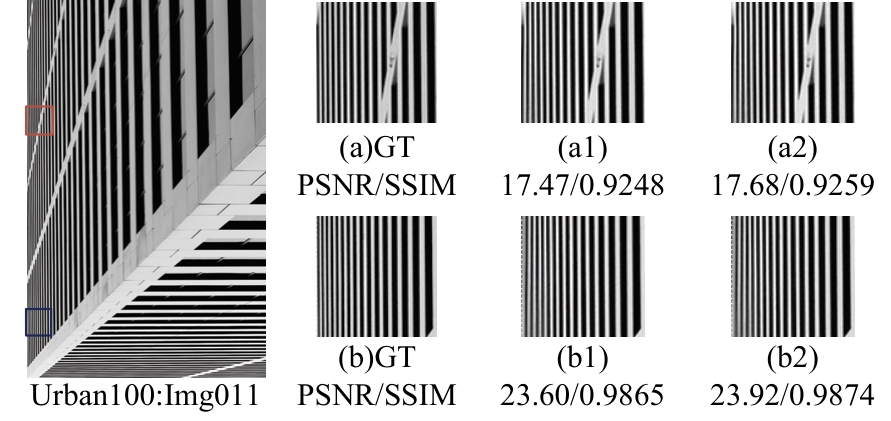
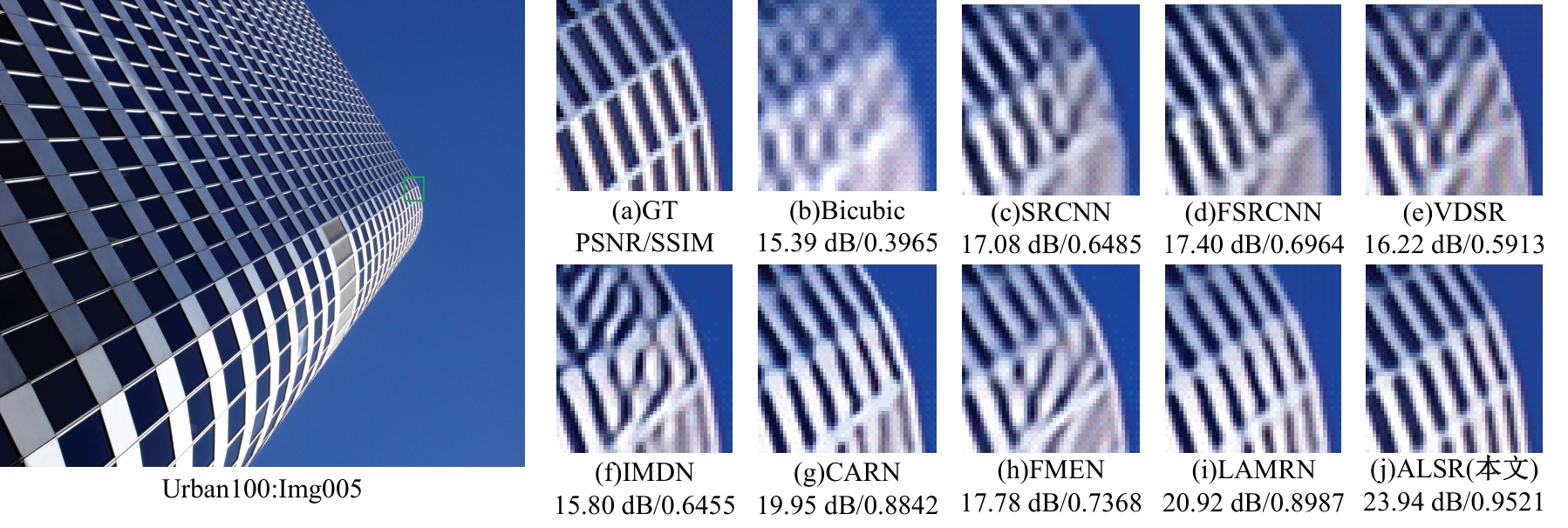
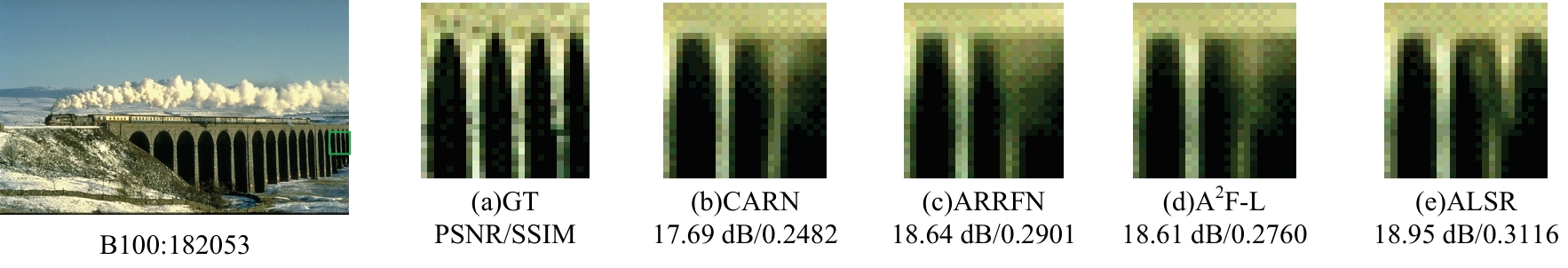
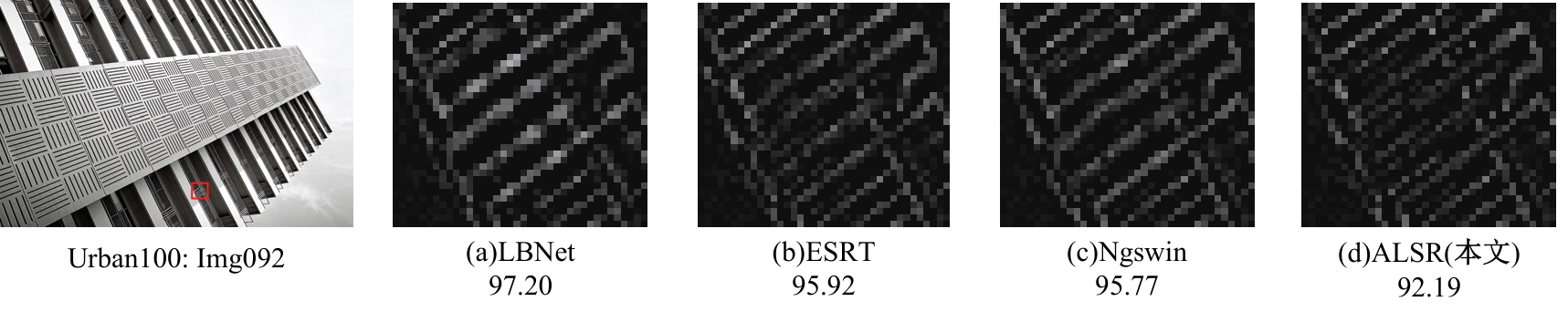
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 1015-1027.
Lightweight image super⁃resolution network based on adaptive large kernel attention fusion
De-qiang CHENG1( ),Gui LIU1,Qi-qi KOU3,Jian-ying ZHANG1,He JIANG1,2(
),Gui LIU1,Qi-qi KOU3,Jian-ying ZHANG1,He JIANG1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Information and Control Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,China
2.Key Laboratory of Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Information Processing,Institutions of Higher Education of Sichuan Province,Chengdu 610106,China
3.School of Computer Science and Technology,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Cheng D Q, Chen L L, Lv C, et al. Light-guided and cross-fusion U-Net for anti-illumination image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transaction on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(12): 8436-8449. |
| 2 | Jebkins W K, Mather B C, Jr D C M. Nearest neighbor and generalized inverse distance interpolation for fourier domain image reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Tampa, USA, 1985:1069-1072. |
| 3 | Blu T, Thevenaz P, Unser M. Linear interpolation revitalized[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(5): 710-719. |
| 4 | Lin C, Shen M, Chang H, et al. The efficient VLSI design of BICUBIC convolution interpolation for digital image processing[C]∥Proceedings of the International Symposium on Circuitsand Systems (ISCAS), Seattle, USA, 2008:480-483. |
| 5 | Dai S, Han M, Xu W,et al. Soft-cuts: a soft edge smoothness prior for color image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(5): 969-981. |
| 6 | Sun J, Xu Z, Shun H Y. Image super-resolution using gradient profile prior[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Reco Anchorage, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2008: 1-8. |
| 7 | Yan Q, Xu Y, Yang X, et al. Single image super resolution based on gradient profile sharpness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015,24(10):3187-3202 . |
| 8 | iang H J, Mujtaba A S A D, Liu J J, et al. Single image detail enhancement via metropolis theorem[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications,2024, 83: 36329-36353. |
| 9 | 程德强, 郭昕, 陈亮亮, 等. 多通道递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建[J].中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(3): 605-618. |
| Cheng De-qiang, Guo Xin, Chen Liang-liang, et al. Image super resolution reconstruction by multi-channel recursive residual networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(3): 605-618. | |
| 10 | Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. |
| 11 | Shi W, Caballero J, Huszár F,et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016:1874-1883. |
| 12 | Lim B, Son S, Kim H,et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu,USA, 2016:1132-1140. |
| 13 | 郭继昌, 吴洁, 郭春乐, 等. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| Guo Ji-chang, Wu Jie, Guo Chun-le, et al.Image super-resolution reconstruction based on residual-connected convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition,2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. | |
| 14 | Zhang Y, Li K. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich Germany, 2018: 286-301. |
| 15 | Niu B, Wen W L, Ren W Q,et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network[C]∥ 2020 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, USA, 2020:191-207. |
| 16 | Vaswan A, Shazeer N, Parmar, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL].[2023-09-15]. |
| 17 | Liang J Y, Cao J Z, Sun G L,et al. Image restoration using swin transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1833-1844. |
| 18 | Lu Z S, Li J C, Liu H, et al. Transformer for single image super-resolution[C]∥Proc IEEE/CVF Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit Workshops, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 456-465. |
| 19 | Kou Q Q, Cheng D Q, Zhang H et al. Single Image super resolution via multi-attention fusion recurrent network[J]. IEEE Access,2023(11): 98653-98665. |
| 20 | Wang Z, Gao G, Li J,et al. Lightweight image super-resolution with multi-scale feature interaction network[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Shenzhen, China, 2021: No.9428136. |
| 21 | Lan R, Sun L, Liu Z,et al. MADNet:a fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021,51(3):1443-1453. |
| 22 | Guo M H, Lu C Z, Liu Z N,et al. Visual attention network[J/OL].[2023-09-18]. |
| 23 | Jie H, Li S, Samuel A, et al. Squeeze-and-excita⁃tion networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni⁃tion, Wellington, New Zealand, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| 24 | Bevilacqua M, Roumy A, Guillemot C, et al. Low-complexity single image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbour embedding[C]∥British Machine Vision Conference, Oxford,UK, 2012:1-10. |
| 25 | Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations[C]∥International Conference on Curves and Surfaces,Avignon, France, 2010: 711-730. |
| 26 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016:1646-1654. |
| 27 | Huang J B, Singh A, Ahuja N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Boston, USA, 2015:5197-5206. |
| 28 | Dong C, Loy C C, Tang X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision,Amsterdam, Holland, 2016:391-407. |
| 29 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646-1654. |
| 30 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA,2016:1637-1645. |
| 31 | Ahh N, Kang B, Sohn K A. Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 256-272. |
| 32 | Hui Z, Gao X, Yang Y, et al. Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Xi'an, China, 2019: 2024-2032. |
| 33 | Wang X H, Wang Q, Zhao Y Z, et al. Lightweight single-image super-resolution network with attentive auxiliary feature learning[C]∥Asian Conference on Computer Vision(ACCV),Kyoto, Japan, 2020: 3023-3041. |
| 34 | Du Z C, Liu D, Liu J, et al. Fast and memory-efficient network towards efficient image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans, USA, 2022 :853-862. |
| 35 | Yan Y, Xu X, Chen W, et al. Lightweight attended multi-scale residual network for single image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 52202-52212. |
| 36 | Qin J, Zhang R. Lightweight single image super-resolution with attentive residual refinement network[J].Neurocomputing, 2022, 500: 846-855. |
| 37 | Gao G W, Wang Z X, Li J C, et al. Lightweight bimodal network for single-image super-resolution via symmetric CNN and recursive transformer[C]∥International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,Shenzhen, China, 2022: 913-919. |
| 38 | Choi H, Lee J, Yang J. N-Gram in swin transformers for efficient lightweight image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canadian, 2023: 2071-2081. |
| 39 | Jie H, Li S, Samuel A, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Wellington, New Zealand, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| [1] | Hua-song DONG,Yuan-feng LIAN. Lightweight detection algorithm for lossless transcoding and heavy compression of massive digital media videos [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 741-747. |
| [2] | Hua CAI,Yan-yang ZHENG,Qiang FU,Sheng-yu WANG,Wei-gang WANG,Zhi-yong MA. Three-dimensional object detection algorithm based on multi-scale candidate fusion and optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 709-721. |
| [3] | Hua CAI,Ting-ting KOU,Yi-ning YANG,Zhi-yong MA,Wei-gang WANG,Jun-xi SUN. Three-dimensional vehicle multi-target tracking based on trajectory optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. |
| [4] | Xin-gang GUO,Ying-chen HE,Chao CHENG. Noise-resistant multistep image super resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [5] | Zi-chao ZHANG,Jian CHEN. A mapping method using 3D orchard point cloud based on hawk-eye-inspired stereo vision and super resolution [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1469-1481. |
| [6] | Guang HUO,Da-wei LIN,Yuan-ning LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Meng YUAN,Di GAI. Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [7] | Ben-huai LI,Yan-wen LIU,Lu WANG,Xue-qian CHEN,Wen-jie ZUO. Crashworthiness optimization for frontal⁃end structure of rail vehicle constrained with absorbed energy and crushed displacements [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 982-988. |
| [8] | Bin-xiang JIANG,Hong-kui XU,Dan HE. Drug Efficiency improvement of drug detection big data based on blockchain [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1666-1678. |
| [9] | Fei-yue DENG, LYUHao-yang,Xiao-hui GU,Ru-jiang HAO. Fault diagnosis of high⁃speed train axle bearing based on a lightweight neural network Shuffle⁃SENet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. |
| [10] | Yong CHEN,Chen-tao LU,Zhen WANG. Detection of foreign object intrusion in railway region of interest based on lightweight network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2405-2418. |
| [11] | Yan-lei XU,Run HE,Yu-ting ZHAI,Bin ZHAO,Chen-xiao LI. Weed identification method based on deep transfer learning in field natural environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [12] | Chao MA,Yun-kai GAO,Zhe LIU,Yue-xing DUAN,Lin-li TIAN. Optimization of multi⁃material and beam cross⁃sectional shape and dimension of skeleton⁃type body [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [13] | Li-sheng JIN,Bai-cang GUO,Fang-rong WANG,Jian SHI. Dynamic multiple object detection algorithm for vehicle forward based on improved YOLOv3 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [14] | Zhe-ming YUAN,Hong-jie YUAN,Yu-xuan YAN,Qian LI,Shuang-qing LIU,Si-qiao TAN. Automatic recognition and classification of field insects based on lightweight deep learning model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [15] | Hui YE,Chang LIU,Kang-kang YAN. Application of fiber reinforced composite in auto⁃body panel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 417-425. |
|
||