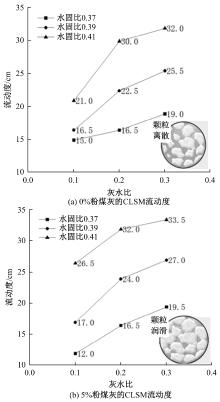
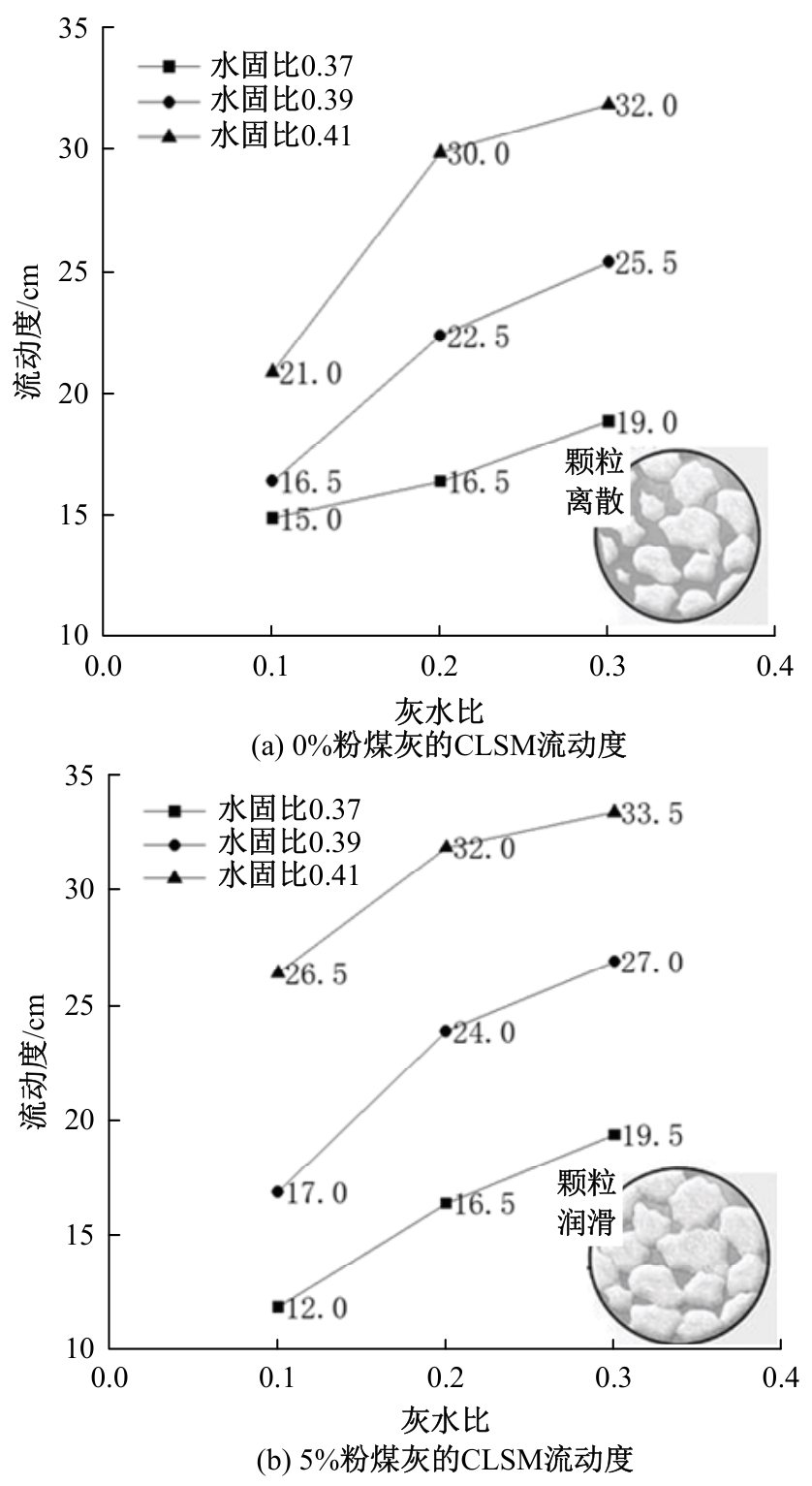
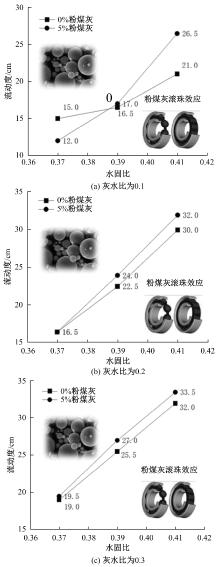
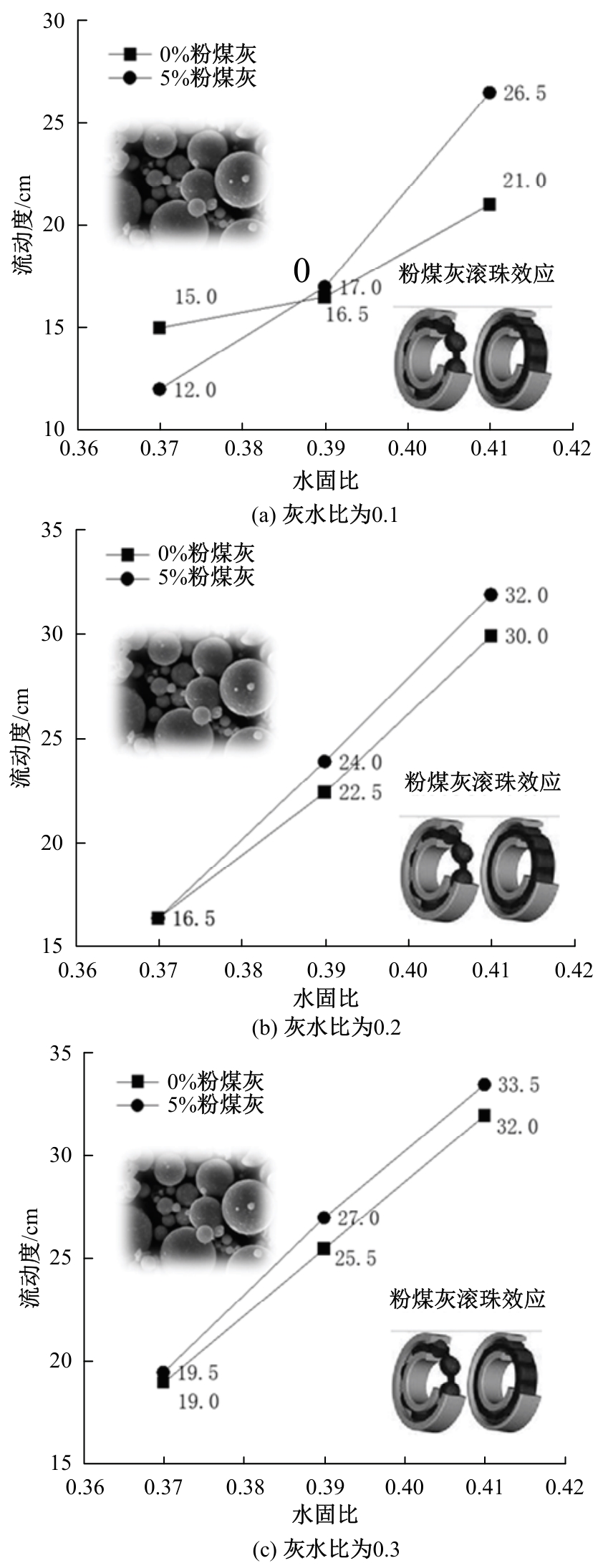
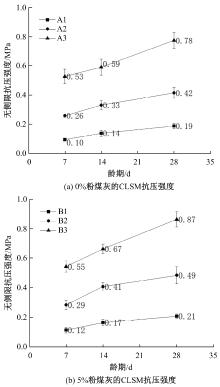
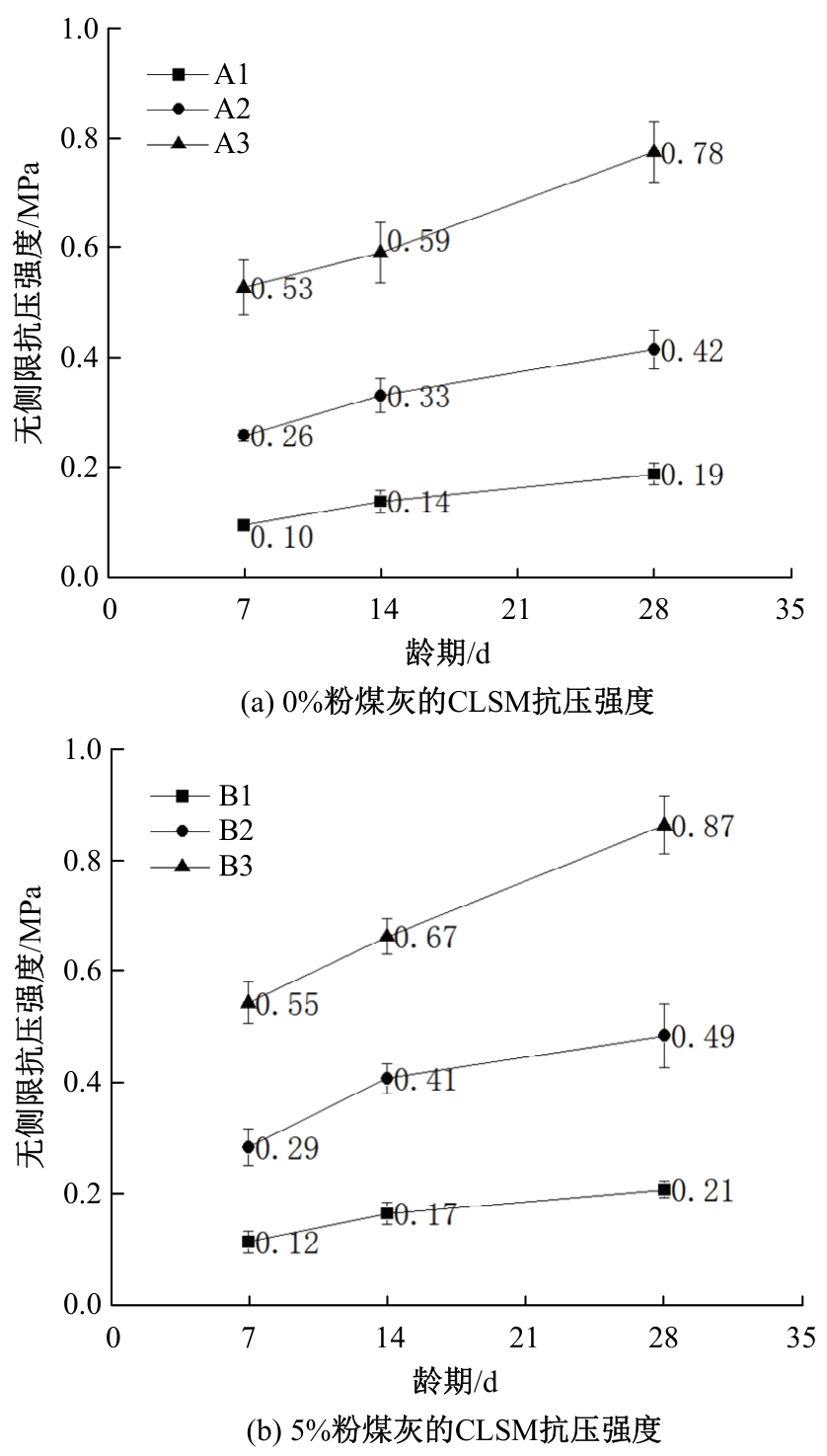
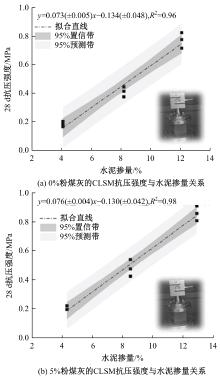
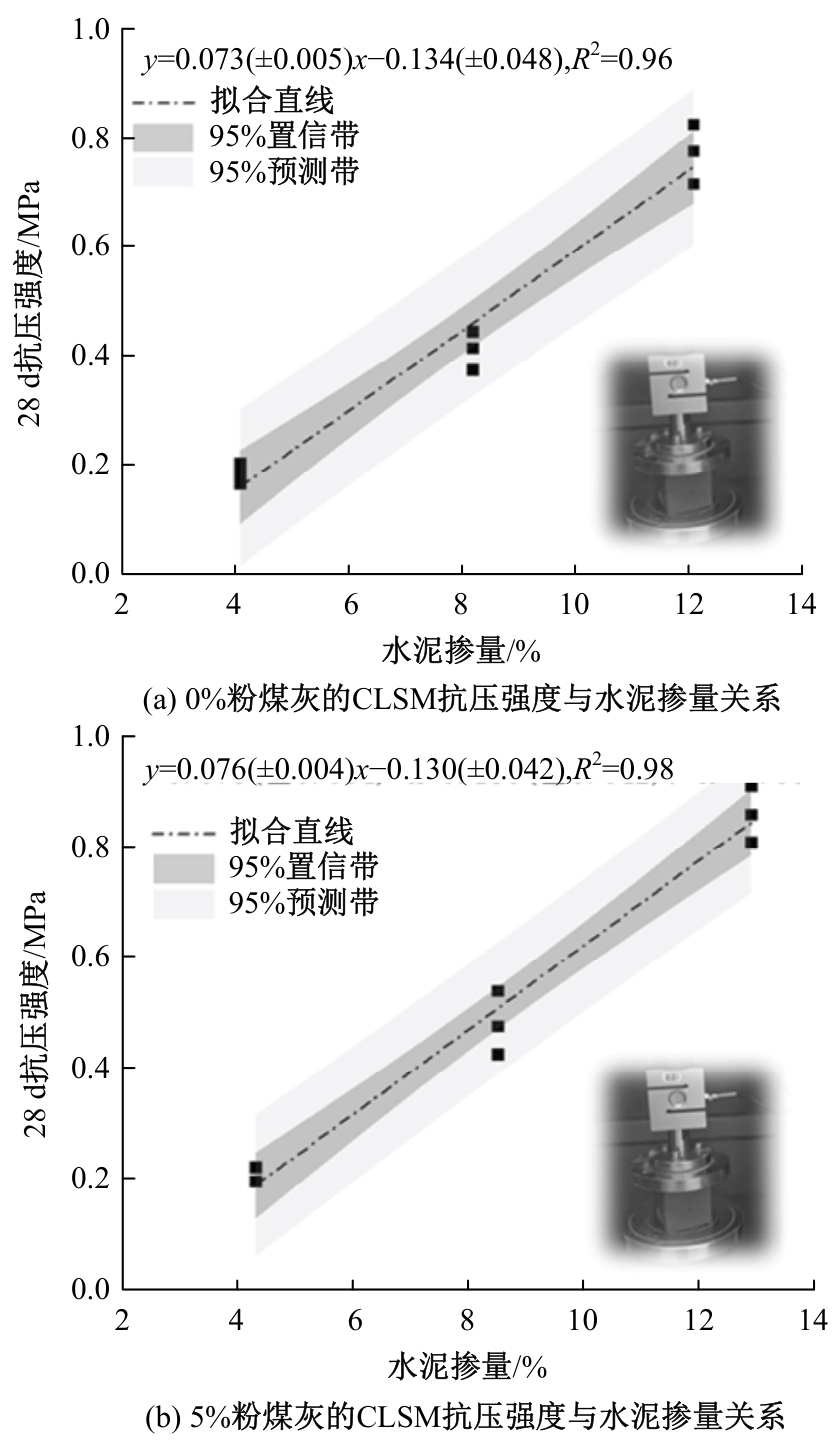
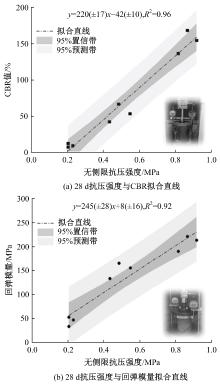
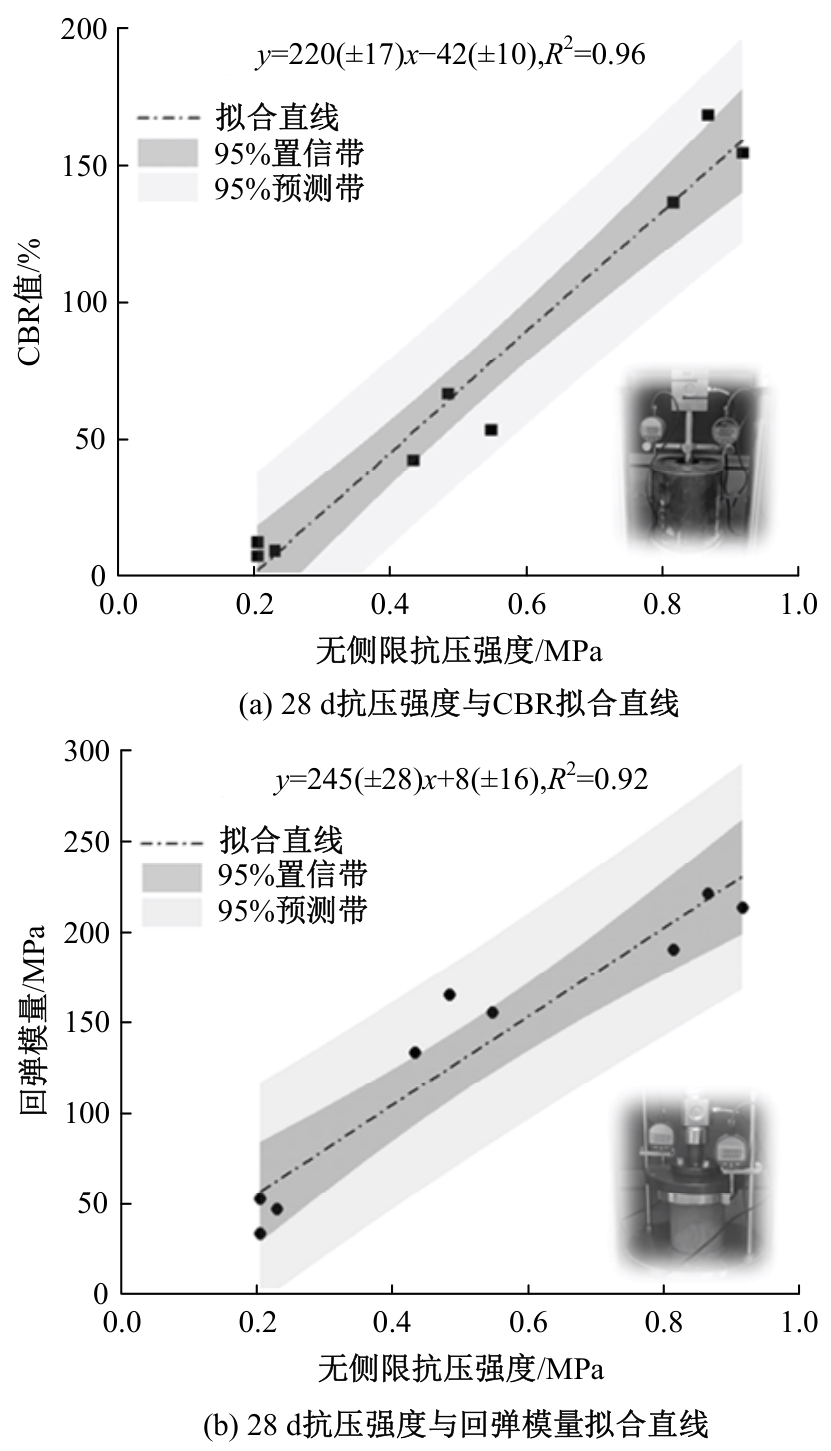
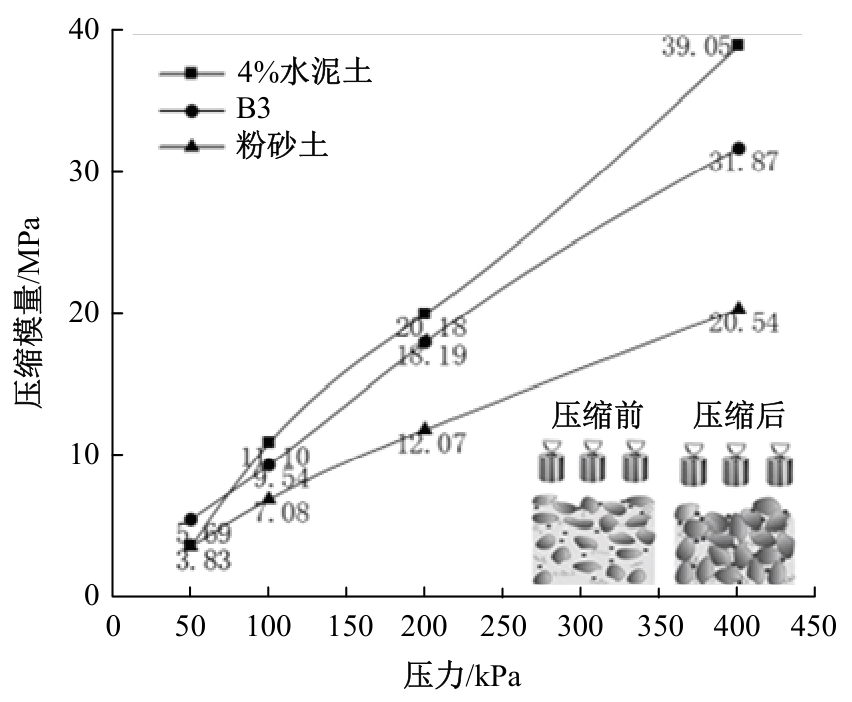
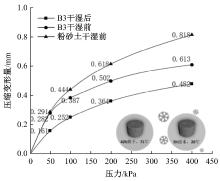
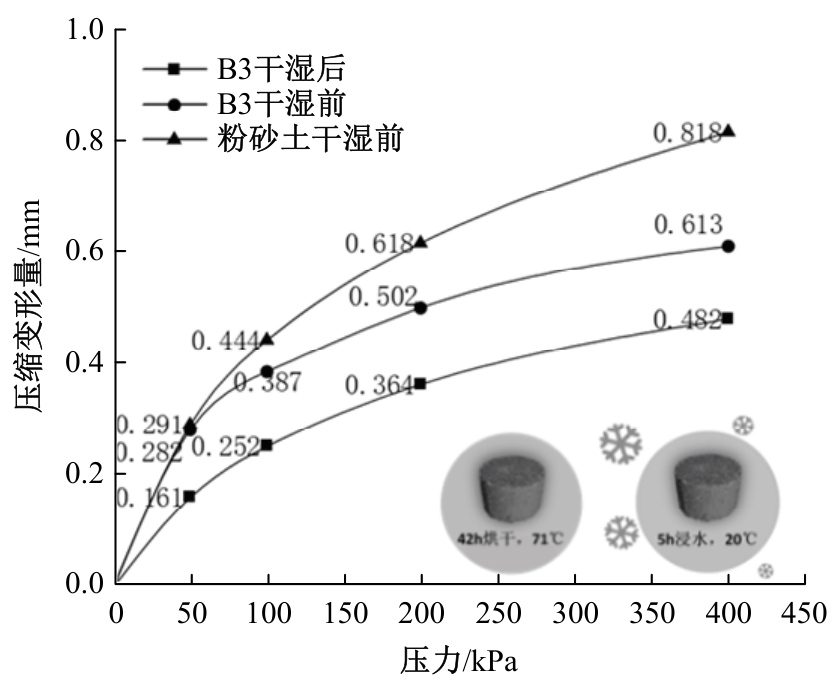
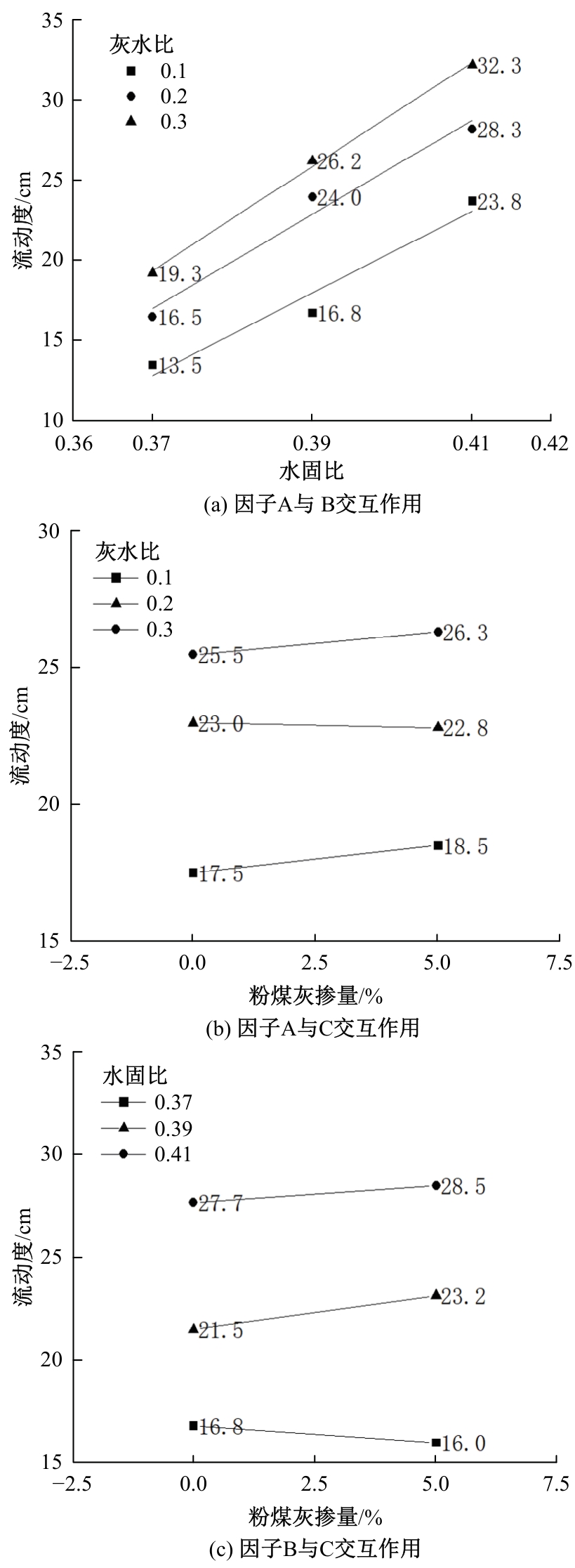
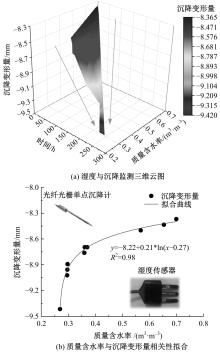
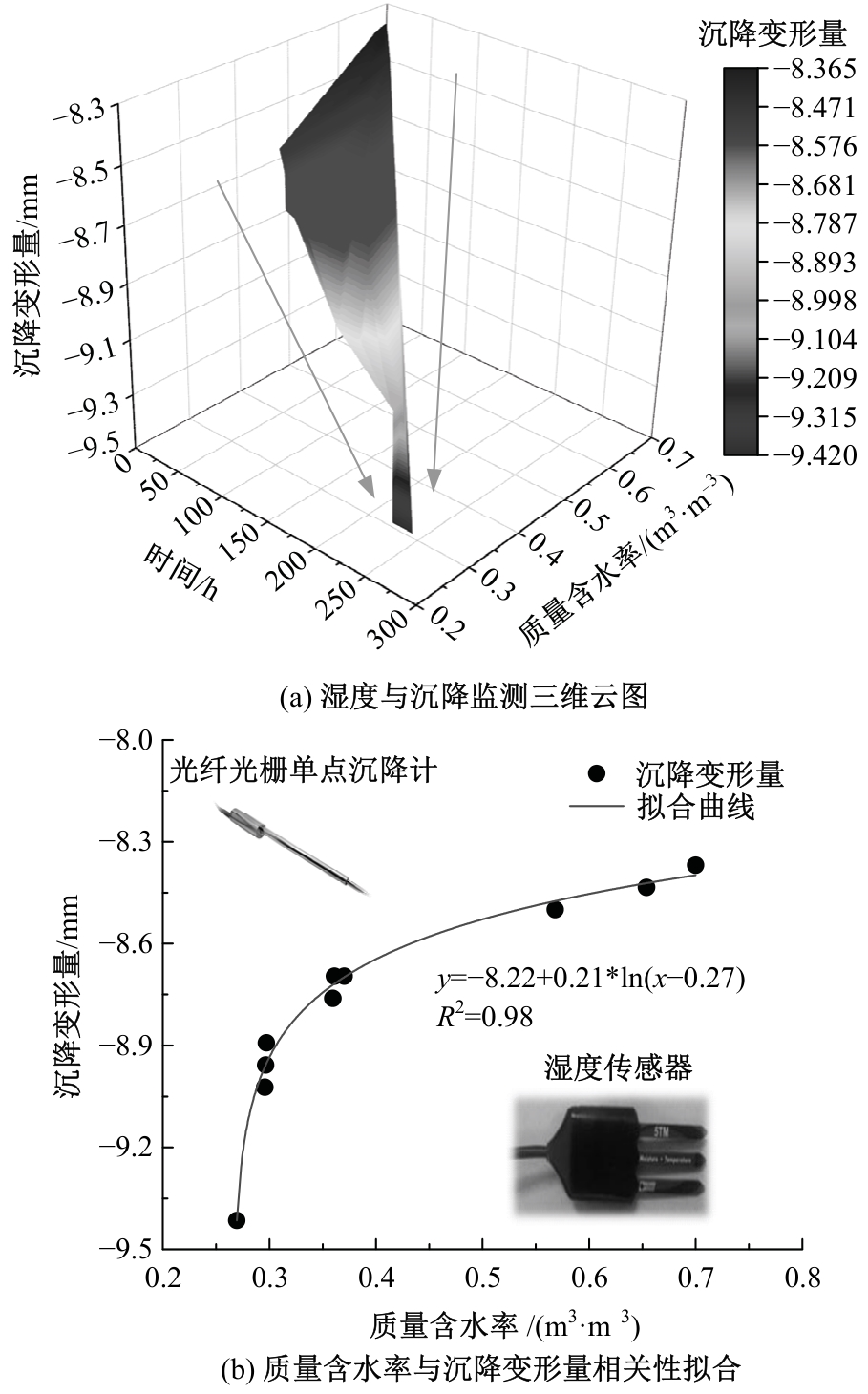
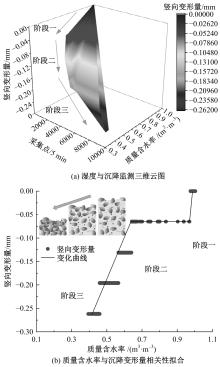
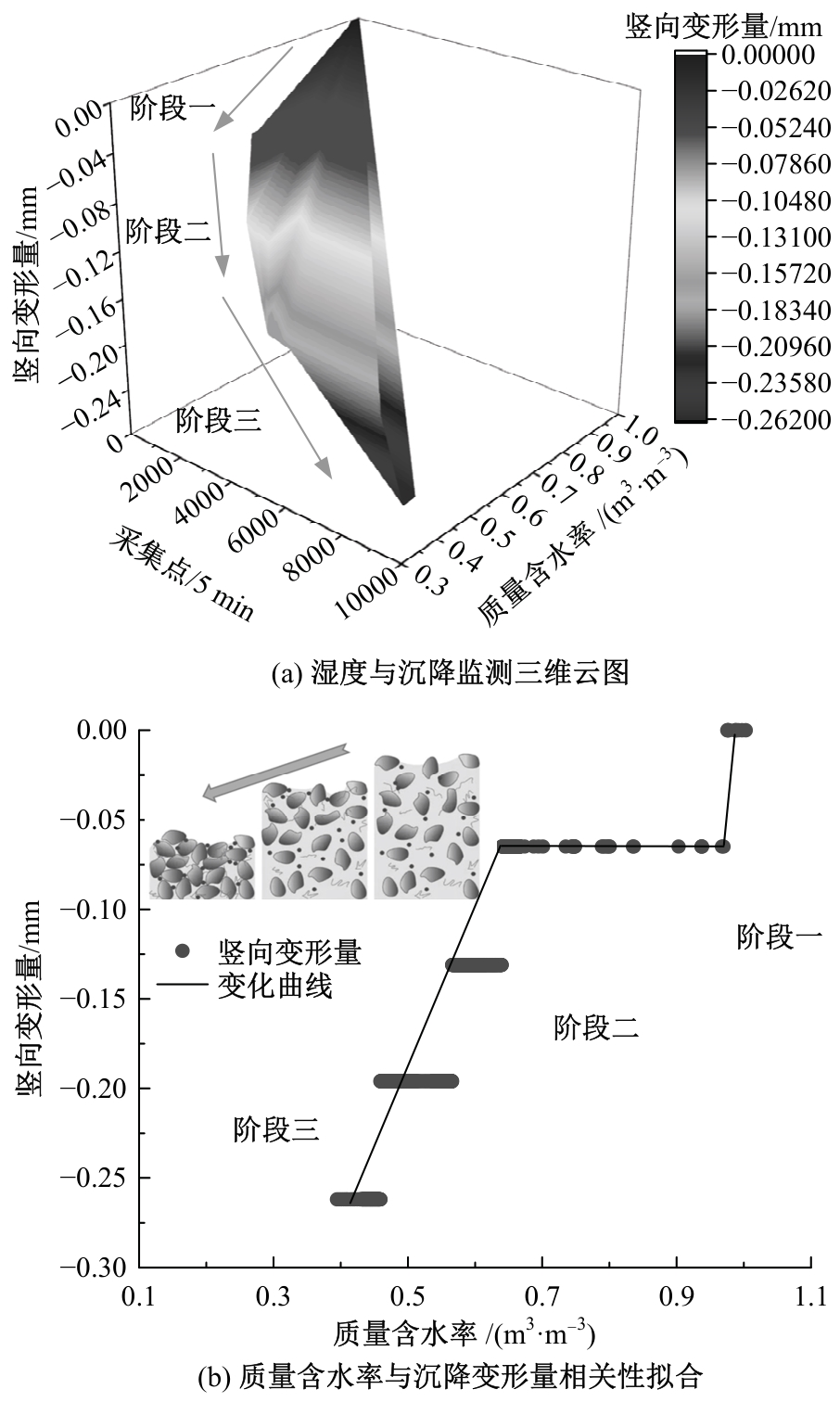
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2657-2668.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231269
Controlled low strength materials based on silty sand and its properties in narrow backfill zone
Ling XU1( ),Xiao-bing WANG1,Jie YUAN1(
),Xiao-bing WANG1,Jie YUAN1( ),Hua-ping REN2,Yi-feng HAN3,Xi-yong XU3
),Hua-ping REN2,Yi-feng HAN3,Xi-yong XU3
- 1.School of Transportation Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.China Airport Planning & Design Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100029,China
3.Shandong Provincial Airport Management Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Jinan 250107,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| [1] | 樊亮, 周圣杰, 侯佳林, 等. 黄河淤积粉土的两种复合稳定方案与性能对比[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(12): 118-124. |
| Fan Liang, Zhou Sheng-jie, Hou Jia-lin, et al. Composite stabilization of silty soil near the yellow river: two methods and performance comparison[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(12): 118-124. | |
| [2] | 刘丽萍. 低液限粉土路基填料工程特性研究[J]. 路基工程, 2010(2): 65-66. |
| Liu Li-ping. Study on engineering characteristics of low liquid limit silt in subgrade filling[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2010(2): 65-66. | |
| [3] | 张晶, 王云, 付伟, 等. 黄淮地区粉土填料长期路用性能试验研究[J]. 路基工程, 2022(1): 62-65. |
| Zhang Jing, Wang Yun, Fu Wei, et al. Experimental study on long-term road performance of silt filler in huanghuai area[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2022(1): 62-65. | |
| [4] | 赵振国. 水撼法施工水泥稳定砂砾的应用研究 [J]. 公路工程, 2013, 38(2): 47-50. |
| Zhao Zhen-guo. Application of cement stabilized gravel constructed with water shake method[J]. Highway Engineering, 2013, 38(2): 47-50. | |
| [5] | 王建刚, 张金喜, 郭阳阳. 建筑垃圾控制性低强度材料性能及工程应用[C]∥世界交通运输大会, 北京,中国, 2018: 161-170. |
| [6] | 鲍远琴. 自流平回填材料的研制及其在检查井中的应用[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学土木与水利工程学院, 2013. |
| Bao Yuan-qin. Development of self-leveling backfill material and its application in the check well[D]. Hefei: School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, 2013. | |
| [7] | Ho L S, Jhang B J, Hwang C L, et al. Development and characterization of a controlled low-strength material produced using a ternary mixture of Portland cement, fly ash, and waste water treatment sludge[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 356: No.131899. |
| [8] | Alizadeh V. Influence of cementing paste volume on properties of controlled low strength materials[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(3): No.04017305. |
| [9] | Siddique R. Utilization of waste materials and by-products in producing controlled low-strength materials[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2009, 54(1): 1-8. |
| [10] | Lee N K, Kim H K, Park I S, et al. Alkali-activated, cementless, controlled low-strength materials (CLSM) utilizing industrial by-products[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 738-746. |
| [11] | Chen T, Yuan N, Wang S, et al. The effect of bottom ash ball-milling time on properties of controlled low-strength material using multi-component coal-based solid wastes[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(16): No.69949. |
| [12] | 杨媛媛, 黄春文, 王夏. 固体废弃物在自流平砂浆中的应用 [J]. 福建建材, 2018(10): 36-38. |
| Yang Yuan-yuan, Huang Chun-wen, Wang Xia. Application of solid waste in self-leveling mortar[J]. Fujian Building Materials, 2018(10): 36-38. | |
| [13] | 朱浩泽, 于峰泉, 耿健, 等. 钛石膏基可控低强度材料强度及体积稳定性研究 [J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(11): 3644-3653. |
| Zhu Hao-ze, Yu Feng-quan, Geng Jian, et al. Strength and volume stability of controlled low-strength material based on titanium gypsum[J]. Bulletin of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2021, 40(11): 3644-3653. | |
| [14] | 范猛, 张金喜, 苗英豪, 等. 非压实回填土性能及工程应用研究 [J]. 公路交通科技: 应用技术版, 2008, 4(): 246-250. |
| Fan Meng, Zhang Jin-xi, Miao Ying-hao, et al. Study on properties and engineering application of uncompacted backfill [J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation (Research and Development Applied Technology Edition), 2008, 4(Sup1): 246-250. | |
| [15] | 王智远, 张宏, 钱劲松, 等. 干旱区工业废渣粉煤灰回填材料拌合物的流动性能研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(4): 160-165. |
| Wang Zhi-yuan, Zhang Hong, Qian Jin-song, et al. Research on the flow ability of mixture of flowable backfill materials using industrial waste fly ash in arid zone[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(4): 160-165. | |
| [16] | Lee K H, Kim J D. Performance evaluation of modified marine dredged soil and recycled in-situ soil as controlled low strength materials for underground pipe[J]. Ksce Journal of Civil Engineering, 2013, 17(4): 674-680. |
| [17] | 刘萌. 建筑渣土制备可控低强材料及性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学土木与交通工程学院, 2016. |
| Liu Meng. Preparation and properties of controlled low-strength materials produced by construction waste[D]. Beijing:School of Civil and Transportation Engineering, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2016. | |
| [18] | 张骏, 兰思杰, 李阳, 等. 用电石渣、钢渣和煤矸石制备可控性低强度材料[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(4): 1967-1972. |
| Zhang Jun, Lan Si-jie, Li Yang, et al. Using steel slag, carbide slag and coal gangue to make controlled low strength material[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(4): 1967-1972. | |
| [19] | 李晶辉, 刘兆爽, 赵文杰. 石膏基自流平地面材料的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(11): 3587-3593. |
| Li Jing-hui, Liu Zhao-shuang, Zhao Wen-jie. Research development of gypsum based self-leveling materials of floor[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 35(11): 3587-3593. | |
| [20] | 李静静. 硅灰对石膏基自流平砂浆性能的影响研究 [J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2020(5): 80-82. |
| Li Jing-jing. Influence of silica fume on properties of gypsum-based self-leveling mortar[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2020(5): 80-82. | |
| [21] | 张雄, 刘恒, 张恒, 等. 聚羧酸减水剂引气效应复配优化研究 [J]. 建筑材料学报, 2019, 22(6): 957-962. |
| Zhang Xiong, Liu Heng, Zhang Heng, et al. Optimization of air entrained effect of polycarboxylate superplasticizer[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2019, 22(6): 957-962. |
| [1] | Gui-shen YU,Xin CHEN,Yue TANG,Chun-hui ZHAO,Ai-jia NIU,Hui CHAI,Jing-xin NA. Effect of laser surface treatment on the shear strength of aluminum-aluminum bonding joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2555-2569. |
| [2] | Yao-gang TIAN,Jing JIANG,Cheng ZHAO,Xiao-min YANG,Jun ZHANG,Kan JIA. Temperature resistance mechanism of high-early-strength cement mortar modified with waterborne epoxy resin [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2203-2211. |
| [3] | Kang YAO,Qiao DONG,Xue-qin CHEN,Bin SHI,Shi-ao YAN,Xiang WANG. Mixed⁃mode mesoscale fracture behavior of concrete based on a phase field regularized cohesive zone model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2286-2297. |
| [4] | Zhi-you LONG,Zhao-long WAN,Shi DONG,Chao YANG,Xiao-yang LIU. Displacement prediction of highway slope based on variational mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2320-2332. |
| [5] | Zhi-jun TENG,Li-bo YU,Ming-zhe LI,Run-sheng MIAO,Ji-hong WANG. WSNs sybil attack detection strategy integrating interactive reputation and RSSR [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2455-2463. |
| [6] | Wan-feng WEI,Hong-gang ZHANG,Yang-peng ZHANG,Fan YANG,Bo-ming TANG,Ling-yun KONG. Research progress on modification mechanism, preparation and performance of waste rubber powder modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1834-1853. |
| [7] | Zhen YANG,Rui-ping ZHENG,Zhe GONG. Highway infrastructure performance and traffic state prediction on road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1973-1983. |
| [8] | Sheng-qi MEI,Xiao-dong LIU,Xing-ju WANG,Xu-feng LI,Teng WU,Xiang-xu CHENG. Prediction of high strength concrete creep based on parametric MIC analysis and machine learning algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1595-1603. |
| [9] | An-shun ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Feng GAO. Shear properties and stress-strain relationships characterization of Changsha compacted clay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1604-1616. |
| [10] | Li-ming WANG,Zi-kun SONG,Hui ZHOU,Wen WEI,Hao YUAN. Rheological response and response mechanism of petroleum asphalt treated with ultrasound [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1346-1355. |
| [11] | Zi-ming HE,Ai-qin SHEN,Lu-sheng WANG,Yin-chuan GUO,Jiang-fei HE. Review on strengthening technology of recycled concrete aggregate and its effect on performance of recycled aggregate concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 790-810. |
| [12] | Liang-liang ZHANG,Hua CHENG,Xiao-jian WANG. Energy evolution law and failure criterion of high strength concrete under conventional triaxial compression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 974-985. |
| [13] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [14] | Jun-peng XU,Chuan-feng ZHENG,Yan-tao DU,Yu-hang WANG,Zheng LU,Wen-jun FAN. Damage effects of water⁃heat⁃force coupling in permeable asphalt mixture in cold region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 877-887. |
| [15] | Yan-hai YANG,Bai-chuan LI,Ye YANG,Chong-hua WANG,Liang YUE. Aggregate ellipsoidal surface base reconstruction with virtual splitting tests [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 653-663. |
|
||