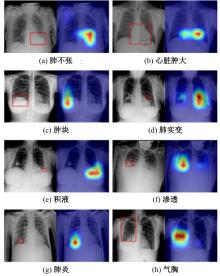
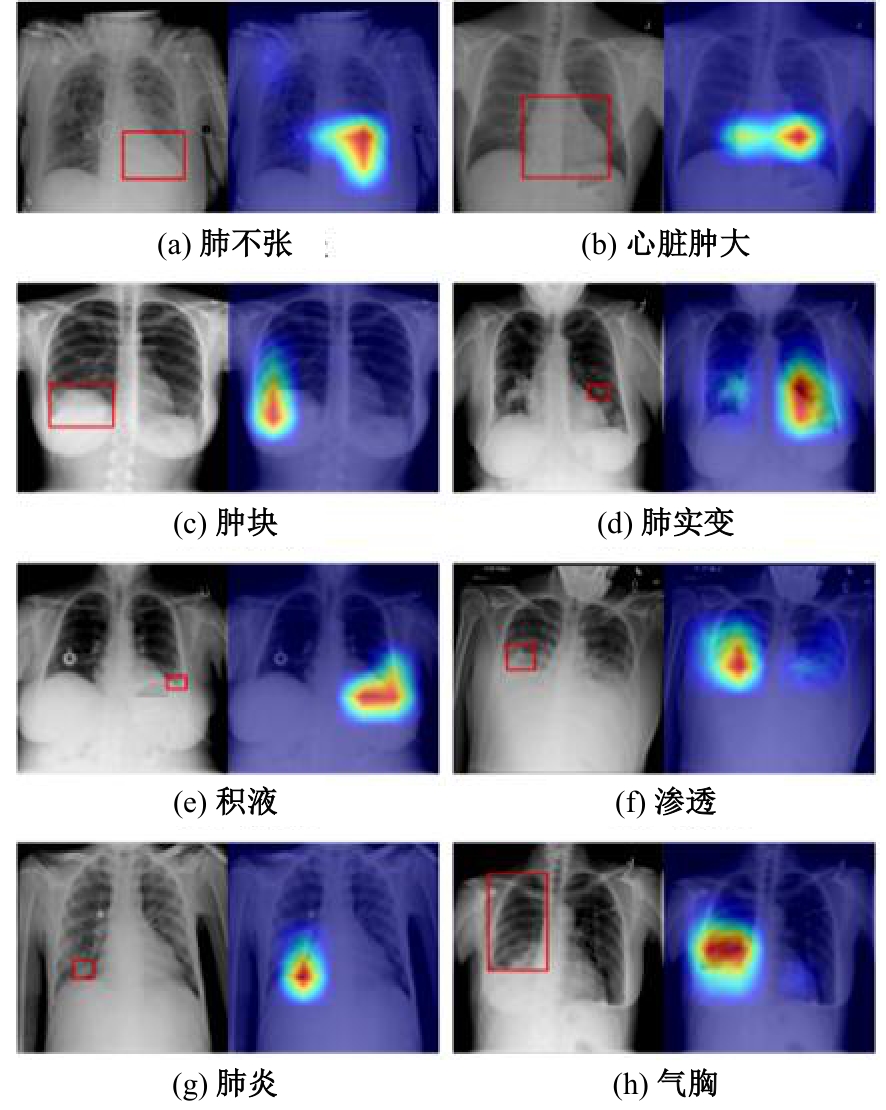
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3686-3696.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240222
Chest X-ray images classification based on multi-scale attention information multiplexing network
Rui-feng ZHANG( ),Fang-zhao GUO,Qiang LI(
),Fang-zhao GUO,Qiang LI( )
)
- School of Microelectronics,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| [1] | Wei X L, Li W, Zhang M M, et al. Medical hyperspectral image classification based on end-to-end fusion deep neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2019, 68(11): 4481-4492. |
| [2] | 刘桂霞, 田郁欣, 王涛, 等. 基于双输入3D卷积神经网络的胰腺分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(12): 3565-3572. |
| Liu Gui-xia, Tian Yu-xin, Wang Tao, et al. Pancreas segmentation algorithm based on dual input 3D convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3565-3572. | |
| [3] | 王雪, 李占山, 吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| Wang Xue, Li Zhan-shan, Ying-da Lyu. Medical image segmentation based on multi-scale context-aware and semantic adaptor[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. | |
| [4] | Wang X S, Peng Y F, Lu L, et al. ChestX-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, USA, 2017: 3462-3471. |
| [5] | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton E G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| [6] | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| [7] | Irvin J, Rajpurkar P, Ko M, et al. CheXpert: A large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Washington, DC: AAAI Press, 2019: 590-597. |
| [8] | Jiang X B, Zhu Y, Cai G, et al. MXT: A new variant of pyramid vision transformer for multi-label chest x-ray image classification[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2022, 14(4): 1362-1377. |
| [9] | Wang W H, Xie E Z, Li X, et al. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]∥2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2021: 548-558. |
| [10] | 胡锦波, 聂为之, 宋丹, 等. 可形变Transformer辅助的胸部X光影像疾病诊断模型[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2023, 57(10): 1923-1932. |
| Hu Jin-bo, Nie Wei-zhi, Song Dan, et al. Chest X-ray imaging disease diagnosis model assisted by deformable transformer[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(10): 1923-1932. | |
| [11] | Wang H Y, Wang S S, Qin Z B, et al. Triple attention learning for classification of 14 thoracic diseases using chest radiography[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 67: 101846. |
| [12] | Zhu X F, Pang S M, Zhang X X, et al. PCAN: Pixel-wise classification and attention network for thoracic disease classification and weakly supervised localization[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2022, 102: 102137. |
| [13] | Chen K, Wang X Q, Zhang S W. Thorax disease classification based on pyramidal convolution shuffle attention neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 85571-85581. |
| [14] | Lu Z C, Deb K, Boddeti V N. MUXConv: Information multiplexing in convolutional neural networks[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, 6: 12041-12050. |
| [15] | Woo S H, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]∥Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Mature Switzerland AG, 2018: 3-19. |
| [16] | Ridnik T, Ben B E, Zamir N, et al. Asymmetric loss for multi-label classification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2021: 82-91. |
| [17] | Guan Q J, Huang Y P, Luo Y W, et al. Discriminative feature learning for thorax disease classification in chest X-ray images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2476-2487. |
| [18] | Lee Y W, Huang S K, Chang R F. CheXGAT: A disease correlation-aware network for thorax disease diagnosis from chest X-ray images[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2022, 132: 102382. |
| [19] | Chen B Z, Zhang Z, Li Y J, et al. Multi-label chest X-ray image classification via semantic similarity graph embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(4): 2455-2468. |
| [20] | Pham H, Le T, Tran D, et al. Interpreting chest X-rays via CNNs that exploit hierarchical disease dependencies and uncertainty labels[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 437: 186-194. |
| [21] | Selvaraju R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2017: 618-626. |
| [1] | Yu-fei ZHANG,Li-min WANG,Jian-ping ZHAO,Zhi-yao JIA,Ming-yang LI. Robot inverse kinematics solution based on center selection battle royale optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2703-2710. |
| [2] | Wen-hui LI,Chen YANG. Few-shot remote sensing image classification based on contrastive learning text perception [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2393-2401. |
| [3] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Liang LI. Graph similarity measurement algorithm combining global and local fine-grained features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2365-2371. |
| [4] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [5] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhe GUO,Yu-si FAN. Feature representation algorithm for imbalanced classification of multi⁃omics cancer data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2089-2096. |
| [6] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [7] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU. A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [8] | Li-ming LIANG,Long-song ZHOU,Jiang YIN,Xiao-qi SHENG. Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [9] | Dondrub LHAKPA,Duoji ZHAXI,Jie ZHU. Tibetan text normalization method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3577-3588. |
| [10] | Yu-xin YE,Luo-jia XIA,Ming-hui SUN. Gesture input method based on transparent keyboard in augmented reality environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3274-3282. |
| [11] | Na CHE,Yi-ming ZHU,Jian ZHAO,Lei SUN,Li-juan SHI,Xian-wei ZENG. Connectionism based audio-visual speech recognition method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2984-2993. |
| [12] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN. Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [13] | Shan XUE,Ya-liang ZHANG,Qiong-ying LYU,Guo-hua CAO. Anti⁃unmanned aerial vehicle system object detection algorithm under complex background [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [14] | Jin-Zhen Liu,Guo-Hui Gao,Hui Xiong. Multi⁃scale attention network for brain tissue segmentation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [15] | Zhen WANG,Xiao-han YANG,Nan-nan WU,Guo-kun LI,Chuang FENG. Ordinal cross entropy Hashing based on generative adversarial network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3536-3546. |
|
||